Journal Description
Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks
Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of sensor and actuator networks, published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), dblp, Inspec, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Computer Science, Information Systems) / CiteScore - Q1 (Control and Optimization)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters of Network and Communications Technology: Future Internet, IoT, Telecom, Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, Network, Signals.
Impact Factor:
4.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
Improving Accuracy in Industrial Safety Monitoring: Combine UWB Localization and AI-Based Image Analysis
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060118 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Industry 4.0 advanced technologies are increasingly used to monitor workers and reduce accident risks to ensure workplace safety. In this paper, we present an on-premise, rule-based safety management system that exploits the fusion of data from an Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Real-Time Locating System (RTLS)
[...] Read more.
Industry 4.0 advanced technologies are increasingly used to monitor workers and reduce accident risks to ensure workplace safety. In this paper, we present an on-premise, rule-based safety management system that exploits the fusion of data from an Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Real-Time Locating System (RTLS) and AI-based video analytics to enforce context-aware safety policies. Data fusion from heterogeneous sources is exploited to broaden the set of safety rules that can be enforced and to improve resiliency. Unlike prior work that addresses PPE detection or indoor localization in isolation, the proposed system integrates an UWB-based RTLS with AI-based PPE detection through a rule-based aggregation engine, enabling context-aware safety policies that neither technology can enforce alone. In order to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach and showcase its potential, a proof-of-concept implementation is developed. The implementation is exploited to validate the system, showing sufficient capabilities to process video streams on edge devices and track workers’ positions with sufficient accuracy using a commercial solution. The efficacy of the system is assessed through a set of seven safety rules implemented in a controlled laboratory scenario, showing that the proposed approach enhances situational awareness and robustness, compared with a single-source approach. An extended validation is further employed to confirm practical reliability under more challenging operational conditions, including varying camera perspectives, diverse worker clothing, and real-world outdoor conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Security and Smart Applications in IoT and Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Design of Rectifier with High-Voltage Conversion Gain in 65 nm CMOS Technology for Indoor Light and RF Energy Harvesting
by
Jefferson Hora, Gene Fe Palencia, Rochelle Sabarillo, Johnny Tugahan, Yichuang Sun and Xi Zhu
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060117 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
In rectifier design, the key parameters are the voltage–conversion ratio and the power conversion efficiency. A new circuit design approach is presented in which a capacitor-based, cross-coupled, differential-driven topology is used to boost the voltage–conversion ratio. The scheme also integrates an auxiliary current
[...] Read more.
In rectifier design, the key parameters are the voltage–conversion ratio and the power conversion efficiency. A new circuit design approach is presented in which a capacitor-based, cross-coupled, differential-driven topology is used to boost the voltage–conversion ratio. The scheme also integrates an auxiliary current path to raise the power conversion efficiency. To demonstrate its practicality, two three-stage rectifiers were designed and fabricated using standard 65 nm CMOS technology. The designs were tested under various conditions to assess their performance. The first rectifier targets indoor light energy harvesting applications. It achieves a peak voltage conversion ratio of 3.94 and a maximum power conversion efficiency of 58.7% when driving a 600 Ω load, while supplying over 2 mA of output current. The second rectifier is optimized for RF energy harvesting at 2.4 GHz. Experimental results indicate that it can deliver 70 µA to a 50 kΩ load, with a peak voltage conversion ratio of 5 and a power conversion efficiency of 17.5%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Wireless Energy Harvesting and Power Transfer for Communications and Networks)
►▼
Show Figures
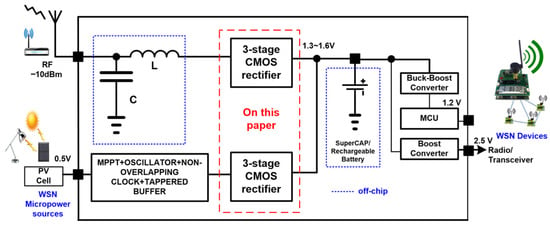
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Wireless Vital Parameter Continuous Monitoring for Critically Ill Patients Hospitalized in Internal Medicine Units: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Filomena Pietrantonio, Alessandro Signorini, Anna Rosa Bussi, Francesco Rosiello, Fabio Vinci, Michela Delli Castelli, Matteo Pascucci, Elena Alessi, Luca Moriconi, Antonio Vinci, Andrea Moriconi and Roberto D’Amico
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060116 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Wireless Vital Parameter Continuous Monitoring (WVPCM) allows the continuous tracking of patient physiological parameters, facilitating the earlier detection of clinical deterioration, especially in low-intensity care settings. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of using WVPCM compared to the
[...] Read more.
