- 3.2Impact Factor
- 6.4CiteScore
- 16 daysTime to First Decision
Development of Polymeric Materials for Biomedical Application
This special issue belongs to the section “Polymeric Materials“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
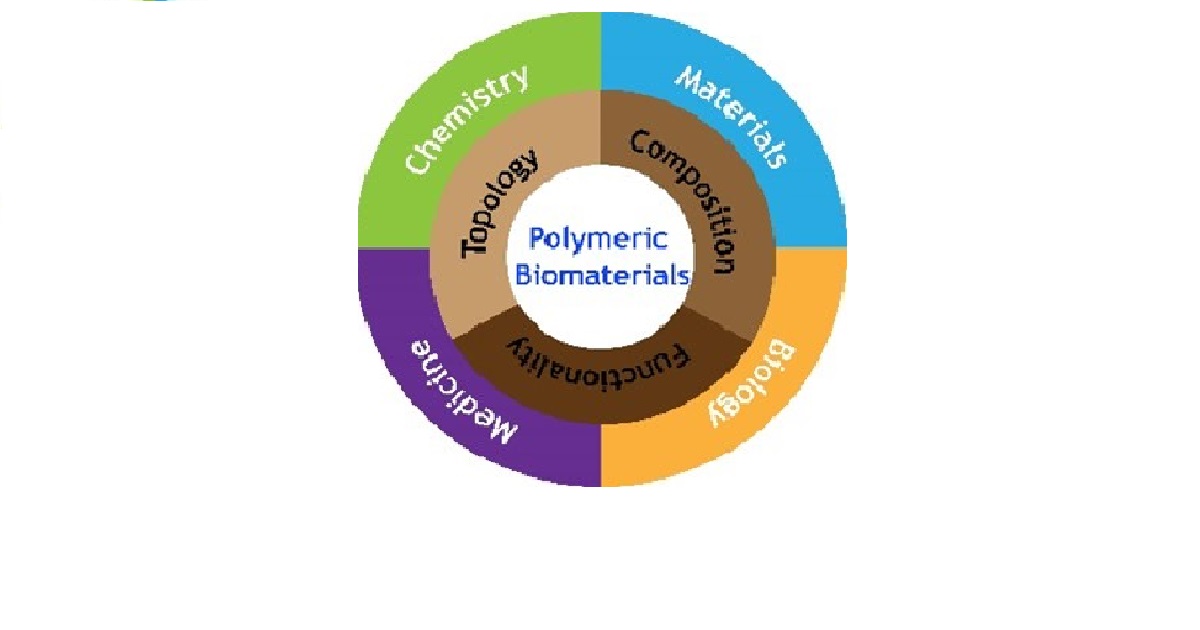
Among the various synthetic materials, polymers are particularly promising for biomedical applications because of their wide monomer availability, diversity in functionalities, ease of synthesis and large-scale production, excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength. Recent advances in polymer chemistry have created powerful platforms for manipulating the chemical composition and topological structures and ultimately their biological functions in tissue engineering applications. For example, depending on the tissue microenvironment, different stimulus-sensitive polymers (e.g., pH, temperature, reactive oxygen species, acidity, etc.) have been developed to produce smart hydrogels for the treatment of chronic wounds and achieve accelerated wound healing, or to target doxrubicin into cancer tissues, with improved therapeutic efficiency and reduced side effects observed. These advances have brought synthetic polymers ever closer to their potential in biomedicine. Therefore, the development of synthetic polymers with tailored chemical composition and topological structure along with various functionalities using advanced synthesis strategies is of great importance to accelerate the maturation of biotechnology and transfer it from the laboratory to the bedside. The aim of this Special Issue is to present recent advances in the field, where synthetic polymers are indispensable, with the expectation of providing new insights into the development of clinically applicable polymeric biomaterials. The guest editors are soliciting original research articles and reviews that cover the emerging strategies for polymer synthesis, new applications of synthetic polymers in various areas of biomedicine, exciting new results both in vitro and in vivo, and potential challenges associated with translating synthetic polymers into the clinic.
Prof. Dr. Dezhong Zhou
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- biomaterial
- polymer synthesis
- polymer functionalization
- drug delivery
- tissue engineering
- bioimaging
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

