Translation and Validation of the Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Intensive Care Unit Patients in Morocco: Reliability and Validity Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Characteristics
Test–Retest Reliability (ICC)
2.2. Validity of AM-RCSQ
2.2.1. Clinical Validity
2.2.2. Construct Validity
2.2.3. Discriminant Validity
2.3. Factor Structure of AM-RCSQ
Exploratory Factor Analysis of AM-RCSQ
3. Methods
3.1. Study Design
3.2. Ethical Issues
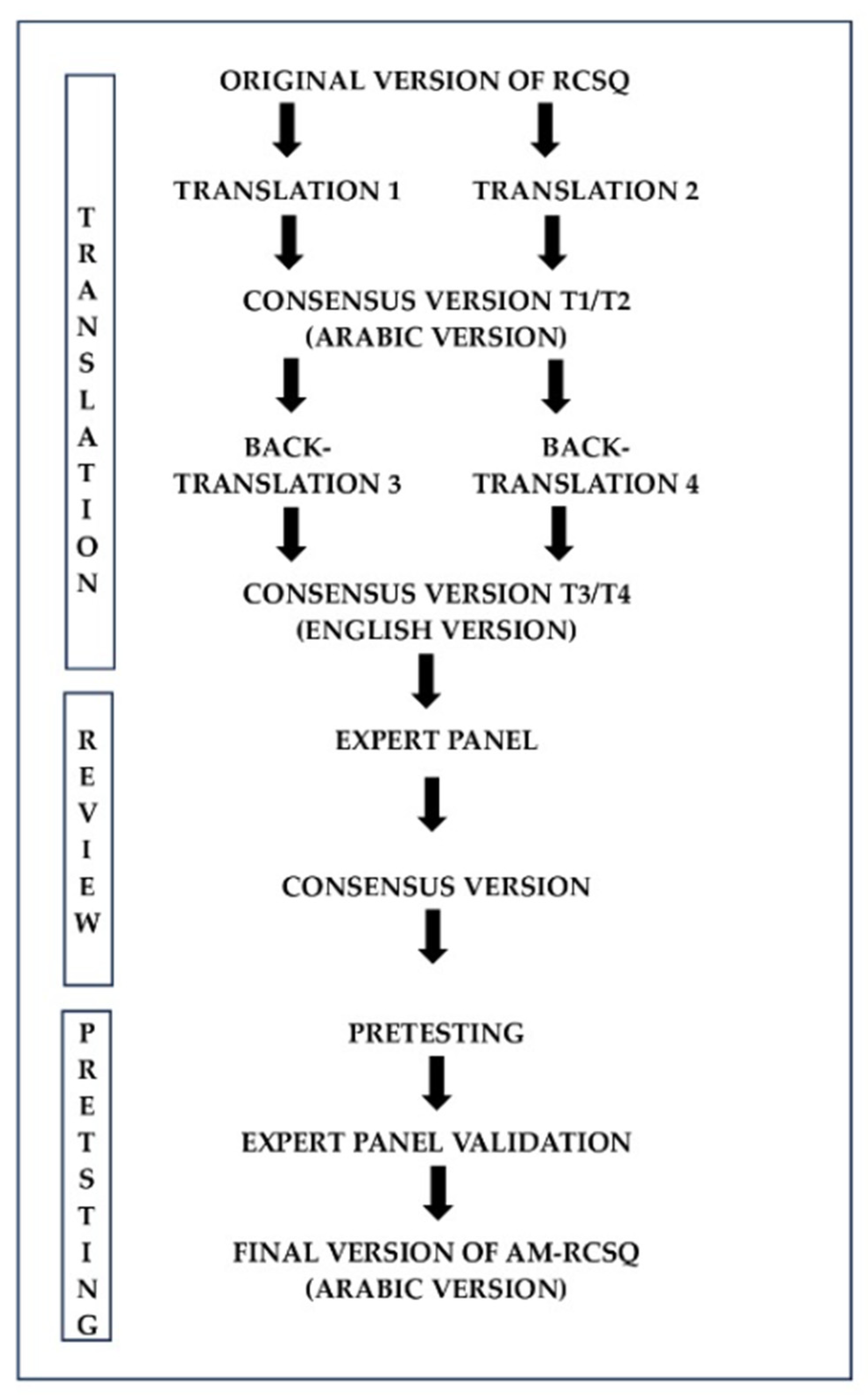
3.3. Translation of the RCSQ
3.4. Setting and Participants
3.5. Patient-Reported Outcome: The Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire (RCSQ)
3.6. Data Collection
3.7. Test–Retest Reliability of the AM-RCSQ
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Strength and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, E.Y.; Wilcox, M.E. Sleep in the intensive care unit. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2022, 28, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.R.; Wheaton, A.G.; Johnson, D.A. Sleep Deprivation, Sleep Disorders, and Chronic Disease. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2023, 20, E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauert, M.P.; Pisani, M.; Redeker, N.; Murphy, T.; Araujo, K.; Jeon, S.; Yaggi, H. Pilot study: An intensive care unit sleep promotion protocol. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2019, 6, e000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, F.; Ugwuoke, U.T. Assessing the Relationship Between Sleep Duration and the Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease Among Veterans in the United States: A 2022 Behavior Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e68538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Yoshiike, T.; Nagao, K.; Utsumi, T.; Tsuru, A.; Otsuki, R.; Ayabe, N.; Hazumi, M.; Suzuki, M.; Saitoh, K.; et al. Association of Subjective Quality and Quantity of Sleep with Quality of Life among a General Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aritake, S.; Asaoka, S.; Kagimura, T.; Shimura, A.; Futenma, K.; Komada, Y.; Inoue, Y. Internet-based survey of factors associated with subjective feeling of insomnia, depression, and low health-related quality of life among Japanese adults with sleep difficulty. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2015, 22, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemilohun, A.C.; Fasesan, O.A.; Ajiro, T.O.; Akande, K.O.; Elikwu, C.J.; Adeleye, O.O. Sleep Quality in a Nigerian Community: Prevalence of Poor Sleep Quality, Risk Factors and Health-Related Quality of Life. West Afr. J. Med. 2022, 39, 729–736. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. Mental health and quality of life according to sleep in cancer survivors. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 2022, 58, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucklin, A.A.; Ganglberger, W.; Quadri, S.A.; Tesh, R.A.; Adra, N.; Da Silva Cardoso, M.; Leone, M.J.; Krishnamurthy, P.V.; Hemmige, A.; Rajan, S.; et al. High prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in the intensive care unit—A cross-sectional study. Sleep Breath. Schlaf Atm. 2023, 27, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxlund, J.; Knudsen, T.; Sörberg, M.; Strøm, T.; Toft, P.; Jennum, P.J. Sleep quality and quantity determined by polysomnography in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients randomized to dexmedetomidine or placebo. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2023, 67, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showler, L.; Deane, A.M.; Litton, E.; Ankravs, M.J.; Wibrow, B.; Barge, D.; Goldin, J.; Hammond, N.; Saxena, M.K.; Young, P.J.; et al. A multicentre point prevalence study of nocturnal hours awake and enteral pharmacological sleep aids in patients admitted to Australian and New Zealand intensive care units. Crit. Care Resusc. J. Australas. Acad. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 26, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solverson, K.J.; Easton, P.A.; Doig, C.J. Assessment of sleep quality post-hospital discharge in survivors of critical illness. Respir. Med. 2016, 114, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter-Rice, K.; McMurray, M.G.; Christoferson, E.; Yeager, H.; Wiggins, B. Sleep in the Intensive Care Unit: Biological, Environmental, and Pharmacologic Implications for Nurses. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, J. Factors influencing sleep quality in the intensive care unit: A descriptive pilot study in Korea. Acute Crit. Care 2023, 38, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, E.K.; Ister, E.D.; Ozdemir, A. The relationship between sleep quality and dyspnoea severity in patients with COPD. Afr. Health Sci. 2020, 20, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittayamai, N.; Wilcox, E.; Drouot, X.; Mehta, S.; Goffi, A.; Brochard, L. Positive and negative effects of mechanical ventilation on sleep in the ICU: A review with clinical recommendations. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldabayan, Y.S.; Alqahtani, J.S.; Al Rajeh, A.M.; Abdelhafez, A.I.; Siraj, R.A.; Thirunavukkarasu, V.; Aldhahir, A.M. Prevalence and Predictors of Sleep Disturbance, Anxiety and Depression among Patients with Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Jin, X.; Shan, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Li, P.; Peng, X.; Peng, Z.; Yu, K.; Bao, W.; et al. Relationship of Sleep Duration With All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, A.M.; Bender, E. Sleep in Hospitalized Patients. Clocks Sleep 2019, 1, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q. Association and prediction of subjective sleep quality and postoperative delirium during major non-cardiac surgery: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, P. Association of subjective cognitive complaints with poor sleep quality: A cross-sectional study among Chinese elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 38, e5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elías, M.N. Assessment and Monitoring of Sleep in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 33, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, L.J.; Litton, E.; Melehan, K.L.; Huang, H.-C.C.; Lopez, V.; Van Haren, F. The feasibility and reliability of actigraphy to monitor sleep in intensive care patients: An observational study. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2021, 25, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.C.; O’Sullivan, P.S.; Phillips, R.L. Measurement of sleep in critically ill patients. J. Nurs. Meas. 2000, 8, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lm, H.; Fulbrook, P.; Ja, D. Sleep assessment of hospitalised patients: A literature review. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2014, 51, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ji, D.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Bai, C.; Liu, H.; Liang, Y. Richards-Campbell sleep questionnaire: Psychometric properties of Chinese critically ill patients. Nurs. Crit. Care 2019, 24, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitisin, N.; Somnuke, P.; Thikom, N.; Raykateeraroj, N.; Poontong, N.; Thanakiattiwibun, C.; Wongtangman, K. Psychometric properties of a Thai version of the Richards-Campbell sleep questionnaire. Nurs. Crit. Care 2022, 27, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varella, N.C.; Almeida, R.S.; Nogueira, L.A.C.; Ferreira, A.S. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for intensive care unit inpatients in Brazil: Internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and measurement error. Sleep Med. 2021, 85, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotsetis, S.; Richards, K.C.; Behncke, A.; Köpke, S. The reliability of the German version of the Richards Campbell Sleep Questionnaire. Nurs. Crit. Care 2017, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Japanese version of the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire: Reliability and validity assessment—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31367403/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Kim, J.K.; Park, J.-H.; Cho, J.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, J. Reliability of the Korean version of the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire. Acute Crit. Care 2020, 35, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiner, D.L.; Kottner, J. Recommendations for reporting the results of studies of instrument and scale development and testing. J. Adv. Nurs. 2014, 70, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, D.E.; Bombardier, C.; Guillemin, F.; Ferraz, M.B. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 2000, 25, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottner, J.; Audigé, L.; Brorson, S.; Donner, A.; Gajewski, B.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Roberts, C.; Shoukri, M.; Streiner, D.L. Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, K.H.; Yates, B.C.; Berger, A.M.; Pozehl, B.; Meza, J. Translating the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Into Arabic. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2010, 32, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 1951, 16, 297–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwee, C.B.; Bot, S.D.M.; de Boer, M.R.; van der Windt, D.A.W.M.; Knol, D.L.; Dekker, J.; Bouter, L.M.; de Vet, H.C.W. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2007, 60, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani Younis, M.; Hayajneh, F.A. Quality of Sleep Among Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Literature Review. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2018, 41, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulami, G.S.; Rice, A.M.; Kidd, L.; O’Neill, A.; Richards, K.C.; McPeake, J. An Arabic Translation, Reliability, Validity, and Feasibility of the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Sleep Quality Assessment in ICU: Prospective-Repeated Assessments. J. Nurs. Meas. 2019, 27, E153–E169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E.; Gandek, B. Methods for testing data quality, scaling assumptions, and reliability: The IQOLA Project approach. International Quality of Life Assessment. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Ha, E.J.; Ha, T.S. 2021 KSCCM clinical practice guidelines for pain, agitation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disturbance in the intensive care unit. Acute Crit. Care 2022, 37, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, S.P.; Doward, L.C. The translation and cultural adaptation of patient-reported outcome measures. Value Health J. Int. Soc. Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 2005, 8, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total (n = 224) |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 49 ± 18.3 |
Gender, n (%)
| 107 (47.76)/117 (52.24) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 23 ± 4.56 |
