-
 Technology-Enabled Active Learning: Assessment of Dentistry Students’ Perception of Digital Prosthodontic Workflow
Technology-Enabled Active Learning: Assessment of Dentistry Students’ Perception of Digital Prosthodontic Workflow -
 Effects of Vitamin D, Melatonin, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Periodontal Health: A Narrative Review
Effects of Vitamin D, Melatonin, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Periodontal Health: A Narrative Review -
 Three-Dimensional Surgical Guides in Orthodontics: The Present and the Future
Three-Dimensional Surgical Guides in Orthodontics: The Present and the Future -
 In Vitro Evaluation of the Effectiveness and pH Variation of Dental Bleaching Gels and Their Effect on Enamel Surface Roughness
In Vitro Evaluation of the Effectiveness and pH Variation of Dental Bleaching Gels and Their Effect on Enamel Surface Roughness
Journal Description
Dentistry Journal
Dentistry Journal
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on dentistry published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Dentistry, Oral Surgery and Medicine) / CiteScore - Q2 (General Dentistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2023)
Latest Articles
Factors Influencing the Selection of Materials and Luting Agents for Single-Crown Restorations
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 207; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050207 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
Objective: Selecting suitable materials and luting agents for single crowns is critical yet challenging, as dentists must consider different factors. This study aimed to assess dentists’ preferences for materials and luting agents under different clinical conditions and evaluate the nonclinical factors influencing their
[...] Read more.
Objective: Selecting suitable materials and luting agents for single crowns is critical yet challenging, as dentists must consider different factors. This study aimed to assess dentists’ preferences for materials and luting agents under different clinical conditions and evaluate the nonclinical factors influencing their preferences. Methods: A paper-based survey supplemented with photographs illustrating anterior and posterior single-crown preparation designs was used, incorporating three clinical scenarios for each as examples. Participants provided demographic data and were asked to select their preferred material and luting agent for each scenario. Comparisons between the crown material/luting agent choices and dentist/practice characteristics were performed. Significant differences were determined using the chi-square test. Results: Overall, 262 (87.3%) dentists participated in this survey. The top-selected material for anterior preparation designs was lithium disilicate; monolithic zirconia was the most selected for posterior preparation designs. Dual-cure resin was the most selected luting agent for all anterior and posterior clinical scenarios, except for posterior subgingival preparation design. There was a significant association between the dentist’s age and the selection of material and luting agent (p < 0.05) in all clinical scenarios, except for the luting agent selection in the posterior subgingival preparation designs (p < 0.05). Other nonclinical factors yielded mixed results; some preparation designs showed significant differences, while others did not, depending on the clinical scenario. Conclusions: Reliance on new materials and luting agents that require minimally invasive treatment with dental ceramics and resin cement is increasing. However, the choice of materials and luting agents is influenced by clinical presentation and nonclinical factors, making it crucial for dentists to be aware of these factors when selecting materials for single-crown restorations. Clinical Implications: An overall trend was observed for the use of strong monolithic ceramics with adhesive resin cements. These findings could assist dentists in reviewing and re-evaluating material choices in their clinical practices, both at a national and regional level. Additionally, the findings could be useful for dental policy makers, wholesale suppliers, and retail distributors in making future decisions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dental Materials Design and Innovative Treatment Approach)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Nickel Ion Release in Nickel-Containing Orthodontics Archwires: A Narrative Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
by
Angelina Stoyanova-Ivanova, Velizar Georgiev and Jorge N. R. Martins
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 206; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050206 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Nickel-containing orthodontic archwires, particularly those made of nickel-titanium (NiTi) and stainless steel (SS), play a crucial role in orthodontic treatment using the fixed technique due to their mechanical properties. However, concerns regarding nickel-induced allergic reactions, cytotoxicity, and metal ion release, especially nickel-related ones,
[...] Read more.
Nickel-containing orthodontic archwires, particularly those made of nickel-titanium (NiTi) and stainless steel (SS), play a crucial role in orthodontic treatment using the fixed technique due to their mechanical properties. However, concerns regarding nickel-induced allergic reactions, cytotoxicity, and metal ion release, especially nickel-related ones, persist. This narrative review aims to explore recent findings on nickel release from orthodontic appliances, building upon prior systematic reviews by analyzing both in vitro and in vivo studies under various environmental conditions. The databases Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed were searched for relevant studies that examined the relationship between nickel ion release from nickel-containing archwires and various environmental conditions. The studies found indicate that while metal ion release occurs during short-term treatment, the levels are lower than harmful thresholds, with factors such as pH, corrosion, length of treatment, and environmental influences affecting release rates. Despite this, long-term studies are few and are usually conducted only in an in vitro or in vivo environment, but not both. To establish causal relationships regarding metal ion release, in vivo monitoring of ions like Ni is critical, with further research needed to assess its prolonged effects. Furthermore, collaborative efforts among practitioners, researchers, and regulatory bodies are vital for developing evidence-based guidelines for orthodontic material selection, prioritizing patient safety and addressing metal ion release risks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Research Topics in Orthodontics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pathways Between Parental Attitudes and Early Childhood Caries in Preschool Children
by
Apolinaras Zaborskis, Aistė Kavaliauskienė, Jaunė Razmienė, Augustė Razmaitė, Vilija Andruškevičienė, Julija Narbutaitė and Eglė Aida Bendoraitienė
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 205; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050205 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Parental attitudes play a crucial role in shaping children’s oral health habits and preventing dental diseases. This study aimed to explore the theoretical pathways through which parental behavior and attitudes toward child oral health can influence the dental caries experience as
