Promising, but Not Completely Conclusive—The Effect of l-Theanine on Cognitive Performance Based on the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis of the Results
2.5. Risk of Bias Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Quality of Evidence
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
Studies Included in the Quantitative Analysis
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Outcomes
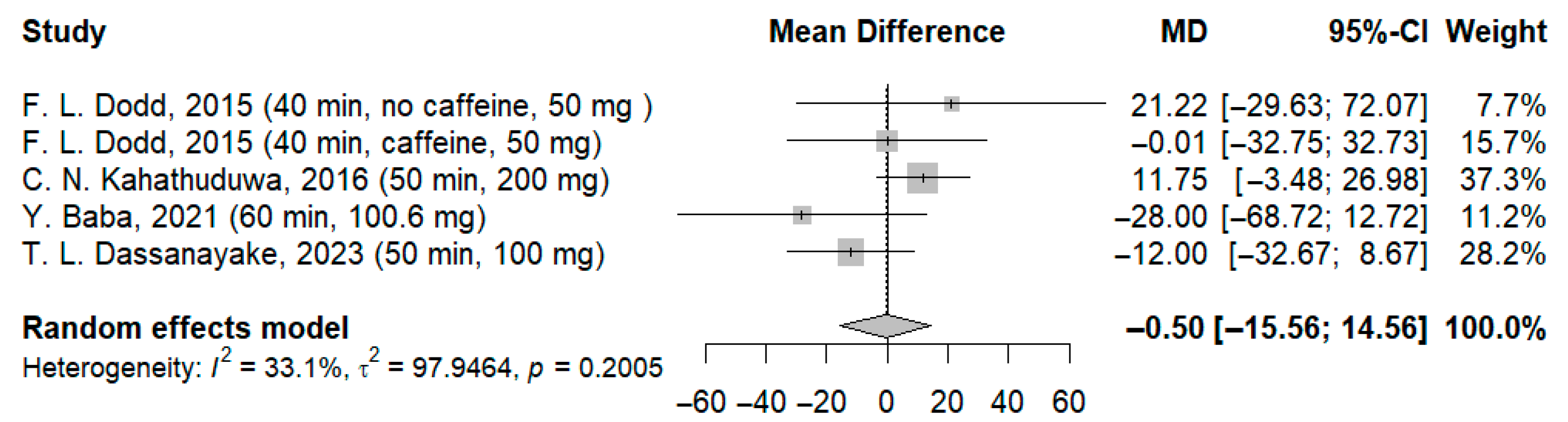
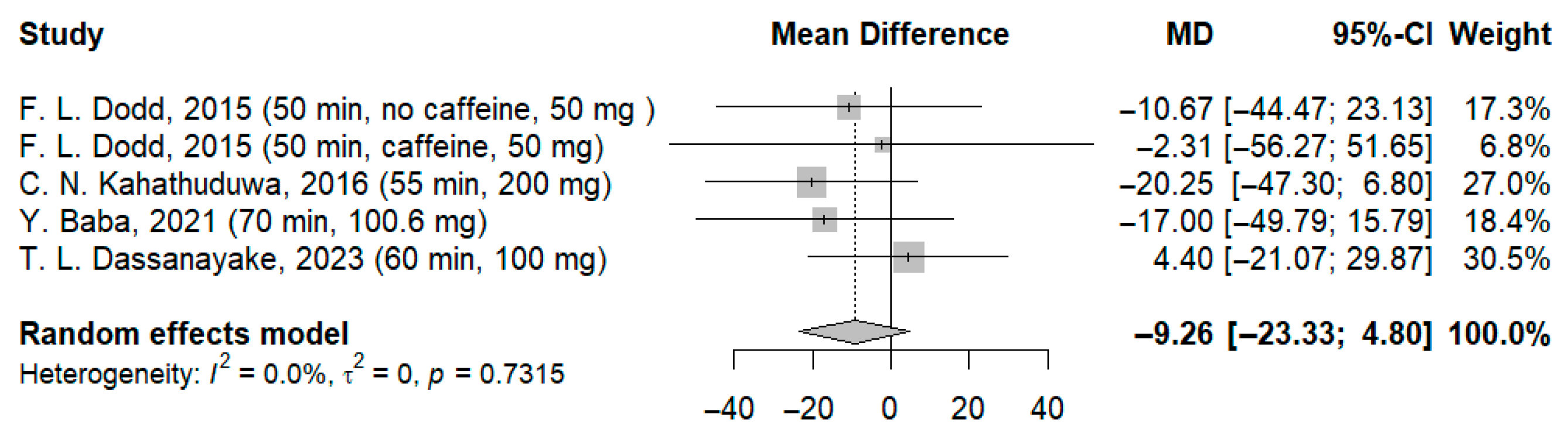
3.3.1. Effects of l-Theanine on Reaction Time to Simple Stimulus
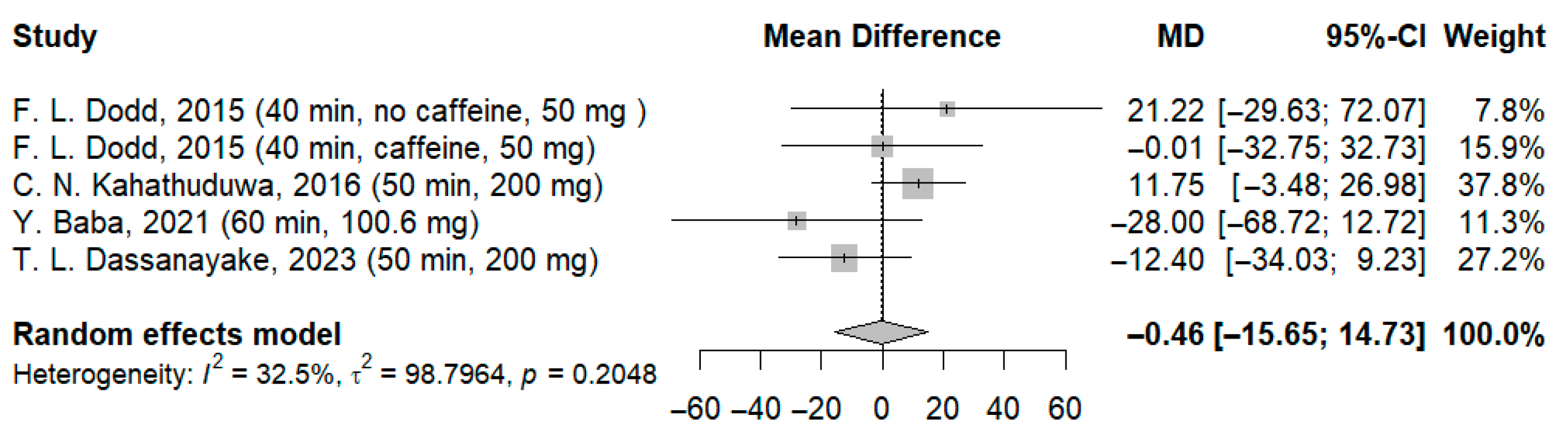
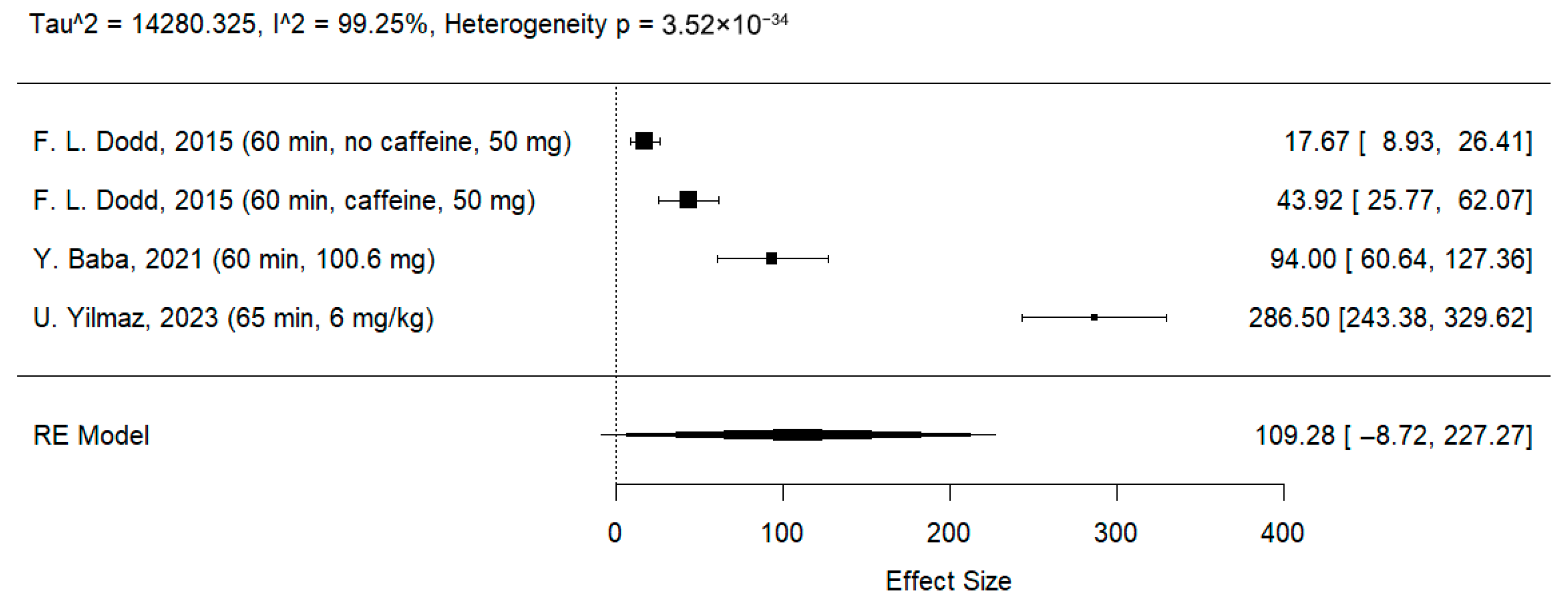
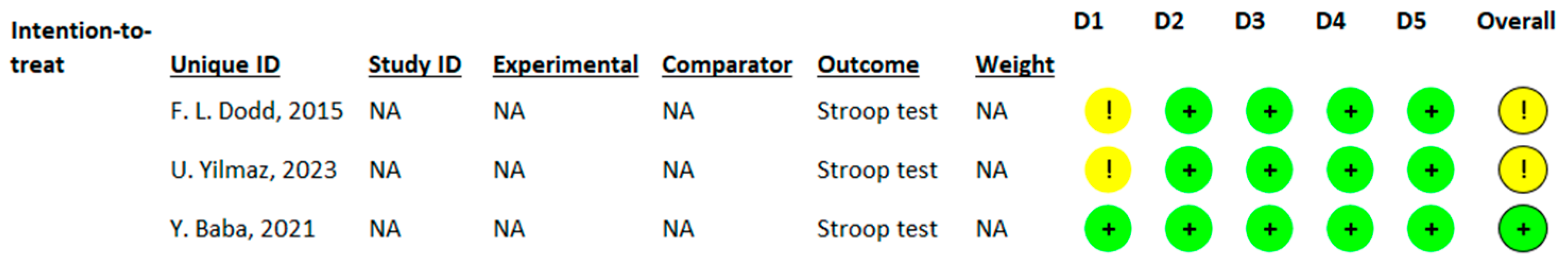
3.3.2. Effects of l-Theanine on Stroop Test
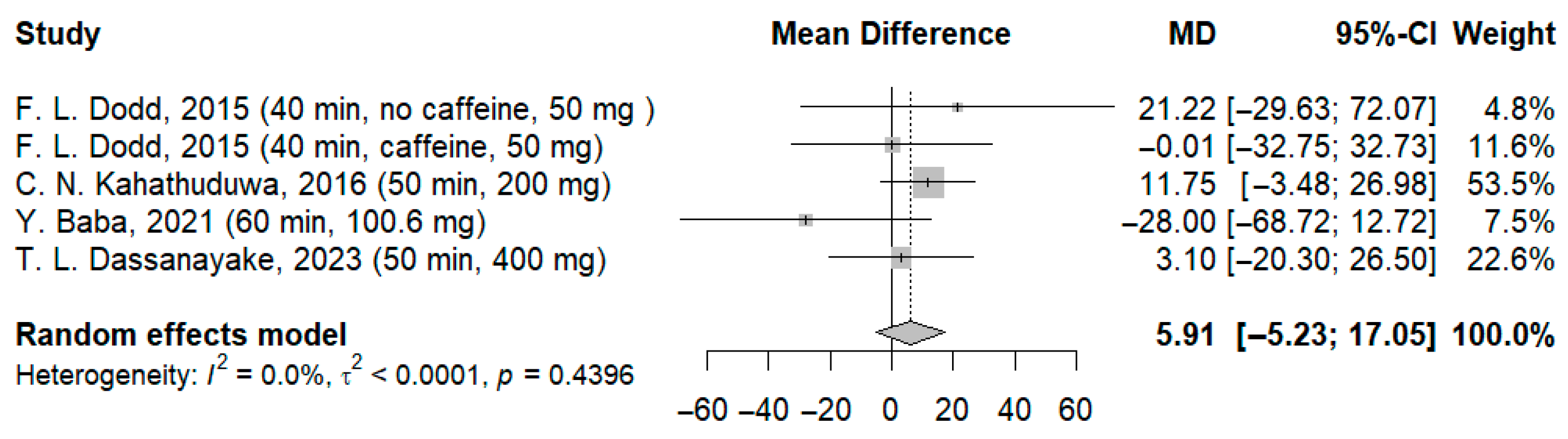
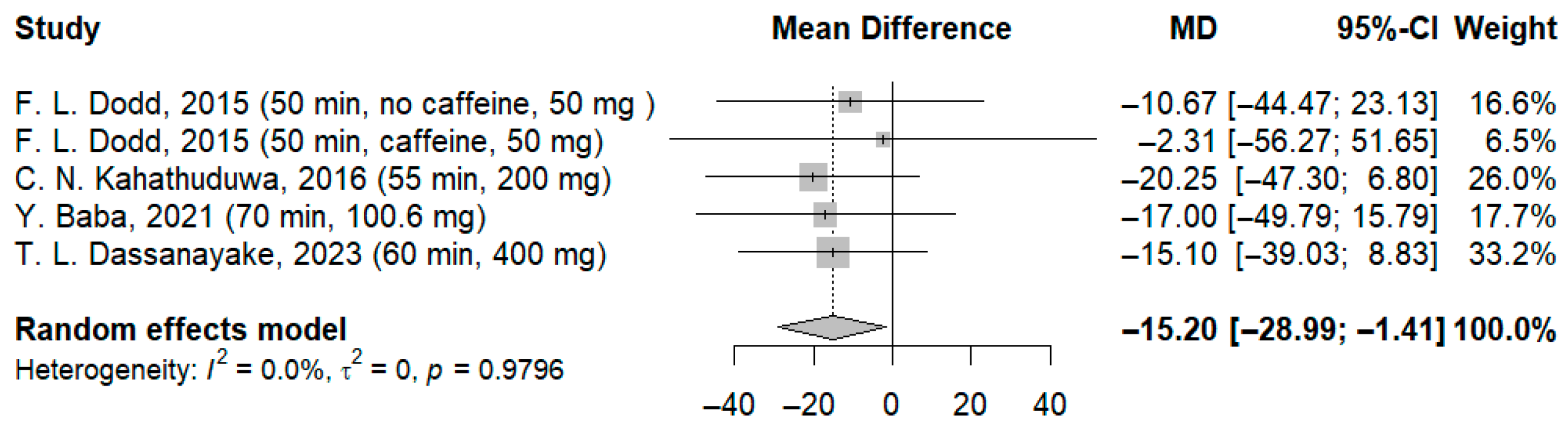
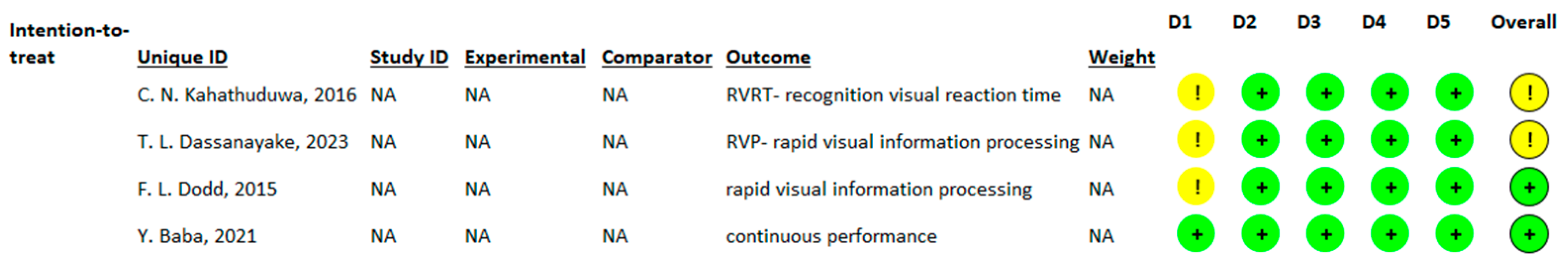
3.3.3. Effects of l-Theanine on Time Required to Process Visual Stimuli (RVIP—Rapid Visual Information Processing/RVRT—Recognition Visual Reaction Time/Continuous Performance)
3.4. Assessment of Risk of Bias of the Included Studies and Publication Bias
3.5. Grade of Evidence
3.6. Studies Included in the Qualitative Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Chang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, E.; Wang, L.; Yi, P. Effect of Green Tea Consumption on Human Brain Function in Resting-State Functional MRI. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 28, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidese, S.; Ogawa, S.; Ota, M.; Ishida, I.; Yasukawa, Z.; Ozeki, M.; Kunugi, H. Effects of L-Theanine Administration on Stress-Related Symptoms and Cognitive Functions in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namal Senanayake, S.P.J. Green Tea Extract: Chemistry, Antioxidant Properties and Food Applications—A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.L.; Everett, J.M.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Keegan, R.J.; McKune, A.J.; Mellor, D.D.; Anstice, N.; Naumovski, N. The Effects of Green Tea Amino Acid L-Theanine Consumption on the Ability to Manage Stress and Anxiety Levels: A Systematic Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorca, C.; Mulet, M.; Arevalo-Caro, C.; Sanchez, M.A.; Perez, A.; Perrino, M.; Bach-Faig, A.; Aguilar-Martinez, A.; Vilella, E.; Gallart-Palau, X.; et al. Plant-Derived Nootropics and Human Cognition: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5521–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, J.A.; Benitez, J. Clinically Significant Pharmacokinetic Interactions Between Dietary Caffeine and Medications. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 39, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.A.; Scheltens, P.; Groot, C.; Ossenkoppele, R. Associations Between Caffeine Consumption, Cognitive Decline, and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 78, 1519–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camfield, D.A.; Stough, C.; Farrimond, J.; Scholey, A.B. Acute Effects of Tea Constituents L-Theanine, Caffeine, and Epigallocatechin Gallate on Cognitive Function and Mood: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türközü, D.; Şanlier, N. L-Theanine, Unique Amino Acid of Tea, and Its Metabolism, Health Effects, and Safety. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersant, H.; He, S.; Maliha, P.; Grossberg, G. Over the Counter Supplements for Memory: A Review of Available Evidence. CNS Drugs 2023, 37, 797–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Kelly, S.P.; Montesi, J.L.; Foxe, J.J. The Effects of L-Theanine on Alpha-Band Oscillatory Brain Activity during a Visuo-Spatial Attention Task. Brain Topogr. 2009, 22, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, T.L.; Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Weerasinghe, V.S. L-Theanine Improves Neurophysiological Measures of Attention in a Dose-Dependent Manner: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxe, J.J.; Morie, K.P.; Laud, P.J.; Rowson, M.J.; de Bruin, E.A.; Kelly, S.P. Assessing the Effects of Caffeine and Theanine on the Maintenance of Vigilance during a Sustained Attention Task. