Abstract
Path planning is a complex task in robotics, requiring an efficient and adaptive algorithm to find the shortest path in a dynamic environment. The traditional path planning methods, such as graph-based algorithms, sampling-based algorithms, reaction-based algorithms, and optimization-based algorithms, have limitations in computational efficiency, real-time adaptability, and obstacle avoidance. To address these challenges, hybrid path planning algorithms combine the strengths of multiple techniques to enhance performance. This paper includes a comprehensive review of hybrid approaches based on graph-based algorithms, sampling-based algorithms, reaction-based algorithms, and optimization-based algorithms. Also, this article discusses the advantages and limitations, supported by a comparative evaluation of computational complexity, path optimization, and finding the shortest path in a dynamic environment. Finally, we propose an AI-driven adaptive path planning approach to solve the difficulties.
1. Introduction
In this industrial era, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) are replacing humans to perform efficient tasks, and also in other fields, such as industrial automation, smart homes, and autonomous driving, are crucial for enhancing production efficiency []. Various types of AMR, like wheeled robots for flat environments, legged robots mimic human locomotion by using legs, aerial robots are capable of flying, and underwater robots to perform their task in marines are available. The types of AMR and their applications are presented in Figure 1. AMR encompasses a broad range of applications, such as mining, military operations, rescue missions, space exploration, agriculture, medical [], and entertainment. In these areas, the successful navigation of AMR largely relies on its intelligence and capabilities [].
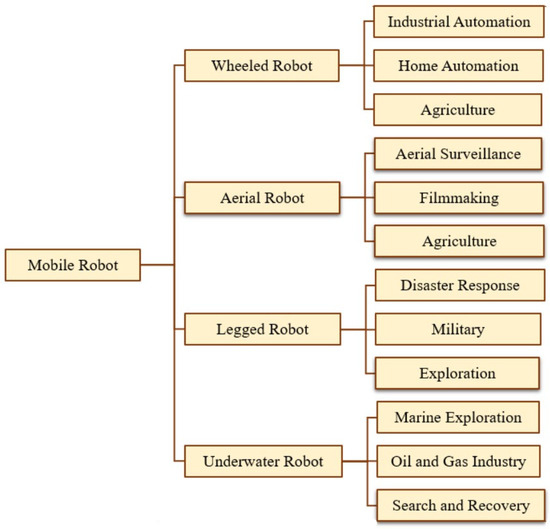
Figure 1.
Various types of mobile robots and their applications.
Path planning (PP) plays an important role in AMR for navigation. PP is to find the feasible path to attain the goal position, and it helps to avoid obstacles in the robot’s path []. It is possible with the help of software, regular sensors for vision and localization, and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Reinforcement Learning (RL) has a significant role in PP []. Hybrid PP algorithms integrate multiple planning strategies to enhance overall performance, enabling the identification of optimal paths and efficient goal attainment within minimal time. Hybrid PP approaches are typically designed to operate in both local and global environments, combining the strengths of each. Accordingly, PP algorithms can be broadly classified into three categories: global, local, and hybrid, as shown in Figure 2. Global PP is performed only in a known environment using graph-based technique. Local PP detects obstacles in its surroundings and navigates to its goal position. Hybrid PP algorithms are particularly effective in addressing complex scenarios, such as navigating narrow spaces or traversing diverse terrains. This paper primarily focuses on hybrid PP while also reviewing local, global, classical, heuristic, and hybrid PP techniques to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape.
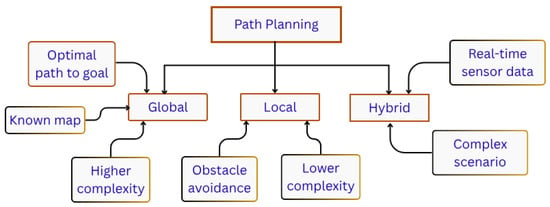
Figure 2.
Types of path planning.
2. Methodology
This review presents a detailed examination of hybrid PP for AMR. The methodology employed for this review involves classifying and analyzing various traditional and hybrid PP techniques, with a focus on their computational efficiency, real-time adaptability, obstacle avoidance, and path optimization. Majorly, various articles were collected from the database, such as “Google Scholar” and “Scopus”, with a keyword combination of ‘Mobile Robot path planning + Classical approach’, ‘Mobile robot path planning + heuristic approach’, ‘AI-driven approach’, and ‘Mobile robot path planning + hybrid approach’. This article encompasses the following classification of PP algorithms:
- ➢
- Graph-based algorithms: This section provides mathematical techniques for determining the shortest path from a start node to a goal node, suitable for a static environment with known obstacles. Algorithms include A*, Dijkstra, Breadth-First Search (BFS), Depth First Search (DFS), Floyd-Warshall, and Bellman-Ford algorithms. The pseudocode for graph-based algorithms is presented in Appendix A.
- ➢
- Sampling-based algorithms: This covers techniques that explore the configuration space by random sampling points and constructing a graph or tree structure to identify feasible paths. Algorithms such as Rapidly Exploring Random Tree (RRT), Probabilistic Road Map (PRM), Batch Informed Tree (BIT), and Single-Query Biased algorithms are analyzed. The pseudocode for PRM, RRT, and BIT algorithms is presented in Appendix A.
- ➢
- Reaction-based algorithms: This part focuses on strategies where robot motion is determined in response to real-time sensors or environmental changes. This includes Artificial Potential Fields (APF), Dynamic Window Approach (DWA), and Vector Field Approach (VFA).
- ➢
- Optimization-based algorithms: These approaches treat path planning as an optimization problem, computing trajectories that minimize a specific cost function while adhering to operational constraints. Algorithms like the Gradient Descent Algorithm (GDA), Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Genetic Algorithm (GA) are discussed.
The paper emphasizes hybrid PP algorithms, which combine the strengths of multiple techniques (typically local and global planning) to enhance navigation efficiency, adaptability, and robustness in complex, dynamic, and partially unknown environments. The advantages and limitations of these hybrid approaches are discussed, along with a comparative evaluation of computational complexity, path optimization, and their ability to find the shortest path in dynamic environments. Finally, the review proposes an AI-driven adaptive PP approach to address existing challenges.
3. Graph-Based Path Planning Algorithms
Graph-based PP algorithms use mathematical techniques to determine the shortest path from a start node to a goal node. This method operates using two types of maps: a grid map and a graph structure. It is suitable only for static environments with known obstacles. Figure 3 presents the various graph-based algorithms considered in this work.
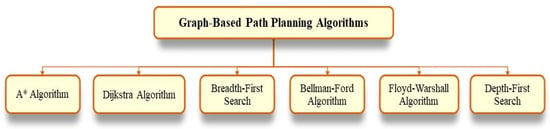
Figure 3.
Graph-based PP algorithms.
3.1. A* Algorithm
The A* algorithm is a heuristic-based global PP technique widely regarded for its effectiveness in finding optimal paths. It enhances search efficiency by employing heuristic functions to guide the exploration process, thereby minimizing the number of nodes evaluated. Due to its balance between performance and accuracy, the A* algorithm applies to a wide range of problem domains and is particularly well-suited for optimization tasks in navigation and robotics []. Experimental findings reported by researchers indicate that the computational time for A* can be substantial. For instance, when applied to a map consisting of 60,000 cells, a standard computing system required over an hour to complete the PP calculations []. In recent years, the A* algorithm has undergone several modifications to suit diverse application domains, referred to as improved or modified A* variants. These enhancements are typically tailored to specific use cases, with the primary objectives of increasing computational efficiency, adaptability, and performance, particularly in dynamic or complex environments. For instance, in Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) control, an enhanced A* algorithm has been shown to effectively identify the shortest path with minimal turns, outperforming traditional methods in both accuracy and execution. Comparative analyses further reveal that the improved A* algorithm demonstrates significantly higher search efficiency than Dijkstra’s algorithm, and marginal improvements over the conventional A* algorithm. Notably, as the calculated path approaches the optimal minimal length, the algorithm’s search efficiency also reaches its maximum potential [].
The path length and number of turns are the major concerns for the A* algorithm. Recent advancements in mobile robot PP have increasingly focused on refining the A* algorithm to overcome its inherent limitations. A range of studies has proposed methodological enhancements aimed at improving computational efficiency, reducing path length, and minimizing the number of turning points. Notable developments include the optimization of node storage structures to accelerate search operations [], the implementation of adaptive weight functions and turn penalties to enhance path smoothness [], and the expansion of search neighborhoods to improve solution quality []. In addition, several works have incorporated kinematic constraints into the A* framework to ensure trajectories are more consistent with the physical motion capabilities of robots []. Hybrid approaches such as integrating A* algorithm with DWA have demonstrated enhanced adaptability for navigation in environments with dynamic obstacles and complex geometries [,]. Furthermore, path smoothing techniques, including the use of Bezier curves, have been employed to refine trajectories and reduce unnecessary directional changes [,]. Collectively, these innovations have achieved substantial improvements in search time, path efficiency, and trajectory smoothness compared to the conventional A* algorithm, highlighting their potential for broader application in real-world robotic navigation tasks.
3.2. Dijkstra Algorithm
The Dijkstra algorithm is a popular algorithm used to find the shortest path between two nodes in a graph and operates on a simple principle: Start by creating a set ‘S’ of vertices, then calculate the path weights from the source point ‘S’ to the vertices in that set. As the algorithm runs, it continuously selects different paths, adding vertices with the most accurate path estimates to ‘S’. When a vertex ‘i’ is added to ‘S’, the algorithm updates the path weights for vertex ‘i’, ultimately determining the shortest path as the one with the lowest weight []. Negative edge weights do not work with the Dijkstra algorithm. It is the best way to find the single-source shortest path by using a greedy approach. The various approaches of Dijkstra algorithms are the Brute-force method, Fibonacci Heap Implementation, Binary heap implementation, and Bi-directional Dijkstra Implementation [].
Recent research in mobile robot PP has investigated a variety of algorithms aimed at optimizing navigation efficiency and obstacle avoidance. The integration of the Dijkstra algorithm with odometry has been shown to significantly enhance the operational performance of warehouse robots, yielding reductions in both travel distance and completion time when compared to conventional line-following approaches []. Similarly, the combination of the Dijkstra algorithm, an improved Artificial Fish Swarm algorithm with Bezier curve-based path smoothing has demonstrated notable gains in planning accuracy and trajectory smoothness, thereby improving the overall navigation capability of a mobile robot in complex environments [].
3.3. Breadth-First Search
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a graph-based algorithm that explores nodes level by level, starting from a source node and visiting all its immediate neighbors before proceeding to the next layer of nodes. In robotic navigation, BFS can be used to identify the shortest unweighted path from the robot’s current position to the next target. Although BFS does not inherently use a heuristic function, unlike A*. It guarantees the shortest path in terms of the number of steps in an unweighted grid or graph []. BFS begins with a source node and initializes a queue (often referred to as the frontier) to manage the list of nodes to be explored, starting with the source itself. The algorithm marks the source node as visited. Then, it repeatedly examines each node at the front of the queue and explores its unvisited neighbors. For each unvisited neighbor, it marks the node as visited, assigns its parent node (for later path reconstruction), and adds it to the queue. This process continues, level by level, until all reachable nodes have been visited. At each iteration, the current frontier is replaced with the next layer of neighbors, ensuring a systematic and complete traversal []. BFS has been applied in multi-robot systems to compute optimal paths while accounting for formation constraints and obstacle avoidance requirements []. The primary drawbacks of the BFS algorithm are its significant memory consumption and its inefficiency in large search spaces, as it explores without any heuristic guidance []. The Bidirectional BFS technique has been integrated into fast PP algorithms to minimize unnecessary exploration of the search space and prevent bifurcations, thereby producing shorter and more efficient paths [].
