Journal Description
Healthcare
Healthcare
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on health care systems, industry, technology, policy, and regulation, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. European Medical Association (EMA) and Ocular Wellness & Nutrition Society (OWNS) are affiliated with Healthcare and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Health Policy and Services) / CiteScore - Q1 (Leadership and Management)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Healthcare include: Trauma Care and European Burn Journal.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
MedScrubCrew: A Medical Multi-Agent Framework for Automating Appointment Scheduling Based on Patient-Provider Profile Resource Matching
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1649; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141649 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: With advancements in Generative Artificial Intelligence, various industries have made substantial efforts to integrate this technology to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of existing processes or identify potential weaknesses. Context, however, remains a crucial factor in leveraging intelligence, especially in high-stakes sectors
[...] Read more.
Background: With advancements in Generative Artificial Intelligence, various industries have made substantial efforts to integrate this technology to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of existing processes or identify potential weaknesses. Context, however, remains a crucial factor in leveraging intelligence, especially in high-stakes sectors such as healthcare, where contextual understanding can lead to life-changing outcomes. Objective: This research aims to develop a practical medical multi-agent system framework capable of automating appointment scheduling and triage classification, thus improving operational efficiency in healthcare settings. Methods: We present MedScrubCrew, a multi-agent framework integrating established technologies: Gale-Shapley stable matching algorithm for optimal patient-provider allocation, knowledge graphs for semantic compatibility profiling, and specialized large language model-based agents. The framework is designed to emulate the collaborative decision making processes typical of medical teams. Results: Our evaluation demonstrates that combining these components within a cohesive multi-agent architecture substantially enhances operational efficiency, task completeness, and contextual relevance in healthcare scheduling workflows. Conclusions: MedScrubCrewprovides a practical, implementable blueprint for healthcare automation, addressing significant inefficiencies in real-world appointment scheduling and patient triage scenarios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Interprofessional Care and Training)
Open AccessArticle
Hospital at Home Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Economic Analysis
by
Vinod Mishra, Tobias Gedde-Dahl, Mats Remberger, Grethe Solvang, Kristin Lien Selvaag, Arne Fosseng, Ingerid W. Abrahamsen, Anders E. Myhre, Terje P. Hagen and Geir E. Tjønnfjord
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1648; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141648 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Advanced home care is becoming increasingly common for cancer patients and serves as a viable alternative to inpatient hospital care. The transition to home care is driven by both the rising costs of healthcare and evidence indicating better quality of care. This
[...] Read more.
Background: Advanced home care is becoming increasingly common for cancer patients and serves as a viable alternative to inpatient hospital care. The transition to home care is driven by both the rising costs of healthcare and evidence indicating better quality of care. This study aims to compare the costs of hospital-at-home treatment and in-hospital care for patients undergoing allo-HSCT. Methods: The cost analysis was conducted as a case–control study comparing the costs of allo-HSCT at home (HaH) to the costs of allo-HSCT for patients receiving in-hospital care (INH). The cost evaluation was conducted from the hospital’s perspective, which means that costs incurred outside the hospital setting were not included. Post-procedural costs for the first year after allo-HSCT included all readmissions and outpatient visits at Oslo University Hospital. Results: The cost for the peritransplant period could be reduced by up to 33% by treating allo-HSCT recipients at home instead of in the hospital. During the study period, 24% of the allo-HSCT recipients were treated at home, but our data from 2021 and 2022 indicate that at least a third of the patients scheduled for allo-HSCT are candidates for HaH. Conclusions: The findings demonstrate that patients in advanced home care experience significantly lower total costs compared to those receiving in-hospital treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Healthcare Quality and Patient Safety)
Open AccessArticle
Development and Feasibility of a Smartphone Application for Promoting Healthy Heart Behaviors Following Open-Heart Surgery: A Mixed-Method Pilot Study
by
Preeyaphorn Songsorn, Pawarat Nontasil, Kornanong Yuenyongchaiwat, Noppawan Charususin, Jitanan Laosiripisan, Sasipa Buranapuntalug and Khanistha Wattanananont
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1647; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141647 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Adherence to healthy behaviors after open-heart surgery is crucial for recovery and long-term health. Traditional patient education methods can be enhanced by using technology to improve engagement and self-care. This study aimed to develop and assess the feasibility of the “Term-Jai” smartphone
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Adherence to healthy behaviors after open-heart surgery is crucial for recovery and long-term health. Traditional patient education methods can be enhanced by using technology to improve engagement and self-care. This study aimed to develop and assess the feasibility of the “Term-Jai” smartphone application for promoting healthy heart behaviors in open-heart surgery patients. Methods: The “Term-Jai” psychological theory-based application was tested quantitatively and qualitatively over a 30-day period with 13 patients (age 44–78 years) following open-heart surgery between November 2023 and March 2024. Participant engagement, healthy behaviors, user experience, and usability were assessed using the System Usability Scale (SUS), satisfaction ratings, healthy behavior questionnaires, and semi-structured interviews. Results: The application was feasible, with 70% of participants remaining engaged during the intervention. The average SUS score was 80.2 ± 10.3, indicating good usability. Participants found the application’s information useful, clear, and easy to understand, showing improvements in health behaviors following application usage. The qualitative analysis highlighted the application’s intuitive design and potential for supporting cardiac rehabilitation. High satisfaction scores suggested its effectiveness despite some barriers to application usage around technical support and personalized exercise progression. Conclusions: The “Term-Jai” application is a promising tool for promoting healthy behaviors in patients following open-heart surgery. The application shows good usability and participant satisfaction, indicating its potential for broader implementation after further refinements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Psychophysiological Responses to Physical Activity, Exercise and/or Nutrition Interventions in Individuals with Cardiometabolic Health Impairments)
►▼
Show Figures
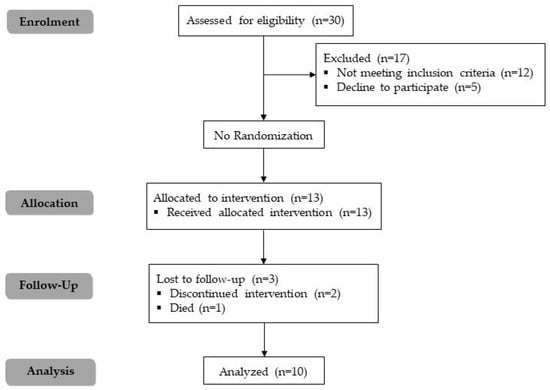
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Relationship Between a Sustainable Healthy Lifestyle and Depression, Stress, and Anxiety: A Structural Model on the Mediating Role of Physical Literacy
by
Mehmet Akarsu, İsmail İlbak, Zeliha Çavuşoğlu, Ratko Pavlović, Ana Maria Vulpe, Adina Camelia Șlicaru, Nicolae Lucian Voinea and Cristina Ioana Alexe
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1646; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141646 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: It is well established that healthy lifestyle behaviors have significant effects not only on physical health but also on psychological well-being; however, the underlying mechanisms of these effects have yet to be fully elucidated. In this context, the aim of this study
[...] Read more.
