-
 Safety and tolerability of diamine oxidase (DAO) in Healthy Volunteers
Safety and tolerability of diamine oxidase (DAO) in Healthy Volunteers -
 To Be Biased or Not to Be: A Play for G-Protein Coupled Receptors
To Be Biased or Not to Be: A Play for G-Protein Coupled Receptors -
 Neoadjuvant Therapy for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer
Neoadjuvant Therapy for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer -
 Comprehensive PBPK Evaluation of Phenytoin and Indomethacin: Dose, Age, Pregnancy and Drug–Drug Interaction Insights
Comprehensive PBPK Evaluation of Phenytoin and Indomethacin: Dose, Age, Pregnancy and Drug–Drug Interaction Insights
Journal Description
International Journal of Translational Medicine
International Journal of Translational Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on major advances in both experimental and clinical medicine, with a particular emphasis on translational research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Medicine (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 28.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- IJTM is a companion journal of Biomedicines.
Latest Articles
From Mammals to Zebrafish, via Cichlids: Advantages and Some Limits of Fish Models for Human Behavioral Pathologies
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010008 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Zebrafish (ZF) have gained increasing attention in developmental neuroscience due to their experimental tractability, favorable ethical profile, and translational value. However, the expanding use of the ZF model has also highlighted the need to consider species-specific differences in relation to early social and
[...] Read more.
Zebrafish (ZF) have gained increasing attention in developmental neuroscience due to their experimental tractability, favorable ethical profile, and translational value. However, the expanding use of the ZF model has also highlighted the need to consider species-specific differences in relation to early social and emotional development. This review adopts a comparative and ethological perspective to examine early social interactions in ZF and mammals, integrating evidence from non-altricial vertebrates and teleost species with parental care (cichlids). Selected illustrative ZF papers were discussed, while Cichlids fish were chosen as a complementary, translationally consistent subject for developmental behavioral studies. The analysis focuses on developmental stages that are relevant for behavioral phenotyping in models of neuropsychiatric conditions. Zebrafish offer multiple methodological advantages, including suitability for high-throughput experimentation and substantial genetic and neurobiological homologies with humans. Nevertheless, the absence of mother–offspring bonding limits the modeling of neurodevelopmental processes shaped by early caregiving, such as imprinting and reciprocal regulatory interactions, instead observed in cichlids. Accumulating evidence indicates that early interactions among age-matched ZF are measurable, developmentally regulated, and sensitive to environmental and experimental manipulations. Within a comparative approach, these early conspecific interactions could be analogs of early social bonding observed in altricial mammals. Rather than representing a critical limitation, such species-specific features can inform the investigation of fundamental mechanisms of social development and support the complementary use of ZF and mammalian models. A contextualized and integrative approach may therefore enhance the translational relevance of ZF-based research, particularly for the study of neurodevelopmental disorders involving early social dysfunction.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Optical Coherence Tomography with Fluorescein Optical Clearing for Transscleral Image Guidance
by
Robert M. Trout, Amit Narawane, Christian Viehland, Vahid Ownagh, Mark Draelos, Al-Hafeez Dhalla, Anthony N. Kuo and Cynthia A. Toth
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010007 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Scattering of the sclera limits optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging of deeper targets including lesions, malignancies, and other surgical targets. While existing applications of fluorescein dye are currently focused on fluorescence properties for tissue labeling, the absorption characteristics of the dye also
[...] Read more.
Background: Scattering of the sclera limits optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging of deeper targets including lesions, malignancies, and other surgical targets. While existing applications of fluorescein dye are currently focused on fluorescence properties for tissue labeling, the absorption characteristics of the dye also hold potential for scleral tissue clearing. Methods: Fluorescein is investigated here to gauge the potential impact of its optical clearing on intrasurgical OCT guidance. Fluorescein was applied topically to ex vivo porcine and human eye models. OCT imaging was conducted over time to assess the increases in imaging depth due to fluorescein clearing. High-speed microscope-integrated OCT was used during pilot trabeculectomy surgery on cleared eye models to assess clearing applications in a surgical context. Results: The OCT depth of imaging increased with fluorescein concentration and application time. The effect saturates at a near-20% concentration with 50 min of application time, with a maximum signal increase of +15 dB. Reversal of the effect was observed following 10 min of rinsing. Conclusions: High-concentration fluorescein dye has novel applications as an optical clearing agent, increasing the OCT imaging depth through highly scattering biological tissue. These properties can be leveraged for improved image guidance in surgical contexts.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Oncofetal Reprogramming: A New Frontier in Cancer Therapy Resistance
by
Anh Nguyen, Molly Lausten and Bruce M. Boman
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010006 - 29 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Oncofetal reprogramming has recently emerged as a critical concept in translational cancer research, particularly for its role in driving therapeutic resistance across a variety of malignancies. This biological process refers to a pattern of gene expression that is restricted to embryogenesis, but becomes
[...] Read more.