3.4. Depth-First Search
Depth-First Search (DFS) is a fundamental graph-based algorithm widely utilized in computer science, robotics, and network analysis. Its ability to explore deep paths before backtracking makes it suitable for tasks involving systematic coverage and exploration. In robotic applications, DFS is employed to generate a path that enables the robot to visit all sampling points within a defined area of interest. This ensures complete coverage while aiming to reduce redundant or unnecessary movements. By recursively visiting each unvisited node (sampling point), DFS guarantees that the robot thoroughly explores the environment, an essential requirement for applications such as radiation mapping, where comprehensive spatial data collection is critical. Despite its strengths, DFS may not always yield the most optimal path in terms of distance, but it remains effective for ensuring full coverage in a structured manner []. DFS is used to establish the order of navigation for the robot through the designated space while guaranteeing full exploration by circumventing unnecessary movements. The designated space utilized a grid mapping framework with open cells marked as 0 and impeded by obstacles as 1. Following the application of Boustrophedon Cell Division to the grid, the resulting segments consist solely of accessible cells. It is also employed to determine the sequence that facilitates the traversal of these cells. Through the DFS, connected graph nodes correspond to cells, and the algorithm proceeds through one cell at a time, ensuring each cell is visited exactly once. Simulation experiments indicate that the combined approach of PP by DFS and radiation field reconstruction via ground penetrating radar effectively represents nuclear radiation environments. This tool can lead to less optimal pathways in domains with complex obstacle layouts, as it prioritizes depth over breadth, potentially resulting in extended travel routes [].
DFS algorithms, while applicable to PP, exhibit several limitations. They often generate circuitous paths and require considerable computational time, particularly in complex or large-scale environments []. Moreover, DFS-based methods may suffer from reduced efficiency in expansive networks, necessitating enhancements such as the integration of relative positional information and improved backtracking conditions []. In contrast, BFS can achieve faster planning times but frequently produces suboptimal and less stable paths []. To overcome these challenges, researchers have investigated advanced techniques, including metaheuristic optimization, machine learning (ML) based methods, and hybrid algorithms that integrate multiple planning strategies []. Notable developments include the Depth Sorting Fast Search (DSFS) algorithm, which improves computational speed without sacrificing accuracy [], and the Dynamic Weighted A* algorithm, which exhibits strong adaptability in dynamic scenarios such as smart parking systems []. DFS’s advantages include simplicity of implementation and low memory requirements compared to BFS. However, DFS does not guarantee the shortest path can become trapped in deep, suboptimal branches, making it less suitable for large-scale or highly dynamic environments without modifications such as iterative deepening or heuristic integration [].
3.5. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
Floyd-Warshall algorithm is a renowned dynamic programming strategy utilized to address the All-Pairs Shortest Paths (APSP) challenge in graphs. This renders it particularly useful for route optimization in intricate networks, such as those encountered in warehouse operations. Within warehouse management, the algorithm adeptly computes the shortest routes between all pairs of nodes, including storage areas, by progressively updating distance matrices. This approach guarantees that order pickers benefit from the most efficient travel routes []. This research highlights the algorithm’s effectiveness in reducing travel distances and numerous nodes. When contrasted with alternative methods like dynamic programming, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm distinguishes itself in scenarios where the primary aim is to minimize travel time, disregarding other constraints such as the load capacity of each picker []. However, it does face a limitation in that it cannot accommodate real-world factors like picker capacity. This challenge can be addressed by combining it with other optimization techniques []. The Floyd-Warshall algorithm is a powerful tool for enhancing warehouse logistics, particularly for diminishing travel distances and increasing operational efficiency.
The Floyd-Warshall algorithm, though valuable for all-pairs shortest path optimization, presents notable limitations in mobile robot PP. Its tendency to produce circuitous routes and incur excessive computational time renders it less suitable for real-time applications, particularly in complex environments []. Comparative analyses indicate that algorithms such as A* or BFS often outperform Floyd-Warshall in terms of efficiency for time–critical navigation tasks []. Nevertheless, its integration with other optimization techniques has shown promising results. For example, coupling Floyd-Warshall with an improved intelligent Water Drop algorithm yielded a 7.7% reduction in path length and a 36.3% reduction in inflection points in robot inspection scenarios []. Similarly, its combination with an enhanced Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) method facilitated the generation of guiding paths and improved pheromone distribution []. In warehouse logistics, Floyd-Warshall exhibited significant variations in total distance calculations compared to alternative methods, underscoring the need for algorithm selection tailored to specific operational contents [].
3.6. Bellman-Ford Algorithm
The Bellman-Ford algorithm is a well-established method for PP that not only computes shortest paths in graphs with negative edge weights but also detects negative cycles, capabilities not offered by algorithms like Dijkstra, A*, RRT, and RRT* [,]. Although its ability to handle diverse graph conditions is advantageous, the Bellman-Ford algorithm’s O(nm) time complexity is significantly slower than that of A* or Dijkstra, rendering it impractical for real-time applications in dynamic smart farm environments, where rapid and precise navigation is crucial to minimize crop damage []. A* is the most suitable algorithm for smart farming applications, as it offers an effective balance of speed, accuracy, and predictability, particularly in environments with a mix of static and dynamic obstacles []. The inefficiency of Bellman-Ford and its lack of relevance to non-negative agricultural path costs further highlight why it is not suitable for these applications, where timely responses and precise localization are crucial [,].
The Bellman-Ford algorithm, while versatile for solving single-source path problems, exhibits several limitations in mobile robot PP. Its tendency to generate circuitous routes and incur substantial computational time makes it less suitable for real-time applications []. In evacuation route planning for multi-floor buildings, this algorithm demonstrated only a marginal 3.5% improvement in initial evacuation speed compared to Dijkstra’s algorithm []. Within autonomous driving systems, Bellman-Ford is categorized among traditional graph-based methods, which are often outperformed by metaheuristic optimization and ML techniques in handling complex, dynamic environments []. Nonetheless, the algorithm offers an advantage in energy efficiency for smaller problem sizes that fit within upper memory hierarchies, consuming up to 2.36 W less power on average compared to Dijkstra’s algorithm, a benefit that could be significant for applications requiring frequent solutions to small-scale instances []. Table 1 presents the comparative analysis of graph-based PP algorithms.

Table 1.
Comparative Analysis of Graph-Based PP Algorithms.
4. Sampling-Based Path Planning Algorithms
Sampling-based algorithms are a class of techniques used to determine feasible paths for an agent within a given environment. These methods explore the configuration space by randomly sampling points and incrementally constructing a graph or tree structure that connects these samples. The path from the start to the goal position is then identified through this structure, enabling efficient navigation even in high-dimensional or complex spaces. The different sampling-based PP algorithms are presented in Figure 4.
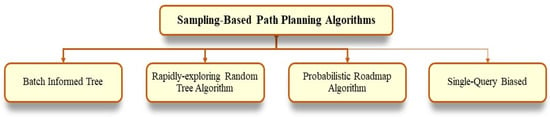
Figure 4.
Sampling-based PP algorithms.
4.1. Rapidly Exploring Random Tree Algorithm
The Rapidly exploring Random Tree (RRT) algorithm is a key player in sampling-based PP, but it does encounter some challenges, including slow convergence, unnecessary node exploration, and limited adaptability in complex environments. Recent developments have tackled these issues with innovative approaches: Adjustable probability and sampling area, and the Dijkstra optimization-based RRT algorithm (APSD-RRT) [] improves efficiency by using adjustable probabilities and reducing the dynamic sampling area, along with Dijkstra pruning and interpolation to create smoother paths. Complex environments rapidly exploring random tree (CERRT) [] features pre-allocated node expansion and a vertex death mechanism to steer clear of local minima, while its bidirectional shrinking optimization enhances path quality in cluttered spaces. Together, these methods mark significant advancements in improving computational efficiency, path quality, and adaptability to different environments, pushing RRT-based solutions forward for real-world autonomous navigation challenges in both static and dynamic settings [].
Recent advancements in mobile robot PP have placed considerable emphasis on the RRT algorithm to address its inherent limitations. An improved RRT* method was proposed to incorporate a generalized Voronoi diagram and an adaptive bias strategy, thereby increasing sampling efficiency and accelerating convergence []. A Bidirectional RRT*-DWA integrated with Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization was developed to enable robust navigation in dynamic environments []. The memorized RRT optimization (MRRTO) algorithm was introduced, which leverages memory-based path refinement to achieve superior performance over the original RRT and comparable algorithms in both computation time and path length []. RRT* with guiding the tree approaching obstacles (GAO-RRT*), which optimizes the tree extension process through dual-weighted sampling, variable step-size extension, and reverse growth strategies. Experimental results demonstrated that GAO-RRT* significantly outperforms RRT*, Quick-RRT* (Q-RRT*), and Fast-RRT* (F-RRT*) in terms of path cost and convergence speed []. Collectively, these challenges in RRT-based PP include slow convergence, limited adaptability to dynamic environments, and suboptimal path generation.
4.2. Probabilistic Roadmap Algorithm
Probabilistic Roadmap Algorithm (PRM) is a popular method for PP that builds a network of nodes and edges free from collisions, facilitating autonomous navigation in complex environments. Research has shown that PRM functions in two main phases: a learning phase, where random configurations are sampled and linked to create a roadmap, and a query phase, which looks for the best paths between starting and goal points. The performance PRM algorithm has been enhanced in narrow channels by incorporating Artificial Potential Fields (APF) to enhance sampling density and using bidirectional A* for quicker pathfinding, ensuring safe routes in cluttered spaces []. The effectiveness of PRM in static environments was confirmed by achieving paths that were 42% shorter with fewer turns compared to the Genetic Algorithm (GA), although they pointed out its limitations in adapting to dynamic changes []. A further step by combining PRM with GA and Kalman Filtering (KF), resulting in GA-PRM, which surpassed A*, RRT, and standalone PRM in medical applications, with an average path length of 25.62 units and the ability to respond in real-time to moving obstacles []. Together, these studies highlight PRM’s flexibility and adaptability, especially when enhanced with additional techniques like APF, GA, or KF, making it essential for various applications, from industrial robotics to healthcare logistics.
Recently, a risk-bounded PRM planner was proposed for arbitrarily shaped robots operating in dynamic environments, explicitly accounting for uncertainty in edge costs to improve safety and reliability []. Advanced PRM-based planning by integrating ML techniques for enhanced trajectory control and path optimization []. The application of Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs) in PP demonstrates improved robustness through the incorporation of broader belief state distributions in probabilistic decision-making []. A comparative analysis of widely adopted roadmap approaches, including PRM, Voronoi diagrams, and RRT*, evaluating their performance across multiple metrics and operational scenarios, was provided []. Collectively, these studies underscore the significance of addressing uncertainty, leveraging ML integration, and tailoring algorithm selection to specific requirements for enhancing mobile robot navigation efficiently and reliability.