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Parental attitudes play a crucial role in shaping children’s oral health habits and preventing dental diseases. This study aimed to explore the theoretical pathways through which parental behavior and attitudes toward child oral health can influence the dental caries experience as measured by the dmf-t index in preschool children in Lithuania. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted involving 302 children aged 4–7 years and their parents (262 mothers). Parental attitudes were assessed using the Parental Attitudes Towards Child Oral Health (PACOH) scale. For the children, the following variables were considered: sex, age, dental caries experience (dmf-t index in the primary dentition), oral hygiene index (Silness–Löe Plaque Index), toothbrushing frequency, and parental assistance with toothbrushing. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was applied for the data analysis. Results: The main path through which parental attitudes towards child oral health influenced the dmf-t index was via toothbrushing frequency (β = −0.17) or parental assistance with toothbrushing (β = 0.24). These factors were then linked to the oral hygiene index (β = 0.20 and β = −0.47, respectively), which ultimately influenced dmf-t (β = 0.52). The parents’ attitudes and toothbrushing frequency per se had no significant effect on children’s dmf-t (β = −0.06 and β = −0.04, respectively). The final model met all goodness-of-fit criteria: Chi-square test p = 0.211, Incremental Fit Index IFI = 0.994, Tucker–Lewis Index TLI = 0.982, Comparative Fit Index CFI = 0.994, and Root Mean Square Error of Approximation RMSEA = 0.038. Conclusions: Findings from this study demonstrate that parents play a significant role in determining children’s oral health. Regular toothbrushing, parental assistance with toothbrushing, and good oral hygiene are critical factors linking parents’ oral health-related attitudes to a child’s experience of early caries. Identifying the associations between dental caries risk factors helps plan interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances in Pediatric Odontology)
►▼
Show Figures
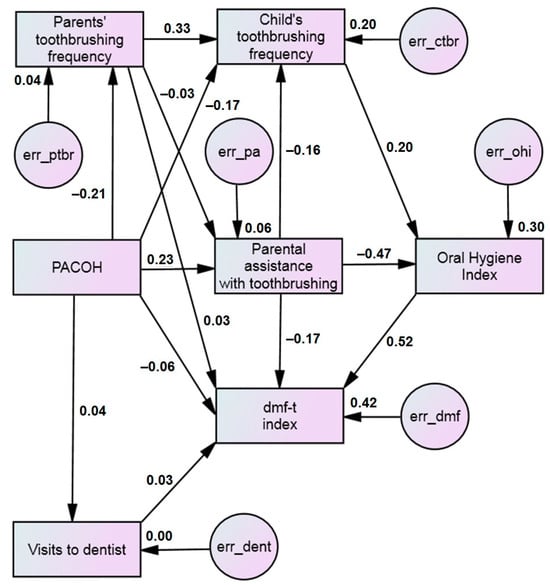
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Measuring the Marginal Gap of Pre-Cemented All-Metal Single Crowns: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
by
James Dudley and Taseef Hasan Farook
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 204; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050204 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
Background: Different methods have been used to fabricate and measure marginal gap in all-metal crowns, yet a systematic review on this topic has not been conducted. Objective: To review the existing literature regarding the measurement methods employed for the in vitro marginal gap
[...] Read more.
Background: Different methods have been used to fabricate and measure marginal gap in all-metal crowns, yet a systematic review on this topic has not been conducted. Objective: To review the existing literature regarding the measurement methods employed for the in vitro marginal gap measurement of pre-cemented all-metal single crowns and examine the influence of crown fabrication method on the marginal gap. Materials and Methods: A systematic search was performed from December 2024 backwards across EBSCO Host, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science databases following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and predefined eligibility criteria. The quality of included articles was evaluated using the Joanna Briggs Critical Appraisal Checklist. Results: Ten studies, involving 180 crowns, assessed marginal gaps using computerised superimposition (102 µm), scanning electron microscopy (89 µm), profilometry (100 µm), photogrammetry (59 µm), impression replica techniques (124 µm), and direct view microscopy (35 µm). Marginal gaps varied across crowns constructed with cobalt–chromium (97 µm), titanium (56 µm), noble metals (127 µm), and base metal alloys (35 µm). No significant differences (t = 1.06, p = 0.315) were observed between CAD/CAM (103.21 ± 58.56 µm) and lost wax casting method (71.59 ± 43.94 µm) of crown fabrication when analysed using an independent t-test. Conclusions: Cobalt–chromium was the most used material for AMCs, while titanium alloys produced the lowest mean marginal gap per crown. No significant differences in reported marginal gaps were observed between crowns fabricated using lost wax casting and CAD/CAM techniques. However, the limited number of studies, variation in measurement methods, and inconsistency in methodological rigour restricted the generalisability of the findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dental Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Tennessean Adults
by
Yeleeya Y. Li, Ying Liu, Memunat Ogunmefun and Kesheng Wang
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 203; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050203 - 1 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Tennessee has one of the worst rankings for older adults’ oral health in the United States. This study aims to evaluate the oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) among older individuals (aged 60 and above) in Tennessee using the Oral Health
[...] Read more.
Background: Tennessee has one of the worst rankings for older adults’ oral health in the United States. This study aims to evaluate the oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) among older individuals (aged 60 and above) in Tennessee using the Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14) questionnaire. Methods: The data were collected from the 233 Tennessee Smile-on program participants in the early phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, between December 2019 and August 2021. The frequency and percentage for each subgroup were calculated. Cronbach’s alpha was used to measure the internal consistency or reliability of OHIP in this study. Factor Analysis (FA) with oblique rotation was conducted to explore the underlying factor structure of the OHIP questionnaire set. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: The majority of participants were retired (59.66%), and there was a significant difference in OHIP_sum scores among different employment statuses (p = 0.018). Cronbach’s alpha showed the domains of psychological discomfort, physical disability, and psychological disability were highly correlated with the total score (alpha = 0.8). Factor analysis identified three main dimensions: physical discomfort, psychological distress, and functional disability, and they can explain over 90% of the total variance. Individuals measure of sampling adequacy (MSA) and overall MSA are greater than 0.9, indicating excellent sampling adequacy. Conclusions: The study suggested that oral health can be assessed not only through examinations by dental professionals but also by considering emotional and social well-being. However, a limitation of the study is that it was conducted during the COVID-19 outbreak, which restricted participant involvement.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Dental Treatment, Including Multiple Extractions, Under General Anaesthesia on Children’s Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Prospective Study
by
Haneen Baty, Ibtesam Alzain, Medhat Abdulla and Khlood Baghlaf
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 202; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050202 - 1 May 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Children who undergo several dental extractions with general anesthesia (GA) may face considerable changes in their oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL), but there is a lack of research on this issue in the Middle East. Aim: This study aimed to assess
