Abstract
Measurement systems such as laser trackers and 3D imaging systems are being increasingly adopted across the manufacturing industry. These metrology technologies can allow for live, high-precision measurement in a digital system, enabling the spatial component of the digital manufacturing twin. In aircraft wing manufacturing, drilling and fastening operations must be guided by precise measurements from a digital design model. With thousands of fasteners on each aircraft wing, even small errors in alignment of surface covers to wing ribs and spars can impact component longevity due to aerodynamic drag. Determining surface conformance of airstream-facing surfaces is currently largely performed though manual gauge checking by human operators. In order to capture the surface details and reverse engineer components to assure tolerance has been achieved, laser scanners could be utilised alongside a precise registration strategy. This work explores the quality of the aerostructure surface in a captured point cloud and the subsequent accuracy of surface normal determination from planar fastener heads. These point clouds were captured with a reference hand-held laser scanner and two terrestrial laser scanners. This study assesses whether terrestrial laser scanners can achieve <0.5° surface normal accuracy for aerospace fastener alignment. Accuracy of the surface normals was achieved with a nominal mean discrepancy of 0.42 degrees with the Leica RTC360 3D Laser Scanner (Leica Geosystems AG, Heerbrugg, Switzerland) and 0.27 degrees with the Surphaser 80HSX Ultra Short Range (Basis Software Inc., Redmond, WA, USA).
1. Introduction
The deduction of information from spatial data allows for the creation of 3D models that can aid in location and identification tasks. This spatial data can also allow for investigation into surface characteristics such as flatness and smoothness. Quantifying these characteristics is especially relevant in aerospace wing manufacturing, when wind resistance and drag caused by manufacturing inaccuracies can lead to object damage and component failure over time.
Obtaining spatial data within aerospace manufacturing environments is often undertaken by human operators with hand-held instruments such as callipers and gauges, which provide quality checks at predefined intervals to a digital model. This example of forward engineering requires a digital design model with known tolerances of the manufactured object. As with any manufacturing scenario, the implementation of regular quality control checks is vital for the successful completion of components within tolerance. Tolerance in manufacturing is application- and task-specific and contained within the digital design model of a given component. On the manufacturing floor these tolerance values would be checked against assembled components. In aerospace, some positioning tasks must be achieved to micron-level accuracy, while other tasks can accommodate millimetre-level positioning errors.
As aerospace manufacturing environments adopt laser-based measurement instruments for a wider range of tasks, some point-based measurements are generated from laser trackers. These instruments create highly accurate measurements for static or non-static reflective targets. However, while laser trackers and some photogrammetric systems achieve the required sub-millimetre accuracy for some aerospace manufacturing tasks, single point measurements do not allow for surface interpretations, which are key in aerodynamic assessment. Point-based measurements do not easily lend themselves to surface reconstruction as it is difficult to capture evenly dispersed measurements over a surface of interest.
Despite their ability to create highly detailed surface measurements, the lower accuracy and consistency of laser scanners has delayed their adoption into manufacturing environments. The vast majority of laser scanners provide a measure of possible coverage within an advertised accuracy tolerance. Additionally, manufacturing environments are typically challenging for laser-based measurement methods due to the presence of highly reflective metallic surfaces. Metallic surfaces are known to cause high-intensity returns, which can be filtered out by built-in processing algorithms. Some previous work has implemented radiometric corrections to quantify and correct for TLS intensity variation from different surfaces [1]. A complete review of material surface effects from laser scanning can be found in [2].
Hand-held scanners can be used to collect surface-based measurements in manufacturing environments. These 3D scanners use an emitted laser line that sweeps over the surface to capture highly accurate point clouds. Hand-held scanners can be tracked around an environment with a laser tracker, automatically registering the measurements into a previously established reference network. Although they can collect extremely dense, high quality point clouds, hand-held scanners require access to the manufactured components. Either a human operator must occupy the manufacturing space to utilise the scanner or the scanner must be attached to a robotic arm and the components placed within a Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM). The required proximity between the scanner and the surface of interest prevents the remote capture of surface information on the assembly line.
A second option for capturing surface information of manufactured objects is a combined laser tracker and imager. These relatively new metrology tools combine indirect point measurement of a laser tracker and direct measurement from an embedded laser scanner. These combined instruments can produce highly accurate point clouds registered into a predefined reference network. A disadvantage of these instruments is their novelty, making them unsuitable to many applications until their function and cost can be proven worthwhile.
A third, largely untested option for capturing surface observations of aerospace assemblies is through the use of medium- or large-volume polar terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) systems and a network of reference spherical targets. Surface capture of an aircraft wing will be explored in this work, specifically as it relates to the detection of fasteners which are used to affix multiple layers of the wing together and must sit flush to the surface of the wing to minimise drag. The functionality of the TLS will be evaluated in this work by detecting the surface normal of fasteners on an aerostructure surface and computing their deviation from a known reference and from the surface of the aerostructure itself. To the author’s knowledge, this measurement strategy has not been previously applied to surface normal estimation of aerospace fasteners.
In this work, three laser scanners were used to capture an aerostructure surface and compute the surface normals of 90 planar fastener heads. The objective was to determine the achievable quality of the surface normal estimation from different TLS instruments. This is highly dependent on factors such as material characteristics, scanning setup, incidence angles, neighbourhood size, and noise. These factors and their impact of surface normal estimation will be explored in the subsequent sections.
The work presented here explores the potential of TLS instruments for high-precision surface capture and subsequent surface normal determination. This provides a quantitative comparison of TLS instruments for surface normal determination of aerospace fastener surfaces. This contribution will help to inform the utility of TLS in high-precision manufacturing environments.
