- Article
Mutations and Efficacy of Pembrolizumab-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Real-World Multicenter Analysis
- Palma Fedele,
- Alessandro Rizzo and
- Matteo Landriscina
- + 15 authors
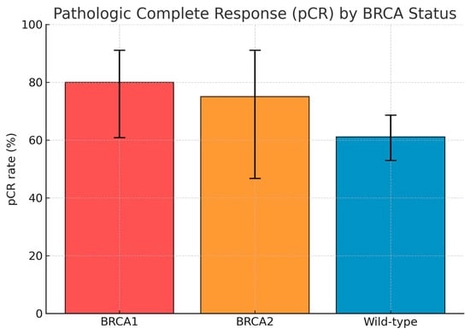
Background: Pembrolizumab has reshaped the neoadjuvant treatment landscape for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, the influence of BRCA1/2 mutational status on the efficacy of chemo-immunotherapy remains unclear, particularly in real-world settings. Since BRCA-mutated tumors exhibit homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) and high genomic instability, they may be more immunogenic and responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. This multicenter study investigated the association between BRCA1/2 mutations and pathologic complete response (pCR) in TNBC patients treated with pembrolizumab-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 184 patients with stage II–III TNBC treated between 2021 and 2024 across eleven Italian oncology centers. All received pembrolizumab combined with platinum- and taxane-based NACT followed by anthracyclines, according to the KEYNOTE-522 regimen. Germline BRCA1/2 status was determined by next-generation sequencing. The primary endpoint was pCR, defined as ypT0/is ypN0. Fisher’s exact test and logistic regression models were used to assess associations between clinical–pathological variables and pCR. Results: Among 184 patients, 25 (13.6%) harbored BRCA1 mutations, 12 (6.5%) BRCA2 mutations, and 147 (79.9%) were wild-type. pCR was achieved in 80.0% of BRCA1-mutated, 75.0% of BRCA2-mutated, and 61.1% of wild-type tumors. When pooled, BRCA1/2-mutated cases showed a higher likelihood of achieving pCR (78.4% vs. 61.1%; odds ratio [OR] = 2.17; 95% CI 1.01–4.97; p = 0.056). High tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (≥30%) were also associated with increased pCR rates. The frequency of BRCA mutations (20.1%) was consistent with that reported in major TNBC series. No comparative analysis of toxicity or survival outcomes was performed due to the retrospective design and limited follow-up. Conclusions: In this multicenter real-world cohort, TNBC patients carrying BRCA1/2 mutations exhibited a trend toward higher pCR rates with pembrolizumab-based NACT compared with wild-type tumors. These findings suggest enhanced chemosensitivity and immune responsiveness in BRCA-deficient disease, warranting further validation in larger prospective studies with survival endpoints.
14 December 2025