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Children who undergo several dental extractions with general anesthesia (GA) may face considerable changes in their oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL), but there is a lack of research on this issue in the Middle East. Aim: This study aimed to assess how the number of dental extractions performed under general anaesthesia due to caries impacts the oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) in children aged from three to six years. Methods: This prospective, single-center cohort study included parents of children aged 3–6 years undergoing dental treatment under general anaesthesia in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Parents completed the validated Arabic Early Childhood Oral Health Impact Scale (A-ECOHIS) before and after treatment to assess changes in OHRQoL. The number of extractions was recorded, and patients were grouped based on extraction frequency: high (≥mean) and low (<mean). Pearson’s correlation was used to evaluate the relationship between the number of extractions and the effect size of OHRQoL. Results: Ninety-three participants met the inclusion criteria and agreed to participate in this study. The mean age of the children was 4.88 years (SD ± 1.06). The most common procedure performed was extraction, with a mean of 5.34 (SD ± 5.53), followed by stainless-steel crown application, with a mean of 4.03 (SD ± 2.01). No correlation between the number of extractions and the effect size in the change in OHRQoL was noted (Pearson r = −0.002, p-value = 0.98). Conclusions: Dental extractions were the most common procedure performed under GA. While multiple extractions showed no significant association with the effect size of OHRQoL, overall treatment under GA led to significant improvement. These findings highlight the need for timely intervention, parental education, and comprehensive treatment protocols. Utilizing tools like ECOHIS may aid in prioritizing high-risk cases and optimizing resource allocation in pediatric dental care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oral Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Determinants)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Efficacy of a Dentifrice Tablet to Prevent Dental Caries: A Microbial Study
by
Bennett Tochukwu Amaechi, Kannan Kanthaiah, Rayane Farah, Kelly Yang, Amos Chiedu Obiefuna, Parveez Ahamed Abdul-Azees and Mahalakshmi Vijayaraghavan
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 201; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050201 - 30 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Dentifrice tablets are a new over-the-counter dentifrice form that are gaining global interest. The aim of this microbial study was to investigate the effectiveness of a dentifrice tablet (DT) containing nanohydroxyapatite (nHAP) to prevent tooth demineralization. Methods: 120 bovine tooth blocks were
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Dentifrice tablets are a new over-the-counter dentifrice form that are gaining global interest. The aim of this microbial study was to investigate the effectiveness of a dentifrice tablet (DT) containing nanohydroxyapatite (nHAP) to prevent tooth demineralization. Methods: 120 bovine tooth blocks were randomly assigned to four treatment groups (30/group): Nanohydroxyapatite DT (5% nHAP), placebo DT (Placebo), NaF toothpaste (1100 ppm Fluoride) and no-treatment (Control). Blocks were subjected to 7-day demineralization by plaque growth in a mixed-organism Microbial Caries Model. Toothpaste was made into slurry (1 toothpaste:3 water), while DT was thoroughly crushed and homogenized with water (1 tablet:3 water) to slurry. Both slurries were applied twice daily for 2 min on each occasion. Demineralization was assessed using Surface Microhardness (SMH) testing before and after plaque exposure. Change (ΔSMH) and percentage change (%∆SMH) in SMH (percentage demineralization [%Dem]), and % demineralization inhibition (%Dem-Inhibition) in each group were calculated. Intra-group (SMH) comparison (paired t-test) and intergroup (%∆SMH) comparison (ANOVA/Tukey’s test) were conducted (α = 0.05). Results: The paired t-test indicated a significant difference (p < 0.001) between pre-treatment and post-treatment SMH in all groups. The intergroup comparison based on their %Dem using ANOVA/Tukey’s test showed that Control (29.93 ± 5.58) had significantly (p < 0.05) higher %Dem than Placebo (22.81 ± 7.47, p < 0.05), nHAP (13.93 ± 11.31, p < 0.001) and Fluoride (14.44 ± 10.65, p < 0.001). The Placebo had significantly (p < 0.01) higher %Dem than nHAP and Fluoride. No significant difference between nHAP and Fluoride. Intergroup comparison based on their %Dem-Inhibition (calculated relative to the control) using ANOVA/Tukey’s test, nHAP (51.74 ± 40.05, p < 0.01) and Fluoride (50.56 ± 37.21, p < 0.05) had significantly higher %Dem-Inhibition than Placebo tablet (21.86 ± 5.55). No significant difference in %Dem-Inhibition between nHAP and Fluoride. Conclusions: The present study demonstrated that dentifrice tablets containing 5% nanohydroxyapatite are as effective as NaF toothpastes containing 1100 ppm fluoride in preventing tooth demineralization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Updates and Highlights in Cariology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
The Influence of Diet and Physical Activity on Periodontal Health: A Narrative Review
by
Giuseppe Balice, Michele Paolantonio, Giovanna Murmura, Matteo Serroni, Stefania Di Gregorio and Beatrice Femminella
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 200; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050200 - 30 Apr 2025
Abstract
Periodontal diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, are chronic inflammatory conditions that compromise the supporting structures of the teeth, often leading to tooth loss and contributing to systemic comorbidities. Increasing evidence underscores the critical role of modifiable lifestyle factors, particularly diet and physical activity,
[...] Read more.
Periodontal diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, are chronic inflammatory conditions that compromise the supporting structures of the teeth, often leading to tooth loss and contributing to systemic comorbidities. Increasing evidence underscores the critical role of modifiable lifestyle factors, particularly diet and physical activity, in influencing periodontal health. This narrative review critically evaluates the current body of literature regarding the impact of dietary constituents and physical activity on the periodontium, with a focus on the molecular mechanisms, key biomarkers, and clinical implications. It aims to provide a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between nutrition, exercise, and periodontal health with potential implications for clinical management and preventive strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Review Papers in Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
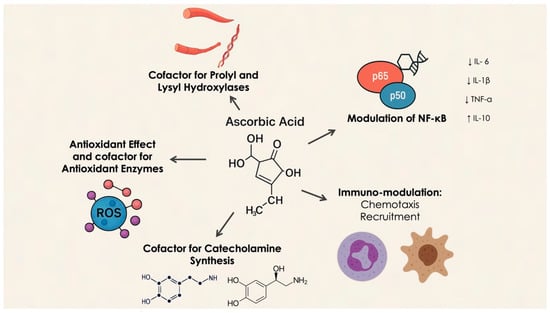
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Premedication and Dental Anxiety on Anesthetic Efficacy in Patients Undergoing Root Canal for Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis in Upper and Lower Molars: A Comparative Study of Articaine and Bupivacaine
by
Luis Manteca-Fernández, Cristina Meniz-García, Fernando Fernández-Cáliz, Cristina Barona-Dorado, Juan Santos-Marino and Natalia Martínez-Rodríguez
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 199; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050199 - 30 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The use of local anesthetics in dentistry is crucial for pain control. Their efficacy may be related to multiple factors, including gender, the clinical status of the patient, anatomical factors, the type of anesthetic, premedication treatment, and the experience of the professional. Aim:
[...] Read more.