2. Background
Geometric primitives can be detected from spatial data. This endeavour began over 40 years ago using data collected from ranging instruments. These instruments would form the prototypes for modern TLS and mobile laser scanners. Development continued as purely range-based scanners began to evolve into more complex measurement instruments. TLS instruments are now widely used in various fields to capture detailed spatial data of complex environments.
These point clouds can be evaluated with different feature detection techniques to extract meaningful information such as geometric primitives and surface normals. Feature detection methods can be largely split into learning-based and logic-based evaluation constructs. Learning-based models use training data to ‘teach’ a system to interpret certain point cloud signatures as distinctive features. During training, a library of known features are created, which are then used to produce sematic labelling for point clouds under test. Logic-based models are built on hard-coded rules garnered from structures and patterns in a given dataset [3]. Both structures perform best in the presence of geometric primitives such as planes, lines, and circles [4].
A surface normal is a line that emits from a seed point in a perpendicular direction to the surface. The surface is defined by a local neighbourhood of points which can be used to estimate the orientation of the surface in 3D space. Surface normals are typically required by surface reconstruction and meshing algorithms in order to approximate a continuous surface. However, these surface reconstruction algorithms and point-based rendering techniques depend on accurate estimations of surface normals. The computation of highly accurate surface normals must be performed with consideration of the quality of the underlying point cloud. When attempting to estimate sub-degree differences between components, the quality of the captured point cloud will influence the accuracy of the computed surface normal.
The computation of surface normals from spatial data has been the subject of research for many decades. Previous work by [5,6,7] has involved comparison studies on different strategies for weighting the points in the neighbourhood to optimise accuracy of the surface normal. These methods include Mean weighted (MW) equally (MWE, 1971), MW by angle (MWA, 1998), MW by sine and edge length reciprocals (MWSELR, 1999), MW by areas of adjacent triangles (MWAAT, 1999), MW by edge length reciprocals (MWELR, 1999), and MW by square root of edge length reciprocals (MWRELR, 1999). Research has demonstrated that MWE requires a larger number of points to correctly estimate the surface normal, and therefore suffers in terms of speed, while MWAAT is not robust in dealing with large outliers in point clouds and should therefore be avoided in laser scanning applications. MWA is proven to be the most robust in terms of point density and computational speed.
The study presented in [6] provided a detailed examination of four common surface normal estimation methods, Plane Single Value Decomposition (SVD), Plane Principal Components Analysis (PCA), VectorSVD, and QuadSVD. The methods were further modified by anchoring the solution on the reference point of the neighbourhood, normalising the vectors of the points in the neighbourhood, and weighting the contributions of the points in the neighbourhood based on their distance from the reference point. Anchoring the planar surface on the neighbourhood mean, rather than the reference point, was found to lead to higher accuracy by reducing the orientation error of the surface by multiple degrees. However, these methods achieved orientation errors over eight degrees, making them unsuitable for high-accuracy measurement tasks.
The neighbourhoods used in the determination of a surface can also be clustered in various ways, based either on neighbourhood searches or dynamic sampling. The most common neighbourhood search, kNN, utilises a k-nearest-neighbour directed graph that connects each point to its k-nearest neighbours based on Euclidean distance. Neighbourhoods can also be defined using Delaunay Tessellation, which uses Voronoi polyhedrals to divide a space into polygonal cells by splitting the distance between adjacent points. Groups of neighbouring points can then be determined by connecting points that share a minimum distance to a common point.
The recent literature on surface reconstruction from point clouds is presented in [7,8,9,10], which provide a thorough exploration of existing algorithms for surface reconstruction, ranging from classical methods to deep learning approaches. The literature concludes that surface reconstruction challenges persist from poor registration, missing points and the influence of outliers and noise, which remain largely unsolved by existing solutions. Further, despite the initial promise of deep learning methods, they struggle with highly complex shapes when compared to classical methods.
Due to computational complexity, typical examples of surface normal estimation use manifold surface representations rather than the point cloud itself. Representations can take the form of mesh models or wire frame models. However, despite an increase in computational load, more detailed surface normals can be assembled from point cloud data itself, if the point cloud has been captured with sufficient coverage and accuracy.
The classic paper by [11] outlines the impacts of variables such as neighbourhood size and noise on the computation of surface normals from point clouds. According to [11], the accuracy of normal estimation depends on the following:
- Point cloud noise;
- Curvature of the underlying manifold;
- Density of the point cloud;
- Neighbourhood size.
It is generally agreed that neighbourhood size is a key variable impacting the estimation of surface normals, and was traditionally manually derived [12]. The concept of an adaptive neighbourhood size was introduced in [11]. When there is no noise in a point set, the radius of the neighbourhood should be as small as possible, and when there is no curvature in the form of the surface, the radius should be as big as possible. Similarly, when the sampling density is high, such as in a dense point cloud, the radius of the neighbourhood used to fit a planar section depends on the standard deviation of the noise amongst the points. Although many surface reconstruction methods have been postulated, many assume the presence of a complex underlying structure composed of multiple small planar surfaces. In this work, the assumption of a single planar surface for each fastener head is utilised. If a planar surface assumption is implemented, the problem shifts from surface reconstruction to accurate surface normal estimation of a single surface.