Oncofetal reprogramming has recently emerged as a critical concept in translational cancer research, particularly for its role in driving therapeutic resistance across a variety of malignancies. This biological process refers to a pattern of gene expression that is restricted to embryogenesis, but becomes expressed again in a subpopulation of cancer cells. These genes are typically suppressed after embryogenesis, and their aberrant re-expression in tumors endows cancer cells with stem-like properties and enhanced adaptability. The goal of this review is the following: (i) comprehensively examine the multifaceted nature of oncofetal reprogramming; (ii) elucidate its underlying molecular mechanisms, including its regulators and effectors; and (iii) evaluate its consequences for the therapeutic response in different cancer types. We comprehensively integrate the latest findings from colorectal, breast, lung, liver, and other cancers to provide a detailed understanding of how oncofetal programs interfere with tumor response to treatment. Among the candidates, YAP1 and AP-1 have emerged as central transcriptional drivers of this reprogramming process, especially in colorectal and breast cancers. We also explore the distinct expression patterns of oncofetal genes across different tumor types and how these patterns correlate with treatment outcomes and patient survival. Lastly, we propose a dual-targeting therapeutic strategy that simultaneously targets both cancer stem cells and oncofetal-reprogrammed populations as a more effective approach to overcome resistance and limit recurrence.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Autopsy by Exome Sequencing Identifies in Fraternal Twins a CARD11 p.Ser995Leu Variant Within GUK Domain
by
Juan Fernández-Cadena, Edwin W. Naylor, Heidi Reinhard and Arindam Bhattacharjee
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010005 - 28 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: We describe the post-mortem analysis of a CARD11 variant allele, p.Ser995Leu, identified in fraternal twins who died in early infancy with no identifiable cause of death. CARD11 variants through varied inheritance models can alter immune function through loss- or gain-of-function mechanisms, involving
[...] Read more.
Background: We describe the post-mortem analysis of a CARD11 variant allele, p.Ser995Leu, identified in fraternal twins who died in early infancy with no identifiable cause of death. CARD11 variants through varied inheritance models can alter immune function through loss- or gain-of-function mechanisms, involving distinct protein domains; yet the significance of GUK domain variants remains poorly characterized. Twin autopsies showed non-specific findings, such as pulmonary macrophage accumulation and splenic white pulp expansion, but without infection or structural abnormalities. Methods: Whole-exome sequencing, performed as part of molecular autopsies, identified the shared CARD11 p.Ser995Leu variant, previously classified as a variant of uncertain significance (VUS). We assessed evolutionary conservation across CARD family proteins and species and predicted functional impact using in silico tools, which estimate the likelihood that a variant is deleterious. AlphaFold-based structural modeling emphasized qualitative biophysical assessment. Using epidemiological data, population allele frequency, and Bayesian ACMG variant classification, we assessed competing hypotheses under an autosomal dominant model. Results: The p.Ser995Leu substitution affects a conserved, surface-exposed β-sheet within the GUK domain. While CADD scores exceeded 20, other predictive algorithms offered only partial support of pathogenicity. Structural modeling suggested a potential GUK domain destabilization. Integrating genetic, pathologic, immunologic, and probabilistic modeling, we propose a biologically plausible model in which the variant, like other GUK variants, may alter NF-κB or other signaling pathways and is likely pathogenic. Conclusions: While the CARD11 p.Ser995Leu variant’s contribution to disease is uncertain without functional validation or parental testing, and phenotypic findings are non-specific, the presence of an ultra-rare GUK domain variant in both twins, combined with in silico and statistical modeling, supports its interpretation as likely pathogenic or high risk. The results highlight the challenges of data-limited post-mortem variant interpretation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current and Emerging Biomarkers in Dermatomyositis: Clinical Utility and Future Directions
by
Fiona Jaederlund, Ka Wei Katty Joo Hu, Claudio Karsulovic and Lia Hojman
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010004 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) comprise a heterogeneous group of autoimmune disorders with variable systemic involvement. Among them, dermatomyositis (DM) is the subtype with the most extensive biomarker characterization due to its defined immunopathology and frequent association with interstitial lung disease (ILD). This narrative
[...] Read more.
