- Article
Intra-Articular Injection in Wistar Rats: Standardization and Experimental Validation of a Precise Protocol for Nanomaterial Administration
- Manuel Flores-Sáenz,
- Belén Chico and
- Maria C. García Alonso
- + 2 authors
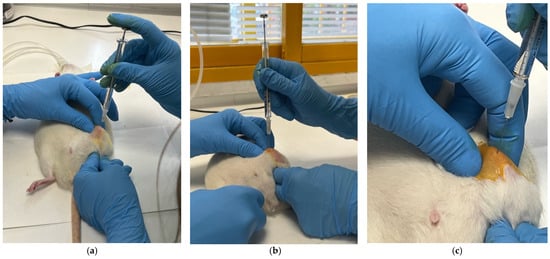
(1) Background: Intra-articular injection is a fundamental technique in preclinical research for evaluating therapeutics and inducing joint disease models in rodents. However, the absence of standardized and validated protocols compromises reproducibility and translational validity. (2) Methods: This study establishes and experimentally validates a refined protocol for precise intra-articular injection in the knee of adult male Wistar rats. The comprehensive procedure specifies anatomical landmarks (medial border of the patellar tendon), instrumentation (27 G needle, 100 µL Hamilton syringe), a maximum volume of 35 µL, and operative verification criteria based on tactile feedback. Experimental validation was performed by administering a suspension of wear particles (2.35 mg/mL) generated from tribocorrosion tests of CoCr surfaces biofunctionalized with graphene oxide-hyaluronic acid (GO-HA) into the left knee of five rats. (3) Results: Histological analysis using the cutting–grinding technique and Toluidine Blue staining confirmed the exclusive intra-articular localization of particles in all injected animals (5/5 success rate). Qualitative assessment revealed abundant particulate distribution within the synovial space, with numerous individual particles and multiple aggregates observed per high-power field, without evidence of extravasation in any case. (4) Conclusions: The protocol demonstrated high intra-operator repeatability and provides a reliable, ethically refined tool for precise intra-articular administration of nanomaterials and for generating robust joint disease models, thereby enhancing reproducibility and animal welfare in preclinical research.
20 December 2025