4.3. Batch Informed Tree
Batch Informed Trees (BIT) is a type of sampling-based PP algorithm that integrates with the concepts from both graph-based and asymptotically optimal methods, such as RRT*. It works like a set of samples in the configuration space to iteratively solve batches of shortest paths. BIT quickly returns an initial feasible path and improves it over time. At the same time, it is asymptotically optimal, guaranteeing convergence to the optimal path with increasing computing time. The main advantage is efficient batch processing; also, it allows for to reuse of previous computing methods, unnecessary edges, and leads to faster intermediate solutions []. To reduce computational overhead, the algorithm defers collision checking until it becomes necessary. This approach significantly improves performance in high-cost environments, such as those involving physics-based simulations. However, it may suffer from slower convergence in highly constrained or unknown spaces due to inefficient sample distribution. The algorithm is well-suited for tasks such as robotic manipulation, autonomous navigation, and sensor-based planning, particularly when near-optimal paths are desired and computation time permits iterative refinement [].
BIT*, a PP algorithm that integrates graph-based and sampling-based methodologies, ensuring probabilistic completeness and asymptotic optimality. Empirical results from both simulation and real-time experiments demonstrate that BIT* consistently outperforms conventional algorithms in terms of efficiency and solution quality []. BIT*, an informed, anytime sampling-based PP algorithm that addresses continuous PP problems through the integration of sampling strategies and heuristic guidance. BIT* is proven to be almost-surely asymptotically optimal and, based on experimental results, demonstrates superior performance compared to existing planners, particularly in high-dimensional problem spaces []. Flexible Informed Tress (FIT*) is introduced as an advanced sampling-based PP algorithm that employs an adaptive batch-size strategy to accelerate initial path convergence. This approach enhances computational efficiency and overall planning performance, particularly in navigating confined environments and addressing real-world robotics tasks, outperforming conventional planners in both convergence speed and adaptability []. BIT* unifies and extends the principles of RRT* and Fast Marching Trees (FMT) through the integration of heuristic guidance. BIT* demonstrates significant potential in reducing computational costs while maintaining asymptotic optimality, offering improved efficiency over existing start-of-the-art planning algorithms [].
4.4. Single-Query Biased
The Single-Query Biased algorithm is designed for the single-query PP problem. If the problem is that only one path from start to goal is required, and there is no need for multi-query optimization or asymptotic optimality []. The main advantage of this algorithm is low computation overhead and fast execution time, that perform in real-time or on constrained systems such as embedded robotics platforms. Due to their non-asymptotic nature, these algorithms do not confirm convergence to an optimal path. Sometimes it fails in high-dimensional or narrow passage environments where exploring a critical and a single attempt may not be sufficient []. The application of a single-query biased planner includes robot navigation in known or unknown environments, autonomous vehicles, and rapid PP for UGVs, especially when fast response is more important than path optimality. Table 2 presents the comparative analysis of sampling-based PP algorithms.

Table 2.
Comparative Analysis of Sampling-Based PP Algorithms.
5. Reaction-Based Path Planning Algorithms
A reaction-based method refers to a strategy where the motion or trajectory of an agent is determined in response to real-time sensor or environmental changes, rather than relying solely on precomputed or global paths. The algorithms considered in the article are shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
Reaction–based PP algorithms.
5.1. Artificial Potential Fields Algorithm
The Artificial Potential Field (APF) algorithm serves as a key method for PP in robotics, utilizing virtual forces to guide movement, attracting robots toward a goal while repelling them from obstacles. Though it is efficient and straightforward, traditional APF faces challenges such as getting stuck in local minima, difficulties in reaching targets near obstacles, and path oscillations. Recent developments have sought to overcome these issues through hybrid and adaptive techniques. For example, an improved APF by merging it with the Informed RRT* (IRRT*), using APF’s directional guidance to minimize the randomness in IRRT*’s sampling and enhance convergence rates in complex settings []. Another approach integrates the APF method with Deep Q-Networks (DQN), where the force-based optimization provided by APF reduces the training time of DQN by approximately 24%, while simultaneously improving success rates in dynamic environments []. Additionally, some research made further improvements by introducing adaptive step adjustments, escape velocity mechanisms, and path smoothing, effectively addressing local minima and unreachable targets while increasing efficiency by 74.8% compared to traditional APF []. Collectively, these advancements highlight APF’s adaptability as a fundamental framework, enhanced by hybrid and adaptive strategies, to improve robustness, efficiency, and practicality in both static and dynamic robotic navigation tasks.
A deterministic annealing strategy was proposed to improve the APF method, effectively mitigating he issue of local minima entrapment []. A Safe APF (SAPF) algorithm was introduced, which integrates repulsive and vortex potentials to ensure safe obstacle clearance []. An APF-enhanced A* algorithm tailored for unmanned surface vehicles was developed to operate in ocean currents, achieving reduced computation time and improved navigational safety []. Further A*-APF hybrid algorithm was optimized for autonomous driving by refining node expansion procedures, implementing a hybrid search strategy, and applying virtual ellipse theory to eliminate ineffective repulsive forces []. Together, these advancements address critical challenges in PP such as local minima avoidance, obstacle clearance optimization, and adaptation to environmental dynamics while enhancing computational efficiency, robustness, and trajectory safety across diverse autonomous system applications.
5.2. Dynamic Window Approach
The DWA is a reaction-based local PP algorithm generally used for real-time obstacle avoidance and path generation for AMR. DWA is not like a global path planner that computes a full geometric path from the starting point to the goal point. It focuses on selecting feasible short-term velocities that give output of both the dynamic constraints of the robot and collision avoidance requirements []. The algorithm works in a dynamic window of achievable velocities within a short time based on the robot’s acceleration and deceleration limits. DWA develops multiple trajectories using a cost function that considers obstacle avoidance and velocity efficiency. In this algorithm, computation efficiency and real-time applicability make it suitable for AMR. It also integrates with sensor data directly into the obstacle avoidance and allowing adaptation to a dynamic environment []. DWA is mostly used in AMR, service robots, and indoor navigation systems, particularly when real-time reaction to moving obstacles is required. It is often combined with a global planner such as A* or the Dijkstra algorithm to provide a complete navigation system [].
A high-speed variant of DWA was introduced, employing a polar coordinate transformation to accelerate computation and improve real-time feasibility []. A safe and efficient DWA was proposed to leverage deterministic sampling to mitigate uncertainties in system dynamics, thereby enhancing trajectory reliability []. A Dynamic Adaptive DWA was developed with the integration of conventional DWA with DL, enabling adaptive responses to environmental changes and dynamic obstacle scenarios. This method demonstrated superior performance compared to both standard DWA and standalone DL based planners []. Extending beyond robotics, the window approach framework is applied to improve nonparametric self-starting control charts in statistical process control, showcasing its versatility across domains []. Collectively, these advancements strengthen DWA’s capabilities in terms of computational speed, safety, adaptability, and cross-disciplinary applicability.
5.3. Vector Field Approach
The Vector Field Approach generates a smooth and continuous guidance mechanism for autonomous systems by establishing a directional flow field across the robot’s workspace []. Within this field, each spatial point is associated with a vector that indicates the direction of motion, guiding the robot according to the vector’s magnitude and orientation. This approach is particularly effective for obstacle avoidance, smooth trajectory planning, and coordinated motion in multi-agent systems. The vector field-based guidance strategy typically incorporates two primary components:
- ➢
- Attractive field: Directs the robot toward the designated goal.
- ➢
- Repulsive field: Emanates from obstacles, exerting a force that diverts the robot to avoid collisions.
By integrating these fields, the algorithm enables autonomous agents to navigate complex environments efficiently and safely []. Table 3 presents the comparative analysis of reaction-based PP algorithms.

Table 3.
Comparative Analysis of Reaction-Based PP Algorithms.
6. Optimization-Based Algorithm
Optimization-based PP methods are widely employed in robotics and autonomous navigation systems. These approaches treat the PP task as an optimization problem, where the goal is to compute a trajectory that minimizes a specific cost function subject to various operational constraints. The cost function may be defined in terms of minimizing travel distance, reducing energy consumption, ensuring smoother motion, maximizing safety margins, or minimizing the total time to reach the destination. Such methods are particularly useful in environments where path quality is critical and multiple competing factors must be balanced. The strength of optimization-based approaches lies in their ability to systematically handle complex criteria and constraints, resulting in solutions that are both feasible and near-optimal in performance. The various algorithms employed for PP are presented in Figure 6.
Figure 6.
Optimization-based PP algorithms.
6.1. Gradient Descent Algorithm
Gradient Descent Algorithm (GDA) is a first-order optimization technique commonly used in PP. It works by iteratively minimizing a differentiable potential function, which usually consists of attractive fields that guide the robot toward its goal and repulsive fields that help to avoid obstacles. GDA is particularly effective in single-query situations due to its computational efficiency and its independence from pre-processed maps, allowing it to adapt to high-dimensional or non-Euclidean spaces []. However, its effectiveness can be limited by issues like getting stuck in local minima, such as when the robot becomes trapped in concave areas with obstacles, and it may struggle in dynamic environments. In contrast, newer methods utilize deep reinforcement learning techniques and spatial attention mechanisms to improve real-time adaptability and robustness []. While GDA is still valued for its straightforward approach to path optimization, recent research is increasingly exploring hybrid methods, including end-to-end learning and dynamic perception, to overcome its limitations, especially in complex logistics tasks that require real-time obstacle avoidance and multi-modal decision-making.
6.2. Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a nature-inspired algorithm that emulates the foraging behavior of real ants, particularly their use of pheromone trails for indirect communication and path formation []. Leveraging swarm intelligence, ACO has been effectively applied to PP problems by incrementally constructing solutions through probabilistic transitions influenced by pheromone intensity and heuristic information. While classical ACO demonstrates strength in global search capabilities, it often suffers from limitations such as slow convergence rates, susceptibility to local optima, and reduced effectiveness in generating smooth and adaptable paths. To address these shortcomings, recent research has focused on enhancing the algorithm through dynamic pheromone updating mechanisms, hybridization with other optimization techniques, and the incorporation of path-smoothing strategies, thereby improving its efficiency and suitability for real-time path planning applications. A Terminal Distance Index-based Multi-Step ACO was introduced, which improves flexibility by allowing variable step sizes and replacing static pheromone updates with a distance heuristic to speed up convergence [].
Meanwhile, an Improved ACO (IACO) was proposed that features gradient-based pheromone initialization, adaptive heuristic factors, and a mechanism for collision avoidance in multi-robot systems, effectively balancing exploration and exploitation while ensuring obstacle-free optimal paths []. Additionally, Li et al. have made strides with an intelligently enhanced ACO, which incorporates non-uniform pheromone distribution, ꞓ-greedy state transitions, and a multi-objective framework that optimizes for path length, safety, and power consumption, demonstrating its effectiveness in complex grid environments and real-world robotics []. Together, these studies illustrate that combining ACO with adaptive strategies, dynamic heuristics, and multi-objective assessments can significantly enhance convergence speed, path quality, and their applicability in dynamic engineering contexts.