Background: It is well established that healthy lifestyle behaviors have significant effects not only on physical health but also on psychological well-being; however, the underlying mechanisms of these effects have yet to be fully elucidated. In this context, the aim of this study is to examine the relationships between a sustainable healthy lifestyle and levels of depression, stress, and anxiety, and to test the mediating role of physical literacy in these associations. Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted among university students in Malatya, Türkiye, and a total of 652 voluntary participants were included. In the theoretical model of the study, a sustainable healthy lifestyle was positioned as the independent variable, depression, stress, and anxiety as dependent variables, and physical literacy as the mediating variable. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with bootstrapping to assess mediation effects. Results: Results obtained from the structural equation modeling indicate that a sustainable healthy lifestyle has significant and protective relationships with psychological well-being. Negative and significant relationships were identified between a sustainable healthy lifestyle and levels of depression, stress, and anxiety. Furthermore, higher levels of physical literacy were associated with lower levels of these psychological symptoms, with physical literacy playing a strong mediating role in these relationships. The model results revealed that lifestyle components such as regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and sufficient sleep enhance individuals’ physical competence and awareness. Physical literacy was also found to have a significant negative relationship with depression, stress, and anxiety. Conclusions: These results indicate that physical literacy is a key variable not only for physical functioning but also for psychological resilience and well-being. Moreover, the impact of a sustainable healthy lifestyle on psychological symptoms appears to be largely mediated through physical literacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Activity, Healthy Lifestyle and Well-Being Across the Lifespan)
Open AccessArticle
Nepalese Cancer Patients’ Willingness to Pay for Improved Quality of Life: A Choice Experiment Study
by
Adnan Shahid and Alok Bohara
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1645; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141645 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: In Nepal, cancer, among non-communicable diseases, has a high mortality rate. The disease significantly affects patients’ quality of life (QoL). This study aims to identify key attributes of QoL and explore patients’ preferences regarding these attributes. Methods: We implement a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: In Nepal, cancer, among non-communicable diseases, has a high mortality rate. The disease significantly affects patients’ quality of life (QoL). This study aims to identify key attributes of QoL and explore patients’ preferences regarding these attributes. Methods: We implement a discrete choice experiment (DCE) survey to understand cancer patients’ preferences for different attributes of QoL, their willingness to pay for improved QoL, and their preference heterogeneity. This study innovatively uses the EuroQol measure in a DCE setting to elicit the patients’ preferences and their willingness to pay. Results: Using a random parameter logit model, we find that cancer patients prefer lower levels of pain and higher levels of performing usual activities. Overall, we find that cancer patients are willing to pay a total amount of about NRS 2.6 million [about USD 26,000] for improved quality of life. Our analysis also shows that preference heterogeneity exists among cancer patients, and the presence of uncertainty in the preferences of patients does not affect the results. Conclusions: This study sheds light on the preferences and willingness to pay for improved quality of life among cancer patients in Nepal. Understanding these preferences can inform healthcare policy and resource allocation decisions aimed at improving the QoL of cancer patients in the region.
Full article
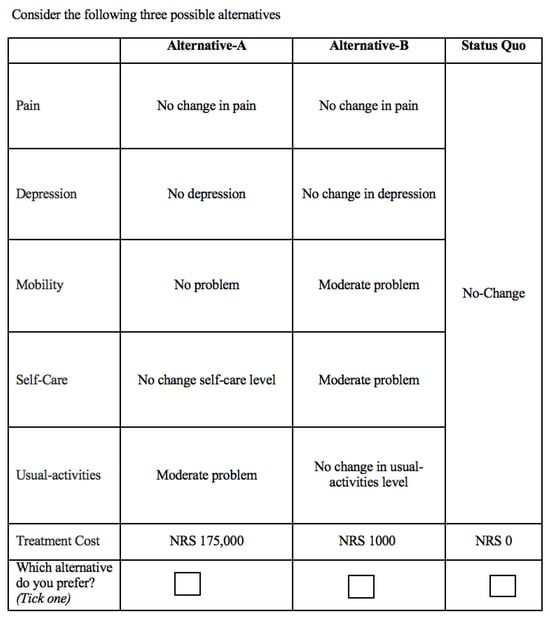
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Truth-Telling to Palliative Care Patients from the Relatives’ Point of View: A Türkiye Sample
by
İrem Kıraç Utku and Emre Şengür
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1644; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141644 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Aim: This study aimed to explore the attitudes of family caregivers toward truth-telling practices in palliative care in Türkiye, a Muslim-majority context where disclosure is often mediated by relatives. Methods: Using a convergent parallel mixed-methods design, data were collected from 100
[...] Read more.
