- Article
Comprehensive Failure Mechanisms of Industrial Mo–W Hot-Work Steel Dies in Hot Stamping: Microstructural Degradation, Reaction-Layer Evolution, and Synergistic Wear Behavior
- Hubiao Wang,
- Xun Liu and
- Jiashuai Du
- + 2 authors
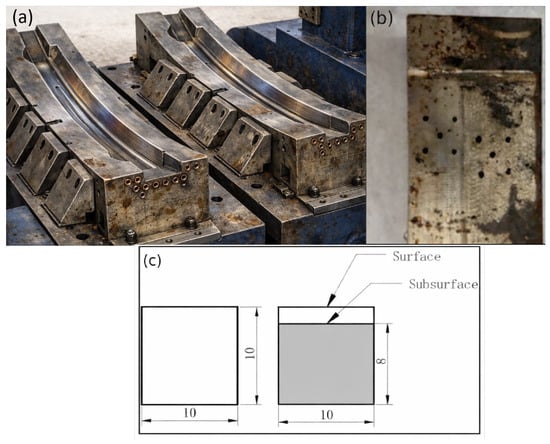
Hot stamping dies fabricated from Mo–W hot-work steels are exposed to severe thermo-mechanical fatigue (TMF), high-temperature oxidation, and complex tribological loading, which collectively accelerate die degradation and reduce production stability. Although individual failure modes have been reported, an integrated understanding linking microstructural evolution, interfacial reactions, and wear mechanisms remains limited. A failed Mo–W hot-work steel die removed from an industrial B-pillar hot stamping line was examined using Rockwell hardness mapping, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Williamson–Hall (W–H) microstrain analysis. Surface (0–2 mm) and subsurface (~8 mm) regions of 10 × 10 × 10 mm samples were compared. Pits, cracks, reaction layers, and debris were quantified from calibrated SEM images. A 17% hardness reduction from surface (46.2 HRC) to subsurface (37.6 HRC) revealed pronounced TMF-induced softening. W–H analysis indicated microstrain of ~0.0021 and crystallite sizes of 50–80 nm in the surface region, reflecting high dislocation density. SEM/EDS showed pit diameters of 150–600 μm, reaction-layer thicknesses of 15–40 μm, and crack lengths of 40–150 μm. Fe–O oxides, Fe–Al intermetallics, and FeSiAl4 reaction phases were identified as major constituents of brittle surface layers and debris. Wear morphology confirmed a mixed mode of adhesive galling and oxide-assisted abrasive plowing.
30 December 2025