Background: Wireless Vital Parameter Continuous Monitoring (WVPCM) allows the continuous tracking of patient physiological parameters, facilitating the earlier detection of clinical deterioration, especially in low-intensity care settings. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of using WVPCM compared to the usual monitoring of critically ill patients hospitalized in Internal Medicine wards. An investigation of the attitude of health professionals towards the use of new technologies in daily practice to improve patient management was also carried out. Methods: The LIght Monitor Study (LIMS) is a prospective, open-label, randomized, multi-center pilot trial comparing WVPCM and conventional nurse monitoring during the first 72 h of hospitalization. A central randomization unit used computer-generated tables to allocate patients to two different types of monitoring. The main outcome was the occurrence of major complications. The study planned to enroll 296 critically ill patients with a Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) ≥ 3 and/or National Early Warning Score (NEWS) ≥ 5 across two Internal Medicine (IM) Units in Italy. The investigation of the attitude of nurses towards the use of WVPCM was carried out by using a questionnaire and a qualitative survey. Results: Due to the COVID-19 outbreak, the study was interrupted early and only 135 patients (WVPCM = 68; standard care = 67) were randomized. One patient in the control group was excluded from analysis because of drop-out, leaving 134 patients for intention to treat analysis. No statistically significant differences between standard care and WVPCM were observed in terms of major complications (37.5%, vs. 31.2% p = 0.475), in-hospital mortality (17.5% vs. 11.1%, p = 0.309), and median hospital length of stay (9 vs. 10 days, p = 0.463). WVPCM decreased nursing workload compared to the control, as the average time spent by nurses on the detection of vital signs per patient was 0 min per patient per day compared to 24.4 min (p < 0.001) observed in the control group. Twenty-two percent of patients in the WVPCM group (15/68) experienced discomfort with the device, resulting in its removal. The investigation of nurses involved 16 out of 18 people participating in the study. Opinions on the wireless device for patient monitoring were particularly favorable; most of them considered remote monitoring clearly superior to traditional in-person visits and easy to use after a brief practice period. All participants recognized the safety benefits of the system. Conclusions: The reduced sample size of this pilot study does not allow us to draw any conclusions on the superiority of WVPCM compared to standard care in terms of clinical outcomes. However, we observed a positive trend in the reduction of major complications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimating Post-Encroachment Time for Pedestrian Safety Using Ultra-Wideband Sensor Technology
by
Salah Fakhoury and Karim Ismail
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060115 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Traffic safety analysis has traditionally relied on historical road collision data. However, this approach has many limitations due to well-known challenges with the availability and quality of collision data. Moreover, collecting sufficient crash data to develop statistical models for traffic safety analysis is
[...] Read more.
Traffic safety analysis has traditionally relied on historical road collision data. However, this approach has many limitations due to well-known challenges with the availability and quality of collision data. Moreover, collecting sufficient crash data to develop statistical models for traffic safety analysis is only possible after the societal damage due to collisions has been sustained. Those problems are more likely when studying pedestrian safety. To address these constraints, researchers utilize traffic conflict indicators to identify the severity of conflicts and develop strategies to enhance road safety. This study evaluates Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology for estimating the post-encroachment time (PET) indicator, a commonly used measure in pedestrian safety. Indoor experiments were conducted to explore potential multipath issues commonly encountered in wireless-based localization systems. The time-division multiple access (TDMA) scheme was utilized by assigning 20 ms time slots for stable communication between a tag and an anchor. To address the different clocks in UWB anchors and tags, the master–slave technique was employed for time synchronization between the devices. The experiments also examined the storage of UWB measurements using a cloud-based global clock for time synchronization. The study found that the mean absolute error (MAE) in PET is 4.92 s under interference conditions and 0.148 s with the TDMA technique between the ground truth and the UWB measurements. The findings offer valuable insights for future studies aimed at enhancing UWB accuracy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Wireless Control Networks)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Operational Fire Management System (OFMS): A Sensor-Integrated Framework for Enhanced Fireground Situational Awareness
by
David Kalina, Ryan O’Neill, Elisa Pevere and Raul Fernandez Rojas
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060114 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