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) comprise a heterogeneous group of autoimmune disorders with variable systemic involvement. Among them, dermatomyositis (DM) is the subtype with the most extensive biomarker characterization due to its defined immunopathology and frequent association with interstitial lung disease (ILD). This narrative review summarizes studies retrieved from PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science up to March 2025, focusing on non-autoantibody biomarkers in DM. Reported categories include soluble proteins, cytokines, chemokines, muscle-specific microRNAs, and transcriptomic signatures reflecting interferon activation, tissue injury, and fibrotic remodeling. Among the most validated molecules, interferon-stimulated genes, ferritin, KL-6, SP-D, and CXCL10 demonstrate diagnostic and prognostic value, particularly in anti-MDA5-positive DM, where they support early identification of patients at risk for rapidly progressive ILD. However, despite increasing evidence, most biomarkers lack disease specificity, standardized cutoffs, and multicenter validation, while molecular assays remain confined to specialized laboratories. Clinically accessible markers such as ferritin, KL-6, and CXCL10 currently offer the highest translational potential. Nevertheless, the heterogeneity of study designs and analytical methods continues to limit comparability and routine clinical integration. Future research should prioritize the validation of composite biomarker panels through standardized, multicentric studies to enhance diagnostic precision and enable precision medicine approaches in DM and related inflammatory myopathies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
GATA-3 and Its Association with Allergic Diseases and Immune Regulation: A Systematic Review
by
Jamal Nasser Saleh Al-Maamari, Junaidi Khotib, Mahardian Rahmadi, Yusuf Alif Pratama and Nadia Ahmed Nasser Hosrom
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010003 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA-3) is a crucial transcription factor that drives type 2 immune responses, and it is actively involved in allergic conditions such as asthma, allergic rhinitis (AR), and atopic dermatitis (AD). However, the molecular mechanisms GATA-3 uses to modulate
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA-3) is a crucial transcription factor that drives type 2 immune responses, and it is actively involved in allergic conditions such as asthma, allergic rhinitis (AR), and atopic dermatitis (AD). However, the molecular mechanisms GATA-3 uses to modulate immune responses and its potential therapeutic targeting are not fully understood. This systematic review aimed to summarize studies on the role of GATA-3 in immune responses, particularly in allergic diseases, and evaluate GATA-3’s potential as a therapeutic target. Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Science Direct for studies published before April 2025. Articles were sifted through using predefined criteria, and risk of bias was measured with RoB 2 for clinical trials and SYRCLE for animal models and in vitro studies; evidence was graded using the GRADE system. Results: Twenty-nine eligible studies reported that GATA-3 is a key regulator of Th2 and ILC2 differentiation, promoting the production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. Animal models and in vitro studies demonstrated its role in exacerbating allergic inflammation and highlighted the promise of targeting strategies such as DNAzymes and nanocapsules. Clinical trials showed that targeting GATA-3, particularly with DNAzymes, can reduce allergic responses in asthma. Conclusions: GATA-3’s role in driving allergic inflammation through Th2 and ILC2 pathways suggests it as a promising therapeutic target. Understanding its broader regulatory mechanisms is imperative for designing effective GATA-3 targeting-based therapies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Early Vasoplegia and Endothelial Protection in Sepsis: A Physiology-Guided Framework for Timely Albumin and Norepinephrine Therapy
by
Christian J. Wiedermann, Arian Zaboli and Gianni Turcato
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010002 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objective: Early hemodynamic instability in sepsis arises from endothelial dysfunction and vasoplegia before capillary leakage and organ failure occur. Albumin administration guided by serum concentration or shock criteria has not improved outcomes. This review synthesized evidence supporting an early, physiology-guided framework for albumin
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Early hemodynamic instability in sepsis arises from endothelial dysfunction and vasoplegia before capillary leakage and organ failure occur. Albumin administration guided by serum concentration or shock criteria has not improved outcomes. This review synthesized evidence supporting an early, physiology-guided framework for albumin and norepinephrine use in pre-δ vasoplegic sepsis. Methods: A narrative synthesis of experimental and clinical studies examined endothelial injury, sepsis phenotypes, hemodynamic monitoring, biochemical markers, and intravascular albumin mass. Evidence from phenotype cohorts was integrated to construct a physiology-based therapeutic framework. Results: The δ phenotype consistently emerged as a vasoplegic, hyperinflammatory endotype with hypoalbuminemia, elevated lactate, and the highest mortality. Studies showed 20–25% of patients with community-acquired sepsis exhibit early vasoplegia, with low systemic vascular resistance and high cardiac output. Mass-balance analyses showed intravascular albumin mass declines early in sepsis, correlate inversely with fluid balance, and predict mortality. These findings suggest early low-dose norepinephrine may stabilize perfusion pressure, while albumin use should follow intravascular albumin mass trajectories. A dynamic exclusion concept proposes withholding albumin during capillary leak and reintroducing it when intravascular albumin mass stabilizes. Conclusions: Albumin therapy in sepsis should shift from late concentration-based to early physiology-guided endothelial protection. Monitoring intravascular albumin mass, lactate, and fluid balance may guide targeted norepinephrine and albumin use before δ-type endothelial failure occurs. This framework needs phenotype-stratified validation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Takotsubo Syndrome After Surgical Treatment of Liver Abscess: A Case Report and Literature Review
by
Aigerim Tanyrbergenova, Zhandos Burkitbayev, Asel Zhumabekova, Daulet Marat, Damesh Orazbayeva, Bekkozha Yeskendirov and Dinara Zharlyganova
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm6010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TTC), also known as stress-induced cardiomyopathy, is an acute but reversible form of left ventricular dysfunction, most commonly triggered by physical or emotional stress. Although well documented in cardiology practice, its occurrence following hepatobiliary surgery is rarely reported. Case presentation:
[...] Read more.