6.3. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the collective behavior observed in biological swarms, such as bird flocks and fish schools. It optimizes solutions by iteratively updating the velocities and positions of particles based on both individual experience (personal best) and social interaction (global best). While classical PSO is lauded for its conceptual simplicity and computational efficiency, it is often hindered by limitations such as premature convergence and entrapment in local optima, particularly in complex or constrained environments. To address these shortcomings, several advanced PSO variants have been proposed. Bi-population PSO (BPPSO) enhances exploration by dividing the swarm into global and local search subpopulations, incorporating random perturbations to prevent stagnation []. Quartic Bézier-enhanced PSO introduces high-order Bézier curves with adaptive velocity control to preserve G3 geometric continuity, enabling smooth and kinematically feasible path generation []. Penalty-based Adaptive PSO (APSO) integrates local search methods and imposes penalties for obstacle overlap, leading to improved collision avoidance and up to a 10% reduction in navigational time in maze-like environments []. These algorithmic innovations through bi-population dynamics, higher-order geometric constraints, and penalty-based constraint handling significantly enhance the robustness and adaptability of PSO. Consequently, they enable more efficient, stable, and collision-aware PP for AMR operating in both static and dynamic environments.
6.4. Genetic Algorithm
Genetic Algorithm (GA), inspired by the principles of natural selection and evolutionary biology, is a population-based meta-heuristic optimization technique. They are particularly effective in addressing complex PP problems that are difficult to solve using traditional deterministic methods []. Finally, GA suffers from high computation, mainly when dealing with real-time applications or difficult pathfinding situations. Also, it converges prematurely to a suboptimal solution if not properly tuned. For generating smooth and dynamically feasible parts are generated for post-processing steps like a path smoothing algorithm. It has been successfully applied in unmanned vehicles like UAV, AGV, and mobile robots, particularly in dynamic or partially known environments where adaptive and global exploration []. Table 4 presents the comparative analysis of optimization-based PP algorithms.

Table 4.
Comparative Analysis of Optimization-Based PP Algorithms.
7. Hybrid Path Planning Algorithms
Hybrid PP algorithms integrate multiple planning strategies, typically global and local techniques, to improve navigation efficiency, adaptability, and robustness. By leveraging the strengths of both global planning (e.g., map-based optimal path computation) and local planning (e.g., real-time obstacle avoidance), hybrid approaches enable autonomous systems to navigate effectively in complex, dynamic, and partially known environments. The primary objective of hybrid PP is to balance computational efficiency with real-time responsiveness, ensuring smooth, collision-free trajectories while maintaining flexibility in the face of environmental uncertainties.
7.1. Hybrid Algorithms
7.1.1. Challenges in Path Planning
Path planning is a significantly challenging task in mobile robotics, necessitating efficient algorithms that enable AMR to navigate through dynamic and complex environments. Traditional PP methods, including A*, Dijkstra, BFS, DFS, Floyd-Warshall, and Bellman-Ford, offer dependable solutions for static settings but often face difficulties with real-time adaptation, computational efficiency, and obstacle avoidance in a dynamic environment. To overcome these issues, hybrid models have emerged, combining classical algorithms with heuristic, optimization, and learning-based techniques to boost their performance. Recent research demonstrates that A* is often paired with GA or reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance its capability to identify paths in environments with shifting obstacles. This mode of hybrid strategy enables robots to effectively balance exploration and exploitation, optimizing pathfinding in real time [].
7.1.2. Search Acceleration
Dijkstra’s algorithm, renowned for its precision in handling weighted graphs, has been combined with ACO to create swarm-based solutions for multi-agent robotic systems. This integration enables AMR to discover optimized paths more quickly while adjusting to real-world limitations. For extensive navigation tasks, the Floyd-Warshall and Bellman-Ford algorithms are used to determine the shortest paths in dense networks, and have been enhanced with PSO and Deep Learning (DL) methods to boost their efficiency in continuously adapting paths []. This hybrid approach ensures that robots can navigate effectively through unstructured terrains, urban traffic situations, and warehouse automation []. Additionally, sampling-based methods like RRT and PRM have been integrated with traditional graph-based techniques to improve motion planning in high-dimensional environments [].
7.1.3. Dynamic Adaptation
Hybrid models are essential for real-time obstacle avoidance. While the Potential Field Algorithm (PFA) is efficient and often encountered with local minima. Researchers found that merging PFA with Model Predictive Control (MPC) can greatly enhance a robot’s obstacle avoidance capabilities while ensuring smooth trajectories to facilitate continuous learning and path correction, particularly in self-optimizing robotic systems. A promising avenue in hybrid PP involves integrating multiple algorithms to develop adaptive systems. Research indicates that combining A* with the DWA proves effective for AMR in cluttered environments, enabling efficient navigation by considering the velocity and trajectory constraints. Furthermore, the integration of Hybrid A* with RRT and APF offers robust navigation solutions for robotic arms and autonomous vehicles []. A popular hybrid approach combines the PFA with A* or GDA to address local minima challenges in pathfinding. Sánchez-Ibáñez et al. noted that this combination facilitates smooth trajectory planning while maintaining global optimality in environments filled with obstacles []. Similarly, Lin et al. combined a hybrid potential field and MPC, which allows for collision-free navigation for both autonomous vehicles and drones []. Fusion of GDA and MPC, where GDA refines the weight adjustments of MPC in motion planning algorithms []. This combination greatly enhances dynamic response and path correction in nonlinear environments.
7.1.4. Probabilistic Approach
These hybrid PP methods are commonly used in areas such as autonomous vehicles, UAV navigation, smart warehouses, and robotic healthcare systems. Ongoing advancements in hybrid models that integrate classical techniques with artificial intelligence, swarm optimization, and predictive control are expected to greatly enhance the field of mobile robotics, leading to more efficient, adaptive, and scalable path planning solutions [,]. Sampling-based PP algorithms have become a key strategy for AMR, especially in intricate and high-dimensional settings. Algorithms like RRT and PRM offer effective solutions for motion planning in situations where traditional deterministic methods struggle due to high computational demands or uncertainties in the environment []. However, these algorithms often face limitations in terms of path smoothness, convergence speed, and adaptability to dynamic obstacles. To overcome these issues, hybrid approaches that combine sampling-based techniques with graph search, Machine Learning (ML), and optimization methods have been developed to improve overall performance. According to the hybrid sampling-based methods are commonly used in robotic manipulators, enhancing collision avoidance and path efficiency by merging RRT with RL []. Similarly, offer a thorough review of hybrid methods, highlighting how the integration of PRM with DL techniques can optimize roadmap generation and enhance real-time path execution []. Ganesan et al. introduce a hybrid sampling-based RRT* algorithm that integrates predictive control to improve collaborative navigation among multiple autonomous agents []. Meanwhile, based on analyzing the efficacy of Fast Marching Trees (FMT), a variant of RRT, combined with ML models to optimize real-time decision-making in complex environments [].
7.1.5. Trajectory Smoothness
Additionally, the combination of sampling-based techniques with heuristic methods such as PSO and ACO has been investigated, enabling dynamic adaptation for real-world navigation tasks []. A significant advancement in hybrid PP is the integration of RRT with artificial intelligence techniques. Shao et al. introduce a Hybrid-RRT method that leverages Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to enhance node expansion, resulting in better path optimality and faster convergence []. In multi-robot systems, hybrid methods play a crucial role in ensuring coordination and obstacle avoidance. The future of hybrid sampling-based PP is set to benefit significantly from the combination of DL, evolutionary algorithms, and adaptive real-time control techniques. Research conducted by Elbanhawi and Simic (2014) indicates that utilizing these hybrid approaches allows AMR to compute paths more quickly, avoid obstacles more efficiently, and adapt in real-time []. This makes such methods essential for various applications, including autonomous vehicles, robotic surgery, warehouse automation, and drone navigation. Optimization-based hybrid PP techniques have become increasingly popular in robotics because they enhance trajectory optimization, enable real-time decision-making, and facilitate dynamic obstacle avoidance. When used in isolation, traditional methods like PFA, Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR), MPC, and GDA often face challenges such as being stuck in local minima, incurring high computational costs, and lacking real-time adaptability. To overcome these issues, researchers have developed hybrid models that combine these traditional approaches with AI, ML, and heuristic-based strategies to improve AMR path planning and control.
A hybrid optimization-based PP that combines PSO and ACO has emerged as an effective strategy for AMR, UAVs, and autonomous vehicles []. These swarm intelligence methods tackle complex optimization challenges by striking a balance between exploration and exploitation. However, using them individually can lead to issues like slow convergence, premature stagnation, and high computational demands. To address these problems, researchers have created hybrid PSO-ACO models that leverage the strengths of both techniques, integrating them with heuristics, graph search, and RL to improve path optimization, real-time adaptability, and collision avoidance. According to Herlambang and Rahmalia, combining PSO and ACO can effectively optimize the proportional-integral-derivative parameters for controlling an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) []. Their research shows that PSO excels in global search capabilities, while ACO focuses on refining local solutions, resulting in quicker convergence and greater accuracy. Similarly, Abualigah et al. introduce a hybrid PSO-ACO method for UAV PP, demonstrating that ACO improves path selection, whereas PSO enhances the smoothness of the trajectory []. The future of hybrid PSO-ACO models is promising, especially with their integration into AI-driven decision-making systems. This will allow for real-time adaptability, better energy efficiency, and improved coordination among multiple robots. Such advancements will be especially useful in areas like autonomous transportation, smart city logistics, and search-and-rescue robotics.
Recent advancements in robust trajectory tracking control for PP have explored diverse strategies to effectively address system uncertainties and external disturbances. A comparison evaluation of PP algorithms and optimization techniques for AMRs, concluding that Hybrid A* (HA*) and Hybrid Black Widow Optimization Algorithm and PSO Algorithm (HBPO) demonstrated superior performance over alternative methods []. A backstepping-based control framework was proposed for underwater vehicles, integrating neural networks and control allocation mechanisms to mitigate model uncertainties []. A learning based control strategy was developed for nonlinear systems, employing the GDA to minimize trajectory tracking errors []. An efficient PP approach that combines jump point search with convex decomposition, supported by a robust control Lyapunov function, was introduced to ensure accurate trajectory tracking in mobile robots []. Tube-based MPC has been applied to articulated vehicles, yielding notable improvements in path tracking accuracy and robustness against external disturbance []. For unmanned ground vehicles, a hybrid strategy integrating stochastic dynamic programming-based MPC with Dijkstra-based algorithms has demonstrated superior capability in managing dynamic obstacles and navigating large-scale maps []. In automated driving applications, an advanced MPC framework combining KF-based obstacle prediction with tube-based MPC for trajectory generation has effectively minimized lateral deviations and tracking errors []. Similarly, for autonomous underwater vehicles, an enhanced tube-based MPC scheme incorporating an ancillary controller has been developed to counter bounded disturbances, ensuring that the disturbed system state remains confined within an optimized tube []. A robust trajectory tracking controller was used for AUVs designed to ensure strict adherence to input and state constraints while operating in dynamic, obstacle-rich environments. The proposed framework integrates an online control law, formulated through the solution of a Finite Horizon Optimal Control problem (FHOCP), with a state-feedback law that guarantees closed-loop stability and convergence verified through simulation studies []. These studies underscore the critical role of adaptive and robust control methodologies in enhancing trajectory tracking performance, enabling improved reliability and resilience across a variety of robotic platforms.