Aim: This study aimed to explore the attitudes of family caregivers toward truth-telling practices in palliative care in Türkiye, a Muslim-majority context where disclosure is often mediated by relatives. Methods: Using a convergent parallel mixed-methods design, data were collected from 100 unpaid family caregivers of terminally ill patients at a palliative care unit. Quantitative data were gathered via a structured questionnaire, and qualitative data through in-depth interviews with a purposively selected subsample of 10 participants. Chi-square tests were used to analyze associations, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: The mean age of caregivers was 47.4 ± 16.5 years, 67% were female. Notably, 67% of participants did not prefer that the patient be informed of irreversible deterioration, while 71% stated they would want to be informed if they were in the patient’s position (p < 0.05). Most preferred a multidisciplinary disclosure process involving physicians, psychologists, and spiritual counselors. Qualitative analysis revealed four themes: emotional conflict, protective family-centered decision-making, spiritual readiness for death, and preference for multidisciplinary communication approach. The participants expressed cultural concerns about psychological harm to the patient and emphasized the family’s role as emotional guardians. Conclusions: The findings highlight a gap between caregivers’ attitudes when acting as family members versus imagining themselves as patients. These results underscore the critical need for culturally sensitive and family-inclusive communication strategies in palliative care settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Communications Challenges in Health and Well-Being, 2nd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
AI—Prediction of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Resistance at the Point of Care from Genomic and Epidemiologic Data
by
Vinothkumar Kolluru, Shreyas Rajendra Hole, Ajeeb Sagar, Advaitha Naidu Chintakunta, Jeevaraj R and Shreekant Salotagi
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1643; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141643 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is an escalating global health challenge, affecting over 82 million individuals each year. The increasing resistance to commonly used antibiotics such as azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and cefixime hinders timely and effective treatment, primarily due to the
[...] Read more.
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is an escalating global health challenge, affecting over 82 million individuals each year. The increasing resistance to commonly used antibiotics such as azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and cefixime hinders timely and effective treatment, primarily due to the delayed detection of resistant strains. Methods: To overcome these limitations, a hybrid machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) framework was developed using a dataset comprising 3786 N. gonorrhoeae isolates. The dataset included clinical metadata and phenotypic resistance profiles. The preprocessing steps involved handling 23% data sparsity, imputing 31 skewed columns, and applying resampling and harmonisation techniques sensitive to data skewness. A predictive pipeline was constructed using both clinical variables and genomic unitigs, and a suite of 33 classifiers was evaluated. Results: The CatBoost model emerged as the top-performing ML algorithm, particularly due to its proficiency in handling categorical data, while a three-layered neural network served as the DL baseline. The ML models outperformed genome-wide association study (GWAS) benchmarks, achieving AUC scores of 0.97 (ciprofloxacin), 0.95 (cefixime), and 0.94 (azithromycin), representing a 4–7% improvement. SHAP analysis identified biologically relevant resistance markers, such as penA mosaic alleles and mtrR promoter mutations, validating the interpretability of the model. Conclusions: The study highlights the potential of ML-driven approaches to enhance the real-time prediction of antimicrobial resistance in N. gonorrhoeae. These methods can significantly contribute to antibiotic stewardship programs, although further validation is required in low-resource settings to confirm their generalisability and robustness across diverse populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Resistance, Healthcare-Associated Infections, and Environmental Microbial Contamination: Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
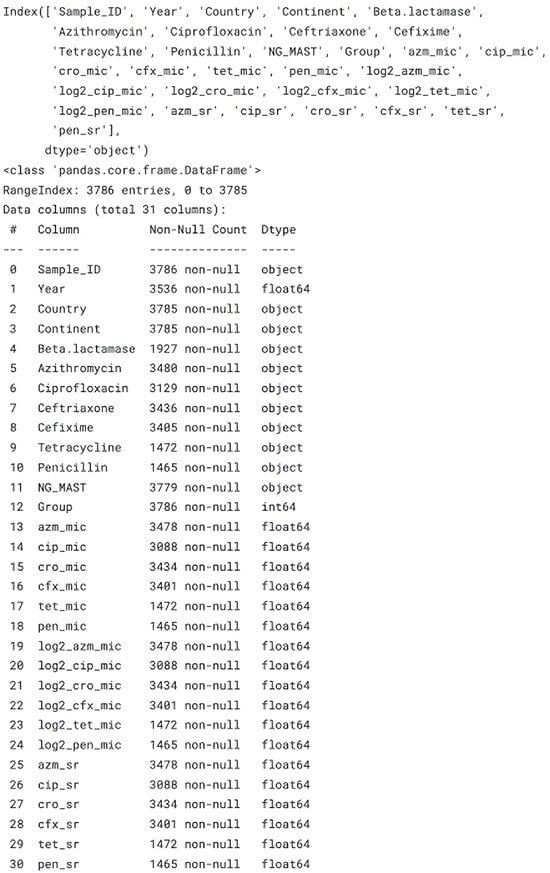
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Healthcare: A Capability and Function-Oriented Review
by
Syed Raza Abbas, Huiseung Seol, Zeeshan Abbas and Seung Won Lee
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1642; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141642 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming smart healthcare by enhancing diagnostic precision, automating clinical workflows, and enabling personalized treatment strategies. This review explores the current landscape of AI in healthcare from two key perspectives: capability types (e.g., Narrow AI and AGI) and functional architectures
[...] Read more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming smart healthcare by enhancing diagnostic precision, automating clinical workflows, and enabling personalized treatment strategies. This review explores the current landscape of AI in healthcare from two key perspectives: capability types (e.g., Narrow AI and AGI) and functional architectures (e.g., Limited Memory and Theory of Mind). Based on capabilities, most AI systems today are categorized as Narrow AI, performing specific tasks such as medical image analysis and risk prediction with high accuracy. More advanced forms like General Artificial Intelligence (AGI) and Superintelligent AI remain theoretical but hold transformative potential. From a functional standpoint, Limited Memory AI dominates clinical applications by learning from historical patient data to inform decision-making. Reactive systems are used in rule-based alerts, while Theory of Mind (ToM) and Self-Aware AI remain conceptual stages for future development. This dual perspective provides a comprehensive framework to assess the maturity, impact, and future direction of AI in healthcare. It also highlights the need for ethical design, transparency, and regulation as AI systems grow more complex and autonomous, by incorporating cross-domain AI insights. Moreover, we evaluate the viability of developing AGI in regionally specific legal and regulatory frameworks, using South Korea as a case study to emphasize the limitations imposed by infrastructural preparedness and medical data governance regulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Role of AI in Predictive and Prescriptive Healthcare)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dietary Habits, TCM Constitutions, and Obesity: Investigating the Protective Effects of Vegetarian Dietary Patterns in Taiwan
by
Po-Yu Huang, Chien-Hsiun Chen, Yen-Feng Chiu, Hong-Chun Lin and Ching-Mao Chang
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1641; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141641 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a global health challenge associated with metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) body constitution theory offers a unique perspective on individual susceptibility to obesity; however, its integration into public health strategies remains underexplored. Objective: To examine the associations
[...] Read more.