The scanning, processing, and reconstruction pipeline can be referred to as reverse engineering. A review of reverse engineering as it pertains to laser scanning and surface reconstruction is provided in [13]. Quality assurance checks that match a physical model to a digital design model must utilise accurate measurements to assure component compliance. Diverse examples of high-accuracy modelling and reconstruction from hand-held scanning can be found in many different research areas. Applications of hand-held laser scanning solutions in forestry are plentiful [14,15]; however, accuracies are typically constrained near the centimetre level due to the scale of the measurement area and the non-static nature of the objects under investigation.
In [16], a hand-held laser scanner was used to assess the quality of welded joints. The method proved successful in its capability to identify under-, proper, and over-treatment of welded specimens to the sub-millimetre level. An aerospace application of robotic drilling was reported in [17], where three laser range sensors attached to a drill bit performed iterative positioning for a drill bit on the end of a robotic arm. Measurements from the three laser range sensors were combined to compute the surface normals of the curved underlying surface and adjust the drill accordingly.
The application of laser scanning in aerospace studies is relatively novel, especially when it comes to TLS systems. TLS systems are typically intended for infrastructure measurement, whereas in this work they will be evaluated for engineering measurements. Novel aerospace measurement solutions and digitisation strategies must include comprehensive evaluation of measurement characteristics and reliability. The work presented in this paper evaluates the measurements collected by engineering surveying-specific instruments, rather than testing a particular strategy by which surface normals are computed. For this reason, a classical least-squares method was utilised to compute the planar surface and its resulting surface normal. As indicated by [11], when a surface with minimal curvature is assumed, such as the planar head of an aerospace fastener, the radius of the neighbourhood should be as large as possible to mitigate the effects of outliers on the direction of the computed surface normal. The next section will describe the scanning procedure and instruments utilised in this experiment.
3. Materials and Methods
In this paper, we report on work using a fastener sample plate equipped with various fasteners that possess small changes in tilt and orientation. The sample plate is a research artefact comprising a 9 × 10 grid of fasteners [Figure 1] varying in size, depth, and tilt. There are three sizes of fasteners on the object which range from 20 to 32 mm in diameter and will be referred to as small, medium, and large fasteners. There are thirty fasteners of each size, and three rows of each size. The goal of this work was to utilise TLS instruments to accurately model the fasteners and compute the direction of their surface normal. The fastener sample plate is a research-specific artefact rather than a component taken from the production assembly line. The 3D nominal model of the fastener sample plate is proprietary to the manufacturer and is not available in the public domain. Instead, an additional hand-held Leica Absolute Scanner AS1 (Hexagon AB, Stockholm, Sweden) triangulation laser scanner tracked in 6DoF with a Leica Absolute Tracker AT960MR (Hexagon AB, Stockholm, Sweden) laser tracker was used to capture the fastener sample plate surface and create a set of reference measurements. The AS1 produces measurements with accuracy levels that are at least one order of magnitude better than either TLS instrument tested in this work. Due to the nature of the laser-tracked AS1 instrument, the captured point cloud was referenced into the laboratory control network. The AS1 hand-held scanner captured the scan from close range within 165 ± 15 mm from the fastener surface into New River Kinematics (NRK) Spatial Analyser (SA) software version 2022.2.0624.8. The AS1 point cloud provided a reference dataset for this work.
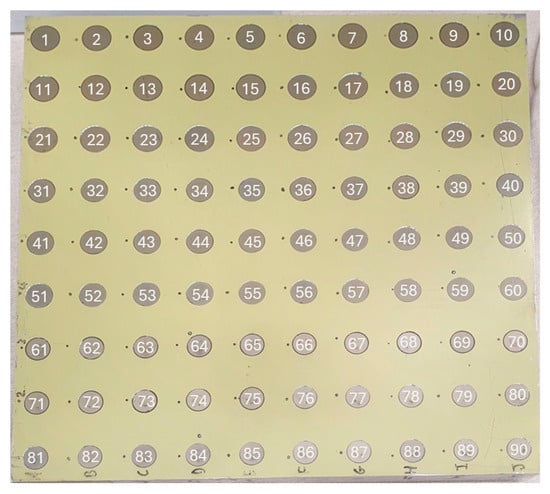
Figure 1.
Fastener sample plate and fastener label numbers (1–90). Large fasteners are in the first three rows at the top of the image, then the medium fasteners in rows 4–6, and the small fasteners in rows 7–9.
Two phase-based TLS were used in this work to capture the reference artefact surface from a single scanning location. The first was the Leica RTC360 laser scanner, which is a fast 3D laser scanner commonly used for building modelling, construction, or other large volume tasks at ranges between 0.5 and 130 m. The second was the Surphaser 80HSX medium range laser scanner, which is generally geared towards metrology applications and can produce point data with small amounts of measurement noise. This instrument is designed to operate at ranges between 0.25 and 7 m. A single scanning location reduces time spent on both data capture and processing, and in this work, it allowed for a focus on the performance of the instruments being tested.
The fastener sample plate was captured once by each scanning instrument in a static laboratory environment. Both the RTC360 and the Surphaser 80HSX captured the surface from a range of 1 m. Although shorter ranges may have produced point clouds with increased density, the extreme short ranges of the RTC360 have been shown to produce inconsistencies in the captured point clouds [18]. Both TLS point clouds were captured at the highest-resolution setting possible, and with the fastener sample plate oriented perpendicular to the laser axis. For the RTC360 the high-resolution setting corresponds to a resolution of 3 mm at a range of 10 m, while for the Surphaser 80HSX, the high-resolution setting corresponds to a vertical and horizontal point density of 360 points per degree and 60 lines per degree. The two test point clouds were registered into the control network using a system of spherical targets and a best-fit points-to-points transformation. By minimising the residuals between the spherical targets and the known control points, each point cloud could be aligned into a common reference system. This allowed for the direct comparison of the surface normal direction for each of the fasteners in each point cloud. The registration was achieved within 0.4 mm for the Surphaser 80HSX and within 0.8 mm for the RTC360.
