- Article
Evaluating the Test Characteristics of a Prototype for AI-Assisted Radiographic Detection
- Rohit Kunnath Menon
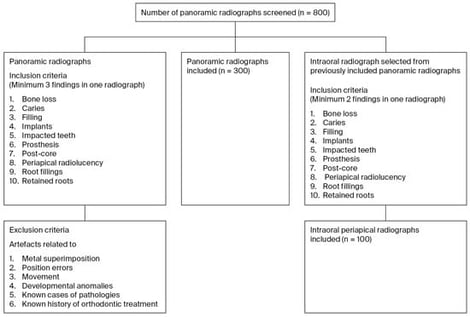
Background/Objectives: It is essential to test the accuracy of artificial intelligence-assisted tools that detect dental pathologies from radiographs. This study aimed to evaluate the test characteristics of an artificial intelligence-assisted convolutional neural network-based prototype used for automated radiographic detection. Methods: A total of 300 panoramic and 100 intraoral periapical radiographs were collected between January 2020 and 2024 and then analyzed by two trained, independent specialist evaluators. The diagnostic consensus, “ground truth”, was labeled as follows: BL: bone loss; C: caries; F: filling; I: implants; IT: impacted teeth; P: prosthesis; PC: post-core; PR: periapical radiolucency; RF: root fillings; and RR: retained roots. The radiographs were uploaded to the prototype, and the results were compared. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were calculated using Stata version 15.0 (StataCorp). Results: Overall, most of the outcomes demonstrated sensitivity greater than 82%, with values ranging from 66.41% (65.47,67.36) for BL to 100% (100.00,100.00) for I. For all outcomes, specificity was greater than 93%, with values ranging from 93.61% (93.12,94.10) for BL to 100% for I. The overall values for all the test characteristics for the periapical radiographs were above 85%. The key errors identified in the qualitative analysis were errors in tooth identification, failure to detect recurrent caries under fillings and crowns, impacted canines, and inaccurate identification of extensive fillings as crowns. Conclusions: The prototype demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity in identifying dental pathologies. Accuracy in identifying bone loss, teeth that have migrated, including impacted canines, secondary caries, and differentiating extensive fillings from crowns requires further improvement.
9 February 2026