Background: Obesity is a global health challenge associated with metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) body constitution theory offers a unique perspective on individual susceptibility to obesity; however, its integration into public health strategies remains underexplored. Objective: To examine the associations between vegetarian dietary patterns, TCM body constitution types (Phlegm stasis, Yang deficiency, and Yin deficiency), and overweight/obesity in a large-scale national cohort. Methods: Data were obtained from 3597 participants enrolled in the Taiwan Biobank. Socio-demographic variables, lifestyle behaviors (diet, smoking, physical activity), and anthropometric indicators (BMI and waist circumference) were assessed. Participants were categorized by weight status and TCM body constitution. Polytomous logistic regression models were used to evaluate associations between vegetarian dietary patterns, constitution types, and overweight/obesity, adjusting for potential confounders. Results: Among participants (mean age, 50.1 ± 9.4 years), 55.6% had normal BMI, 27.3% were overweight, and 17.1% were obese. Vegetarian dietary patterns were significantly associated with lower odds of Phlegm stasis (OR: 0.96; p < 0.001), Yang deficiency (OR: 0.97; p < 0.001), and Yin deficiency (OR: 0.97; p < 0.001), as well as with lower odds of overweight (OR: 0.72; p < 0.05) and obesity (OR: 0.67; p < 0.05). Physical activity was also associated with lower odds of all three constitution types and obesity. Phlegm stasis constitution was associated with higher odds of obesity (range of ORs: 1.18–1.58; p < 0.001). Conclusions: Vegetarian dietary patterns and regular physical activity were associated with lower odds of obesity and TCM constitution imbalances, particularly Phlegm stasis. These findings suggest a potential role for constitution-informed strategies in obesity-related public health approaches. Longitudinal studies are warranted to clarify temporal relationships and mechanisms. Clinical Trials Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03938207 (Study Start: 1 October 2022).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Obesity and Overweight: Prevention, Causes and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
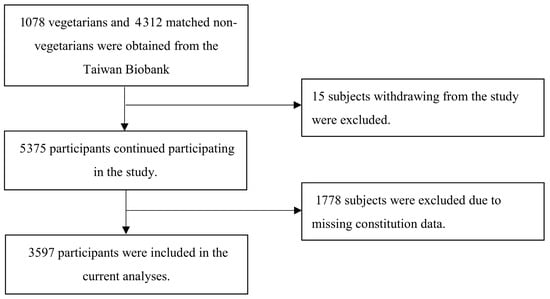
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mental Health Professionals’ Views on the Influence of Media on Self-Harm in Young People: A Critical Discourse Analysis
by
Tharushi Denipitiya, Annette Schlösser and Jo Bell
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1640; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141640 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Self-harm in young people is influenced by multiple factors, with media playing a significant role. While research has examined its harmful and protective effects, little attention has been paid to how healthcare professionals interpret and respond to media’s role in shaping young
[...] Read more.
Background: Self-harm in young people is influenced by multiple factors, with media playing a significant role. While research has examined its harmful and protective effects, little attention has been paid to how healthcare professionals interpret and respond to media’s role in shaping young people’s experiences of self-harm. To our knowledge, no research has examined adolescent mental health professionals’ perspectives and, crucially, how these are constructed and understood. The study aimed to examine the following: (1) how mental health practitioners construct and use discourses to interpret the role of media in young people’s self-harm; and (2) how these discourses shape clinical understanding and practice. Methods: This qualitative study employed semi-structured interviews with ten clinicians from child and adolescent mental health services across England working with young people who self-harm. Data were analysed using critical discourse analysis to uncover how broader societal and institutional narratives shape clinicians’ perspectives. Results: Two dominant discourses were identified: “Media as Disruptor” and “The Hidden World of Youth”. These discourses framed media as both a risk factor and a potential intervention tool, positioning media as a powerful yet morally ambiguous force in young people’s lives. Clinicians largely framed media’s influence as negative but acknowledged its capacity for education and intervention. Conclusions: This research offers new insights into how media-related self-harm risks and benefits are framed and managed in mental health care settings. The study underscores the need for systemic changes in clinical practice, enhanced training, updated guidelines and a shift towards broader sociocultural perspectives in understanding self-harm and suicidal behaviour.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Health Risk Behaviours: Self-Injury and Suicide in Young People)
Open AccessArticle
The Effectiveness of 360-Degree Virtual Reality-Based Mechanical Ventilation Nursing Education for ICU Nurses
by
Doo Ree Kim and Jaeyong Yoo