7.1.6. Real-Time Adaptability and Energy Optimization
- AI-Driven Hybrid Algorithms:
Most of the AI used in a hybrid PP is the closed-loop integration of AI modules, motion execution, and environmental perception, which allows robots to function in dynamic and uncertain environments. Multi-sensor perception is the first step in this integration, which is followed by AI-based interpretation and, at the end, hybrid planning decisions that are updated as the environment changes. Based on the PP methods, sensor fusion takes an important role, as it links environmental data to AI decision-making. Figure 7 illustrates the framework of an AI-driven approach with sensor fusion and AI integration for hybrid PP in uncertain environments.
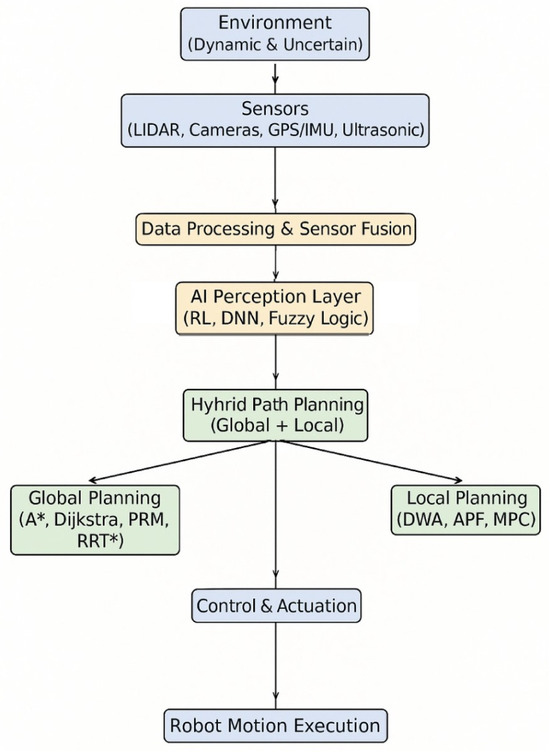
Figure 7.
Framework for AI-based hybrid algorithms.
The LiDAR, camera, and odometry data were used for the DRL model to find local navigation action with a global plan []. To provide the framework for integrating multiple sensors for path planning in AMR, and also define how sensor output data can be directly fed into the hybrid planner []. Fuzzy logic supports indoor navigation using proximity data [], then a type-2 fuzzy controller was developed to handle an uncertain environment in both simulation and real autonomous robots []. In a hybrid approach combined with AI learning and with classical planner for real-time operation. The integration of Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) with the DWA finds local control information by live LiDAR data []. DWA with DRL-based velocity selection was developed for improving obstacle avoidance. Integration of DRL with variable-direction potential fields helps to learn policies to adopt force-based obstacle avoidance under sensor uncertainty [].
A DL-enhanced RRT algorithm was proposed for UAV PP in dynamic environments, leveraging neural networks to integrate various sensor data and improve adaptability []. For mobile charging robots, a hybrid strategy combining an improved A* algorithm with DWA was developed, resulting in enhanced path safety and adaptability in complex operational scenarios []. A hybrid PP method was introduced for transoceanic underwater gliders, employing Dijkstra’s algorithm for initial global planning and Q-learning for trajectory optimization under dynamic ocean current conditions. These hybrid approaches consistently outperform traditional methods, offering improvements in path optimality, operational safety, and energy efficiency []. Complementing these developments, a comprehensive review of classical, heuristic, and metaheuristic PP algorithms, systematically analyzing their underlying principles, performance characteristics, and application domains through a simulated comparative study, was provided []. These studies underscore the versatility and efficacy of transformer-based architectures and metaheuristic algorithms in addressing diverse and complex PP challenges, offering substantial gains in safety, computational efficiency, and predictive accuracy across multiple domains.
- Transformer-Based Hybrid Algorithms:
Recent advancements in robotics have increasingly adopted transformer-based architectures to enhance PP performance. A hybrid approach integrating a transformer encoder with incremental RL was proposed for unmanned ground vehicles, achieving superior adaptability and task performance []. A conditional variational autoencoder-transformer framework that incorporates mission specifications was introduced to enhance trajectory quality and mission compliance []. A transformer-based policy neural network was applied to multi-robot PP, enabling start-of-the-art performance in dense environments without explicit inter-robot communication []. The Transformer-Enhanced Motion Planner (TEMP) was developed, which employs an environmental information semantic encoder and motion planning transformer to optimize sampling-based motion planning []. In autonomous driving, transformer-based deep inverse RL has been applied to enhance both safety and interpretability by extracting salient traffic features and determining attention allocation toward surrounding vehicles []. A transformer neural network was applied for spacecraft powered descent guidance to predict optimal guidance solutions, thereby reducing computational complexity while maintaining high precision []. For UAV trajectory optimization in wireless power transfer-assisted IoT systems, an attention-based framework was proposed, leveraging graph transformers to optimize both the number of UAVs deployed and their trajectories [].
- Cooperative Multi-Agent Hybrid Algorithm:
Recent advancements in cooperative guidance and PP for unmanned systems have significantly expanded their operational capabilities. A comprehensive review of cooperative terminal guidance, proposing a five-layer development framework and highlighting critical research directions, including networked cooperation and intelligent coordination strategies, was presented []. In multi-robot PP, an enhanced ACO algorithm for both 2D and 3D environments, achieving notable improvements in computation time and path length optimization []. For UAVs cylindrical coordinate PSO planner with gene targeting (GTCPSO) was developed to address complex multi-UAV cooperative planning scenarios. This method integrates cylindrical coordinate representation with gene targeting operations, enabling the generation of feasible, dynamically consistent trajectories while accommodating UAV kinematic constraints []. Building on these advancements in cooperative guidance, hybrid PP strategies are emerging as a promising avenue to integrate complementary algorithms, enhance adaptability in dynamic environments, and address the computational and coordination challenges inherent to multi-agent unmanned systems. Table 5 presents a comparison of hybrid PP algorithms. The performance of various hybrid algorithms in terms of path distance, path smoothness, number of nodes visited, convergence rate and success rate are presented in Table 6.

Table 5.
Comparison of Hybrid PP Algorithms.

Table 6.
Relative performance comparison of hybrid algorithms.
7.2. Applications of Hybrid Path Planning Algorithms
Recent advancements in AMR navigation underscore the growing significance of PP strategies, with particular emphasis on hybrid approaches. These methods integrate traditional, heuristic, and ML techniques to overcome the inherent limitations of individual strategies and enhance overall navigation performance [,]. Notably, hybrid algorithms account for approximately 27% of reported methods and are increasingly favored for their capability to operate effectively in complex and dynamic environments while balancing exploration and exploitation in search processes []. Their application in UAV navigation is especially prominent, where they address critical challenges such as obstacle avoidance, energy efficiency, and trajectory optimization []. Classical techniques, including roadmap methods, cell decomposition, and APF, are often combined with heuristic algorithms such as GA, ACO, and GWO to enhance efficiency across diverse operational scenarios []. This shift toward hybrid strategies reflects an ongoing effort to achieve greater autonomy, robustness, and adaptability in next-generation mobile robot navigation systems. The applications of hybrid PP algorithms are as follows:
- ➢
- Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics: Utilized in self-driving cars to ensure efficient and safe navigation through dynamic urban environments. Used in robotic arms for precise movement in constrained spaces []. Improves navigation for multiple robots in industrial automation settings [].
- ➢
- Autonomous driving system: Meta-heuristic optimization methods are widely adopted for their effectiveness in addressing complex and high-dimensional PP problems. ML and DL methods are increasingly favored due to their adaptive learning capabilities and rapid decision-making in dynamic environments [].
- ➢
- Multi-Agent Systems: Enable cooperative PP, formulation keeping, and consensus control while adapting to changing environments []. A method combining consensus control and PP for coordinating multiple AMRs in a multi-agent system [].
- ➢
- Multi-Robot path planning: The hybridisation of the Sine-Cosine algorithm, which was inspired by the Kidney, was employed for Multi-Robot PP []. For multi-robot PP in a cluttered environment, a hybrid improved PSO-DV (Dynamic Vortex) algorithm was employed []. A novel hybrid optimization approach based on the Cuckoo Search –Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (CS-ANFIS) methodology was used for multiple mobile robot navigation [].
- ➢
- Warehouse Automation: Combining PSO with simulated annealing (SA) (PSO-SA) improves navigation in warehouses and traffic flow management in AGV systems [].
- ➢
- Aerial and Maritime Navigation: Utilized in UAVs to enhance flight path planning across diverse terrains []. Utilized in the navigation of both autonomous underwater and surface vehicles [].
- ➢
- Agriculture and Industrial Automation: Improves automated harvesting and robotic pollination in farming []. Utilized by warehouse robots to enhance the efficiency of storage and retrieval paths.
7.3. Advantages of Hybrid Path Planning Algorithms
Hybrid PP algorithms provide some benefits compared to conventional PP techniques.
- ➢
- Improved Efficiency and Speed: Integrates global planning for optimal route selection with local planning for real-time obstacle avoidance, thereby minimizing the overall computational burden.
- ➢
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Reduces energy usage and travel expenses, making it perfect for drones, self-driving cars, and industrial uses.
- ➢
- Enhanced Safety and Reliability: Minimizes collision risks and facilitates smooth trajectory planning in high-risk environments.
8. Discussion
This comprehensive review has highlighted the significant advancements in PP for AMR, particularly through the evolution from traditional to hybrid algorithms. The inherent limitations of traditional PP techniques, such as computational inefficiency, lack of real-time adaptability, and challenges in dynamic obstacle avoidance, underscore the necessity for more robust solutions, which hybrid approaches noticeably offer. Traditional graph-based algorithms like A* and Dijkstra, whereas effective for static and known environments, often struggle with dynamic and challenging environments due to their significant computational time. Similarly, sampling-based methods, while adept at navigating high-dimensional spaces, can suffer from slow convergence and issues with path smoothness. Reaction-based algorithms, such as APF and DWA, excel in real-time obstacle avoidance but are prone to local minima or may not guarantee global optimality. Optimization-based algorithms provide a systematic way to balance multiple factors like distance, energy, and safety, but often face challenges such as premature convergence and high computational demands.