The use of local anesthetics in dentistry is crucial for pain control. Their efficacy may be related to multiple factors, including gender, the clinical status of the patient, anatomical factors, the type of anesthetic, premedication treatment, and the experience of the professional. Aim: The objective of this study was to analyze whether premedication or the degree of patient anxiety influences the anesthetic efficacy of 4% articaine with epinephrine 1:100,000 and 0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine 1:100,000 in patients undergoing root canal treatment for symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in the upper and lower molars. The null hypothesis (H0) of this study was that articaine and bupivacaine would have a similar anesthetic efficacy when used during the treatment of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis of the posterior mandibular and maxillary teeth, independent of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) premedication or the patient’s anxiety levels. Methods: A total of 140 patients presenting with pulpitis in the upper and lower molars were randomly assigned to one of two anesthetics: articaine or bupivacaine. Before root canal treatment, patients completed the Modified Corah Dental Anxiety Scale (MDAS) and a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for pain intensity. Inferior alveolar nerve block was performed for the lower molars and buccal infiltration for the upper molars, and the anesthetic efficacy was verified by the Endo Coldspray® test. During the procedure, the patients’ heart rate and oxygen saturation were monitored using a pulse oximeter. The patients reported their pain levels using a VAS twenty-four hours postoperatively. Results: High levels of dental anxiety were significantly associated with higher pain scores (p = 0.000) for both groups. The hemodynamic changes during treatment remained within normal limits. The need for anesthetic reinforcement was higher in the bupivacaine group (p = 0.004). The patients in both groups reported low-intensity postoperative pain, although the pain level was slightly lower in the bupivacaine group. Conclusions: The anesthetic efficacy of articaine and bupivacaine in patients with irreversible pulpitis did not appear to be influenced by the degree of anxiety or the intake of AINEs as premedication. The intrinsic anesthetic efficacy was higher for articaine, which required less reinforcement than bupivacaine. Comparing the results obtained when performing buccal infiltration and inferior alveolar nerve block further highlighted the differences between the two anesthetics; these differences were more pronounced in the bupivacaine group, leading to rejection of the null hypothesis proposed at the beginning of the study.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
AI-Driven Advancements in Orthodontics for Precision and Patient Outcomes
by
David B. Olawade, Navami Leena, Eghosasere Egbon, Jeniya Rai, Aysha P. E. K. Mohammed, Bankole I. Oladapo and Stergios Boussios
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 198; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050198 - 30 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming orthodontic care by providing personalized treatment plans that enhance precision and efficiency. This narrative review explores the current applications of AI in orthodontics, particularly its role in predicting tooth movement, fabricating custom aligners, optimizing treatment times, and
[...] Read more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming orthodontic care by providing personalized treatment plans that enhance precision and efficiency. This narrative review explores the current applications of AI in orthodontics, particularly its role in predicting tooth movement, fabricating custom aligners, optimizing treatment times, and offering real-time patient monitoring. AI’s ability to analyze large datasets of dental records, X-rays, and 3D scans allows for highly individualized treatment plans, improving both clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. AI-driven aligners and braces are designed to apply optimal forces to teeth, reducing treatment time and discomfort. Additionally, AI-powered remote monitoring tools enable patients to check their progress from home, decreasing the need for in-person visits and making orthodontic care more accessible. The review also highlights future prospects, such as the integration of AI with robotics for performing orthodontic procedures, predictive orthodontics for early intervention, and the use of 3D printing technologies to fabricate orthodontic devices in real-time. While AI offers tremendous potential, challenges remain in areas such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the cost of adopting AI technologies. However, as AI continues to evolve, its capacity to revolutionize orthodontic care will likely lead to more streamlined, patient-centered, and effective treatments. This review underscores the transformative role of AI in modern orthodontics and its promising future in advancing dental care.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Time Interval, Temperature, and Storage Condition on Fluoride Release and Recharge from Silorane-Based Restorative Materials
by
Prashanthi S. Madhyastha, Dilip G. Naik, Srikant Natarajan and Rachel Sarah Vinodhini
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 197; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050197 - 30 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objectives: The fluoride-releasing properties of restorative materials are crucial for the prevention of secondary caries as these can act as fluoride reservoirs. Hence, the present study aimed to investigate, assess, and compare the impact of time, temperature, and storage conditions on the fluoride
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The fluoride-releasing properties of restorative materials are crucial for the prevention of secondary caries as these can act as fluoride reservoirs. Hence, the present study aimed to investigate, assess, and compare the impact of time, temperature, and storage conditions on the fluoride release of silorane-based composites (SBCs) and methacrylate-based composites (MBCs), and also evaluate the variation in their reuptake of fluoride (after recharge). Methods: SBC and MBC test samples of 10 mm × 2 mm dimensions were prepared and tested for fluoride release and recharge in distilled water and artificial saliva at temperatures of 4 °C, 37 °C, and 55 °C. The amount of fluoride released (at 1, 7, 14, and 28 days) and re-released after recharge (with 5000 ppm neutral sodium fluoride (NaF) solution for 5 min at 1, 3, and 7 days for 3 weeks) were studied with the help of a fluoride-selective ion electrode. Results: SBCs had a greater release of fluoride at low temperature in artificial saliva (0.07 ± 0.03) when compared to MBCs (0.04 ± 0.005). Fluoride release increased on day 7 but decreased over time (p < 0.05). Fluoride re-release was greater in MBCs than SBCs and it increased with time (p < 0.05). Conclusion: The amount of fluoride release and recharge depends on the time interval, temperature, and storage condition. These restorative materials can serve as fluoride reservoirs and contribute to sustained fluoride release in oral fluids, thereby preventing the initiation of secondary caries and the failure of restorations. In addition, it may assist in developing measures to improve fluoride delivery for topical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dental Materials Design and Innovative Treatment Approach)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perioperative/Periprocedural Antithrombotic Management in Oral Health Procedures. A Prospective Observational Study