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1639; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141639 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Mechanical ventilation management is a critical competency for intensive care unit (ICU) nurses; however, traditional training methods are often insufficient to prepare nurses for the complexities of alarm management and clinical decision-making. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Mechanical ventilation management is a critical competency for intensive care unit (ICU) nurses; however, traditional training methods are often insufficient to prepare nurses for the complexities of alarm management and clinical decision-making. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a 360-degree virtual reality (VR)-based mechanical ventilation nursing education program for ICU nurses in Korea. Methods: A quasi-experimental pre-test–post-test design was employed with 65 ICU nurses (32 in the experimental group and 33 in the control group). Data were collected from May to October 2023. The VR-based program, developed using the ADDIE instructional design model, incorporated simulation-based scenarios focusing on ventilator alarm management and clinical reasoning. Outcome measures included knowledge of ventilation nursing, self-efficacy, clinical reasoning, learning immersion, turnover intention, and educational satisfaction. Data were analyzed using normality tests, descriptive statistics, independent t-tests, and paired t-tests. Results: The experimental group demonstrated significantly greater improvements in knowledge (Δ = 5.54), self-efficacy (Δ = 0.94), clinical reasoning (Δ = 0.76), and learning immersion (Δ = 0.88) compared to the control group (all p < 0.001), where Δ denotes the change score (post-test minus pre-test). Post-test assessments were conducted immediately after the intervention. Educational satisfaction was also significantly higher in the experimental group (p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed in turnover intention between the groups, suggesting a limited short-term impact on this outcome. Conclusions: A 360-degree VR-based education program effectively enhanced key competencies among ICU nurses. While these findings reflect short-term outcomes, future research is warranted to assess the long-term effects and sustainability of VR-based learning in ICU continuing education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Nursing)
►▼
Show Figures
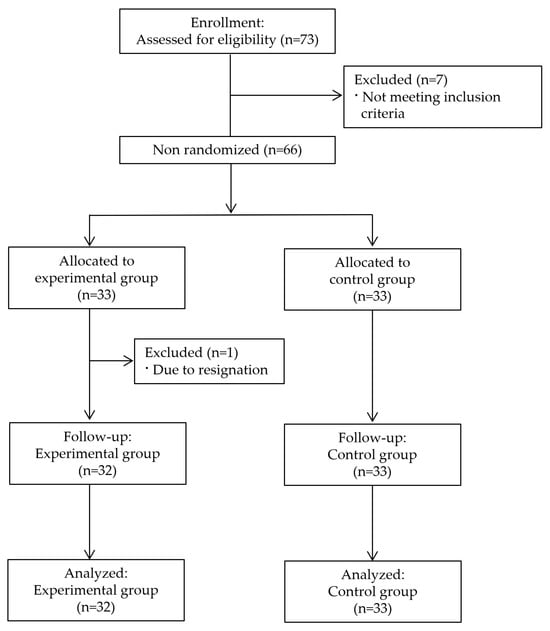
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of COVID-19 on Incident Depression and Anxiety: A Population-Based Observational Study Using Statewide Claims Data
by
Jaewhan Kim, Khanh N. C. Duong, Emeka Elvis Duru, Rachel Weir, Karen Manotas, Kristi Kleinschmit, Aaron Fischer, Peter Weir and Fernando A. Wilson
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1638; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141638 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Objectives: Evidence suggests that COVID-19 infection contributes to elevated risks of psychiatric disorders, including depression and anxiety, however, this association remains underexplored. This study aimed to examine the incidence of depression and anxiety in individuals with COVID-19 compared to those without any
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Evidence suggests that COVID-19 infection contributes to elevated risks of psychiatric disorders, including depression and anxiety, however, this association remains underexplored. This study aimed to examine the incidence of depression and anxiety in individuals with COVID-19 compared to those without any infection. Method: Using the Utah All Payers Claims Database (2019 to 2021), we examined adult patients with continuous insurance enrollment. Individuals with pre-existing depression or anxiety were excluded. COVID-19 infection in 2020 was identified using diagnostic and procedural codes. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) method was applied to select covariates, followed by entropy balancing to adjust for baseline differences. Weighted logistic regression models were used to estimate the association between COVID-19 infection and incident mental health diagnoses in 2021. Results: Among 356,985 adults included in the final analytic sample for depression analysis, 37.6 percent had a documented COVID-19 infection in 2020. Individuals with prior infection had significantly higher odds of receiving a depression diagnosis in 2021 compared to those without infection (OR = 1.48, p < 0.01). A similar pattern was observed for anxiety: among 371,491 adults, 38.1 percent had a COVID-19 infection, and infected individuals had 46 percent greater odds of receiving an anxiety diagnosis (OR = 1.46, p < 0.01), after adjusting for demographic and clinical characteristics. Conclusions: This study highlights the elevated risk of depression and anxiety among patients who had been infected with COVID-19, emphasizing the importance of addressing the mental health needs of individuals affected by the virus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Coronaviruses (CoV) and COVID-19 Pandemic)
Open AccessSystematic Review
Home-Based Community Elderly Care Quality Indicators in China: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Xi Chen, Rahimah Ibrahim, Yok Fee Lee, Tengku Aizan Hamid and Sen Tyng Chai
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1637; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141637 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: China’s rapidly aging population has increased the need for effective community-based eldercare services. However, the lack of standardized, culturally relevant evaluation frameworks hinders consistent service quality assessment and improvement. Objective: This systematic review aims to identify, synthesize, and critically evaluate
[...] Read more.