For each point cloud, the fastener heads were separated from the surface of the fastener sample plate. This was achieved by using the visible outline of the fasteners in the 80HSX point cloud and will be further explained in the following section. Different point densities were achieved by each scanner, producing a mean of 1525, 421, and 593 points per fastener for the AS1, RTC360, and Surphaser 80HSX. For each point cloud, a planar surface was fitted to each of the fastener heads, and their surface normals were compared. A planar surface was also fitted to the aerostructure surface in order to ensure the point clouds were contained within a common reference frame, as far as the planar surface is concerned, so that the fastener heads could be justifiably compared.
The planar fit method uses iterative least squares to minimise the residuals of the plane from each group of points representing a single fastener head. An equal weighting of observations on the surface of each fastener is used. The size of the noise and the number of points differed for each point cloud based on the capture strategy and internal design mechanics of the scanning instrument.
The direction of the surface normal of a planar section is represented by the equation of a plane using ABCD notation, where A, B, and C are the components of the surface normal unit vector, and D is the distance between the origin of the coordinate frame and the closest point on the planar section.
The direction of the surface normal on the fastener head can be compared to the direction of the aerostructure reference surface normal to compute the tilt. The direction of the surface normal can also be compared to the direction of the fastener head as estimated by the reference instrument. In this way, both the accuracy and the consistency of the surface normal estimation using the TLS instrument can be evaluated.
The angle between two surface normals can be computed using a dot product. In this case, each surface normal vector is composed of three components (A, B, and C) so the angle between them can be computed as follows:
By fitting a plane to a group of points in a point cloud, an angular representation of the surface normal can also be computed. The direction of the normal is composed of the principal projected angles, which are represented by , where
These spherical angles are converted to a 3D unit vector, [x y z], to better visualise the deviation of the surface normals from the reference values in the analysis. See the equation below where is equal to Rx and is equal to Rz.
Conventionally, in computer graphics, the x, y, and z components are represented as a normal map by the colours red, green, and blue, respectively, and will have values between –1 and 1. For example, a plane found on the YZ axis with a surface normal pointing along the x axis would have a vector of [1 0 0] and would be represented by the colour red on a surface normals map. A visual representation can be seen in Figure 2.
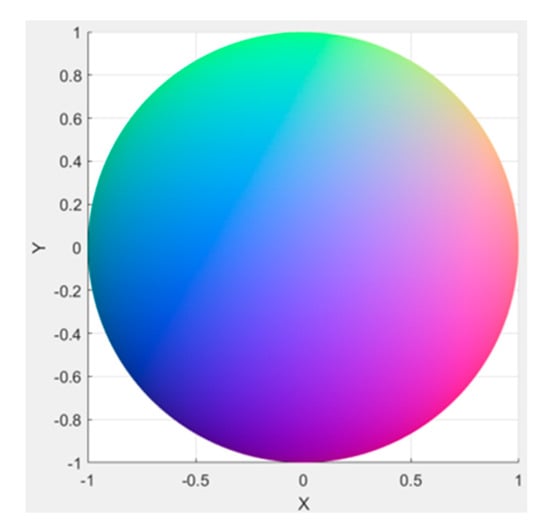
Figure 2.
Surface normals on a hemisphere. A graphical representation of the colours that represent the direction of surface normals.
It should be noted that the angles of the surface normals discussed in this paper are small (less than 1.1 degrees). The data have therefore been scaled using the maximum and minimum for each dataset.
4. Results
The analysis began with identification of the fastener heads in each of the three registered point clouds. Each fastener head on the artefact was manufactured to be nearly flush with the aerostructure surface in order to represent manufacturing and assembly departures that might be realistic for an aircraft wing skin surface. Due to the point density of the AS1 point cloud and the lack of colour or intensity information within it, in a visual graphic sense, it was extremely difficult to manually identify the fastener heads. The 80HSX collected intensity information, which, due to the difference in optical material properties between the fastener heads and the aerostructure surface, made the fasteners clearly discernible from the aerostructure. The points in the 80HSX point cloud belonging to the fastener heads were separated from the remaining points. This created a point cloud with 90 clusters of points belonging to the fastener heads. The common alignment between the three point clouds allowed the 80HSX point cloud to be used as a template for the AS1 and the RTC360 point data. Whilst the RTC360 scanner also collected colour and intensity informationthe distinction between the fastener heads and the aerostructure was not as clear when compared to the detail in the 80HSX point cloud.
In a similar way, the points belonging to the fastener heads were clustered using a nearest classified point process. A small buffer around the fastener head was included in the clustering strategy in order to ensure that no points belonging to the chamfer edge were included in the planar fit. These edge points could have suffered from edge effects and the size of the chamfer varied between fasteners due to changes in tilt, so their inclusion in the solution would have deteriorated the quality of the planar fit. An example of these edge chamfer points can be seen in Figure 3. The vector graph shows the impact of the inclusion of the edge and its effect of pulling the fitted plane towards the scanner.
Figure 3.
AS1 example fastener with included edge and chamfer. Vector graph from planar fit has been included with magnitude ×100 to show potential impact on surface estimation.
Once the point clouds had been clustered to only include points belonging to the fastener heads, a best-fit planar surface was fitted to each cluster of points in each point cloud. The resulting 90 planar surfaces for each scanner point cloud allowed for an assessment of the estimated surface normal direction and the quality of the planar fit. Statistics regarding the quality of the points to the planar fit are presented in Table 1, including the maximum and minimum deviations from the best-fit plane and the root mean square (RMS) of the planar fit.