Background: Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TTC), also known as stress-induced cardiomyopathy, is an acute but reversible form of left ventricular dysfunction, most commonly triggered by physical or emotional stress. Although well documented in cardiology practice, its occurrence following hepatobiliary surgery is rarely reported. Case presentation: We describe the case of a 67-year-old woman with a history of arterial hypertension and prior cholecystectomy who was admitted for elective hepatobiliary surgery due to choledocholithiasis complicated by a liver abscess. She underwent laparotomy with choledocholithotomy, hepaticojejunostomy, and abdominal drainage. The postoperative course was complicated by intra-abdominal bleeding, requiring reoperation, and subsequent intestinal leakage, necessitating a second re-laparotomy. On the tenth postoperative day after the second surgery, she developed chest discomfort and dyspnea upon minimal exertion. Electrocardiography revealed T-wave inversions in leads V3–V6, while echocardiography demonstrated a reduced ejection fraction of 45% with apical akinesis. Plasma levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT–proBNP) were elevated, whereas troponin remained within normal limits. Coronary angiography excluded obstructive coronary artery disease, and ventriculography confirmed apical ballooning consistent with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Conclusions: This case highlights Takotsubo cardiomyopathy as a rare but important postoperative complication of major hepatobiliary surgery. Awareness of this condition in surgical patients presenting with acute chest symptoms is essential, as timely recognition and differentiation from acute coronary syndrome directly influence management and prognosis.
Full article
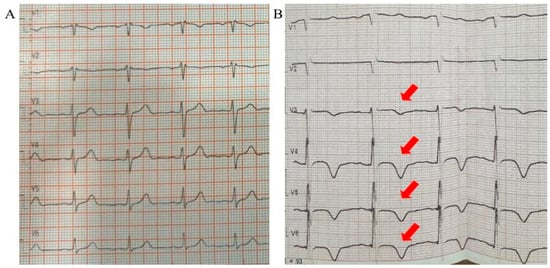
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive PBPK Evaluation of Phenytoin and Indomethacin: Dose, Age, Pregnancy and Drug–Drug Interaction Insights
by
Mariana Godinho, Lara Marques and Nuno Vale
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040058 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Understanding the pharmacokinetics (PK) of antiepileptic and anti-inflammatory drugs under different physiological conditions is essential for optimizing therapy. Phenytoin, a widely used antiepileptic, and indomethacin, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, are frequently prescribed in women of reproductive age. This study aimed to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Understanding the pharmacokinetics (PK) of antiepileptic and anti-inflammatory drugs under different physiological conditions is essential for optimizing therapy. Phenytoin, a widely used antiepileptic, and indomethacin, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, are frequently prescribed in women of reproductive age. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of age, pregnancy, and dosing regimens on the PK of both drugs, as well as to investigate potential drug–drug interactions (DDIs). Methods: PK parameters of phenytoin and indomethacin were systematically analyzed in women aged 20–45 years under non-pregnant and pregnant conditions. Different dosing regimens were compared, and coadministration studies were conducted to assess DDI. Results: Phenytoin demonstrated stable absorption and bioavailability across ages and during pregnancy. Single daily dosing (300 mg once daily) yielded slightly higher peak concentration (Cmax) values, while fractionated dosing (100 mg q8h) produced significantly higher drug exposure (AUC) and absorption fraction, particularly with prolonged administration, reflecting saturable metabolism. During pregnancy, systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC) was modestly reduced, while absorption and distribution remained unchanged. Indomethacin showed minimal age-related variability and linear pharmacokinetics across dosing regimens. In pregnancy, exposure was reduced (lower Cmax and AUC) with delayed Tmax, indicating slower absorption. Importantly, no PK DDI was observed, as indomethacin parameters remained unchanged except for Tmax, which was lower in the interaction scenario compared with baseline, suggesting a faster absorption rate without affecting overall exposure or peak concentration in the presence of phenytoin. Conclusions: Phenytoin and indomethacin exhibit stable and predictable PK across ages and during pregnancy, with dose-dependent characteristics that align with their known metabolic profiles. The absence of clinically relevant DDI supports their safe concomitant use. These findings provide preliminary reassuring evidence for clinicians and contribute to a better understanding of their pharmacological behavior in diverse patient populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Polygenic Score Profiling Reveals Autism Spectrum Disorder Subgroups with Different Genetic Predisposition Related to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Urea, and Body Mass Index
by
Takuya Miyano and Tsuyoshi Mikkaichi
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040057 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex and heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder. This study aims to demonstrate the potential of comprehensive polygenic scores (PGSs) as clinical biomarkers for stratifying individuals with ASD and for advancing the understanding of ASD’s heterogeneous etiology. Methods
[...] Read more.