This paper presents the design, development, and field testing of an Operational Fire Management System (OFMS) aimed at enhancing situational awareness and improving the safety and efficiency of firefighting operations. The system integrates real-time intelligence and remote monitoring to provide emergency management personnel
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the design, development, and field testing of an Operational Fire Management System (OFMS) aimed at enhancing situational awareness and improving the safety and efficiency of firefighting operations. The system integrates real-time intelligence and remote monitoring to provide emergency management personnel and first responders with accurate information on vehicle location, communication status, and water level monitoring. Developed in collaboration with the Australian Capital Territory Rural Fire Service (ACT RFS), the OFMS prototype encompasses three core subsystems: the Monitoring and Environmental Sensing Subsystem (MESS), the Communication and Vital Monitoring Subsystem (CVMS), and the Command-and-Control Interface Subsystem (CCIS). MESS introduces a tilt-compensated ultrasonic algorithm for accurate water level estimation in moving fire trucks, CVMS leverages an open-source smartwatch with LoRa communication for real-time physiological tracking, and CCIS offers a cloud-based interface for live visualisation and coordination. Together, these subsystems form a practical and scalable framework for supporting frontline operations, particularly in rural firefighting contexts where vehicles are required to operate off-road and deliver large volumes of water to isolated locations. By providing real-time visibility of resource availability and crew status, the system strengthens operational coordination and decision-making in environments where connectivity is often limited. This paper discusses the design and implementation of the prototype, highlights key performance results, and outlines opportunities for future development, including improved environmental resilience, expanded sensor integration, and multi-agency interoperability. The findings confirm that the OFMS represents a novel and field-ready approach to fireground management, empowering firefighting teams to respond more effectively to emergencies and better protect lives, property, and the environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends)
►▼
Show Figures
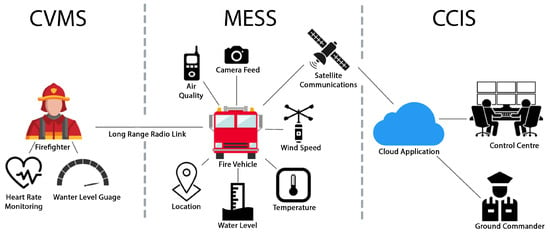
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
EMG-Based Simulation for Optimization of Human-in-the-Loop Control in Simple Robotic Walking Assistance
by
Arash Mohammadzadeh Gonabadi, Nathaniel H. Hunt and Farahnaz Fallahtafti
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 113; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060113 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Exoskeletons offer promising solutions for enhancing human mobility; however, personalizing assistance parameters to optimize physiological outcomes remains challenging. Human-in-the-loop (HIL) optimization has emerged as an effective strategy for tailoring device control, often using electromyography (EMG) as a real-time proxy for metabolic cost. This
[...] Read more.
Exoskeletons offer promising solutions for enhancing human mobility; however, personalizing assistance parameters to optimize physiological outcomes remains challenging. Human-in-the-loop (HIL) optimization has emerged as an effective strategy for tailoring device control, often using electromyography (EMG) as a real-time proxy for metabolic cost. This study simulates HIL optimization using surrogate models built from the average root mean square of the muscles’ activations (EMG-RMS) derived from treadmill walking trials with a robotic waist tether. Nine surrogate models were evaluated for prediction accuracy, including gradient boosting (GB), random forest, support vector regression, and Gaussian process variants. Seven global optimization algorithms were compared based on convergence time, EMG-RMS at optimum, and efficiency metrics. GB achieved the highest predictive accuracy (1.57% RAEP). Among optimizers, the gravitational search algorithm (GSA) produced the lowest EMG-RMS value (0.17 normalized units) and the fastest convergence (0.32 s), while particle swarm optimization (PSO) achieved 0.36 EMG-RMS in 1.61 s. These findings demonstrate the value of EMG-based simulation frameworks in guiding algorithm selection for HIL optimization, ultimately reducing the experimental burden in developing personalized exoskeleton assistance strategies.
Full article
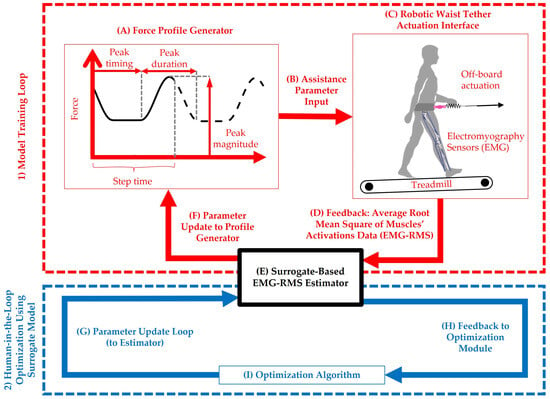
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Digital Dementia: Smart Technologies, mHealth Applications and IoT Devices, for Dementia-Friendly Environments
by
Suvish, Mehrdad Ghamari and Senthilarasu Sundaram
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 112; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060112 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global increase in dementia cases, which is predicted to exceed 152 million by 2050, poses substantial challenges to healthcare systems and caregiving structures. Concurrently, the expansion of mobile health (mHealth) technologies offers scalable, cost-effective opportunities for dementia care. This study systematically reviews
[...] Read more.