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2320–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, G.N.; Parnell, H.; De Bruin, E.A.; Rycroft, J.A. The Combined Effects of L-Theanine and Caffeine on Cognitive Performance and Mood. Nutr. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Ozeki, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Ohira, H. L-Theanine Reduces Psychological and Physiological Stress Responses. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas Sohail, A.; Ortiz, F.; Varghese, T.; Fabara, S.P.; Batth, A.S.; Sandesara, D.P.; Sabir, A.; Khurana, M.; Datta, S.; Patel, U.K. The Cognitive-Enhancing Outcomes of Caffeine and L-Theanine: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e20828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Brennan, M.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Lange, K.W.; Brennan, C. How Does the Tea L-Theanine Buffer Stress and Anxiety. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A Basic Introduction to Fixed-Effect and Random-Effects Models for Meta-Analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; McKenzie, J.E.; Angeliki, A. Chapter 10: Analysing Data and Undertaking Meta-Analyses|Cochrane. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Cochrane: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- GRADE Handbook. Available online: https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html#h.svwngs6pm0f2 (accessed on 17 October 2025).
- Dodd, F.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Riby, L.M.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating the Effects of Caffeine and L-Theanine Both Alone and in Combination on Cerebral Blood Flow, Cognition and Mood. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Dassanayake, T.L.; Amarakoon, A.M.T.; Weerasinghe, V.S. Acute Effects of Theanine, Caffeine and Theanine–Caffeine Combination on Attention. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 20, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.; Inagaki, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Kaneko, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takihara, T. Effects of L-Theanine on Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Subjects: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Med. Food 2021, 24, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassanayake, T.L.; Wijesundara, D.; Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Weerasinghe, V.S. Dose–Response Effect of L-Theanine on Psychomotor Speed, Sustained Attention, and Inhibitory Control: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, U.; Buzdagli, Y.; Polat, M.L.; Bakir, Y.; Ozhanci, B.; Alkazan, S.; Ucar, H. Effect of Single or Combined Caffeine and L-Theanine Supplementation on Shooting and Cognitive Performance in Elite Curling Athletes: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2267536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O.; Milne, A.L.; Wesnes, K.A.; Scholey, A.B. The Effects of L-Theanine, Caffeine and Their Combination on Cognition and Mood. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 77, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Wake, G.; Savelev, S.; Tildesley, N.T.J.; Perry, E.K.; Wesnes, K.A.; Scholey, A.B. Modulation of Mood and Cognitive Performance Following Acute Administration of Single Doses of Melissa Officinalis (Lemon balm) with Human CNS Nicotinic and Muscarinic Receptor-Binding Properties. Psychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Dhanasekara, C.S.; Chin, S.-H.; Davis, T.; Weerasinghe, V.S.; Dassanayake, T.L.; Binks, M. L-Theanine and Caffeine Improve Target-Specific Attention to Visual Stimuli by Decreasing Mind Wandering: A Human Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Nutr. Res. 2018, 49, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, A.; Htay, H.H.; Ozeki, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Kapoor, M.P. Effects of L-Theanine on Attention and Reaction Time Response. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Lin, W.; Ahammed, G.J.; Wang, W.; Ma, R.; Shi, M.; Ge, S.; Mohamed, A.S.; Wang, L.; et al. L-Theanine Metabolism in Tea Plants: Biological Functions and Stress Tolerance Mechanisms. Plants 2025, 14, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashwood, R.; Visioli, F. L-Theanine: From Tea Leaf to Trending Supplement—Does the Science Match the Hype for Brain Health and Relaxation? Nutr. Res. 2025, 134, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. A Comprehensive Review on Bioavailability, Safety and Antidepressant Potential of Natural Bioactive Components from Tea. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogoshi, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Terashima, T. Effect of Theanine, r-Glutamylethylamide, on Brain Monoamines and Striatal Dopamine Release in Conscious Rats. Neurochem. Res. 1998, 23, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, E.M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Rashad, E.; Yasin, N.A.E.; Ghaiad, H.R.; Mehana, N.A. Therapeutic Role of l-Theanine in Mitigating Cognitive Dysfunction and Neuropathology in Scopolamine-Treated Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2025, 16, 2528–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Loake, V.I.P.; Bao, X.; Loake, G.J. Improvement of Both Human and Animal Memory by Synergy between Fructooligosaccharide and l-theanine Function Establishing a Safe and Effective Food Supplement. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4966–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, A.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Marx, W.; Turner, M.; McKune, A.; Naumovski, N. The Effects of L-Theanine Consumption on Sleep Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2025, 81, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, V.S.; Kahathuduwa, C.; Amarakoon, T.; Dassanayake, T. Synergistic Effect of Theanine and Caffeine on Visual Reaction Time, Evoked Potentials and Cognitive Event Related Potentials. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, F.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Riby, L.M.; Wilde, A.; Haskell, C.F. An Evaluation of the Cerebral Blood Flow, Cognitive and Mood Effects of Caffeine and l-Theanine Both Alone and in Combination. Appetite 2011, 57, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, Y. Green Tea Amino Acid Products for Prevention of Cognitive Declines. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 133, S22. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda, Y.; Kuramoto, N. The Green Tea Amino Acid Theanine for Possible Improvement of Cognitive Declines. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Eri, W.; Kuchta, K.; Mari, K.; Rauwald, H.W.; Kamei, T.; Imanishi, J. On the Fatigue Reducing Effects of Japanese Green Tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) from Uji. Planta Med. 2013, 79, PN29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, E.M.R.; Balentine, D.A.; Einöther, S.J.L.; Rycroft, J.A.; De Bruin, E.A. Emerging Science Demonstrates That L-Theanine and Caffeine in Combination Can Help Improve Attention. FASEB J. 2009, 23, LB456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.A. A Cup of Tea. J. Perinat. Neonatal Nurs. 2010, 24, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Natarajan, R. A Story in a Tea Cup. BMJ 2017, 356, i5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R. 200 Mg of Zen: L-Theanine Boosts Alpha Waves, Promotes Alert Relaxation. Altern. Complement. Ther. 2001, 7, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Kuriki, K.; Otsuka, R.; Kato, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Tange, C.; Tomida, M.; Imai, T.; Ando, F.; Shimokata, H. Association between Green Tea Intake and Risk of Cognitive Decline, Considering Glycated Hemoglobin Level, in Older Japanese Adults: The NILS-LSA Study. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Yuki, S.; Dohmoto, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Samuraki, M.; Iwasa, K.; Yokogawa, M.; Asai, K.; Komai, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Consumption of Green Tea, but Not Black Tea or Coffee, Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Cognitive Decline. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, S.; Hozawa, A.; Ohmori, K.; Shimazu, T.; Matsui, T.; Ebihara, S.; Awata, S.; Nagatomi, R.; Arai, H.; Tsuji, I. Green Tea Consumption and Cognitive Function: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Tsurugaya Project. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.M. L-Theanine (Suntheanin): Effects of L-Theanine, an Amino Acid Derived from Camellia Sinensis (Green Tea), on Stress Response Parameters. Holist Nurs Pr. 2014, 28, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, T. Tea and Coffee Consumption, Cognitive Impairment and Prognosis in Older Inhabitants. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1385–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yan, Z.; Sun, B.; Cai, C.; Jiang, H.; Kua, E.-H.; Ng, T.-P.; Qiu, C. Tea Consumption and Depressive Symptoms in Older People in Rural China. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C. Tea Drinking Prevents Memory Loss? Nutr. Bull. 2005, 30, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, M.J.; Martaindale, M.H.; Dillard, C.C.; McCullough, R. Impact of L-Theanine and L-Tyrosine on Markers of Stress and Cognitive Performance in Response to a Virtual Reality Based Active Shooter Training Drill. Stress 2024, 27, 2375588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füeßl, H.S. Green tea consumption promotes the cognitive function. MMW-Fortschr. Med. 2006, 148, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, M.F.; Martins, A.; Schimidt, H.L.; Santos, F.W.; Izquierdo, I.; Mello-Carpes, P.B.; Carpes, F.P. Effects of Green Tea and Physical Exercise on Memory Impairments Associated with Aging. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 78, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Jung, I.-C.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, H.K.; Go, H.J.; Kim, K.; Lim, N.K.; Hong, J.T.; Ly, S.Y.; et al. A Combination of Green Tea Extract and L-Theanine Improves Memory and Attention in Subjects with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furushima, D.; Sugiyama, I.; Nomura, Y.; Unno, K.; Yamada, H. Effect of Combined Ingestion of L-Theanine and l-Arginine for Short-Term Psychological Stress in Young Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2022, 68, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einöther, S.J.L.; Martens, V.E.G.; Rycroft, J.A.; De Bruin, E.A. L-Theanine and Caffeine Improve Task Switching but Not Intersensory Attention or Subjective Alertness. Appetite 2010, 54, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, E.; Johnson, M.; Jones, M.; Viglizzo, R.; Bobe, J.; Zimmerman, N. Measuring the Effects of Caffeine and L-Theanine on Cognitive Performance: A Protocol for Self-Directed, Mobile N-of-1 Studies. Front. Comput. Sci. 2020, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbrecht, T.; Rycroft, J.A.; Rowson, M.J.; De Bruin, E.A. The Combination of L-Theanine and Caffeine Improves Cognitive Performance and Increases Subjective Alertness. Nutr. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.; Burns, A.; Pase, M.; Pipingas, A. Acute Cognitive, Mood and Cardiovascular Effects of Green and Black Tea. Proc. Nutr. Soc. USA 2020, 79, E676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, M.; Molina-Hidalgo, C.; Alcantara, J.M.A.; Ruiz, J.R.; Jurado-Fasoli, L. Acute Effect of a Dietary Multi-Ingredient Nootropic as a Cognitive Enhancer in Young Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Triple-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 858910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, K.; Yamada, H.; Iguchi, K.; Ishida, H.; Iwao, Y.; Morita, A.; Nakamura, Y. Anti-Stress Effect of Green Tea with Lowered Caffeine on Humans: A Pilot Study. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.J.; de Klerk, S.; Woods, W.; Gondalia, S.; Noonan, C.; Scholey, A.B. Anti-Stress, Behavioural and Magnetoencephalography Effects of an l-Theanine-Based Nutrient Drink: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2016, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, D.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Z. Effect of Coffee and Green Tea on Executive Ability and Plasma Levels of Inflammatory Factors in Soldiers with 48-Hour Total Sleep Deprivation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 19354–19362. [Google Scholar]