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex and heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder. This study aims to demonstrate the potential of comprehensive polygenic scores (PGSs) as clinical biomarkers for stratifying individuals with ASD and for advancing the understanding of ASD’s heterogeneous etiology. Methods: We calculated 2602 PGSs—representing all publicly available, license-cleared PGSs in the PGS Catalog—for 75 individuals with ASD by utilizing the database of the Tohoku Medical Megabank Birth and Three-generation cohort study. Results: Unsupervised clustering revealed three ASD subgroups. We identified twenty PGSs with the most significant differences among these subgroups as distinctive PGSs for each subgroup. PGS set enrichment analysis associated these distinctive PGSs with different traits in each subgroup: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol measurements, urea measurement, and body mass index. Furthermore, distinctive PGSs indicated consistent genetic predisposition directions: lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in subgroup 1, higher urea levels in subgroup 2, and lower body mass index in subgroup 3. Conclusions: Comprehensive PGSs extending beyond psychiatry-related traits represent promising clinical biomarkers for identifying ASD subgroups with different genetic predispositions. Such stratification may enhance understanding of heterogenous genetic backgrounds and targeted drug development.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
To Be Biased or Not to Be: A Play for G-Protein Coupled Receptors
by
Nikitas G. Liolitsas, Evangelia Pantazaka and Evangelia Papadimitriou
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040056 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of diverse receptors in eukaryotic organisms, playing a critical role in modulating human physiology. It therefore comes as no surprise that about 36% of all currently available drugs target this superfamily. When an agonist binds
[...] Read more.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of diverse receptors in eukaryotic organisms, playing a critical role in modulating human physiology. It therefore comes as no surprise that about 36% of all currently available drugs target this superfamily. When an agonist binds to a GPCR, it induces conformational changes in the receptor that allow it to interact with intracellular proteins. This interaction triggers downstream signaling cascades that alter the cell’s activity. GPCR signaling is complex, as GPCRs transmit signals through coupling with G proteins, arrestins, and numerous other intracellular effectors. Different ligands, receptor subtypes, and cellular environments can result in the activation of distinct signaling pathways. Biased signaling through GPCRs has emerged as a frontier area in pharmacological research efforts towards designing targeted therapeutic interventions and enhancing drug efficacy and safety. This review presents the types of bias associated with GPCRs and the mechanisms underlying biased signaling. Examples of biased ligands and their therapeutic implications will be discussed. In addition, the inherent challenges in measuring signaling bias, and especially the translational gap between in vitro and in vivo assays and clinical outcomes, will be outlined.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neoadjuvant Therapy for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer
by
Julia Groszewska, Michał Romaniuk and Ewa Małecka-Wojciesko
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040055 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal cancers, with poor survival even after surgical resection. Clinical stages include resectable (R-PDAC), borderline resectable (BR-PDAC), locally advanced, and metastatic disease. Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT)—chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy before surgery—has emerged as a promising strategy
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal cancers, with poor survival even after surgical resection. Clinical stages include resectable (R-PDAC), borderline resectable (BR-PDAC), locally advanced, and metastatic disease. Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT)—chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy before surgery—has emerged as a promising strategy to improve outcomes by increasing margin-negative resection rates and enhancing overall survival. For R-PDAC, surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy remains the standard, but NAT may be considered in high-risk patients, such as those with severe pain, elevated CA 19-9, or large tumors. For BR-PDAC, NAT is the primary approach, significantly increasing R0 resection rates and prolonging survival. Common regimens include mFOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine-based combinations. NAT also carries risks, including disease progression during therapy, loss of resectability, and uncertainty in evaluating response. Current tools, such as imaging and CA 19-9, offer limited predictive value. The role of NAT in R-PDAC remains under debate, while its benefits in BR-PDAC are more established. This review summarizes current evidence and guidelines on NAT in PDAC, with a focus on treatment strategies, patient selection, and emerging approaches.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Disease Localization and Bowel Resections as Predictors of Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D Status in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
by
Maxwell A. Barffour, Mustafa Gandhi, Harleen Chela, Serena Crawford, Zguri Liridon, Kwame Frimpong, Elizabeth Karanja, Kevin Luton, Emily Reznicek, Hayford Frimpong, Emily Bosak and Yezaz A. Ghouri
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040054 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Terminal ileum inflammation and surgical resections impair absorption of vitamin B12 and D in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). We assessed differences in subclinical deficiencies of vitamin B12 (<350 pg/mL) or D (<50 nmol/L), by lesion localization (namely
[...] Read more.
Background: Terminal ileum inflammation and surgical resections impair absorption of vitamin B12 and D in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC). We assessed differences in subclinical deficiencies of vitamin B12 (<350 pg/mL) or D (<50 nmol/L), by lesion localization (namely non-ileal CD, ileal CD, and UC) and surgical resection status (namely no resection, non-ileal small bowel resections, ileocecal resections, and colonic resections) in CD and UC patients. Methods: We analyzed data from 571 patients (17–93 years), with UC (51%) and CD (49%, including 47 non-ileal (8%), 244 ileal-CD (46%)) managed at the University of Missouri Health Care System (Jan 2017–April 2022). Results: Prevalence of vitamin B12 and vitamin D deficiencies was 19% and 83%, respectively. Prevalence of resection was 26%, including 5% with non-ileal small bowel resections, 11% with ileocecal resections, and 10% with colonic resections. CD with ileal involvement was associated with a 3-fold elevated risk of B12 deficiency (p = 0.004), but not vitamin D. Ileocecal resections were associated with a >3-fold increase in both B12 deficiency (OR = 3.53, p = 0.001) and D deficiency (OR = 3.35, p = 0.044). Conclusions: CD patients with ileal involvement and ileocecal resections have an elevated risk of vitamin B12 and D deficiency, and may benefit from adjunctive supplementation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Abdominal Surgery Performed in Awake Patients Under Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Systematic Review Across Surgical Specialties
by
Carlo Ferrari, Jacopo Crippa, Paola Floris, Davide Vailati, Benedetta Basta, Roberto Santalucia, Salvatore Barbaro and Carmelo Magistro
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040053 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Neuraxial anesthesia (NA) is increasingly utilized across various surgical specialties, particularly for abdominal procedures, making it a potential alternative to general anesthesia (GA). Methods: This narrative review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews to report on the
[...] Read more.