The global increase in dementia cases, which is predicted to exceed 152 million by 2050, poses substantial challenges to healthcare systems and caregiving structures. Concurrently, the expansion of mobile health (mHealth) technologies offers scalable, cost-effective opportunities for dementia care. This study systematically reviews 100 publicly available dementia-related mobile applications on the Apple App Store (iOS) and the Google Play Store (Android), categorised using the Mobile App Rating Scale (MARS), as well as the targeted end-users, Internet of Things (IoT) integration, data protection, and cost burden. Applications were evaluated for their utility in cognitive training, memory support, carer education, clinical decision-making, and emotional well-being. Findings indicate a predominance of carer resources and support tools, while clinically integrated platforms, cognitive assessments, and adaptive memory aids remain underrepresented. Most apps lack empirical validation, inclusive design, and integration with electronic health records, raising ethical concerns around data privacy, transparency, and informed consent. In parallel, the study identifies promising pathways for energy-optimised IoT systems, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) technologies in fostering dementia-friendly, sustainable environments. Key gaps include limited use of low-power wearables, energy-efficient sensors, and smart infrastructure tailored to therapeutic needs. Application domains such as cognitive training (19 apps) and carer resources (28 apps) show early potential, while emerging innovations in neuroadaptive architecture and emotional computing remain underexplored. The findings emphasize the need for co-designed, evidence-based digital solutions that align with the evolving needs of people with dementia, carers, and clinicians. Future innovations must integrate sustainability principles, promote interoperability, and support global aging populations through ecologically responsible, person-centred dementia care ecosystems.
Full article
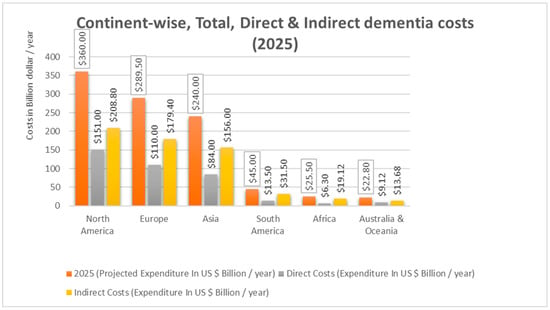
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Analysis of LoRa Network Wireless Signal Quality in Indoor Propagation Environments
by
Josip Lorincz, Krešimir Levarda, Mario Čagalj and Amar Kukuruzović
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060111 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
This paper investigates how key Long-Range (LoRa) sensor network transmission parameters and the number and material composition of physical obstacles on the signal propagation path impact wireless signal transmission quality in indoor propagation environments. A dedicated test platform was developed to assess how
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates how key Long-Range (LoRa) sensor network transmission parameters and the number and material composition of physical obstacles on the signal propagation path impact wireless signal transmission quality in indoor propagation environments. A dedicated test platform was developed to assess how different combinations of the LoRa transmission parameters, which include spreading factor, transmit power, transmit duty cycle, message payload size, and the quantity and material composition of physical obstacles, with the signal propagation path length influence critical signal quality indicators, specifically the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the received signal strength indicator (RSSI). The developed experimental test platform was implemented for a real-world indoor LoRa network composed of LoRa end devices (DVs) and gateways (GWs), utilizing technologies such as Node-RED for service orchestration, InfluxDB for data storage, The Things Network (TTN) for LoRa wide-area network connectivity, and Grafana for data visualization. The results of the performed analyses reveal how different combinations of LoRa transmission parameters, specifically the number and material composition of physical obstacles encountered during signal transmission among the LoRa end DVs and GWs, affect wireless signal quality indicators, namely RSSI and SNR, in indoor propagation environments of LoRa sensor networks. The obtained findings contribute to the optimization of LoRa transmission parameter selection for reliable and efficient signal transmission in LoRa indoor sensor network deployment, such as in urban environments with obstacles of varying structural composition and density encountered on the communication paths of different lengths between the LoRa end DVs and GWs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Data-Driven, Real-Time Diagnostics of 5G and Wi-Fi Networks Using Mobile Robotics
by
William O’Brien, Adam Dooley, Mihai Penica, Sean McGrath and Eoin O’Connell
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 110; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060110 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wireless connectivity plays a pivotal role in enabling real-time telemetry, sensor feedback, and autonomous navigation within Industry 4.0 environments. This paper presents a ROS 2-based mobile robotic platform designed to perform real-time network diagnostics across both private 5G and Wi-Fi technologies in a
[...] Read more.
Wireless connectivity plays a pivotal role in enabling real-time telemetry, sensor feedback, and autonomous navigation within Industry 4.0 environments. This paper presents a ROS 2-based mobile robotic platform designed to perform real-time network diagnostics across both private 5G and Wi-Fi technologies in a live smart manufacturing testbed. The system integrates high-frequency telemetry acquisition with spatial localization, multi-protocol connection analysis, and detailed performance monitoring. Metrics such as latency, packet loss, bandwidth, and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) data stream health are continuously logged and analysed. Telemetry is captured during motion and synchronously stored in an InfluxDB time-series database, enabling live visualization through Grafana dashboards. A key feature of the platform is its dual-path transmission architecture, which provides communication redundancy and allows side-by-side evaluation of network behaviour under identical physical conditions. Experimental trials demonstrate the platform’s ability to detect roaming events, characterize packet loss, and reveal latency differences between Wi-Fi and 5G networks. Results show that Wi-Fi suffered from roaming-induced instability and packet loss, whereas 5G maintained stable and uninterrupted connectivity throughout the test area. This work introduces a modular, extensible framework for mobile network evaluation in industrial settings and provides practical insights for infrastructure tuning, protocol selection, and wireless fault detection.