The emergence of hybrid PP algorithms directly addresses these individual shortcomings by integrating the strengths of various algorithms. For instance, combining global planners (like A* or Dijkstra) with local planners (like DWA or APF) allows AMRs to compute optimal routes while simultaneously reacting to dynamic obstacles in real-time. The review demonstrates how enhancements to A* with GA or RL improve path identification in dynamic environments. Similarly, the integration of Dijkstra with ACO facilitates quicker discovery of optimized paths for multi-agent systems, and the fusion of PRM with DL or RL enhances roadmap generation and real-time execution. These hybrid strategies collectively contribute to improved efficiency, enhanced safety, optimized resource utilization, and greater adaptability in complex settings. Despite their numerous advantages, hybrid PP methods have a few challenges. These include increased computational overhead due to the integration of multiple algorithms, scalability issues in large-scale multi-agent systems, and ensuring real-time responsiveness in highly unpredictable environments. For example, the Bellman-Ford algorithm, while capable of handling negative edge weights, is often too slow for real-time applications. Similarly, integrating complex ML models or metaheuristic algorithms can significantly increase computational demands.
9. Limitations and Future Directions in Hybrid Path Planning
Effective PP is essential for AMRs to operate reliably in dynamic and heterogeneous environments. However, the design of robust PP algorithms remains a significant challenge, requiring innovative methodologies to address issues such as real-time adaptability, obstacle avoidance, and computational efficiency. Overcoming these challenges not only advances the capabilities of AMRs but also opens new avenues for research and practical applications in increasingly complex operational domains.
- Environmental challenges:
- ➢
- Dynamic and Uncertain Environments: AMRs frequently operate in settings characterized by unpredictable obstacles, varying terrains, and moving entities. Ensuring safe and efficient navigation requires PP algorithms capable of rapidly adapting to these dynamic conditions, including sudden changes in obstacle positions and unexpected terrain variations.
- ➢
- Limited sensor range and accuracy: Although advanced sensors such as LiDAR, RGB-D cameras, and GPS provide continuous environmental feedback, their inherent noise, resolution limits, and susceptibility to environmental interference can lead to localization errors. These inaccuracies can propagate through the planning process, compromising the reliability and safety of navigation.
- Computational Challenges
- ➢
- High computational cost: Real-time PP requires identifying optimal routes while simultaneously minimizing costs such as path distance, number of nodes visited, energy usage, and computational cost. In densely populated environments, particularly in multi-robot systems, the computational cost escalates, demanding high processing power and efficient algorithmic solutions.
- ➢
- Local minima issues in heuristic algorithms: Many traditional and heuristic-based approaches, especially in environments with narrow or cluttered configurations, are prone to becoming trapped in local minima. This can result in suboptimal or even infeasible paths, reducing operational efficiency.
- ➢
- Energy efficiency and Resource constraints: For battery-powered AMRs, energy-efficient PP is critical. Algorithms must balance navigation efficiency with the conservation of onboard energy resources to maximize operational endurance without compromising safety or task competition.
- Future Work
Addressing these limitations presents opportunities for further research and technological developments. Future studies should focus on:
- ➢
- Developing adaptive hybrid algorithms that integrate learning absed and optimization-driven methods to enhance real-time responsiveness.
- ➢
- Leveraging sensor fusion and advanced filtering techniques to mitigate localization errors.
- ➢
- Incorporating predictive modeling for dynamic obstacle trajectories to enhance safety in uncertain environments.
- ➢
- Designing energy-aware planning frameworks that consider battery state and mission-critical constraints in real time.
- ➢
- Future research is expected to focus on several critical directions, including the integration of AI-driven adaptive systems, collaborative multi-robot coordination, and cloud robotics for scalable data sharing and decision-making. Moreover, establishing standardized frameworks for interoperability and benchmarking will be essential for broader deployment.
- ➢
- Such advancements will significantly improve the robustness, adaptability, and operational efficiency of AMRs, enabling their deployment in increasingly complex and dynamic environments.
10. Conclusions
Hybrid PP algorithms have significantly advanced the navigation capabilities of AMR. This review has analyzed the performance of various hybrid PP strategies, highlighting how the integration of global and local algorithms addresses the limitations inherent in individual techniques. Particular emphasis has been placed on key factors such as computational complexity, adaptability in dynamic environments, and robust obstacle avoidance. Hybrid algorithms have demonstrated superior efficiency and versatility, especially in domains such as autonomous vehicles, UAVs, and AMR. By providing a comparative evaluation of different hybrid approaches, including their operating principles and real-world applicability, this study offers a comprehensive understanding of their potential and current limitations.
Despite their advantages, hybrid PP methods face several challenges, namely, increased computational overhead, scalability in multi-agent systems, and real-time responsiveness in unpredictable environments. Addressing these challenges through advances in artificial intelligence, meta-learning, and cloud-based control frameworks will be essential for the next generation of intelligent, adaptive robotic platforms. Hybrid PP represents a promising and scalable solution within the broader field of intelligent robotics. Its ongoing develAopment continues to enable high-performance autonomous navigation across increasingly complex and unstructured environments, underscoring its critical role in the future of robotics and automation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T. and S.G.; methodology, M.T.; software, M.S.; validation, M.T. and S.G.; formal analysis, M.T.; investigation, M.T.; resources, M.S.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.T. and S.G.; visualization, M.T.; supervision, M.T.; project administration, M.T.; funding acquisition, M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
It is a review article, and no new data were created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
- Graph-based algorithms:
- A* Search []
- Mathematical model
- f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
- g(n): The actual cost from the start node to the current node.
- h(n): The estimated cost from the current node to the goal.
- For example, if it needs to be modified to weighted A*. This formula will be converted into
- f(n) = g(n) + w * h(n)
- w: weight to the heuristic function
- Pseudocode
- A_STAR(G, w, s, t, h):
- for v in V: g[v] ← +∞; parent[v] ← NIL
- g[s] ← 0
- OPEN ← priority-queue by f[v] = g[v] + h(v)
- PUSH (OPEN, s)
- CLOSED ← ∅
- while OPEN not empty:
- u ← EXTRACT-MIN(OPEN) // by f
- if u = t: return RECONSTRUCT (parent, t)
- add u to CLOSED
- for each (u, v) in E:
- tentative ← g[u] + w(u, v)
- if v ∈ CLOSED and tentative ≥ g[v]: continue
- if tentative < g[v]:
- parent[v] ← u
- g[v] ← tentative
- if v not in OPEN: PUSH(OPEN, v) else DECREASE-KEY(OPEN, v, g[v] + h(v))
- return “no path”
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm []
- Mathematical model
- Greedy relaxation under invariant:
- When a vertex u is extracted, d(u) = δ(s,u) (true shortest distance).
- Relaxation step for edge (u,v):
- d(v)←min
- Pseudocode
- DIJKSTRA(G, w, s):
- for v in V: d[v] ← +∞; parent[v] ← NIL
- d[s] ← 0
- Q ← priority-queue keyed by d[·] with all vertices
- while Q not empty:
- u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q)
- for each (u, v) in E:
- if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v):
- d[v] ← d[u] + w(u, v)
- parent[v] ← u
- DECREASE-KEY(Q, v, d[v])
- return d, parent
- Breadth-First Search (BFS) []
- Pseudocode
- BFS(G, s):
- for v in V: d[v] ← +∞; parent[v] ← NIL
- d[s] ← 0
- Q ← queue; ENQUEUE(Q, s)
- while Q not empty:
- u ← DEQUEUE(Q)
- for each (u, v) in E:
- if d[v] = +∞:
- d[v] ← d[u] + 1
- parent[v] ← u
- ENQUEUE(Q, v)
- return d, parent
- Floyd-Warshall []
- Mathematical model
- D(0)[i,j] = w(i,j) (or +∞, 0 on diagonal)
- D(k)[i,j] = min(D(k−1)[i,j], D(k−1)[i,k] + D(k−1)[k,j]).
- Pseudocode
- FLOYD_WARSHALL(W): // W is n×n, W[i][i] = 0; +∞ if no edge
- D ← W
- for k in 1..n:
- for i in 1..n:
- for j in 1..n:
- if D[i][j] > D[i][k] + D[k][j]:
- D[i][j] ← D[i][k] + D[k][j]
- return D
- Depth-First Search (DFS) []
- Pseudocode
- DFS(G):
- for v in V: color[v] ← WHITE; parent[v] ← NIL
- time ← 0
- for v in V:
- if color[v] = WHITE: DFS_VISIT(v)
- DFS_VISIT(u):
- color[u] ← GRAY; time ← time + 1; d[u] ← time
- for each (u, v) in E:
- if color[v] = WHITE:
- parent[v] ← u
- DFS_VISIT(v)
- color[u] ← BLACK; time ← time + 1; f[u] ← time
- Bellman–Ford []
- Pseudocode
- BELLMAN_FORD(G, w, s):
- for v in V: d[v] ← +∞; parent[v] ← NIL
- d[s] ← 0
- for i in 1..(n − 1):
- updated ← false
- for each (u, v) in E:
- if d[u] + w(u,v) < d[v]:
- d[v] ← d[u] + w(u,v)
- parent[v] ← u
- updated ← true
- if not updated: break
- // detect negative cycle
- for each (u, v) in E:
- if d[u] + w(u,v) < d[v]: return “negative cycle”
- return d, parent
- Sampling-based algorithms:
- Probabilistic Roadmap (PRM) []
- Pseudocode
- PRM (G, N_samples, k or r):
- V ← ∅; E ← ∅
- for i = 1 to N_samples:
- q ← SAMPLE_C_FREE()
- V ← V ∪ []
- for each q in V:
- neighbors ← NEAR (V, q, k or radius r)
- for each q’ in neighbors:
- if LocalPlan (q, q’):
- E ← E ∪ []
- add start, goal to V; connect to neighbors similarly
- return graph (V, E)
- PRM_QUERY (graph, start, goal):
- return SHORTEST_PATH (graph, start, goal)
- Rapidly Exploring Random Tree (RRT) []
- Pseudocode
- RRT(q_init, K, Δq):
- V ← (q_init)c; E ← ∅
- for k = 1 to K:
- q_rand ← SAMPLE_C_FREE()
- q_near ← NEAREST(V, q_rand)
- q_new ← STEER(q_near, q_rand, Δq)
- if LocalPlan(q_near, q_new):
- V ← V ∪ (q_new)
- E ← E ∪ [(q_near, q_new)]
- return (V, E)
- Batch Informed Trees (BIT) []
- Pseudocode
- BIT*(start, goal, batch_size, heuristic h):
- initialize tree T with start
- best_cost ← ∞
- while time remains:
- S_batch ← SAMPLE_BATCH(batch_size)
- build implicit RGG over existing vertices + S_batch
- E_queue ← PRIORITIZE_EDGES_BY_ESTIMATED_COST()
- while E_queue not empty and first estimate < best_cost:
- extract edge (u, v), evaluate true cost via LocalPlan
- if cost + g(u) + h(v) < best_cost:
- add/update edge in T, update costs and best_cost
- prune nodes with cost + h ≥ best_cost
- return best path in T
References
- Zhang, S.; Tang, W.; Li, P.; Zha, F. Mapless Path Planning for Mobile Robot Based on Improved Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm. Sensors 2024, 24, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreerag, S.; Lekshmi, R.R. Allocation of Medicine Dispensing Mobile Robot Considering Path Plan and Battery SoC. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Interdisciplinary Approaches in Technology and Management for Social Innovation (IATMSI), Gwalior, India, 14–16 March 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeil, F.H.; Ibraheem, I.K.; Sahib, M.A.; Humaidi, A.J. Multi-objective path planning of an autonomous mobile robot using hybrid PSO-MFB optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 89, 106076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, T.; Dinesh, T.; Guruchandhramavli, B.; Sanjai, S.; Sheshadhri, B. Mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance using hybrid algorithm. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 4481–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudugosula, H.; Kochuvila, S. Path Planning of Robots Using Classical Reinforcement Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 First International Conference on Innovations in Communications, Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICICEC), Davangere, India, 24–25 October 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y. Research on the A Star Algorithm for Finding Shortest Path. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchoň, F.; Babinec, A.; Kajan, M.; Beňo, P.; Florek, M.; Fico, T.; Jurišica, L. Path Planning with Modified a Star Algorithm for a Mobile Robot. Procedia Eng. 2014, 96, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Wu, Z.; Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Cao, M.; Ou, X.; Su, X.; Li, W.; et al. Path planning of automated guided vehicles based on improved A-Star algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; pp. 2071–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Huang, D. Research on path planning for intelligent mobile robots based on improved A* algorithm. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lü, X. Research on global path planning algorithm for mobile robots based on improved A. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 243, 122922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Mobile robot path planning based on kinematically constrained A-star algorithm and DWA fusion algorithm. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, R.; Xu, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z. A mobile robot path planning algorithm based on improved A* algorithm and dynamic window approach. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 57736–57747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu-Xi, W. The improved dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm and its application. Procedia Engineering 2012, 29, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Messon, D.; Rastogi, M.; Singh, A. Comparative Study of Various Approaches of Dijkstra Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computing, Communication, and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS), Greater Noida, India, 19–20 February 2021; pp. 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ubaidillah, A.; Sukri, H. Application of Odometry and Dijkstra algorithm as navigation and shortest path determination system of warehouse mobile robot. J. Robot. Control (JRC) 2023, 4, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-F.; Du, Y.; Jia, K.