by
María González-Zamora, Nagore Ambrosio, Raquel González, Paula Anguita, Ana Molina, David Herrera, Mariano Sanz, Francisco Marín, María Anguita-Gámez, Raquel Ferrandis, David Vivas, Manuel Anguita and Elena Figuero
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 196; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050196 - 29 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This paper evaluates the incidence of thrombotic and/or hemorrhagic adverse events within 30 days after oral health procedures (OHPs) in patients taking antithrombotic agents. Secondary objectives were to determine proper antithrombotic management and its association with adverse events. Methods: As part of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This paper evaluates the incidence of thrombotic and/or hemorrhagic adverse events within 30 days after oral health procedures (OHPs) in patients taking antithrombotic agents. Secondary objectives were to determine proper antithrombotic management and its association with adverse events. Methods: As part of a multicenter multispecialty prospective observational study (ReQXAA), individuals with antithrombotic therapy and receiving at least one OHP were selected. Before OHP, participants were referred to their medical doctors to indicate the antithrombotic therapy management. Adverse events were evaluated thirty days after OHP by phone call. Proportions and odds ratios (ORs) were generated applying Fisher’s exact test, chi-square tests and multiple regression models. Results: A total of 138 patients underwent 144 OHPs. Fifteen adverse events (10.5%) were registered, among which the most frequent was slight bleeding (n = 13), which was followed by bleeding that required suspension of the antithrombotic agent (n = 1) and a myocardial infarction (n = 1). Antithrombotic management was appropriate in 122 (84.7%) cases. In 15.3% of the cases it was inappropriate, the main reason being the unnecessary interruption of the antithrombotic medication (n = 11; 50%). Inadequate management was associated with a higher incidence of adverse events (OR = 4.7; 95% confidence interval [1.3, 16.3]; p = 0.016) after adjusting for confounding factors. Conclusions: The incidence of adverse events 30 days after OHPs was low (10.5%). An inappropriate perioperative/periprocedural antithrombotic management occurred in 15.3% of the cases and was associated with a higher incidence of adverse events (OR = 4.7).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Oral Health Management and Disease Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SEM and Bacteriological Evidence of Laser-Activated Irrigation Compared to Ultrasonic-Activated Irrigation: A Pilot Study
by
David E. Jaramillo, Ji W. Jeong, Zhen Shen and Enrico Divito
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 195; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050195 - 29 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Pulp tissue debridement and the eradication of microorganisms from an infected root canal system before obturation is a primary focus of endodontic treatment and the best predictor for the long-term success of endodontic treatment. Objective: The purpose of this in vitro laboratory
[...] Read more.
Background: Pulp tissue debridement and the eradication of microorganisms from an infected root canal system before obturation is a primary focus of endodontic treatment and the best predictor for the long-term success of endodontic treatment. Objective: The purpose of this in vitro laboratory study was to evaluate pulp tissue debridement and the disinfection efficacy of two different Er;Cr:YSGG laser units, with a 2790 nm wavelength, compared to ultrasonic-activated irrigation (UAI) in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis. Methods: Human non-infected mandibular first molars were extracted, disinfected, and cultured with Enterococcus faecalis. Different types of Er;Cr:YSGG laser irrigation and UAI were performed according to the manufacturers’ protocols. The teeth were then processed for bacteriological and SEM analyses. Results: The different laser-activated irrigation protocols showed multiple areas of remaining bacteria, biofilm, tissue, and thermal ablation. The laser fiber tips also displayed significant tip degradation after use, which might affect efficacy. Conclusions: In this in vitro study, laser-activated irrigation using Er;Cr:YSGG technology and UAI were inefficient in eliminating pulp tissue from difficult-to-reach areas and Enterococcus faecalis from infected root canals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Endodontics: From Technique to Regeneration)
►▼
Show Figures
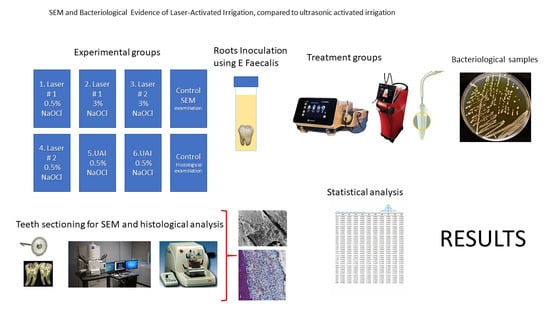
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Salivary Tumor Marker CA-125 Among Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients and Healthy Individuals
by
Riham Mohammed, Mariam El Sheikh, Nada Tawfig Hashim, Nallan CSK Chaitanya and Ahmed Suleiman
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 194; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050194 - 29 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: In Sudan, oral cancer is one of the top ten most common cancers, with OSCC representing the majority of the cases. To date, despite the fact that saliva can be collected simply and non-invasively, there is no approved salivary tumor marker
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In Sudan, oral cancer is one of the top ten most common cancers, with OSCC representing the majority of the cases. To date, despite the fact that saliva can be collected simply and non-invasively, there is no approved salivary tumor marker for OSCC. This study aimed to investigate the reliability of salivary CA-125 as a tumor marker for OSCC by measuring and comparing its level among OSCC and healthy individuals as well as its level across different histopathological grades. Methods: A total of 100 subjects were enrolled; 50 were patients with OSCC, while the other 50 were matched healthy individuals. Non-stimulated whole saliva was collected before the administration of definitive treatment, and the concentration of salivary CA-125 was quantified using an automated immunoassay analyzer that employs a one-step sandwich fluorescent enzyme immunoassay (FEIA). Results: The level of salivary CA-125 was 342.65 U/mL in the cases group, which was significantly increased compared with 203.65 U/mL in the healthy controls (p = 0.017). Statistically significant differences in the level of salivary CA-125 among different histopathological grades were observed (p = 0.014). The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and positive and negative predictive values were 48%, 78%, 63%, 68.6%, and 60%, respectively. Conclusions: This study suggests that salivary CA-125 could serve as a potential tumor marker for OSCC. However, its clinical application requires further validation.