Full article
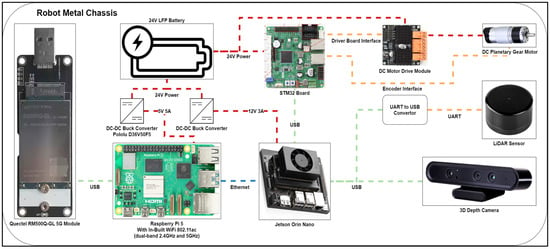
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Internet of Things: State-of-the-Art, Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects
by
Akeem Abimbola Raji and Thomas O. Olwal
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060109 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices due to remarkable developments in mobile connectivity has caused a tremendous increase in the consumption of broadband spectrums in fifth generation (5G) mobile access. In order to secure the continued growth of IoT, there is
[...] Read more.
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices due to remarkable developments in mobile connectivity has caused a tremendous increase in the consumption of broadband spectrums in fifth generation (5G) mobile access. In order to secure the continued growth of IoT, there is a need for efficient management of communication resources in the 5G wireless access. Cognitive radio (CR) is advanced to maximally utilize bandwidth spectrums in the radio communication network. The integration of CR into IoT networks is a promising technology that is aimed at productive utilization of the spectrum, with a view to making more spectral bands available to IoT devices for communication. An important function of CR is spectrum sensing (SS), which enables maximum utilization of the spectrum in the radio networks. Existing SS techniques demonstrate poor performance in noisy channel states and are not immune from the dynamic effects of wireless channels. This article presents a comprehensive review of various approaches commonly used for SS. Furthermore, multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MADRL) is proposed for enhancing the accuracy of spectrum detection in erratic wireless channels. Finally, we highlight challenges that currently exist in SS in CRIoT networks and further state future research directions in this regard.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Implementation of a Cloud-Based AI-Enabled Monitoring System in Machining, Utilizing Public 5G Infrastructure
by
Grigorios Kotsakis, Christos Papaioannou, Thanassis Souflas, Dimitris Tsolkas, Alex Kakyris, Panagiotis Gounas and Panagiotis Stavropoulos
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060108 - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cloud monitoring systems combine physical sensors with cloud computing capabilities. Modern manufacturing techniques and smart factories under Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 call for the integration of monitoring systems as part of the broader digitization process. Digitization typically occurs by integrating external sensors
[...] Read more.
Cloud monitoring systems combine physical sensors with cloud computing capabilities. Modern manufacturing techniques and smart factories under Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0 call for the integration of monitoring systems as part of the broader digitization process. Digitization typically occurs by integrating external sensors onto existing legacy machines. Data obtained can be utilized in digital twins, simulations, machine learning models, and Industrial Internet Of Things (IIoT) applications. The adaptation of these new technologies usually stalls due to the reluctance of end users to make modifications to already existing equipment, the legacy equipment that is in use and does not provide the information needed, and the substantial costs of integrating new measuring systems that typically require additional IT infrastructure. Having identified the need for easily scalable affordable measurement systems, new disseminated systems that utilize cloud solutions and use 5G as an enabler for real-time communication are on the rise. This publication proposes a methodology, and tests and demonstrates a relevant manufacturing use case for integrating a non-invasive-to-IT-infrastructure, cloud-based and artificial intelligence-powered monitoring system focused on high performance applications. The proposed methodology has been evaluated in a real industrial environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Security and Smart Applications in IoT and Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks)
►▼
Show Figures
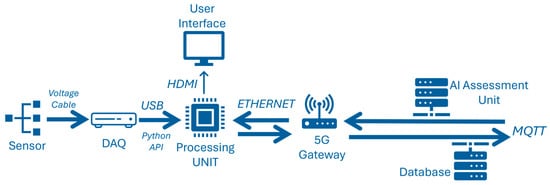
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Compact Bio-Inspired Terahertz Ultrawideband Antenna: A Viburnum tinus-Based Approach for 6G and Beyond Applications
by
Jeremiah O. Abolade, Dominic B. O. Konditi, Pradeep Kumar and Grace Olaleru
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060107 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A compact bio-inspired terahertz wideband antenna is presented in this work. The proposed antenna is based on Viburnum tinus leaf shape, a defective ground plane, a folded-ring slot, and parasitic elements. The footprint of the proposed antenna is
[...] Read more.