-J. Path planning and smoothing of mobile robot based on improved artificial fish swarm algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaposhnikova, S.; Omelian, D. Towards effective strategies for mobile robot using reinforcement learning and graph algorithms. Autom. Technol. Bus. Process. 2023, 15, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, S.; Asanovic, K.; Patterson, D. Direction-optimizing Breadth-First Search. In Proceedings of the SC ‘12: Proceedings of the International Conference on High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 10–16 November 2012; pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Xiong, Z. A novel graph-based motion planner of multi-mobile robot systems with formation and obstacle constraints. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 40, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, A.; Gayathri, M.P.; Jayapandian, N.; Chris, A.; Thaleeparambil, N.R. Efficient Pathfinding in a Maze to overcome Challenges in Robotics and AI Using Breadth-First Search. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 14th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), Bhopal, India, 7–9 March 2025; pp. 727–732. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xie, F.; Zhao, J.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Suo, H. FPS: Fast path planner algorithm based on sparse visibility graph and bidirectional breadth-first search. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rahman, N.A.; Sahari, K.S.M.; Hamid, N.A.; Hou, Y.C. A coverage path planning approach for autonomous radiation mapping with a mobile robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2022, 19, 17298806221116483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Jiao, T.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Li, W. Radiation Mapping based on DFS and Gaussian Process Regression. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th URSI Atlantic Radio Science Meeting (AT-RASC), Meloneras, Spain, 19–24 May 2024; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Sun, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X. Path planning algorithms for smart parking: Review and prospects. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, P.; Sun, Y. Improving path planning efficiency for underwater gravity-aided navigation based on a new depth sorting fast search algorithm. Def. Technol. 2024, 32, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, M.; Onsy, A.; Haikal, A.Y.; Ghanbari, A. Path planning algorithms in the autonomous driving system: A comprehensive review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2024, 174, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne Gareau, J.; Beaudry, É.; Makarenkov, V. Fast and optimal branch-and-bound planner for the grid-based coverage path planning problem based on an admissible heuristic function. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 9, 1076897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.A.; Shariff, S.S.; Supadi, S.S.; Masudin, I. Modelling the Shortest Path for Inner Warehouse Travelling Using the Floyd–Warshall Algorithm. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Majeed, A.; Akram, M.; Al-shamiri, M. Floyd-Warshall Algorithm Based on Picture Fuzzy Information. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 136, 2873–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NageswaraGuptha, M.N. Autonomous UAV object Avoidance with Floyd-warshall differential evolution approach. Intel. Artif. 2022, 25, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. Path planning of inspection robot based on improved intelligent water drop algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 119993–120000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, B. Research on smooth path planning method based on improved ant colony algorithm optimized by Floyd algorithm. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 955179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, K.; Neamah, H.A.; Korondi, P. Obstacle Avoidance and Path Planning Methods for Autonomous Navigation of Mobile Robot. Sensors 2024, 24, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, J.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Son, H.I. Field Evaluation of Path-Planning Algorithms for Autonomous Mobile Robot in Smart Farms. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 60253–60266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Rao, P.K.; Kamath, C.R.; Tandon, V.; Vizzapu, P. Comparative analysis of Bellman-Ford and Dijkstra’s algorithms for optimal evacuation route planning in multi-floor buildings. Cogent Eng. 2024, 11, 2319394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, O.; Al-Hashimi, M. On the Energy Behaviors of the Bellman–Ford and Dijkstra Algorithms: A Detailed Empirical Study. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2024, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tong, Y. Path planning of a mobile robot based on the improved RRT algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. CERRT: A mobile robot path planning algorithm based on RRT in complex environments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchio, V.; Chaudhari, P.; Frazzoli, E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning using process algebra specifications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 5326–5332. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, E. Path planning of a mobile robot based on the improved rapidly exploring random trees star algorithm. Electronics 2024, 13, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, W.; Menebo, M.; Merga, C.; Negash, L. Optimal path planning using bidirectional rapidly-exploring random tree star-dynamic window approach (BRRT*-DWA) with adaptive Monte Carlo localization (AMCL) for mobile robot. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 035212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhsen, D.K.; Sadiq, A.T.; Raheem, F.A. Memorized rapidly exploring random tree optimization (mrrto): An enhanced algorithm for robot path planning. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2024, 24, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Duan, P.; Meng, L.; Yang, X. GAO-RRT*: A path planning algorithm for mobile robot with low path cost and fast convergence. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 12011–12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Luo, X.; Luo, Q. An Optimized Probabilistic Roadmap Algorithm for Path Planning of Mobile Robots in Complex Environments with Narrow Channels. Sensors 2022, 22, 8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarabi, S.; Luo, C.; Santora, M. A PRM Approach to Path Planning with Obstacle Avoidance of an Autonomous Robot. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), Prague, Czech Republic, 18–20 February 2022; pp. 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sabeeh, S.; Sabri, I. Efficient Path Planning in Medical Environments: Integrating Genetic Algorithm and Probabilistic Roadmap (GA-PRM) for Autonomous Robotics. Iraqi J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 20, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.F.; Wang, J.; Sha, Z. Risk-Bounded and Probabilistic Roadmap-Based Motion Planner for Arbitrarily Shaped Robots With Uncertainty. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2025, 25, 081002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kamil, S.J.; Szabolcsi, R. Optimizing path planning in mobile robot systems using motion capture technology. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.V.; Harikrishnan, R.; Walambe, R. POMDP-based probabilistic decision making for path planning in wheeled mobile robot. Cogn. Robot. 2024, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawli, B.B.K.; Dawson, J.K.; Badu, E.; Ayawli, I.E.B.; Lamusah, D. Comparative analysis of popular mobile robot roadmap path-planning methods. Robotica 2025, 43, 1548–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedeen, J.; Droge, G. Batch Informed Trees (BIT*). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobilarov, M. Cross-entropy motion planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Shen, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, T. A Kinematic Constrained Batch Informed Trees algorithm with varied density sampling for mobile robot path planning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 6912–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammell, J.D.; Barfoot, T.D.; Srinivasa, S.S. Batch informed trees (bit*): Informed asymptotically optimal anytime search. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 543–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bing, Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, L.; Cai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Krumbholz, P.; Yuan, Z.; Haddadin, S. Flexible informed trees (FIT*): Adaptive batch-size approach in informed sampling-based path planning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–18 October 2024; pp. 3146–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Gammell, J.D.; Srinivasa, S.S.; Barfoot, T.D. BIT*: Sampling-based optimal planning via batch informed trees. In Proceedings of the The Information-Based Grasp and Manipulation Planning Workshop, Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Berkeley, CA, USA, 12–13 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, D.; Latombe, J.-C.; Kurniawati, H. On the Probabilistic Foundations of Probabilistic Roadmap Planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, J.; Veloso, M. Real-time randomized path planning for robot navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; Volume 2383, pp. 2383–2388. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Wei, L.; Wang, G.; Tian, L.; Dai, G. APF-IRRT*: An Improved Informed Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees-Star Algorithm by Introducing Artificial Potential Field Method for Mobile Robot Path Planning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, A.; Vinod, B. Artificial Potential Field Incorporated Deep-Q-Network Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Prediction. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2023, 35, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siming, W.; Tiantian, Z.; Weijie, L. Mobile Robot Path Planning Based on Improved Artificial Potential Field Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference of Intelligent Robotic and Control Engineering (IRCE), Lanzhou, China, 24–27 August 2018; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Dai, J.; Jiang, B.; Karimi, H.R. Robot path planning based on artificial potential field with deterministic annealing. ISA Trans. 2023, 138, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, R. Safe artificial potential field-novel local path planning algorithm maintaining safe distance from obstacles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4823–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Pan, J.; Wei, K.; Lu, M.; Jia, S. A novel unmanned surface vehicle path-planning algorithm based on A* and artificial potential field in ocean currents. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Shao, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, S.; Sun, F. Research and validation of self-driving path planning algorithm based on optimized A*-artificial potential field method. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 24708–24722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.; Burgard, W.; Thrun, S. The Dynamic Window Approach to Collision Avoidance. Robot. Autom. Mag. IEEE 1997, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuderer, M.; Gulati, S.; Burgard, W. Learning driving styles for autonomous vehicles from demonstration. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, DC, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2641–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. In Proceedings of the 1985 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Louis, MO, USA, 25–28 March 1985; pp. 500–505. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Taguchi, R. Faster implementation of the dynamic window approach based on non-discrete path representation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.; Kumagai, T.; Yoshida, H. Safe and efficient dynamic window approach for differential mobile robots with stochastic dynamics using deterministic sampling. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrevski, M.; Skočaj, D. Dynamic adaptive dynamic window approach. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 40, 3068–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, C.G.; Cazzaro, M.; Chiodini, P.M. The Dynamic Window Approach as a Tool to Improve Performance of Nonparametric Self-Starting Control Charts. Mathematics 2025, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitanyuk, Y.A.; Proskurnikov, A.V.; Cao, M. A Guiding Vector-Field Algorithm for Path-Following Control of Nonholonomic Mobile Robots. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujeni, Z.; Mohammadi, M.; Neumann, D.; Goehring, D.; Rojas, R. Autonomous Car Navigation Using Vector Fields. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Suzhou, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 794–799. [Google Scholar]