- Okello, E.J.; Abadi, A.M.; Abadi, S.A. Effects of Green and Black Tea Consumption on Brain Wave Activities in Healthy Volunteers as Measured by a Simplified Electroencephalogram (EEG): A Feasibility Study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Shen, C.; Ezaki, Y.; Inamura, N.; Fukushima, Y.; Masuoka, N.; Hisatsune, T. Effects of Matcha Green Tea Powder on Cognitive Functions of Community-Dwelling Elderly Individuals. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, N.; Higuchi, T.; Suzuki, H. Effects of Simultaneous Intake of Green Tea Extracts and Fish Oil on Cognitive Function and Plasma Lipids in the Elderly. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmidt, A.; Hammann, F.; Wölnerhanssen, B.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Drewe, J.; Beglinger, C.; Borgwardt, S. Green Tea Extract Enhances Parieto-Frontal Connectivity during Working Memory Processing. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3879–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Yamada, H.; Takuma, N.; Park, M.; Wakamiya, N.; Nakase, J.; Ukawa, Y.; Sagesaka, Y.M. Green Tea Consumption Affects Cognitive Dysfunction in the Elderly: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagoplan, U.M. Green Tea Could Improve the Performance of Cognitive Tasks: A Pilot Study with Wearable Brain Imaging Device. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems (ICAMechS), Zhengzhou, China, 30 August–2 September 2018; pp. 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, N.; Baker, D.; Sharples, A.; Braakhuis, A. Improving Mental Performance in an Athletic Population with the Use of Ārepa(®), a Blackcurrant Based Nootropic Drink: A Randomized Control Trial. Antioxid 2020, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoto, A.; Murao, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yokogoshi, H. Intake of Green Tea Inhibited Increase of Salivary Chromogranin A after Mental Task Stress Loads. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2014, 33, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, S.; Hammann, F.; Scheffler, K.; Kreuter, M.; Drewe, J.; Beglinger, C. Neural Effects of Green Tea Extract on Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, B.J.; Rawson, K.S.; Martin, C.; Eisel, S.L.; Sanberg, C.D.; McEvoy, C.L.; Sanberg, P.R.; Shytle, R.D.; Tan, J.; Bickford, P.C. Nutraceutical Intervention Improves Older Adults’ Cognitive Functioning. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Kellett, J.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; McKune, A.J.; Mellor, D.D.; Naumovski, N. Physicochemical, Antioxidant and Sensory Properties of Mango Sorbet Containing L-Theanine as a Potential Functional Food Product. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4833–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, K.; Noda, S.; Kawasaki, Y.; Yamada, H.; Morita, A.; Iguchi, K.; Nakamura, Y. Reduced Stress and Improved Sleep Quality Caused by Green Tea Are Associated with a Reduced Caffeine Content. Nutrients 2017, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.; Tuckey, M.; Einöther, S.J.L.; Garczarek, U.; Garrick, A.; De Bruin, E.A. Relationships between Tea and Other Beverage Consumption to Work Performance and Mood. Appetite 2012, 58, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.; Bove, M.; Colletti, A.; Rizzo, M.; Fogacci, F.; Giovannini, M.; Borghi, C. Short-Term Impact of a Combined Nutraceutical on Cognitive Function, Perceived Stress and Depression in Young Elderly with Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot, Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 4, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, K.; Furushima, D.; Hamamoto, S.; Iguchi, K.; Yamada, H.; Morita, A.; Horie, H.; Nakamura, Y. Stress-Reducing Function of Matcha Green Tea in Animal Experiments and Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; McKune, A.J.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Kellett, J.