A compact bio-inspired terahertz wideband antenna is presented in this work. The proposed antenna is based on Viburnum tinus leaf shape, a defective ground plane, a folded-ring slot, and parasitic elements. The footprint of the proposed antenna is

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improving Audio Steganography Transmission over Various Wireless Channels
by
Azhar A. Hamdi, Asmaa A. Eyssa, Mahmoud I. Abdalla, Mohammed ElAffendi, Ali Abdullah S. AlQahtani, Abdelhamied A. Ateya and Rania A. Elsayed
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060106 - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
Ensuring the security and privacy of confidential data during transmission is a critical challenge, necessitating advanced techniques to protect against unwarranted disclosures. Steganography, a concealment technique, enables secret information to be embedded in seemingly harmless carriers such as images, audio, and video. This
[...] Read more.
Ensuring the security and privacy of confidential data during transmission is a critical challenge, necessitating advanced techniques to protect against unwarranted disclosures. Steganography, a concealment technique, enables secret information to be embedded in seemingly harmless carriers such as images, audio, and video. This work proposes two secure audio steganography models based on the least significant bit (LSB) and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) techniques for concealing different types of multimedia data (i.e., text, image, and audio) in audio files, representing an enhancement of current research that tends to focus on embedding a single type of multimedia data. The first model (secured model (1)) focuses on high embedding capacity, while the second model (secured model (2)) focuses on improved security. The performance of the two proposed secure models was tested under various conditions. The models’ robustness was greatly enhanced using convolutional encoding with binary phase shift keying (BPSK). Experimental results indicated that the correlation coefficient (Cr) of the extracted secret audio in secured model (1) increased by 18.88% and by 16.18% in secured model (2) compared to existing methods. In addition, the Cr of the extracted secret image in secured model (1) was improved by 0.1% compared to existing methods. The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of the steganography audio of secured model (1) was improved by 49.95% and 14.44% compared to secured model (2) and previous work, respectively. Furthermore, both models were evaluated in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system over various wireless channels, i.e., Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN), fading, and SUI-6 channels. In order to enhance the system performance, OFDM was combined with differential phase shift keying (DPSK) modulation and convolutional coding. The results demonstrate that secured model (1) is highly immune to noise generated by wireless channels and is the optimum technique for secure audio steganography on noisy communication channels.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neural Interfaces for Robotics and Prosthetics: Current Trends
by
Saket Sarkar and Redwan Alqasemi
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060105 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
The integration of neural interfaces with assistive robotics has transformed the field of prosthetics, rehabilitation, and brain–computer interfaces (BCIs). From brain-controlled wheelchairs to Artificial Intelligence (AI)-synchronized robotic arms, the innovations offer autonomy and improved quality of life for people with mobility disorders. This
[...] Read more.
The integration of neural interfaces with assistive robotics has transformed the field of prosthetics, rehabilitation, and brain–computer interfaces (BCIs). From brain-controlled wheelchairs to Artificial Intelligence (AI)-synchronized robotic arms, the innovations offer autonomy and improved quality of life for people with mobility disorders. This article discusses recent trends in brain–computer interfaces and their application in robotic assistive devices, such as wheelchair-mounted arms, drone control systems, and robotic limbs for activities of daily living (ADLs). It also discusses the incorporation of AI systems, including ChatGPT-4, into BCIs, with an emphasis on new innovations in shared autonomy, cognitive assistance, and ethical considerations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Actuators, Sensors and Devices)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Fault Diagnosis in IoT Applications: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Giovanni Cicceri and Fabrizio De Vita
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(6), 104; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14060104 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way industrial, structural, and environmental systems are monitored and maintained [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fault Diagnosis in the Internet of Things Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Development of Optical and Electrical Sensors for Non-Invasive Monitoring of Plant Water Status
by
Nasreddine Makni, Riccardo Collu and Massimo Barbaro
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(5), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050103 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
Monitoring plant water status is vital for optimizing irrigation in precision agriculture. This study explores the use of two simple, affordable, and non-invasive sensor systems, electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, to assess plant water status directly from leaf tissues. This
[...] Read more.
Monitoring plant water status is vital for optimizing irrigation in precision agriculture. This study explores the use of two simple, affordable, and non-invasive sensor systems, electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and infrared (IR) spectroscopy, to assess plant water status directly from leaf tissues. This approach is well-suited for the realization of large networks of distributed sensors wirelessly connected to a central hub. An outdoor experiment was conducted over two phases of 20 day-experiment involving six Hydrangea macrophylla plants subjected to two irrigation treatments: a control group (well-irrigated) and a test group (poorly irrigated) designed to induce water stress. The standard relative water content (RWC) method validated the treatment effects on the plants, and both EIS and IR sensors effectively distinguished between the two groups. Impedance-derived parameters, particularly the normalized intracellular resistance (R0) and the cell membrane capacitance (C0), exhibited statistically significant differences between the treatments. In addition, the IR measurements showed moderate correlations with RWC, with determination coefficients of R2 = 0.56 and R2 = 0.51 for first and second phases of the experiment, respectively. Despite some limitations concerning the electrode–leaf conformity and external sunlight interference, the results point to the advantages of these methods for real-time plant monitoring and decision-making in smart irrigation systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enabling Adaptive Food Monitoring Through Sampling Rate Adaptation for Efficient, Reliable Critical Event Detection
by
Elia Henrichs, Dana Jox, Pia Schweizer and Christian Krupitzer
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(5), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050102 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Monitoring systems are essential in many fields, such as food production, storage, and supply, to collect information about applications or their environments to enable decision-making. However, these systems generate massive amounts of data that require substantial processing. To improve data analysis efficiency and
[...] Read more.