- Jogeshwar, B.K.; Lochan, K. Algorithms for Path Planning on Mobile Robots. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gan, Y.; Xiong, S. Optimization of Mobile Robot Delivery System Based on Deep Learning. J. Comput. Sci. Res. 2024, 6, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L.M. Ant colonies for the travelling salesman problem. Biosystems 1997, 43, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Cai, J.; Ma, K.; Tan, T. Research on Terminal Distance Index-Based Multi-Step Ant Colony Optimization for Mobile Robot Path Planning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2023, 20, 2321–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Song, X.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y. Improved ant colony algorithm in path planning of a single robot and multi-robots with multi-objective. Evol. Intell. 2024, 17, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wei, L.; Wu, D. An Intelligently Enhanced Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Global Path Planning of Mobile Robots in Engineering Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, B.; Kim, J.-H. Mobile robot path planning based on bi-population particle swarm optimization with random perturbation strategy. J. King Saud. Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cao, M.; Song, B. A new approach to smooth path planning of mobile robot based on quartic Bezier transition curve and improved PSO algorithm. Neurocomputing 2022, 473, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.K.; Kumbhar, C.; Parhi, D.R.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Jayagopal, P.; Haque, A. Trajectory Planning and Collision Control of a Mobile Robot: A Penalty-Based PSO Approach. Math. Probl. Eng. 2023, 2023, 1040461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamini, C.; Benhlima, S.; Elbekri, A. Genetic Algorithm Based Approach for Autonomous Mobile Robot Path Planning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 127, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, T.; Pan, X.; Hu, M. Multi-objective mobile robot path planning algorithm based on adaptive genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; pp. 4460–4466. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Kang, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. Hybrid A*-Guided Model Predictive Path Integral Control for Robust Navigation in Rough Terrains. Mathematics 2025, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Lian, J.; Wu, F. A Hybrid Multi-objective Heuristic Algorithm for Automated Guided Vehicle Path Planning. In Proceedings of the 2024 43rd Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Kunming, China, 28–31 July 2024; pp. 4778–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Liu, C.; Lai, Q.; Huang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, M. The Local Path Planning Algorithm for Amphibious Robots Based on an Improved Dynamic Window Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.; Park, J.K. Fast Path Generation Algorithm for Mobile Robot Navigation Using Hybrid Map. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Kang, Y.; Yang, L.; Jia, H.; Wang, S. Optimization Algorithm for 3D Smooth Path of Robotic Arm in Dynamic Obstacle Environments. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ibáñez, J.R.; Pérez-del-Pulgar, C.J.; García-Cerezo, A. Path Planning for Autonomous Mobile Robots: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Yang, J.H.; Quan, Y.S.; Chung, C.C. Potential field-based path planning for emergency collision avoidance with a clothoid curve in waypoint tracking. Asian J. Control 2022, 24, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Optimization of Model Predictive Control for Autonomous Vehicles Through Learning-Based Weight Adjustment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Kotpalliwar, S.; Kanellakis, C.; Nikolakopoulos, G. Multi-agent Path Planning Based on Conflict-Based Search (CBS) Variations for Heterogeneous Robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2025, 111, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaValle, S.M.; Kuffner, J.J. Randomized Kinodynamic Planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J. Hybrid Sampling-Based Path Planning for Mobile Manipulators Performing Pick and Place Tasks in Narrow Spaces. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Path planning techniques for mobile robots: Review and prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 227, 120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Ramalingam, B.; Mohan, R.E. A hybrid sampling-based RRT* path planning algorithm for autonomous mobile robot navigation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 258, 125206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, P.; Qian, S.; Quan, H.; Miao, J.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Memetimin, E. Path Planning Technique for Mobile Robots: A Review. Machines 2023, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Shao, S.; Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z. Review of Autonomous Path Planning Algorithms for Mobile Robots. Drones 2023, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanhawi, M.; Simic, M. Sampling-Based Robot Motion Planning: A Review. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlambang, T.; Rahmalia, D.; Yulianto, T. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) for optimizing PID parameters on Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) control system. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1211, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, F.; Mir, I.; Abualigah, L.; Sumari, P.; Forestiero, A. A Consolidated Review of Path Planning and Optimization Techniques: Technical Perspectives and Future Directions. Electronics 2021, 10, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.A.; Abed, I.A.; Al-Hussaibi, W.A. Path planning and trajectory tracking control for two-wheel mobile robot. J. Robot. Control (JRC) 2024, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wen, T.; He, X.; Xu, G. Robust trajectory tracking and control allocation of X-rudder AUV with actuator uncertainty. Control Eng. Pract. 2023, 136, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyhanoglu, M.; Jafari, M. A simple learning approach for robust tracking control of a class of dynamical systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, M.; Ding, W.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Knoll, A. Efficient online planning and robust optimal control for nonholonomic mobile robot in unstructured environments. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 3559–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Jeong, Y. A tube-based model predictive control for path tracking of autonomous articulated vehicle. Actuators 2024, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Guivant, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, X. Hybrid model predictive control for unmanned ground vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 9, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, T.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiang, C. An improved model predictive control-based trajectory planning method for automated driving vehicles under uncertainty environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 3999–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.-Y.; Wang, R.-Z.; Shen, C.; Shi, Y. Trajectory tracking control of autonomous underwater vehicles using improved tube-based model predictive control approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 5647–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati-alamdari, S.; Nikou, A.; Dimarogonas, D.V. Robust Trajectory Tracking Control for Underactuated Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 58th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Nice, France, 11–13 December 2019; pp. 8311–8316. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, Y.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qin, T. Autonomous navigation by mobile robot with sensor fusion based on deep reinforcement learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ušinskis, V.; Nowicki, M.; Dzedzickis, A.; Bučinskas, V. Sensor-Fusion Based Navigation for Autonomous Mobile Robot. Sensors 2025, 25, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásconez, J.P.; Calderón-Díaz, M.; Briceño, I.C.; Pantoja, J.M.; Cruz, P.J. A Behavior-Based Fuzzy Control System for Mobile Robot Navigation: Design and Assessment. In International Conference on Advanced Research in Technologies, Information, Innovation and Sustainability; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 412–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hachani, S.; Nechadi, E. Type-2 Fuzzy Logic-Based Robot Navigation in Uncertain Environments: Simulation and Real-World Implementation. J. Robot. Control (JRC) 2025, 6, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Kim, J.-H. Deep reinforcement learning-based local path planning in dynamic environments for mobile robot. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Fang, X. A Hybrid Path Planning Framework Integrating Deep Reinforcement Learning and Variable-Direction Potential Fields. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xian, Y.; Zhu, X.; Deng, H. A hybrid deep learning model for UAV path planning in dynamic environments. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 67459–67475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, Z. Research on Path Planning for Mobile Charging Robots Based on Improved A* and DWA Algorithms. Electronics 2025, 14, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; He, B. Path Planning for Transoceanic Underwater Glider Based on Hybrid Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 32271–32282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, K.C.; Nnanna, N.A.; Abdullahi, S.E.-Y. Simulation-based review of classical, heuristic, and metaheuristic path planning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Fan, J.; Zhou, N.; Gao, Z. Highly Self-Adaptive Path-Planning Method for Unmanned Ground Vehicle Based on Transformer Encoder Feature Extraction and Incremental Reinforcement Learning. Machines 2024, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Im, E.; Cho, K. Mission-Conditioned Path Planning with Transformer Variational Autoencoder. Electronics 2024, 13, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Mo, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H. Transformer-based imitative reinforcement learning for multirobot path planning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10233–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H. Transformer-Enhanced Motion Planner: Attention-Guided Sampling for State-Specific Decision Making. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 8794–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Zhang, R.; Yin, G.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W. Safe and Interpretable Human-Like Planning With Transformer-Based Deep Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 12134–12146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briden, J.; Gurga, T.; Johnson, B.; Cauligi, A.; Linares, R. Transformer-based tight constraint prediction for efficient powered descent guidance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2025, 48, 1054–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Y. Attention-based UAV trajectory optimization for wireless power transfer-assisted IoT systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 8463–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lin, Z.; Huang, W.; Yan, B. Technical development and future prospects of cooperative terminal guidance based on knowledge graph analysis: A review. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2025, 26, 605–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, J. Cooperative path planning study of distributed multi-mobile robots based on optimised ACO algorithm. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2024, 179, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ma, H.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W. Cooperative Path Planning of Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Using Cylinder Vector Particle Swarm Optimization With Gene Targeting. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 8470–8480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasti, S.; Chishti, M.; Najar, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Path Planning Techniques for Mobile Robot Navigation in Known and Unknown Environments. Int. J. Comput. Exp. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 10–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yu, W.; Zhang, G.; Xia, X.; Yao, K. Multi-robot Collaborative 3D Path Planning Based On Game Theory and Particle Swarm Optimization Hybrid Method. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, A.; Ahmad, N.S. A systematic review on recent advances in autonomous mobile robot navigation. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2023, 40, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.T.; Dung, N.B. Hybrid algorithms in path planning for autonomous navigation of unmanned aerial vehicle: A comprehensive review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsaheb, J.A.; Kadhim, D.J. Classical and heuristic approaches for mobile robot path planning: A survey. Robotics 2023, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Xue, Z.; Qian, R. Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning-Based UAV Swarm Confrontation: Integrating QMIX Algorithm with Artificial Potential Field Method. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Kuching, Malaysia, 6–10 October 2024; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, G.; Cai, J.; Gong, J.; Tian, Z.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y. Cooperative following of multiple autonomous robots based on consensus estimation. Electronics 2022, 11, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K. Hybridization of Kidney-Inspired and sine–cosine algorithm for multi-robot path planning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 2883–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Behera, H.S.; Das, S.; Tripathy, H.K.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Pradhan, S. A hybrid improved PSO-DV algorithm for multi-robot path planning in a clutter environment. Neurocomputing 2016, 207, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.K.; Parhi, D.R. A new hybrid optimization algorithm for multiple mobile robots navigation based on the CS-ANFIS approach. Memetic Comput. 2015, 7, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Kong, X. An intelligence-based hybrid PSO-SA for mobile robot path planning in warehouse. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 67, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M. Efficient motion planning for chili flower pollination mechanism based on BI-RRT. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 232, 110063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B. A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.B.; Sudhagar, K.; RajaRajeswari, G. Optimal path forecasting of an autonomous mobile robot agent using breadth first search algorithm. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2014, 14, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, R.W. Algorithm 97: Shortest path. Commun. ACM 1962, 5, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjan, R.E. Depth-First Search and Linear Graph Algorithms. SIAM J. Comput. 1972, 1, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R. ON A ROUTING PROBLEM. Q. Appl. Math. 1958, 16, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavraki, L.E.; Svestka, P.; Latombe, J.C.; Overmars, M.H. Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammell, J.D.; Srinivasa, S.S.; Barfoot, T.D. Batch Informed Trees (BIT*): Sampling-based optimal planning via the heuristically guided search of implicit random geometric graphs. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, DC, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 3067–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, S.; Walter, M.R.; Perez, A.; Frazzoli, E.; Teller, S. Anytime motion planning using the RRT. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1478–1483. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).