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Mellor, D.; Naumovski, N. The Effect of L-Theanine Incorporated in a Functional Food Product (Mango Sorbet) on Physiological Responses in Healthy Males: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. Foods 2020, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, K.; Tanida, N.; Ishii, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Iguchi, K.; Hoshino, M.; Takeda, A.; Ozawa, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Juneja, L.R.; et al. Anti-Stress Effect of Theanine on Students during Pharmacy Practice: Positive Correlation among Salivary α-Amylase Activity, Trait Anxiety and Subjective Stress. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 111, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidese, S.; Ota, M.; Wakabayashi, C.; Noda, T.; Ozawa, H.; Okubo, T.; Kunugi, H. Effects of Chronic L-Theanine Administration in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: An Open-Label Study. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017, 29, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoto, A.; Motoki, M.; Murao, S.; Yokogoshi, H. Effects of L-Theanine or Caffeine Intake on Changes in Blood Pressure under Physical and Psychological Stresses. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2012, 31, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobre, A.C.; Rao, A.; Owen, G.N. L-Theanine, a Natural Constituent in Tea, and Its Effect on Mental State. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S1), 167–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giles, G.E.; Mahoney, C.R.; Brunyé, T.T.; Taylor, H.A.; Kanarek, R.B. Caffeine and Theanine Exert Opposite Effects on Attention under Emotional Arousal. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.P.; Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Montesi, J.L.; Foxe, J.J. L-Theanine and Caffeine in Combination Affect Human Cognition as Evidenced by Oscillatory Alpha-Band Activity and Attention Task Performance. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1572S–1577S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.J.; Smith, J.E.; Heatherley, S.V.; Pleydell-Pearce, C.W. Time for Tea: Mood, Blood Pressure and Cognitive Performance Effects of Caffeine and Theanine Administered Alone and Together. Psychopharmacology 2008, 195, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Wakamiya, N.; Park, M.; Takuma, N.; Fujii, S.; Nakahara, A.; Suzuki, T.; Nakase, J.; Ukawa, Y.; Sagesaka, Y.M.; et al. Effects of Green Tea Consumption on Cognitive Dysfunction: An Exploratory Clinical Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 333, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Yamada, H.; Takuma, N.; Kawasaki, Y.; Harada, S.; Nakase, J.; Ukawa, Y.; Sagesaka, Y.M. Effects of Green Tea Consumption on Cognitive Dysfunction in an Elderly Population: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, J.; Byrne, G.J.; Cribb, L.; Oliver, G.; Murphy, J.; Macdonald, P.; Nazareth, S.; Karamacoska, D.; Galea, S.; Short, A.; et al. L-Theanine in the Adjunctive Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 110, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, M.R.; Kapoor, M.P.; Juneja, L.R. The Effects of L-Theanine (Suntheanine®) on Objective Sleep Quality in Boys with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| First Author, Year of Publication | Country | Study Type | Subgroup | Group | Sample Size | Patient Characteristics | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years; Mean) | No of Male Participants | |||||||
| Dodd, 2015 | UK | RCT | non-habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 12 | 20.4 (1.88) | 5 | [21] |
| placebo | 12 | |||||||
| habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 12 | 23.3 (3.65) | 5 | ||||
| placebo | 12 | |||||||
| Kahathuduwa, 2016 | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 20 | 21.9 | 20 | [24] | |
| placebo | 20 | |||||||
| Baba, 2021 | Japan | RCT | l-theanine | 26 | 57.7 | 12 | [23] | |
| placebo | 24 | 57.9 | 11 | |||||
| Dassanayake, 2023 | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 32 | 26.2 (2.2) | 20 | [24] | |