Background: China’s rapidly aging population has increased the need for effective community-based eldercare services. However, the lack of standardized, culturally relevant evaluation frameworks hinders consistent service quality assessment and improvement. Objective: This systematic review aims to identify, synthesize, and critically evaluate the existing quality indicators (QIs) currently utilized for home-based community elderly care HCEC in China. It also aims to highlight gaps to inform the development of a more comprehensive and context-appropriate quality framework. Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, systematic searches were conducted across Web of Science, PubMed, Wiley, and CNKI databases for studies published in English and Chinese from 2008 onward. Extracted QIs from eligible studies were categorized using Donabedian’s structure–process–outcome (SPO) model. Results: Fifteen studies met the inclusion criteria, with QI sets ranging from 5 to 64 indicators. Most studies emphasized structural and procedural aspects, while outcome measures were limited. Key gaps include inconsistent terminology, insufficient medical care integration, narrow stakeholder engagement, and limited cultural adaptation of Western theoretical frameworks. Furthermore, subjective weighting methods predominated, impacting indicator reliability. Conclusions: Currently, there is no formal quality framework to guide service providers in HCEC, and therefore, quality indicators can be described as fragmented and lack cultural specificity, medical integration, and methodological robustness. Future research should prioritize developing culturally anchored and medically comprehensive QI frameworks, standardize indicator terminology, actively involve diverse stakeholders through participatory methods, and adopt hybrid methodological approaches combining subjective expert insights and objective, data-driven techniques. Alignment with established international standards, such as the OECD long-term care quality indicators, is essential to enhance eldercare quality and support evidence-based policymaking.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Healthcare Practice in Community)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Patient Safety Through Predictors of Job Performance in Greek Critical Care Nurses
by
Thalia Bellali, George Panayiotou, Polyxeni Liamopoulou, Theodora Mantziou, Evgenia Minasidou and Georgios Manomenidis
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1636; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141636 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Job performance among critical care nurses is a pivotal determinant of patient safety. While individual psychosocial factors such as self-care and self-compassion have been separately linked to professional efficacy, limited research has examined their integrated contribution to job performance in high-stakes
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Job performance among critical care nurses is a pivotal determinant of patient safety. While individual psychosocial factors such as self-care and self-compassion have been separately linked to professional efficacy, limited research has examined their integrated contribution to job performance in high-stakes healthcare environments. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in five public hospitals in Northern Greece. A convenience sample of 311 critical care nurses and nurse assistants completed validated self-report measures assessing self-care, self-compassion, mindfulness, physical activity, secondary traumatic stress, and job performance. The data were analyzed using non-parametric statistics and multivariate linear regression. Results: Higher levels of self-care (p = 0.003) and self-compassion (p = 0.042), and lower levels of secondary traumatic stress (p = 0.04), were significantly associated with better job performance. The final regression model explained 31% of the variance in performance scores (R2 = 0.31). Mindfulness and physical activity were not significantly associated with job performance. Secondary traumatic stress emerged as the strongest negative predictor. Conclusions: Internal psychosocial resources, particularly self-care and self-compassion, significantly contribute to job performance among critical care nursing personnel. These findings underscore the relevance of embedding staff well-being strategies into organizational patient safety agendas. This multidimensional model provides a novel framework for developing targeted interventions in high-acuity healthcare settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Enhancing Patient Safety in Critical Care Settings)
Open AccessArticle
Direct and Interactive Effects of Work Stress and Professional Identity on Job Burnout Among Elderly Care Workers for Old People in China: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Luqi Li, Qi Wang, Qiaoqiao Wang, Yating Chen, Tao Sun, Caiming Xu and Li Li
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1635; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141635 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to explore the relationships between work stress, professional identity, and job burnout in elderly care workers and to assess whether work stress and professional identity interact to influence job burnout. Methods: A survey of 439 elderly care
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aimed to explore the relationships between work stress, professional identity, and job burnout in elderly care workers and to assess whether work stress and professional identity interact to influence job burnout. Methods: A survey of 439 elderly care workers was conducted from July to September 2021. T-tests and ANOVA were used to identify the main different characteristics involved in work stress and professional identity, and four multiple regression models were used to identify the determinants of job burnout. Results: Work stress and professional identity were moderate among respondents. Work stress positively correlated with job burnout, while professional identity showed a negative correlation. An interactive effect was found between the sub-dimension of work stress concerning the consistency between rewards and responsibilities and professional identity on job burnout. Conclusions: Managers in pension institutions should focus on addressing work stress and professional identity, especially balancing alignment between rewards and responsibilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy of Sesame-Based Oil Pulling in Plaque Reduction: A Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Christine Zürcher, Markus Nagl, Kristian Vukoje, Ingrid Heller, Sigrun Eick and Ines Kapferer-Seebacher
Healthcare 2025, 13(14), 1634; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13141634 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: To evaluate and compare the plaque-reducing efficacy of sesame-based oil pulling versus distilled water in a randomized controlled, examiner-blinded parallel-group study. Materials and Methods: Forty participants with gingivitis (community periodontal index of treatment needs grade 1 or 2) were randomly assigned to
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To evaluate and compare the plaque-reducing efficacy of sesame-based oil pulling versus distilled water in a randomized controlled, examiner-blinded parallel-group study. Materials and Methods: Forty participants with gingivitis (community periodontal index of treatment needs grade 1 or 2) were randomly assigned to either the test group (sesame-based oil) or the control group (distilled water). Participants were instructed to perform oil pulling daily in the morning for 15 min over an eight-week period. The Rustogi Modified Navy Plaque Index (RMNPI) and gingival bleeding index (GBI) were evaluated at the baseline, as well as after four and eight weeks. Additionally, biofilm samples were collected for microbiological analysis. Results: The RMNPI was statistically significantly reduced after eight weeks of pulling with sesame-based oil (p < 0.001), as well as with distilled water (p < 0.001), without a significant difference between the groups. The GBI was statistically significantly reduced after eight weeks of pulling with sesame-based oil (p < 0.002), as well as with distilled water (p < 0.002), without a significant difference between the groups. No significant microbiological changes were detected in biofilm samples. Conclusions: Both plaque and gingival indices significantly decreased with oil pulling after eight weeks of intervention. Preclinical studies are necessary to clarify the mechanism of plaque reduction by oil pulling.