Background: Neuraxial anesthesia (NA) is increasingly utilized across various surgical specialties, particularly for abdominal procedures, making it a potential alternative to general anesthesia (GA). Methods: This narrative review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews to report on the application of NA worldwide and across various surgical fields. Results: The findings indicate that while NA is gaining popularity, its adoption varies significantly by procedure type and specialty. Evidence supporting its use in major abdominal surgeries remains limited, with most studies focusing on pelvic and minor procedures. The emerging concept of awake surgery under NA shows promising potential, as preliminary data suggest benefits in reducing perioperative morbidity and enhancing recovery. Despite these advancements, gaps in the literature highlight the need for further high-quality trials to establish NA as a safe and routine alternative to GA. Conclusions: NA is increasingly explored across different surgical specialties as a feasible and effective option for abdominal procedures. However, despite this growing interest, solid evidence supporting its use in major abdominal surgery remains limited.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Preclinical and Prodromal Frontotemporal Dementia: Challenges and Opportunities
by
Federica Palacino, Paolo Manganotti and Alberto Benussi
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040052 - 15 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) represents a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders with overlapping clinical, pathological, and genetic characteristics. Increasing evidence indicates that disease mechanisms begin decades before the appearance of clinical symptoms, highlighting the importance of identifying preclinical and prodromal stages. This review
[...] Read more.
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) represents a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders with overlapping clinical, pathological, and genetic characteristics. Increasing evidence indicates that disease mechanisms begin decades before the appearance of clinical symptoms, highlighting the importance of identifying preclinical and prodromal stages. This review provides a comprehensive synthesis of current knowledge on the complexity of FTLD, emphasizing early detection and intervention strategies. It integrates findings from neuropathological, neuroimaging, fluid biomarker, genetic, and clinical studies in both familial and sporadic forms, with particular attention to gene-specific trajectories, biomarker evolution, and emerging therapeutic approaches targeting presymptomatic and prodromal phases. Recent advances in biomarker discovery and neuroimaging are enabling earlier diagnosis and intervention, offering the potential to delay phenoconversion and preserve brain function.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hyperostosis Cranii Ex Vacuo in Shunted Children: A Proposed Fifth Subtype of CSF Overdrainage Syndrome
by
Mateusz Zajączkowski, Łukasz Klasa, Olga Milczarek and Stanisław Kwiatkowski
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040051 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunting remains a crucial intervention in the treatment of paediatric hydrocephalus. Overdrainage syndrome is a well-recognised but potentially severe complication, in which hyperostosis cranii ex vacuo—diffuse thickening of the cranial bones—emerges as an adaptive response to chronic intracranial hypotension.
[...] Read more.
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunting remains a crucial intervention in the treatment of paediatric hydrocephalus. Overdrainage syndrome is a well-recognised but potentially severe complication, in which hyperostosis cranii ex vacuo—diffuse thickening of the cranial bones—emerges as an adaptive response to chronic intracranial hypotension. Currently, no established diagnostic criteria exist to reliably identify and classify this phenomenon, nor are there defined strategies to prevent associated complications of reduced intracranial compliance. Objective: This study aimed to characterise the morphoradiological and clinical phenotype of hyperostosis cranii ex vacuo in paediatric patients with long-term shunt dependency and to propose its classification as a fifth subtype of CSF overdrainage syndrome with direct implications for long-term neurosurgical care. Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted on nine paediatric patients with radiologically confirmed diffuse calvarial thickening secondary to surgical treatment of hydrocephalus. Quantitative morphometric analysis of frontal, parietal, and occipital bones, sella turcica dimensions, and dural enhancement was performed using high-resolution neuroimaging. Clinical records were reviewed for hydrocephalus aetiology, shunt revision history, and neurological impairment. Results: All patients exhibited a mean two-fold increase in age-adjusted calvarial thickness. Premature craniosynostosis was identified in 33.3% of cases. Diffuse pachymeningeal enhancement was noted in all patients with contrast-enhanced imaging. Neurological comorbidities included epilepsy, spastic paraparesis, and features of Chiari type I malformation. Conclusions: Hyperostosis cranii ex vacuo represents a distinct and underrecognised consequence of chronic CSF overdrainage. We propose preliminary diagnostic criteria and a structured management pathway—from radiological recognition through ICP assessment to tiered surgical intervention. Formal recognition of this entity as a fifth subtype of CSF overdrainage syndrome may enhance early diagnosis, improve risk stratification, and guide long-term surveillance of shunted children.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in International Journal of Translational Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
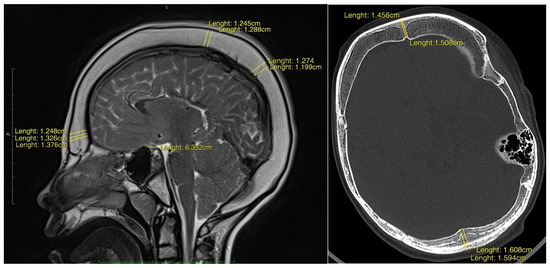
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Radiomic-Based Machine Learning for Differentiating Brain Metastases Recurrence from Radiation Necrosis Post-Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: A Feasibility Study
by
Mateus Blasques Frade, Paola Critelli, Eleonora Trifiletti, Giuseppe Ripepi and Antonio Pontoriero
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040050 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Radiation therapy is a key treatment modality for brain metastases. While providing a treatment alternative, post-treatment imaging often presents diagnostic challenges, particularly in distinguishing tumor recurrence from radiation-induced changes such as necrosis. Advanced imaging techniques and artificial intelligence (AI)-based radiomic analyses emerge
[...] Read more.