| placebo | 32 | |||||||
| Yilmaz, 2023 | Turkey | RCT | l-theanine | 22 | 20.2 | no information | [25] | |
| placebo | 22 | |||||||
| First Author, Year of Publication | Country | Study Type | Subgroup | Group | Dose | Intervention Form | Sample Size (n) | Outcome | Results (Milisecundum) | Adverse Events | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre Dose | Post Dose | |||||||||||
| Dodd, 2015 | UK | RCT | non-habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 12 | Simple reaction time | 329.85 ± 19.73 (mean ± SEM) | 365.31 ± 20.98 (mean ± SEM) | No adverse events have been reported. | [21] |
| placebo | capsule | 12 | 326.54 ± 16.59 | 344.09 ± 15.26 | ||||||||
| habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 12 | 288.71 ± 11.38 | 308.37 ± 11.77 | ||||||
| placebo | capsule | 12 | 294 ± 11.19 | 308.38 ± 11.85 | ||||||||
| Kahathuduwa, 2016 | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 200 mg | solution | 20 | Simple visual reaction time | 230.30 (18.33) mean (SD) | 235.40 (25.33) mean (SD) | None developed any adverse effects. | [22] | |
| placebo (distilled water) | liquid | 20 | 224.20 (25.51) | 223.65 (23.78) | ||||||||
| Baba, 2021 | Japan | RCT | l-theanine | 100.6 mg | capsule | 26 | (Stroop test: Part 1.) Simple reaction time | 378 ± 138 | 337 ± 84 | No adverse events have been reported. | [23] | |
| placebo (corn starch) | capsule | 24 | 411 ± 145 mean ± SD | 365 ± 62.0 mean ± SD | ||||||||
| Dassanayake, 2023 * | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 100 mg | solution | 32 | Simple reaction time | 306.4 (45.0) mean (SD) | 291.7 (40.6) mean (SD) | No adverse events have been reported. | [24] | |
| l-theanine | 200 mg | solution | 32 | 306.6 (53.4) | 291.3 (44.6) | |||||||
| l-theanine | 400 mg | solution | 32 | 310.0 (51.9) | 306.8 (51.5) | |||||||
| placebo (distilled water) | liquid | 32 | 302.1 (52.1) | 303.7 (43.7) | ||||||||
| First Author, Year of Publication | Country | Study Type | Subgroup | Group | Dose | Intervention Form | Sample Size (n) | Outcome | Results | Adverse Events | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congruent | Incongruent | |||||||||||||
| Pre Dose (ms) | Post Dose (ms) | Pre Dose (ms) | Post Dose (ms) | |||||||||||
| Dodd, 2015 | UK | RCT | non-habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 12 | Stroop test | 692.9 ± 57.09 | 672.17 ± 40.69 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 14.17 ± 14.36 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 17.67 ± 4.46 | No adverse events have been reported. | [21] |
| placebo | capsule | 12 | 628.92 ± 26.50 | 660.33 ± 28.40 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 12.67 ± 12.96 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 7.92 ± 8.6 | ||||||||
| habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 12 | 659.5 ± 49.91 | 637.08 ± 25.4 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 25.00 ± 15.19 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 43.92 ± 9.26 | ||||||
| placebo | capsule | 12 | 651.67 ± 26.36 | 641.25 ± 22.65 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 11.33 ± 15.55 | Stroop interference RT (ms) 32.92 ± 7.86 | ||||||||
| Yilmaz, 2023 | Turkey | RCT | l-theanine | 6 mg/kg | powder | 22 | Stroop test | 616 ± 108.95 | 902.5 ± 144.05 | No adverse events have been reported. | [25] | |||
| placebo (maltodextrin) | powder | 22 | 720 * ± 129.18 | 1025 ± 122.24 | ||||||||||
| Baba, 2021 | Japan | RCT | l-theanine | 100.6 mg | capsule | 26 | Stroop test | 706 ± 122 | 667 ± 97.8 | 802 ± 121 | 761 ± 120 | No adverse events have been reported. | [23] | |
| placebo (corn starch) | capsule | 24 | 734 ± 124 | 706 ± 133 | 841 ± 129 | 809 ± 98.2 | ||||||||
| First Author, Year of Publication | Country | Study Type | Subgroup | Group | Dose | Intervention Form | Sample Size | Outcome | Results (Millisecond) | Adverse Events | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre dose | Post dose | |||||||||||
| Dodd, 2015 | UK | RCT | non-habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 11 | Rapid visual information processing | 480.70 ± 13.99 mean ± SEM | 471.87 ± 13.28 mean ± SEM | No adverse events have been reported. | [21] |