Admitting reason
| 71(27.3)/189 (72.7) |
Admission diagnosis, n (%)
| 70 (26.9) 115 (44.2) 60 (23.1) 15 (5.8) |
| Smokers | 52(20) |
| APACHE-II scores, mean ± SD | 9.60 ± 5.87 |
| Charlson comorbidities score mean ± SD | 1.02 ± 1.34 |
| EVA-score, mean ± SD | 3.79 ± 3.18 |
| ICU length of stay (days), med (IQR) | 5 (4–6) |
| RCSQ Items | Descriptive | Internal Consistency | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Cronbach’s α (If Item Omitted) | |
| Sleep depth | 36 ± 27.8 | 0–90 | 0.946 |
| Sleep latency | 32.7 ± 26 | 0–80 | 0.969 |
| Awakenings from sleep | 32.7 ± 25.8 | 0–80 | 0.967 |
| Ability to return to sleep | 33.8 ± 26.2 | 0–90 | 0.969 |
| Sleep quality | 37 ± 21.6 | 0–80 | 0.968 |
| Item Optional: Noise | 34.3 ± 19.1 | 0–80 | 0.969 |
| Total score RCSQ | 34.8 ± 24 | 0–80 | 0.960 |
| Test | Retest | Test–Retest Reliability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (CV) | Mean ± SD (CV) | ICC2.1 | 95%CI | |
| Sleep depth | 56.7 ± 25.8 | 55.3 ± 24.8 | 0.971 | 0.919–0.990 |
| Sleep latency | 48.3 ± 29.1 | 52 ± 20.1 | 0.960 | 0.889–0.986 |
| Number of awakenings | 48.3 ± 22.1 | 48 ± 28.1 | 0.938 | 0.830–0.978 |
| Ability to return to sleep | 53.3 ± 28.1 | 47.3 ± 18.5 | 0.967 | 0.909–0.989 |
| Overall sleep quality | 53.3 ± 22.9 | 51.7 ± 26.3 | 0.950 | 0.861–0.983 |
| Total RCSQ score (Average across the 5 items above) | 51.4 ± 18.2 | 50.9 ± 17.3 | 0.978 | 0.936–0.992 |
| Variable | RCSQ | p-Value AM-RCSQ Version | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Good Sleep Quality | Poor Sleep Quality | ||
| Age | 40.1(17.4) | 51.7(17.7) | <0.001 ** |
| Pain mean ± SD | 1.78(2.57) | 4.44(3.12) | <0.001 ** |
| Gender: M/W | 24/20 | 83/97 | 0.315 * |
| Anxiety: Yes/No | 2/42 | 35/145 | 0.017 * |
| Sleep Depth | Sleep Latency | Number of Awakenings | Returning to Sleep | Sleep Quality | Noise | Total RCSQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PQSI | r: −0.588 | r: −0.583 | r: −0.551 | r: −0.554 | r: −0.598 | r: −0.537 | r: −0.635 |
| p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 | p: <0.001 |
| PCA ** | MSA * | |
|---|---|---|
| General | NA | 0.937 |
| Sleep depth | 0.953 | 0.898 |
| Sleep latency | 0.906 | 0.955 |
| Awakenings from sleep | 0.921 | 0.930 |
| Ability to return to sleep | 0.900 | 0.955 |
| Sleep Quality | 0.911 | 0.948 |
| Item Optional: Noise | 0.920 | 0.947 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lkoul, A.; Oum’barek, K.; Baba, M.A.; Jniene, A.; Dendane, T. Translation and Validation of the Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Intensive Care Unit Patients in Morocco: Reliability and Validity Assessment. Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7030031
Lkoul A, Oum’barek K, Baba MA, Jniene A, Dendane T. Translation and Validation of the Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Intensive Care Unit Patients in Morocco: Reliability and Validity Assessment. Clocks & Sleep. 2025; 7(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLkoul, Abdelmajid, Keltouma Oum’barek, Mohamed Amine Baba, Asmaa Jniene, and Tarek Dendane. 2025. "Translation and Validation of the Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Intensive Care Unit Patients in Morocco: Reliability and Validity Assessment" Clocks & Sleep 7, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7030031
APA StyleLkoul, A., Oum’barek, K., Baba, M. A., Jniene, A., & Dendane, T. (2025). Translation and Validation of the Richards–Campbell Sleep Questionnaire for Intensive Care Unit Patients in Morocco: Reliability and Validity Assessment. Clocks & Sleep, 7(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7030031