Background: Radiation therapy is a key treatment modality for brain metastases. While providing a treatment alternative, post-treatment imaging often presents diagnostic challenges, particularly in distinguishing tumor recurrence from radiation-induced changes such as necrosis. Advanced imaging techniques and artificial intelligence (AI)-based radiomic analyses emerge as alternatives to help lesion characterization. The objective of this study was to assess the capacity of machine learning algorithms to distinguish between brain metastases recurrence and radiation necrosis. Methods: The research was conducted in two phases and used publicly available MRI data from patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery. In the first phase, 30 cases of local recurrence of brain metastases and 30 cases of radiation-induced necrosis were considered. Image segmentation and radiomic feature extraction were performed on these data using MatRadiomics_1_5_3, a MATLAB-based framework integrating PyRadiomics. Features were then selected using point-biserial correlation. In the second phase, a classification was performed using a Support Vector Machine model with repeated stratified cross-validation settings. Results: The results achieved an accuracy on the test set of 83% for distinguishing metastases from necrosis. Conclusions: The results of this feasibility study demonstrate the potential of radiomics and AI to improve diagnostic accuracy and personalized care in neuro-oncology.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Efficacy of Mandibular Advancement Devices in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review
by
Alessio Danilo Inchingolo, Angelo Michele Inchingolo, Claudia Ciocia, Francesca Calò, Sara Savastano, Francesco Inchingolo, Andrea Palermo, Giuseppe Giudice, Daniela Di Venere, Grazia Marinelli and Gianna Dipalma
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040049 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Mandibular advancement devices (MADs) are widely used for mild-to-moderate obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). We aimed to synthesize recent evidence on their clinical effectiveness and tolerability. Methods: A systematic review was conducted. Ten studies were included, evaluating MAD therapy in adults
[...] Read more.
Background: Mandibular advancement devices (MADs) are widely used for mild-to-moderate obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). We aimed to synthesize recent evidence on their clinical effectiveness and tolerability. Methods: A systematic review was conducted. Ten studies were included, evaluating MAD therapy in adults with mild-to-moderate OSA. The review reported on standard outcomes, including the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), oxygenation, daytime sleepiness (Epworth Sleepiness Scale, ESS), quality of life, adherence, and adverse events. Risk of bias was also assessed. Results: Across the included studies, MADs consistently reduced AHI from baseline and improved ESS and/or snoring. In head-to-head comparisons, MADs generally yielded smaller reductions in AHI than CPAP but achieved comparable improvements in symptoms and quality of life, with higher nightly adherence. Reported adverse effects were mostly mild and transient. Conclusions: MAD therapy is an effective and generally well-tolerated option for adults with mild-to-moderate OSA and for the patients intolerant to CPAP, although average AHI reduction is smaller than with CPAP. Given the low certainty and heterogeneity of current evidence, high-quality randomized trials with objective adherence tracking and standardized titration are needed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Silico Identification of DNMT Inhibitors for the Treatment of Glioblastoma
by
Meyrem Osum, Louai Alsaloumi and Rasime Kalkan
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040048 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Gliomas are the most common tumours of the central nervous system (CNS), classified into grades I to IV based on their malignancy. Genetic and epigenetic alterations play a crucial role in glioma progression. DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) are vital enzymes responsible for
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Gliomas are the most common tumours of the central nervous system (CNS), classified into grades I to IV based on their malignancy. Genetic and epigenetic alterations play a crucial role in glioma progression. DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) are vital enzymes responsible for DNA methylation, with DNMT1 and DNMT3 catalysing the addition of a methyl group to the 5-carbon of cytosine in CpG dinucleotides. Targeting DNMTs with DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) has become a promising therapeutic approach in tumour treatment. In this study, in silico screening tools were employed to evaluate potential inhibitors of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Methods: The Gene2Drug platform was used to screen compounds and rank them based on their capacity to dysregulate DNMT genes. PRISM viability assays were performed on 68 cell lines, and DepMap data were analyzed to assess the antitumor