| placebo | capsule | 11 | 481.36 ± 15.76 | 482.54 ± 11.00 | ||||||||
| habitual caffeine consumers | l-theanine | 50 mg | capsule | 12 | 501.75 ± 18.82 | 511.05 ± 17.77 | ||||||
| placebo | capsule | 12 | 502.55 ± 18.02 | 513.36 ± 21.03 | ||||||||
| Kahathuduwa, 2016 | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 200 mg | solution | 20 | Recognition visual reaction time | 385.60 (54.27) mean (SD) | 363.20 (42.85) mean (SD) | None developed any adverse effects. | [22] | |
| placebo (distilled water) | liquid | 20 | 380.55 (50.28) | 383.45 (44.43) | ||||||||
| Baba, 2021 | Japan | RCT | l-theanine | 100.6 mg | capsule | 26 | Time required to process visual stimuli–Cognitrax subtest–continuous performance | 492 ± 80.4 mean ± SD | 483 ± 72.1 mean ± SD | No adverse events have been reported. | [23] | |
| placebo (corn starch) | capsule | 24 | 511 ± 50.7 | 500 ± 43.8 | ||||||||
| Dassanayake, 2023 * | Sri Lanka | RCT | l-theanine | 100 mg | solution | 32 | Rapid visual information processing | 382.5 (50.8) mean (SD) | 381.3 (50.0) mean (SD) | No adverse events have been reported. | [24] | |
| l-theanine | 200 mg | solution | 32 | 380.8 (58.1) | 363.1 (55.7) | |||||||
| l-theanine | 400 mg | solution | 32 | 375.8 (48.6) | 361.8 (43.2) | |||||||
| placebo (distilled water) | liquid | 32 | 383.5 (46.5) | 376.9 (53.9) | ||||||||
| Certainty Assessment | Number of Patients | Effect | Certainty | Importance | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Studies a | Study Design | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other Considerations | L-Theanine c | Placebo c | Relative (95% CI) | Absolute (95% CI) | ||
| Effects of l-theanine on reaction time to simple stimulus | ||||||||||||
| 5 | RCT | Not serious | Serious | No -serious | Not serious | None | 102 b | 100 b | - | MD: −0.46 ms (CI: −15.65; 14.73) c | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low d,e | Critical |
| Effects of l-theanine on congruent stimuli based on the Stroop test | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCT | Not serious | Serious | Not serious | Serious | None | 72 | 70 | - | MD: −37.38 ms (CI −86.39; 11.62) | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low d,e | Critical |
| Effects of l-theanine on incongruent stimuli based on the Stroop test | ||||||||||||
| 4 | RCT | Not serious | Very serious | Not serious | Very serious | None | 72 | 70 | - | MD: 109.28 ms (CI −8.72; 227.27) | ⨁◯◯◯ Very low d,e | Critical |
| Effects of l-theanine on time required to process visual stimuli | ||||||||||||
| 5 | RCT | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | None | 101 | 99 | - | MD: −15.20 ms (CI −28.99; −1.41) f | ⨁⨁◯◯ Low d,e | Critical |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mátyus, R.O.; Szikora, Z.; Bodó, D.; Vargáné Szabó, B.; Csupor, É.; Csupor, D.; Tóth, B. Promising, but Not Completely Conclusive—The Effect of l-Theanine on Cognitive Performance Based on the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7710. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217710
Mátyus RO, Szikora Z, Bodó D, Vargáné Szabó B, Csupor É, Csupor D, Tóth B. Promising, but Not Completely Conclusive—The Effect of l-Theanine on Cognitive Performance Based on the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7710. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217710
Chicago/Turabian StyleMátyus, Rebeka Olga, Zsóka Szikora, Diána Bodó, Bettina Vargáné Szabó, Éva Csupor, Dezső Csupor, and Barbara Tóth. 2025. "Promising, but Not Completely Conclusive—The Effect of l-Theanine on Cognitive Performance Based on the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7710. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217710
APA StyleMátyus, R. O., Szikora, Z., Bodó, D., Vargáné Szabó, B., Csupor, É., Csupor, D., & Tóth, B. (2025). Promising, but Not Completely Conclusive—The Effect of l-Theanine on Cognitive Performance Based on the Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7710. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217710