Full article
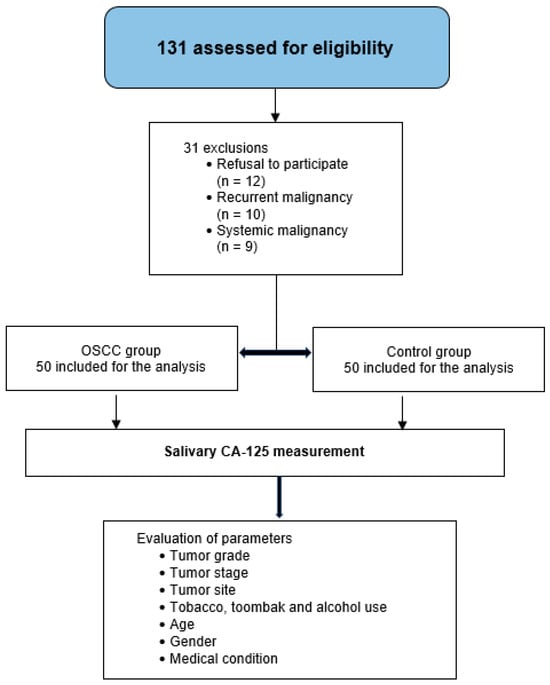
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Crestal Hydraulic Sinus Lift with Simultaneous Implant Insertion: A Retrospective Case Series
by
Francesco Mattia Ceruso, Aurea Immacolata Lumbau, Francesco Pernice, Alessandro Mastroianni, Michele Miranda, Silvio Mario Meloni, Marco Gargari, Marco Tallarico and Milena Pisano
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 193; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050193 - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objectives: This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the increase in vertical bone height following sinus lift procedures using the CAS (Crestal Approach Sinus) kit technique in combination with tissue-level implants. Additionally, the quantity of bone between the implant apex and the Schneiderian
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the increase in vertical bone height following sinus lift procedures using the CAS (Crestal Approach Sinus) kit technique in combination with tissue-level implants. Additionally, the quantity of bone between the implant apex and the Schneiderian membrane was assessed to determine the effectiveness and safety of this minimally invasive approach. Methods: The study included 15 patients (20 implants) who underwent sinus lift procedures with the CAS kit technique and tissue-level implants in the posterior maxilla between September 2021 and October 2024. Inclusion criteria required a minimum residual bone height (RBH) of 2 mm. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans were used for initial screening, and panoramic radiography evaluated outcomes at implant placement and nine months postoperatively. Primary outcomes included implant and prosthetic survival rates, as well as biological and technical complications. Secondary outcomes were vertical bone height and the amount of bone above the implant tip. Statistical analyses were conducted using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test with a significance level of 0.05. Results: All implants achieved successful osseointegration, with no implant or prosthetic failures and no biological or technical complications reported. The mean RBH at implant placement was 4.2 ± 1.4 mm, which increased to an overall membrane elevation of 13.8 ± 1.8 mm. At the 9-month follow-up, the overall membrane elevation was slightly reduced to 13.0 ± 1.6 mm (p = 0.000), with a mean bone gain of 9.6 ± 2.4 mm. The amount of bone above the implant tip was 3.4 ± 1.7 mm at placement, decreasing to 3.0 ± 1.2 mm at follow-up (p = 0.007). Conclusions: The CAS kit technique combined with tissue-level implants demonstrated significant vertical bone gain and high implant survival rates without complications. This minimally invasive approach proved effective and safe for sinus augmentation in patients with limited residual bone height. The findings support the CAS kit’s potential as a preferred technique for maxillary sinus elevation. Further research with larger cohorts and long-term follow-up is needed to validate these results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oral Implantology and Bone Regeneration)
►▼
Show Figures
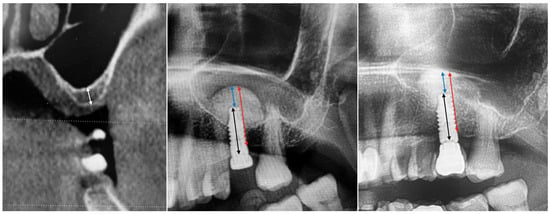
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Minimally Invasive Root Canal Cleaning: Evaluating Supplementary Irrigation Techniques
by
Alissa Tiscareño, P. S. Ortolani-Seltenerich, Ana Ramírez-Muñoz, Omar Pérez-Ron, Pedro M. Mendez S, Carmen Leal-Moya, Giulia Malvicini, Gaya C. S. Vieira and Alejandro R. Pérez
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 192; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050192 - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of cleaning in minimally shaped mesial and oval distal canals of 3D models of mandibular molars, focusing on positive pressure irrigation, wireless and conventional passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), and diode laser (DL) at 980 nm.
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of cleaning in minimally shaped mesial and oval distal canals of 3D models of mandibular molars, focusing on positive pressure irrigation, wireless and conventional passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI), and diode laser (DL) at 980 nm. Methods: Forty-four 3D-printed resin models, based on eleven natural mandibular molars (each with mesial and distal canals), were divided into four groups (n = 11 per group) to evaluate different irrigation methods. A total of 22 mesial canals (size 20/.04) and 11 oval distal canals (size 25/.04) were analyzed per group. Each root canal was uniformly filled with an artificial hydrogel to simulate a biofilm mixture. Following this preparation, the specified irrigation techniques were applied to the respective groups. Quantitative evaluations of pre- and post-irrigation images were performed to assess the efficiency of tissue removal along the entire length of the canal and in the apical, middle, and coronal thirds. Results: The findings revealed no significant differences in the initial amount of tissue between the samples, indicating uniform filling. In the apical region of mesial canals, conventional PUI showed the highest cleaning efficiency (14.1% residual tissue), significantly outperforming the other methods (p < 0.05). Cordless PUI and DL also surpassed positive pressure irrigation, leaving 30.4% and 29.3% residual tissue, respectively, compared to 42.2% with positive pressure. In the middle third, all methods tested performed better than needle irrigation (p < 0.05), but there were no significant differences in the coronal third or over the full canal length. Distal oval canals showed no significant differences in cleaning effectiveness among methods. Conclusions: Although no single method was superior regarding the full canal length, supplementary techniques such as PUI and DL offer potential benefits over conventional irrigation methods, particularly in the apical third of the canal. Complementary approaches such as conventional PUI and diode laser at 980 nm showed superior cleaning efficiency, particularly in the apical third. These results suggest their integration could improve the effectiveness of cleaning in minimally instrumented mesial canals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dentistry in the 21st Century: Challenges and Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures
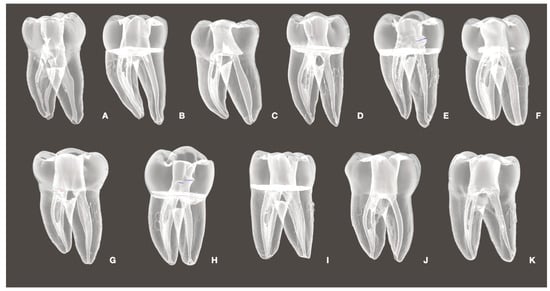
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pediatric Dentists’ Practice Patterns in the Management of Permanent Teeth Needing Endodontic Treatment
by
Nuha Ashraf, Linda Sangalli, Jackson Seagroves and Caroline M. Sawicki
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 191; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050191 - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The objective of this study was to evaluate practice patterns among pediatric dentists for the management of permanent teeth needing endodontic treatment. Methods: An electronic nationwide survey was sent to all members of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD).