Table 1.
Planar fit statistics from AS1, RTC360, and 80HSX. Deviations are computed as the distance between the points and the fitted plane along the direction of the estimated surface normal.
A clear distinction in the size of the deviation between the different laser scanners can be seen in Table 1. Part of this deviation can be associated with measurement noise. TLS instrument noise is typically reported on albedo surfaces, i.e., surfaces with no specularity. The RTC360 reports 0.4 mm of range noise at 10 m on surfaces with 89% albedo [19]. The 80HSX reports 0.14 mm of range noise at 0.25 to 4 m on surfaces with 10% reflectivity [20]. Both values are reported with confidence levels of 68%. Being based on triangulation, the AS1 does not report a range noise value, but scans with an accuracy of 0.013 mm, at least one order of magnitude more accurate than the TLS being tested. In accordance with the presented range noise values, the 80HSX appears to be operating close to its specification, whereas a significant amount of the noise in the plane fit for the RTC360 is unaccounted for. This could be due to interaction between the incident light from the scanning instrument and the optical material properties of the fastener heads. Larger noise could also be due to the spot size of the laser, which could cause mixed pixels at fastener boundaries.
The angle between each of the 90 fastener heads and the surface of the aerostructure were computed for each of the scanner point clouds. In addition, the angular discrepancy between each fastener in the AS1 reference and each fastener in the test point cloud were computed to evaluate the accuracy of the surface normal determination from the TLS point clouds. These two measures are illustrated in Figure 4.
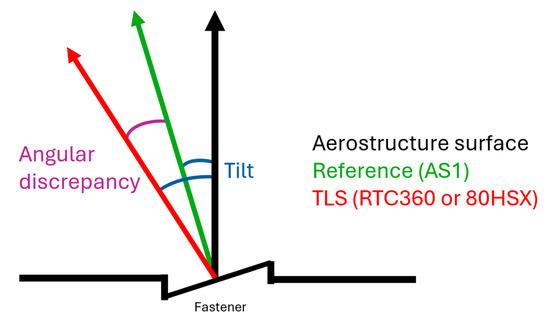
Figure 4.
Description of quality measures: tilt and angular discrepancy.
Figure 5 illustrates the direction of the surface normals of the planar fit for each fastener head (as described in Section 3). Results from the AS1 scanner, which was used as a reference measure, are blue/purple in colour, indicating that their fastener heads are relatively planar with a surface normal predominantly pointing in the direction of the z axis, i.e., towards the scanner. When comparing the surface normal orientations for the RTC360 and 80HSX scanners, the results vary up to approximately one degree from the reference. This can be visualised by the inconsistencies in colour of the fastener heads when compared to the AS1, particularly for the RTC360. Note that the graphic contained within Figure 5 is a visualisation of the direction of the surface normal, rather than the magnitude of the surface normal.

Figure 5.
Surface normal directions of individual planes relative to the aerostructure surface for each fastener measured with the AS1, RTC360, and 80HSX. Legend hemisphere colour shows the direction of the scaled vector relative to vectors for all scanners. Given the results seen in Table 2, the colour scale shows a variation of 1 degree.
The maximum and minimum tilt of the 90 fasteners are presented in Table 2 in degrees. This was computed by taking the difference between the surface normal of the fastener and the surface normal of the aerostructure surface. The maximum tilt of any fastener found by the RTC360 was larger than either the AS1 or the 80HSX.

Table 2.
Mean angular tilt from estimated surface normal computation for all 90 fasteners in each point cloud relative to the aerostructure surface normal.
For the RTC360, maximum tilt angles are approximately one degree with larger values found predominantly down the right-hand column of fasteners. The 80HSX had maximum tilt angles of approximately 0.7 degrees, with the largest values found on the fasteners along the bottom edge of the fastener sample plate. The large deviations in the RTC360 point cloud could be due to an edge effect where the laser spot is incident on both the aerostructure and the fastener. What is clear from the intensity of the point cloud is that high-intensity return signals are produced when the angle of incidence between the incident light and the fastener surface is close to zero. These high-intensity returns could saturate the sensor and potentially deteriorate the surface normal estimation.
The fastener head angular discrepancy was then computed by taking the difference between the surface normal from the AS1 and the computed surface normal from the TLS for each fastener head. This was performed for each fastener in each point cloud to evaluate the accuracy of the method. The results for the RTC360 and the 80HSX are shown in Figure 6. The large tilt values indicated for the RTC360 in Figure 5 are correlated with the large angular discrepancies along the right-hand side of the fastener sample plate.

Figure 6.
Angular discrepancy in degrees between AS1 reference surface normal and TLS computed surface normal for each fastener. Direction is not indicated.
The mean values of the angular discrepancies are presented in Table 3. As expected, the mean angular discrepancy between surface normals is lower for the 80HSX than for the RTC360 when compared to the AS1. However, despite the noise of the RTC360 instrument, presented in Table 1, the surface normals were estimated to be within half a degree of the reference. The surface normal discrepancies relative to the diameter of the fastener heads were computed; however, no systematic trends were identified.

Table 3.
Angular discrepancy between estimated surface normals from TLS and reference (AS1).