Monitoring systems are essential in many fields, such as food production, storage, and supply, to collect information about applications or their environments to enable decision-making. However, these systems generate massive amounts of data that require substantial processing. To improve data analysis efficiency and reduce data collectors’ energy demand, adaptive monitoring is a promising approach to reduce the gathered data while ensuring the monitoring of critical events. Adaptive monitoring is a system’s ability to adjust its monitoring activity during runtime in response to internal and external changes. This work investigates the application of adaptive monitoring—especially, the adaptation of the sensor sampling rate—in dynamic and unstable environments. This work evaluates 11 distinct approaches, based on threshold determination, statistical analysis techniques, and optimization methods, encompassing 33 customized implementations, regarding their data reduction extent and identification of critical events. Furthermore, analyses of Shannon’s entropy and the oscillation behavior allow for estimating the efficiency of the adaptation algorithms. The results demonstrate the applicability of adaptive monitoring in food storage environments, such as cold storage rooms and transportation containers, but also reveal differences in the approaches’ performance. Generally, some approaches achieve high observation accuracies while significantly reducing the data collected by adapting efficiently.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Modeling and Detection of Vascular Stenosis Based on Molecular Communication in the Internet of Things
by
Zitong Shao, Pengfei Zhang, Xiaofang Wang and Pengfei Lu
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(5), 101; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050101 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
Molecular communication (MC) has emerged as a promising paradigm for nanoscale information exchange in Internet of Bio-Nano Things (IoBNT) environments, offering intrinsic biocompatibility and potential for real-time in vivo monitoring. This study proposes a cascaded MC channel framework for vascular stenosis detection, which
[...] Read more.
Molecular communication (MC) has emerged as a promising paradigm for nanoscale information exchange in Internet of Bio-Nano Things (IoBNT) environments, offering intrinsic biocompatibility and potential for real-time in vivo monitoring. This study proposes a cascaded MC channel framework for vascular stenosis detection, which integrates non-Newtonian blood rheology, bell-shaped constriction geometry, and adsorption–desorption dynamics. Path delay and path loss are introduced as quantitative metrics to characterize how structural narrowing and molecular interactions jointly affect signal propagation. On this basis, a peak response time-based delay inversion method is developed to estimate both the location and severity of stenosis. COMSOL 6.2 simulations demonstrate high spatial resolution and resilience to measurement noise across diverse vascular configurations. By linking nanoscale transport dynamics with system-level detection, the approach establishes a tractable pathway for the early identification of vascular anomalies. Beyond theoretical modeling, the framework underscores the translational potential of MC-based diagnostics. It provides a foundation for non-invasive vascular health monitoring in IoT-enabled biomedical systems with direct relevance to continuous screening and preventive cardiovascular care. Future in vitro and in vivo studies will be essential to validate feasibility and support integration with implantable or wearable biosensing devices, enabling real-time, personalized health management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
VeMisNet: Enhanced Feature Engineering for Deep Learning-Based Misbehavior Detection in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
by
Nayera Youness, Ahmad Mostafa, Mohamed A. Sobh, Ayman M. Bahaa and Khaled Nagaty
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(5), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050100 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ensuring secure and reliable communication in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) is critical for safe transportation systems. This paper presents Vehicular Misbehavior Network (VeMisNet), a deep learning framework for detecting misbehaving vehicles, with primary contributions in systematic feature engineering and scalability analysis. VeMisNet
[...] Read more.