Full article
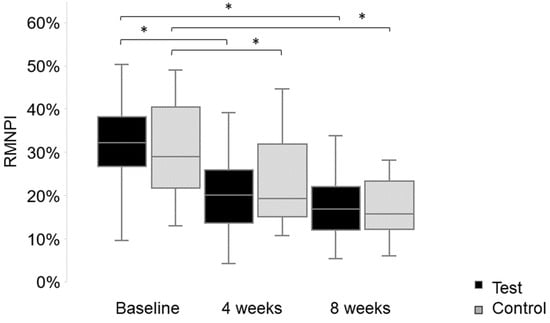
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Trends in Laryngeal Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Central Serbia (1999–2023): A Joinpoint Regression Analysis
by
Vladimir Nešić, Dragana Krstić Nešić, Sandra Šipetić Grujičić, Bojana Bukurov, Dragan Miljuš, Snežana Živković Perišić and Aleksandra Nikolić
Healthcare 2025, 13(13), 1633; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131633 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Laryngeal cancer (LC) accounts for 1–3% of all malignant neoplasms. The aim of this study was to analyze temporal trends in the incidence and mortality of LC in Central Serbia over a 25-year period (1999–2023). Methods: Data on newly diagnosed cases and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Laryngeal cancer (LC) accounts for 1–3% of all malignant neoplasms. The aim of this study was to analyze temporal trends in the incidence and mortality of LC in Central Serbia over a 25-year period (1999–2023). Methods: Data on newly diagnosed cases and deaths, stratified by sex and age group, were obtained from the Serbian Cancer Registry. Crude, age-specific, and age-standardized incidence and mortality rates were calculated. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate average annual percent changes (AAPCs) and assess their statistical significance. Results: The average annual age-standardized incidence rate (ASR-W) was 11.1 per 100,000 in men and 1.4 in women, with corresponding mortality rates of 5.4 and 0.5, respectively. The highest incidence was observed in the 60–69 age group for both sexes (61.1/100,000 in men; 7.4/100,000 in women), while the highest mortality was recorded in individuals aged ≥70 (35.7/100,000 in men; 3.8/100,000 in women). A statistically significant annual decline among men was observed in both incidence (ASR-W: −0.7%) and mortality (ASR-W: −2.0%). In contrast, trends among women were not statistically significant, indicating overall stability. Conclusions: Although the Cancer Registry in Serbia faces limitations primarily due to data quality issues, it is a key tool for understanding LC trends, guiding health policies, and effectively allocating resources. Given the substantially higher burden among men, it is essential to strengthen tobacco and alcohol control, improve occupational safety, and promote early detection and timely treatment to reduce the disease burden.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence and Determinants of Suicidal Ideation Among Physicians in Saudi Arabia
by
Ayedh H. Alghamdi, Mohammed A. Aljaffer, Ahmad H. Almadani, Saleh A. Alghamdi, Hasan R. Alshehri, Akeel A. Alyateem, Refan T. Hashim and Fahad D. Alosaimi
Healthcare 2025, 13(13), 1632; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131632 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The mental health of physicians has become a pressing global concern. High rates of depression, anxiety, and burnout are reported in the literature, with each condition linked to reduced job satisfaction, increased medical errors, and ultimately suicidal ideation (SI). Although research on
[...] Read more.
Background: The mental health of physicians has become a pressing global concern. High rates of depression, anxiety, and burnout are reported in the literature, with each condition linked to reduced job satisfaction, increased medical errors, and ultimately suicidal ideation (SI). Although research on physicians’ mental health is emerging in Saudi Arabia, data on suicidality remain scarce. Objective: This study aims to determine the prevalence of SI and its determinants among physicians in Saudi Arabia. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 423 physicians across all medical specialties of all ranks, who were recruited using a convenience sampling technique. The study tool comprised three main sections. The first section included questions regarding sociodemographic factors, lifestyle, and work-related factors. The second section included items on suicidality and the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 to screen for depressive symptoms. The third section included the Brief Resilient Coping Scale (BRCS) to measure the coping mechanisms of the participants. Results: SI was disclosed by 9.7% of the respondents, with 0.5% reporting previous suicide attempts. Suicidal ideation was independently associated with low income (OR = 3.94, 95% CI 1.32–11.76, p = 0.014) and higher depression scores (OR = 1.09 per point, 95% CI 1.02–1.16, p = 0.008). Moreover, knowing a colleague with suicidal behavior (i.e., knowing a colleague who had contemplated suicide or had attempted suicide/died by suicide) was significantly associated with SI among our participants (p < 0.001 and p < 0.006, respectively). Higher scores on the BRCS, specifically with respect to growing from adversity and actively replacing losses, were linked to lower odds of SI (p < 0.001 and p < 0.045, respectively). Conclusions: Physicians in Saudi Arabia experience an alarming level of SI that is associated with low income and depression. The results of this study underscore the importance of additional research to evaluate the effectiveness of intervention programs designed to enhance mental health support for physicians, encourage adaptive coping mechanisms, foster peer support networks, and combat stigma associated with mental illnesses.