Figure 7 shows the surface normals for each point found in the individual fastener head point cloud collected with the AS1 scanner. The surface normals were calculated in CloudCompare version 2.13.1 using the Point Cloud Library Wrapper [21]. These diagrams illustrate the systematic nature of surface effects identified from the AS1 scanner, in particular the uneven capture and alignment of scanlines as seen on Fastener 1. Fastener 45 also shows an apparent doming of the fastener itself, indicated by the varying surface normal direction over the extent of the fastener head. Note that the direction of the surface normals has been scaled to identify key areas of interest and therefore Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 should not be intercompared.

Figure 7.
Surface normals of individual points on fastener head collected with the AS1 for Fastener 1 and Fastener 45. Colours are scaled for AS1 data to highlight differences and range from 0.08° to 2.45° from the vertical direction.

Figure 8.
Surface normals of individual points in point cloud collected with the RTC360 for Fastener 1 and Fastener 45. Colours are scaled for RTC data to highlight differences and range from 0.18° to 30.94° from the vertical direction.

Figure 9.
Surface normals of individual points in point cloud collected with the 80HSX for Fastener 1 and Fastener 45. Colours are scaled for 80HSX data to highlight differences and range from 0.08° to 4.71° from the vertical direction.
The directions of the surface normals on fastener heads in the RTC360 point cloud are represented in Figure 8, and in Figure 9 for the 80HSX. For the RTC360, consistency in surface normal direction is exhibited over the course of Fastener 1 and Fastener 45, failing to detect the fastener head doming that was identified with the AS1 scanner. Edge effects can be seen from changes in surface normal direction near the outside of the fastener. This is likely due to laser spot size and resulting mixed pixels from fastener chamfers or edges. The size of the noise in the RTC360 point cloud could also be obscuring additional surface effects on the fastener head. This will be explored later in this section.
For the 80HSX, the discrepancies in surface normal determination appear larger; however, these relative results can be explained through the scaling of the colours. There appears to be a spatial trend in both of the fastener heads in Figure 9, with bands of surface normals with larger discrepancies spread across the fastener head in a wave-like pattern.
To investigate the cause of the fastener head surface normal angular discrepancies, individual point intensities can be examined. The intensity values in a point cloud represent the strength of the returning signal and can be used to indicate the reflectivity of a given surface. Both the RTC360 and the 80HSX operate on the same 1550 nm wavelength, and therefore a comparison of their backscattered intensity signals can help to clarify the quality of the measured data. A systematic intensity distribution of the RTC360 and the 80HSX point cloud can be seen in Figure 10 and Figure 11. The intensity of the respective point clouds have been adjusted to fit the same scale and therefore can be directly compared. For the RTC360, the intensity values are centred around the middle of the fastener plate, and slowly decrease as they radiate outwards. As the incidence angle of the light increases, the high reflectivity of the metallic surface has less of an effect on the returning signal. At the centre of the diagram, the fastener heads produce a distinctly different intensity signature when compared to the aerostructure surface. However, near the edges of the fastener sample plate, the fastener heads and the aerostructure surface have similar intensity returns. These systematic variations challenge intensity-based feature detection of fastener heads in the RTC360 point cloud.

Figure 10.
RTC360 intensity distribution on fastener sample plate. The apparent gridded structure of the point cloud is a display artefact and is not representative of structures within the point cloud.
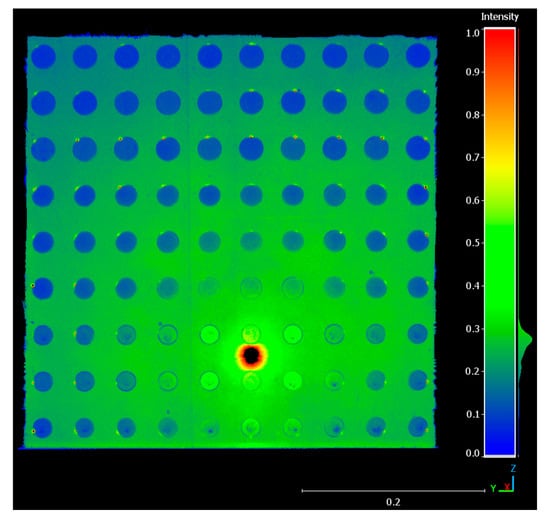
Figure 11.
Surphaser 80HSX intensity distribution on fastener sample plate.
Some of the large deviations in surface normal direction seen in Figure 5 for the RTC360 can be explained by the intensity distribution. However, the large deviations along the right-hand edge of Figure 5 and Figure 6 for the RTC360 are not explained by the intensity distribution. Some of the random nature of the surface normal direction can be attributed to the size of the surface noise in the captured point cloud.
For the 80HSX, the mean intensity is lower than the RTC360, with the majority of the fastener heads producing lower intensity reflections than the painted aerostructure surface. The majority of the fastener heads are clearly visible in the intensity diagram. The highest intensity reflections are not located in the centre of the fastener sample plate due to misalignment of the height of the instrument setup during data collection. The high-intensity reflections are located near the small fasteners, specifically fasteners 65–67, 75–77, 86, and 87, which correlates to some of the large discrepancies in fastener head surface normal direction seen in Figure 5 for the 80HSX.
The doming effect seen in Figure 7 was further investigated by examining the vector graph produced from the least-squares planar surface fitting procedure. Results are presented in Figure 12. The vector graph, an enlarged view of which was presented in Figure 3 for a single fastener, shows the magnitude of the deviations of the points utilised in the surface normal fit. These vectors point in the direction of the z axis along the surface normal. The vectors are colourised based on their magnitude and direction from blue to red, so large vectors pointing in the direction of the z axis are blue and large vectors pointing in the direction of the -z axis are red.

Figure 12.
