- Case Report
Double Trouble: The First Reported Case of Evans Syndrome Following RSV Vaccination
- Mohammad Abu-Tineh,
- Deepika Beereddy and
- Ilse Ivonne Saldivar Ruiz
- + 1 author
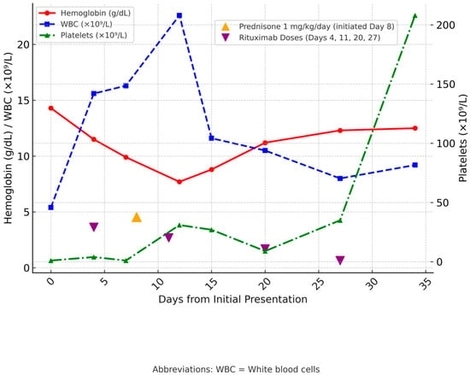
Background: Evans syndrome is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), and autoimmune neutropenia, typically triggered by an episode of immune dysregulation or multiple other factors. We present what appears to be the first reported case of Evans syndrome developing in a 66-year-old female following respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccination. Case Presentation: A 66-year-old female presented with a petechial rash on her arms, legs, and face. Laboratory tests revealed a platelet count of 1 × 109/L, significantly lower than her historical baseline of >200 × 109/L. On hospital day 4, her hemoglobin declined from 14.3 g/dL to 9.9 g/dL, with laboratory evidence of hemolysis, including elevated bilirubin, low haptoglobin, and increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Bone marrow biopsy revealed megakaryocytic hyperplasia consistent with ITP, along with a small polyclonal B-cell population lacking CD20 expression. Imaging was unremarkable, showing no interval changes aside from stable pre-existing pulmonary nodules and no lymphadenopathy. These findings supported a diagnosis of Evans syndrome. Initial therapy with dexamethasone and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for presumed ITP was ineffective. Due to refractory thrombocytopenia, the patient initially received one dose of rituximab, followed by one dose of romiplostim. Subsequently, the patient received rituximab infusions every week at a rate of 375 mg/m2 for four doses, as well as prednisone at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day. Within five weeks, her blood count returned to normal. Conclusions: This case raises concern for a potential temporal association between RSV vaccination and the onset of Evans syndrome. It underscores the need for heightened clinical awareness and further investigation into immune-mediated hematologic complications following RSV immunization.
1 December 2025