- Case Report
Progressive Hand Stiffness and Numbness in a Child: An Atypical Neurological Presentation of Scheie Syndrome—A Case Report
- Ayidh Saad Alharthi,
- Chafik Ibrahim Hassan and
- Ali Alsayed Alsharkawy
- + 2 authors
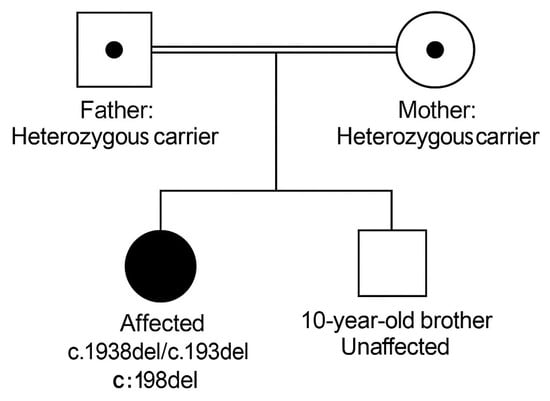
Background/Objectives: Scheie syndrome is the attenuated phenotype of mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I), a lysosomal storage disorder resulting from partial deficiency of α-L-iduronidase. The attenuated clinical spectrum and absence of cognitive impairment often delay recognition. Early manifestations may mimic common pediatric conditions, leading to repeated evaluations without a definitive diagnosis. Methods: We describe a 12-year-old girl who presented with slowly progressive bilateral hand stiffness, weak grip strength, and intermittent sensory symptoms over one year. Her initial investigations—including laboratory studies, electrophysiology, imaging, and multispecialty evaluations—were unremarkable. Results: The gradual progression of symptoms involving joints, motor function, and vision prompted metabolic testing. Whole exome sequencing revealed a homozygous IDUA variant, and enzymatic testing confirmed markedly reduced α-L-iduronidase activity, establishing the diagnosis of Scheie syndrome. Early initiation of enzyme replacement therapy was pursued. Conclusions: This case emphasizes that children with unexplained musculoskeletal and sensory symptoms should be evaluated for attenuated MPS I, especially when routine studies are inconclusive. Heightened clinical suspicion can reduce diagnostic delay and improve long-term outcomes.
17 December 2025