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The objective of this study was to evaluate practice patterns among pediatric dentists for the management of permanent teeth needing endodontic treatment. Methods: An electronic nationwide survey was sent to all members of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD). The survey assessed provider training on and confidence (0–100, with 100 = “most confident”) in treating pediatric patients needing endodontic treatment on permanent teeth, referral patterns, and preferred educational resources. A logistic regression identified significant predictors of confidence levels. Results: The final sample included 259 respondents, with 71% having over 10 years of experience in practice. A total of 47% of respondents reported performing endodontic treatments on permanent teeth in pediatric patients, with direct pulp capping (70%) and partial or full pulpotomy (62%) being the most common procedures. Although the respondents moderately agreed (53 ± 32) that they received sufficient training during their residency to perform endodontic treatment on permanent teeth, their reported comfort levels with performing these procedures were low (0.001 ± 33). The adequacy of the training received during their residency was identified as a significant predictor of a higher level of confidence (p < 0.001, 95% CI 0.437, 0.667). The respondents highlighted additional continuing education courses and training, dedicated lectures at the AAPD Annual Session, and annual joint symposia or meetings between the AAPD and the American Association of Endodontists as the most valuable educational resources for the endodontic management of permanent teeth in pediatric patients. Conclusions: The findings suggest that enhancing residency training and expanding access to targeted continuing education opportunities are critical for improving pediatric dentists’ confidence and competence in the endodontic management of permanent teeth in pediatric patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dental Education: Innovation and Challenge)
►▼
Show Figures
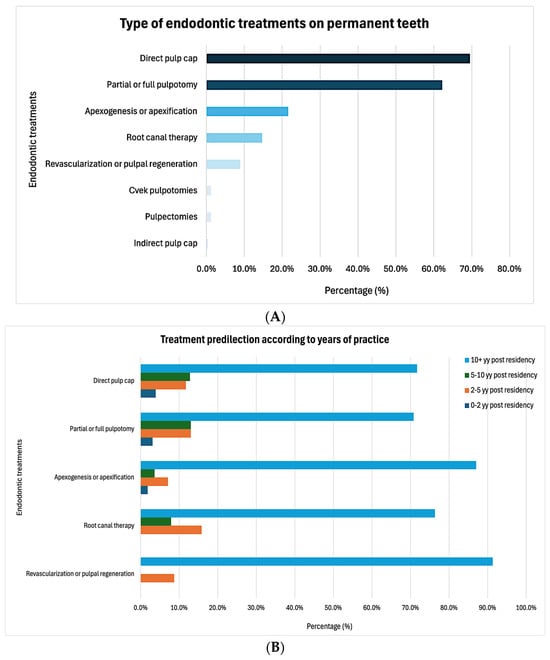
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Vascular Photobiomodulation in the Postoperative Period of Alveolar Bone Grafting
by
Nicole Rosa de Freitas, Luisa Belluco Guerrini, Denise Sabbagh Haddad, Roberta Martinelli de Carvalho, Renato Yassutaka Faria Yaedú and Ana Lúcia Pompéia Fraga de Almeida
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 190; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050190 - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study evaluated the effects of vascular photobiomodulation (VPBM) on pain intensity, edema, and facial temperature variation in patients undergoing alveolar bone grafting (ABG) surgery. Methods: A total of 42 patients with cleft lip and palate (aged 9–25 years) scheduled for ABG
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study evaluated the effects of vascular photobiomodulation (VPBM) on pain intensity, edema, and facial temperature variation in patients undergoing alveolar bone grafting (ABG) surgery. Methods: A total of 42 patients with cleft lip and palate (aged 9–25 years) scheduled for ABG using iliac crest bone were randomly assigned in equal numbers (14 per group) to one of three groups: control (ABG only), test (ABG + VPBM), and placebo (ABG + simulated VPBM). Iliac and facial pain and edema were clinically evaluated 24 h post-surgery, along with thermographic facial analysis. Follow-up was conducted via phone calls for one week. Results: No statistically significant differences were observed among the groups regarding facial pain and edema at 24 h post-surgery. However, iliac pain significantly differed between the placebo and control groups (p = 0.045). A significant time-related effect on both facial and iliac pain outcomes was noted during follow-up, irrespective of the group. The need for rescue medication and self-perception of reduced edema did not differ significantly. Thermographic analysis reveals a significantly lower temperature variation in the test group (2.36 °C) compared to the other groups (p = 0.007). Conclusions: Overall, VPBM therapy influenced postoperative pain in the early recovery phase and temperature in the immediate postoperative period but did not significantly affect edema.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Laser Dentistry: The Current Status and Developments)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Color Stability and Marginal Integrity in Provisional Restorations: A Study of Milling, 3D Printing, and Conventional Fabrication Methods
by
Austin Galbraith, Mai Doan, Tyson Galbraith and Neamat Hassan Abubakr
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 189; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050189 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The quality of a provisional restoration, especially its color and marginal integrity, can play a critical role in its survival and overall patient satisfaction. This study aims to evaluate the color stability and marginal fit differences between provisional restorations fabricated by non-traditional
[...] Read more.