Ensuring secure and reliable communication in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs) is critical for safe transportation systems. This paper presents Vehicular Misbehavior Network (VeMisNet), a deep learning framework for detecting misbehaving vehicles, with primary contributions in systematic feature engineering and scalability analysis. VeMisNet introduces domain-informed spatiotemporal features—including DSRC neighborhood density, inter-message timing patterns, and communication frequency analysis—derived from the publicly available VeReMi Extension Dataset. The framework evaluates Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), and Bidirectional LSTM architectures across dataset scales from 100 K to 2 M samples, encompassing all 20 attack categories. To address severe class imbalance (59.6% legitimate vehicles), VeMisNet applies SMOTE post train–test split, preventing data leakage while enabling balanced evaluation. Bidirectional LSTM with engineered features achieves 99.81% accuracy and F1-score on 500 K samples, with remarkable scalability maintaining >99.5% accuracy at 2 M samples. Critical metrics include 0.19% missed attack rates, under 0.05% false alarms, and 41.76 ms inference latency. The study acknowledges important limitations, including reliance on simulated data, single-split evaluation, and potential adversarial vulnerability. Domain-informed feature engineering provides 27.5% relative improvement over dimensionality reduction and 22-fold better scalability than basic features. These results establish new VANET misbehavior detection benchmarks while providing honest assessment of deployment readiness and research constraints.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Smart Crop Technologies for Resource Constrained Environments: Leveraging Multimodal Data Fusion, Edge-to-Cloud Computing, and IoT Virtualization
by
Damilola D. Olatinwo, Herman C. Myburgh, Allan De Freitas and Adnan M. Abu-Mahfouz
J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14(5), 99; https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan14050099 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
Smart crop technologies offer promising solutions for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability, particularly in the face of global challenges such as resource scarcity and climate variability. However, their deployment in infrastructure-limited regions, especially across Africa, faces persistent barriers, including unreliable power supply, intermittent
[...] Read more.
Smart crop technologies offer promising solutions for enhancing agricultural productivity and sustainability, particularly in the face of global challenges such as resource scarcity and climate variability. However, their deployment in infrastructure-limited regions, especially across Africa, faces persistent barriers, including unreliable power supply, intermittent internet connectivity, and limited access to technical expertise. This study presents a PRISMA-guided systematic review of literature published between 2015 and 2025, sourced from the Scopus database including indexed content from ScienceDirect and IEEE Xplore. It focuses on key technological components including multimodal sensing, data fusion, IoT resource management, edge-cloud integration, and adaptive network design. The analysis of these references reveals a clear trend of increasing research volume and a major shift in focus from foundational unimodal sensing and cloud computing to more complex solutions involving machine learning post-2019. This review identifies critical gaps in existing research, particularly the lack of integrated frameworks for effective multimodal sensing, data fusion, and real-time decision support in low-resource agricultural contexts. To address this, we categorize multimodal sensing approaches and then provide a structured taxonomy of multimodal data fusion approaches for real-time monitoring and decision support. The review also evaluates the role of IoT virtualization as a pathway to scalable, adaptive sensing systems, and analyzes strategies for overcoming infrastructure constraints. This study contributes a comprehensive overview of smart crop technologies suited to infrastructure-limited agricultural contexts and offers strategic recommendations for deploying resilient smart agriculture solutions under connectivity and power constraints. These findings provide actionable insights for researchers, technologists, and policymakers aiming to develop sustainable and context-aware agricultural innovations in underserved regions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Remote Sensing and IoT Application for Smart Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- JSAN Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
19 November 2025
Meet Us Virtually at the 1st International Online Conference on Sensor and Actuator Networks (CSAN 2026), 9–10 July 2026
Meet Us Virtually at the 1st International Online Conference on Sensor and Actuator Networks (CSAN 2026), 9–10 July 2026

6 November 2025
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, Electronics, JSAN, Technologies
Emerging AI+X Technologies and Applications
Topic Editors: Byung-Seo Kim, Hyunsik Ahn, Kyu-Tae LeeDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, JSAN, Technologies, BDCC, Sensors, Telecom, Electronics
Electronic Communications, IOT and Big Data, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Teen-Hang Meen, Charles Tijus, Cheng-Chien Kuo, Kuei-Shu Hsu, Jih-Fu TuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Mechanics, JLPEA, JSAN, ASI
Application of IOT on Manufacturing, Communication and Engineering, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Teen-Hang Meen, Chun-Yen Chang, Charles Tijus, Cheng-Fu Yang, Shu-Han LiaoDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Electronics, Future Internet, Information, JSAN, Sensors, IoT
Privacy Challenges and Solutions in the Internet of Things
Topic Editors: Abdul Majeed, Safiullah KhanDeadline: 30 June 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JSAN
Federated Learning: Applications and Future Directions
Guest Editors: Giovanni Paragliola, Laura Verde, Fiammetta Marulli, Rosario CatelliDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
JSAN
Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks: Innovations and Future Trends
Guest Editors: Dionisis Kandris, Eleftherios Anastasiadis, Purav ShahDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
JSAN
Recent Advances in Industrial Network Security
Guest Editors: Sabeen Tahir, Sheikh Tahir Bakhsh, Xu-An WangDeadline: 10 February 2026
Special Issue in
JSAN
AI and IoT Convergence for Sustainable Smart Manufacturing
Guest Editors: Chun-Cheng Lin, Tony HuangDeadline: 28 February 2026