AS1 non-planarity of medium-size fasteners, middle three rows.
As seen in Figure 12, the medium-size fasteners located in rows 4, 5, and 6 display a systematic pattern in their vector graphs. There appear to be large deviations represented by the blue vectors in the centre of each of the medium fastener heads. The same effect did not occur for either the small or the large fasteners. The nature of the vector graphs for the medium fastener heads suggests that instead of having a planar surface, the medium fasteners were domed in the direction of the z axis. This effect occurred on the order of 0.1 mm and therefore was not identified with either of the TLS used in this study. A vector graph of medium fastener #31 is included in Figure 13.

Figure 13.
Medium fastener #31 vector graph from AS1, units are millimetres.
An explanation as to why the doming of the fasteners occurred in the direction of the incident light could be that when the fasteners are tightened through the aircraft wing’s skin surface, over- or under-tightening could cause a bowing of the fastener, which would pull it down along the central axis of the fastener. This could result in a non-planar fastener head. Results suggest that a hand-held scanner such as the AS1 could identify not only the tilt and orientation of a fastener, but also the extent to which a fastener has tightened and potentially deformed during assembly.
A second surface effect seen in the point clouds from the fastener sample plate is exhibited in Figure 9. A ‘wave’ or ‘ripple’ effect was observed in the surface normals of the fastener heads from the 80HSX. It was theorised that this same ‘ripple’ effect may be present in the RTC360 point cloud but was obscured by large amounts of surface noise. In order to investigate this effect, surface noise was removed from the fastener heads in the RTC360 point cloud from approximately 0.7 mm to 0.2 mm. The surface noise was removed in the Spatial Analyser software environment during the plane fitting process. This mimicked the size of the surface noise in the 80HSX point cloud. A planar surface was fitted to the remaining smoothed points, and the vector graph of each fastener head planar fit is presented in Figure 14.

Figure 14.
RTC360 ‘ripple’ effect; noise has been removed to 0.2 mm.
A clear systematic trend is visible in the vector graphs of the fastener head planar fits from the RTC360 following noise reduction. The remaining points appear to be rippling outward from the centre of the fastener sample plate. This directly correlates with the intensity distribution shown in Figure 10. The undulating points on the surface of each fastener head, especially near the centre of the fastener sample plate, could be the cause of some of the inaccuracies in the estimated surface normals. A close up of medium fastener #34 is included in Figure 15.
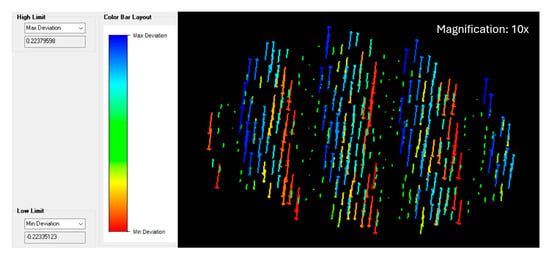
Figure 15.
Medium fastener #34 vector graph from RTC360, units are millimetres.
Further investigation into the doming and ripple effects identified here will be a topic of future research.
5. Discussion
The work conducted herein examined the suitability of medium- and large-volume polar TLS instruments for high-accuracy estimation of surface normals from a sample aerospace fastener and wing cover surface reference object. Surface normals were estimated using an iterative least-squares method to minimise the residuals of individual planar fitting to extracted point clouds representing each fastener head. The estimated direction of the surface normal from each fastener head was compared to the estimated surface normal of the surrounding painted aerostructure surface, as well as to the reference surface normal value for each fastener head obtained using the AS1 scanner. These tilt and angular discrepancy values were presented both graphically and by magnitude. The maximum fastener tilt detected by the AS1 was 0.41 degrees, while the TLS360 was measured at 1.03 degrees and the 80HSX was measured at 0.67 degrees. The magnitude of the noise from each scanning instrument was presented, and the effect of the noise on the estimation of surface normals was explored. The angular discrepancies of the surface normals from the reference instrument and the tested TLSs showed mean values of 0.42 degrees for the RTC360 and 0.27 degrees for the 80HSX.
Despite the noise present in the point cloud data from each instrument and the non-ideal material surface, surface normals with angular discrepancies of less than half a degree could prove useful for some quality control tasks in aerospace manufacturing. Whilst mechanical gauging is the traditional method used to assess fastener flushness and orientation to aerospace requirements, laser triangulation, fringe projection and structured light techniques can be used to assess clusters of fasteners at sub-millimetre levels and could be applied in these and other manufacturing scenarios. The aim of this paper was to assess if a TLS system can approach such demanding levels of quality assurance using a single scan position. The method developed herein could be directly implemented onto the manufacturing line in a quality assurance setting, enabling large angular discrepancies in magnitude or direction to be flagged for further investigation.
Exemplified in this work, specifically in Figure 7, is a persistent problem regarding variant density over point clouds collected by hand-held scanners. There was a large difference in spatial point density between regions in the AS1 point cloud; some fastener heads contained thousands more points than others despite being the same size. These structural variations in the point cloud can cause issues for the performance of automated feature detection algorithms. One solution is to down-sample using a consistent distance between points, but the situation could be better addressed by selecting a spatial point density at the data capture stage. In this case the selected point density would be of the order of a point per 0.1 mm that could have been collected with a TLS.
Due to the nature of a hand-held scanner, multiple scan passes are captured over the surface of an object. These passes are often captured at various orientations of the scanner in relation to the object and the laser tracker to overcome occlusions and challenging object geometries. Different scan head to laser tracker orientations can cause systematic misalignments of the scanlines if one or multiple of the tracking sensors on the hand-held scanner are not accurately tracked. This can result in a stratified point cloud, which can lead to misidentification of objects such as edges or features of interest.