Background: The quality of a provisional restoration, especially its color and marginal integrity, can play a critical role in its survival and overall patient satisfaction. This study aims to evaluate the color stability and marginal fit differences between provisional restorations fabricated by non-traditional methods compared to manual fabrication. Methods: A total of 80 extracted teeth were prepared for ceramic crowns and randomly divided into four groups: acrylic, 3D printing, computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM), and bis-acryl. The examined teeth were subjected to artificial aging using a thermocycling machine dwelling for 5000 cycles (simulating 6 clinical months). Color stability and marginal integrity were measured before and after thermal aging using a VITA Easyshade V spectrophotometer and 3D surface non-contact profilometer. ANOVA was used to determine whether the mean value difference was significantly different. Results: The 3D-printed and bis-acryl provisional crowns displayed the lowest change in marginal integrity, while the acrylic provisional crowns showed the greatest change in marginal integrity (p = 0.0001). Additionally, the acrylic provisional material revealed a significantly greater color change. Conclusions: The 3D-printed provisional crowns demonstrated the best marginal integrity and color stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Digital Dentistry)
►▼
Show Figures
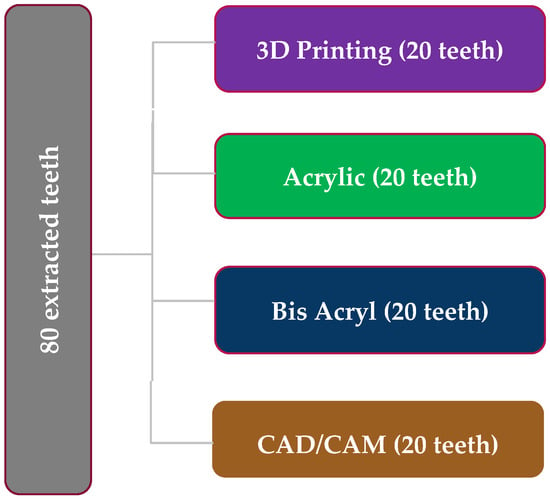
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Association Between Periodontal Disease and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Vincenzo Bitonti, Tiziana Perri, Lorenzo Cigni, Domenico Familiari, Giuseppe Vazzana and Rocco Franco
Dent. J. 2025, 13(5), 188; https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13050188 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Periodontal disease (PD) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are two prevalent conditions that have been independently associated with systemic inflammation and hormonal dysregulation. Emerging evidence suggests a potential bidirectional relationship between these conditions, but the nature and strength of this association remain
[...] Read more.
Background: Periodontal disease (PD) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are two prevalent conditions that have been independently associated with systemic inflammation and hormonal dysregulation. Emerging evidence suggests a potential bidirectional relationship between these conditions, but the nature and strength of this association remain unclear. Objective: This systematic review aimed to evaluate and synthesize the existing evidence on the association between periodontal disease and polycystic ovary syndrome, following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in multiple databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, from 1990 to 2025. Studies investigating the association between PD and PCOS in terms of prevalence, severity, and shared pathophysiological mechanisms were included. Two independent reviewers screened studies for eligibility, extracted data, and assessed methodological quality using validated tools. Discrepancies were resolved through consensus. Meta-analysis was conducted where appropriate. Results: A total of nine studies were included. Most studies reported a higher prevalence and severity of periodontal disease among women with PCOS compared to controls. Shared mechanisms, including systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hormonal dysregulation, were frequently proposed as underlying factors. However, heterogeneity in study designs, diagnostic criteria, and confounding adjustments limited the comparability of findings. Conclusions: This systematic review supports a potential association between periodontal disease and polycystic ovary syndrome, likely mediated by common inflammatory and metabolic pathways. However, the evidence is limited by heterogeneity and methodological biases. Further well-designed longitudinal studies are needed to clarify causal relationships and explore the clinical implications of integrating periodontal health management into PCOS care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dentistry in the 21st Century: Challenges and Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures
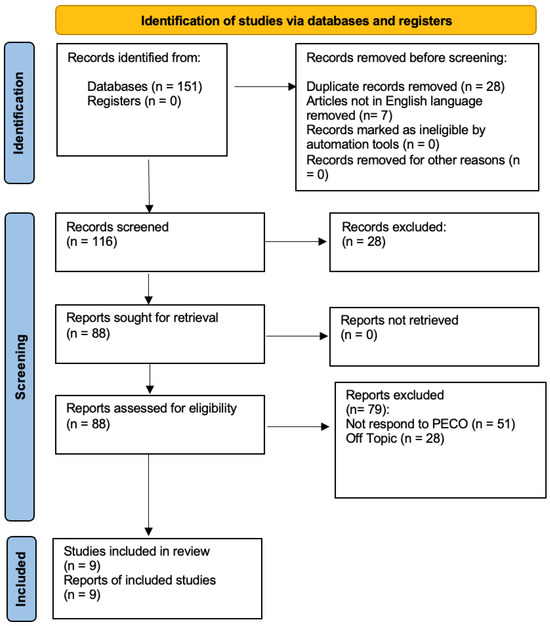
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Dentistry Journal Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biology, JCM, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Assessment of Craniofacial Morphology: Traditional Methods and Innovative Approaches
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 20 June 2025
Topic in
Dentistry Journal, JCM, Materials, Biomedicines, Life
Medical and Dental Care, Photobiomodulation and Photomedicine
Topic Editors: Samir Nammour, Chukuka Samuel Enwemeka, Aldo Brugnera JuniorDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Children, Dentistry Journal, JCM
Preventive Dentistry and Public Health
Topic Editors: Denis Bourgeois, Elena BardelliniDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Dentistry Journal, JCM, Materials, Medicina
Advances in Dental Materials
Topic Editors: Vincenzo D'Antò, Daniele Botticelli, Piero Antonio ZeccaDeadline: 31 May 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Current Advances in Pediatric Odontology
Guest Editors: Klaus Pieper, Andreas G. SchulteDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
New Perspectives in Periodontology and Implant Dentistry
Guest Editor: Daniele CardaropoliDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Preventive Dental Care, Chairside and Beyond
Guest Editors: Chun Hung Chu, Chloe JiangDeadline: 15 May 2025
Special Issue in
Dentistry Journal
Studies on Dental Enamel
Guest Editor: Sofia PessanhaDeadline: 15 May 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Novel Ceramic Materials in Dentistry
Collection Editors: Roberto Sorrentino, Gianrico Spagnuolo
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Bio-Logic Approaches to Implant Dentistry
Collection Editors: Luigi Canullo, Donato Antonacci, Piero Papi, Francesco Gianfreda, Bianca Di Murro, Carlo Raffone
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Feature Papers in Dental Education
Collection Editors: Jelena Dumancic, Božana Lončar Brzak
Topical Collection in
Dentistry Journal
Dental Traumatology and Sport Dentistry
Collection Editor: Enrico Spinas