activities of these compounds and their target genes. Candidate drug similarity was evaluated using DSEA, and compounds with p < 1 × 10−3 were considered statistically significant. Gene-compound interactions for DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B were confirmed using Expression Public 24Q2, while Prism Repositioning Public data were analyzed via DepMap. Results: Glioblastoma cell lines showed sensitivity to compounds including droperidol, demeclocycline, benzthiazide, ozagrel, pizotifen, tracazolate, norcyclobenzaprine, monocrotaline, dydrogesterone, 6-benzylaminopurine, and nifedipine. SwissTargetPrediction was utilised to identify alternative molecular targets for selected compounds, revealing high-probability matches for droperidol, pizotifen, tracazolate, monocrotaline, dydrogesterone, and nifedipine. Conclusions: Integrating computational approaches with biological insights and conducting tissue-specific and experimental validations may significantly enhance the development of DNMT-targeted therapies for gliomas.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrating Genomics and Deep Phenotyping for Diagnosing Rare Pediatric Neurological Diseases: Potential for Sustainable Healthcare in Resource-Limited Settings
by
Nigara Yerkhojayeva, Nazira Zharkinbekova, Sovet Azhayev, Ainash Oshibayeva, Gulnaz Nuskabayeva and Rauan Kaiyrzhanov
Int. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 5(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtm5040047 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Rare pediatric neurological diseases (RPND) often remain undiagnosed for years, creating prolonged and costly diagnostic odysseys. Combining Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO)-based deep phenotyping with exome sequencing (ES) and reverse phenotyping offers the potential to improve diagnostic yield, accelerate diagnosis, and support sustainable
[...] Read more.
Background: Rare pediatric neurological diseases (RPND) often remain undiagnosed for years, creating prolonged and costly diagnostic odysseys. Combining Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO)-based deep phenotyping with exome sequencing (ES) and reverse phenotyping offers the potential to improve diagnostic yield, accelerate diagnosis, and support sustainable healthcare in resource-limited settings. Objectives: To evaluate the diagnostic yield and clinical impact of an integrated approach combining deep phenotyping, ES, and reverse phenotyping in children with suspected RPNDs. Methods: In this multicenter observational study, eighty-one children from eleven hospitals in South Kazakhstan were recruited via the Central Asian and Transcaucasian Rare Pediatric Neurological Diseases Consortium. All patients underwent standardized HPO-based phenotyping and ES, with variant interpretation following ACMG guidelines. Reverse phenotyping and interdisciplinary discussions were used to refine clinical interpretation. Results: A molecular diagnosis was established in 34 of 81 patients (42%) based on pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants. Variants of uncertain significance (VUS) were identified in an additional 9 patients (11%), but were reported separately and not included in the diagnostic yield. Reverse phenotyping clarified or expanded clinical features in one-third of genetically diagnosed cases and provided supportive evidence in most VUS cases, although their classification remained unchanged. Conclusions: Integrating deep phenotyping, ES, and reverse phenotyping substantially improved diagnostic outcomes and shortened the diagnostic odyssey. This model reduces unnecessary procedures, minimizes delays, and provides a scalable framework for advancing equitable access to genomic diagnostics in resource-constrained healthcare systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
IJMS, Metabolites, Molecules, Proteomes, Biomedicines, IJTM
Liquid Biopsy: A Modern Method Transforming Biomedicine
Topic Editors: Michele Costanzo, Marianna CaterinoDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Cancers, CIMB, Current Oncology, Sci. Pharm., Antibodies, IJMS, IJTM
Antibody-Mediated Therapy and Other Emerging Therapies in Cancer Treatment
Topic Editors: Won Sup Lee, Yaewon Yang, Seil GoDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Biophysica, CIMB, IJMS, IJTM, Lymphatics, Sci. Pharm.
Smart Delivery Systems for Biomolecular Therapeutics
Topic Editors: Biana Godin, Vivek GuptaDeadline: 31 October 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, CIMB, Brain Sciences, IJMS, IJTM
Autism: Molecular Bases, Diagnosis and Therapies, 3rd Volume
Topic Editors: Lello Zolla, Kunio YuiDeadline: 1 December 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
IJTM
Hallmarks of Cancer: New Approaches and Treatment Strategies
Guest Editors: Caroline De Fátima Aquino Moreira-Nunes, Maria Elisabete Amaral De MoraesDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
IJTM
Gene and Cell Therapy: New Findings from Medical Research and Treatment
Guest Editors: Lorella Tripodi, Antonio Di StasiDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
IJTM
Feature Papers in International Journal of Translational Medicine
Collection Editor: Joan Oliva