The fasteners modelled in this work are contained within a simple planar surface, mimicking an aircraft wing skin. With regard to scanning directions, fasteners held within more complex geometric surfaces could prove difficult to capture and model. Variation in incidence angle and the requirement of multiple scan positions could lead to increased capture and processing times, along with registration errors.
Various surface effects from all three instruments have been identified in this work. This is the subject of further work and will be investigated by the authors in subsequent studies. The doming identified by the AS1 would require further investigation into systematic effects on the order of 0.1 mm. As the AS1 was the reference instrument in this study, there was no other data with which to verify the results. The AS1 utilises Leica SHINE (Systematic High Intensity Noise Elimination), which is advertised to reduce the impact of highly reflective surfaces, such as those encountered in this work. This is achieved with dynamic exposure settings and filtering algorithms that reduce point cloud noise. Specific details regarding the filtering techniques of these algorithms are proprietary.
Both the RTC360 and the 80HSX displayed a systematic ‘wave’ or ‘ripple’ effect in the distribution of the point noise on the fastener head surface. For the RTC360, this effect was shown to correlate with the intensity of the return signals and was present on both the fastener head and the aerostructure surface. The ‘wave’ effect was less pronounced for the 80HSX but was identified in the surface normal computation of individual points on the fastener head surface. These effects will be further explored by the authors in future work. This may involve scans at varying incidence angles, multi-scan registered approaches, implementing surface coatings, and independent validation using a non-scanning reference measurement such as camera-based photogrammetry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.P. and S.R.; methodology, K.P.; software, K.P.; validation, K.P., S.R. and H.C.; formal analysis, K.P.; investigation, K.P.; resources, K.P. and S.R.; data curation, K.P.; writing—original draft preparation, K.P.; writing—review and editing, K.P., S.R. and H.C.; visualisation, K.P. and H.C.; supervision, S.R.; project administration, K.P.; funding acquisition, K.P. and S.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a UCL EPSRC DTP Research Studentship, grant number EP/R513143/1 and EP/T517793/1.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because they contain information regarding proprietary research objects. The data are also part of an ongoing study.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Airbus for the use of research objects and tools, and Mike Davies at MD3D UK for the use of the Surphaser 80HSX.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sanchiz-Viel, N.; Bretagne, E.; Mouaddib, E.M.; Dassonvalle, P. Radiometric correction of laser scanning intensity data applied for terrestrial laser scanning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 172, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzali, M.; Pilgrim, L. A Comprehensive Review of Mathematical Error Characterization and Mitigation Strategies in Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Mei, Z. Computational Methods of Acquisition and Processing of 3D Point Cloud Data for Construction Applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 479–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.; Levine, M.D. Extracting Geometric Primitives. CVGIP Image Underst. 1993, 58, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, N. Weights for Computing Vertex Normals from Facet Normals. J. Graph. Tools 1999, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lewis, R.R.; West, D. A comparison of algorithms for vertex normal computation. Vis. Comput. 2005, 21, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Xi, F.J.; Guo, S.; Ming, Z.; Lin, Y. A comparison study of algorithms for surface normal determination based on point cloud data. Precis. Eng. 2015, 39, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.; Mordohai, P. A quantitative evaluation of surface normal estimation in point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 4220–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Tagliasacchi, A.; Seversky, L.M.; Alliez, P.; Guennebaud, G.; Levine, J.A.; Sharf, A.; Silva, C.T. A Survey of Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Jia, K. Surface Reconstruction From Point Clouds: A Survey and a Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 9727–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, N.J.; Nguyen, A. Estimating surface normals in noisy point cloud data. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual Symposium on Computational Geometry, San Diego, CA, USA, 8 June 2003; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 322–328. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, H.; DeRose, T.; Duchamp, T.; McDonald, J.; Stuetzle, W. Surface reconstruction from unorganized points. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, SIGGRAPH’92, New York, NY, USA, 1 July 1992; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, R.H.; Lemu, H.G. A case study on use of 3D scanning for reverse engineering and quality control. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 5255–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stal, C.; Verbeurgt, J.; De Sloover, L.; De Wulf, A. Assessment of handheld mobile terrestrial laser scanning for estimating tree parameters. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupinambá-Simões, F.; Pascual, A.; Guerra-Hernández, J.; Ordóñez, C.; de Conto, T.; Bravo, F. Assessing the Performance of a Handheld Laser Scanning System for Individual Tree Mapping—A Mixed Forests Showcase in Spain. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, K.; Safa, M.; Yeung, J.; Walbridge, S.; Haas, C.; Dubois, S. Quality assurance for high-frequency mechanical impact (HFMI) treatment of welds using handheld 3D laser scanning technology. Weld World 2015, 59, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yuan, P.; Wang, T.; Yu, L.; Xing, H.; Huang, W. A novel method of surface-normal measurement in robotic drilling for aircraft fuselage using three laser range sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 11 July 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pexman, K.; Robson, S. Optimizing Incidence Angle and Range for Single-Shot Laser Scanning Point Clouds to Model Aerospace Fasteners. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 48, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leica Geosystems AG. Leica RTC360 Product Specifications; Leica Geosystems AG: St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Basis Software Inc. Surphaser 80HSX Product Specifications; Basis Software Inc.: Redmond, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. Cloud Compare, 3D is here: Point Cloud Library (PCL), version 2.13.1; GPL software: Shanghai, China, May 2024.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).