Full article
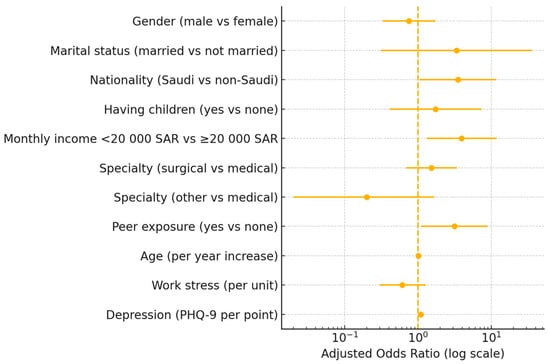
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Dental Practice Management in Romania: A Cross-Sectional Case–Control Study on the Perceived Impact of Managerial Training on Efficiency, Collaboration, and Care Quality Dental
by
Georgiana Ioana Potra Cicalău, Liana Todor, Roxana Alexandra Cristea, Ramona Hodișan, Olivia Andreea Marcu, Ioan Andrei Țig, Lucia Georgeta Daina and Gabriela Ciavoi
Healthcare 2025, 13(13), 1631; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131631 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The effective management of dental practices is increasingly recognized as a key factor in ensuring high-quality care, efficient operations, and interdisciplinary collaboration. While many dentists assume managerial responsibilities, formal training in healthcare or dental practice management may influence the quality of these
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The effective management of dental practices is increasingly recognized as a key factor in ensuring high-quality care, efficient operations, and interdisciplinary collaboration. While many dentists assume managerial responsibilities, formal training in healthcare or dental practice management may influence the quality of these practices. This study aims to evaluate the differences in organization, efficiency, and quality of care between dental clinics managed by dentists who have completed management training and those who have not. It also explores dentists’ knowledge and attitudes regarding dental practice management. Methods: A cross-sectional, observational, case–control study was conducted between 14 April and 14 May 2023, using an online questionnaire distributed to licensed dental practitioners in Romania. A total of 136 dentists participated, divided into a study group (n = 60), who had completed management courses and a control group (n = 76) who had not. Descriptive statistics and comparative analyses (t-tests, Chi-square tests) were performed using SPSS version 24, with significance set at p < 0.05. Results: Dentists with managerial training demonstrated greater implementation of strategic planning, financial performance monitoring, quality management, and use of digital tools. They also reported higher collaboration with interdisciplinary professionals—orthodontist 76.7% in the study group vs. 63.2% in the control group, medical assistant 78.3% in the study group vs. 47.4% in the control group, front desk 43.3% in the study group vs. 18.4% in the control group; better delegation of tasks—61.7% in the study group vs. 27.6% in the control group; and greater concern for team development—95% in the study group vs. 71% in the control group; and patient rights—81.7% in the study group vs. 75% in the control group. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were noted in management practices, opinions about the optimal manager for a dental practice, and the use of software tools. Conclusions: Managerial training equips dentists with critical skills for enhancing operational efficiency and care quality. Integrating management education into dental curricula and continuing professional development can substantially improve the sustainability and performance of dental practices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Health Service Improvement, Nursing Management and Simulation)
Open AccessCommentary
Advancing Gender Equity in International Eyecare: A Roadmap in Creating the Women Leaders in Eye Health (WLEH) Initiative
by
Clare Szalay Timbo, Armaan Jaffer, Maria Jose Montero Romero, Gabriela Cubias, Heidi Chase, Sara T. Wester, Femida Kherani and Erin M. Shriver
Healthcare 2025, 13(13), 1630; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13131630 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
Gender inequality remains a persistent issue in healthcare, especially in ophthalmology, where women face systemic barriers such as pay gaps, limited surgical opportunities, harassment, and unequal family expectations. Despite increasing entry into the field, women remain underrepresented in leadership, affecting career advancement and
[...] Read more.
Gender inequality remains a persistent issue in healthcare, especially in ophthalmology, where women face systemic barriers such as pay gaps, limited surgical opportunities, harassment, and unequal family expectations. Despite increasing entry into the field, women remain underrepresented in leadership, affecting career advancement and patient care. This study examines how virtual platforms, and co-led initiatives can address gender disparities in eye health. In 2021, Women in Ophthalmology, Seva Foundation, and Orbis International launched the Women’s Leaders in Eye Health (WLEH) initiative—a global community promoting mentorship, networking, and leadership development. Starting with virtual webinars and informal networking, the initiative expanded to in-person events in 2023 due to strong global engagement and demand. Early virtual programming, including webinars and “Coffee Hour” sessions, proved effective and laid the groundwork for broader offerings such as mentorship and professional development grants. WLEH’s success underscores the power of collaboration in promoting gender equity. By fostering connections and leadership pathways, WLEH offers a scalable model to break down gender challenges and uplift the next generation of women leaders to deliver more accessible eyecare globally.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bullying in the Workplace, Gender Inequality: Challenges for the Quality and Safety of Health Care)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Healthcare Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Healthcare, JCM
The Use of New Technologies for Health and Clinical Practice
Topic Editors: Luca Marin, Matteo Vandoni, Vittoria CarnevaleDeadline: 25 July 2025
Topic in
Healthcare, IJERPH, JCM, Safety, Toxics
New Research in Work-Related Diseases, Safety and Health
Topic Editors: Alicja Bortkiewicz, Małgorzata KurpesaDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
IJERPH, JPM, Healthcare, BDCC, Applied Sciences, Sensors
eHealth and mHealth: Challenges and Prospects, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Antonis Billis, Manuel Dominguez-Morales, Anton CivitDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topic in
Behavioral Sciences, EJIHPE, Healthcare, Social Sciences, Sustainability
Global Mental Health Trends
Topic Editors: Naiara Ozamiz-Etxebarria, Nahia Idoiaga-Mondragon, Maitane Picaza Gorrotchategi, Idoia Legorburu Fernandez, Israel AlonsoDeadline: 30 November 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Digital Healthcare Innovation in Medical Imaging: The Past, the Present and the Future
Guest Editor: Barbara BrognaDeadline: 15 July 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Sleep Disorders Management in Primary Care—Second Edition
Guest Editor: Izolde BouloukakiDeadline: 15 July 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Advances in Manual Therapy: Diagnostics, Prevention and Treatment
Guest Editors: Adam Kawczyński, Rafal StudnickiDeadline: 30 July 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Patient-Centered Care for Enhancing Health-Related Quality of Life: Integrating Clinical, Behavioral, and Social Determinants of Health
Guest Editor: Milica ZekovićDeadline: 30 July 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Promoting Mental Health and Wellbeing in Chronic Illness Using Art
Collection Editors: Helen Noble, Claire Carswell
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Why Some Patients Never Fully Recover: Post Active Phase of Infection Syndromes (PAPIS)
Collection Editors: Kenneth Friedman, Patricia A. Fennell, Evan Spivack, James Oleske, Nancy Klimas, Pawel Zalewski, Susan Levine
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
The Impact of COVID-19 on Healthcare Services
Collection Editors: Giuseppe Di Martino, Tommaso Staniscia, Fabrizio Cedrone
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
COVID-19: Impact on Public Health and Healthcare
Collection Editors: Manoj Sharma, Kavita Batra








