- Article
Barrier-Diffusion Controlled Adsorption at Anomalous Diffusion: Fractional Calculus Approach
- Ivan Bazhlekov and
- Emilia Bazhlekova
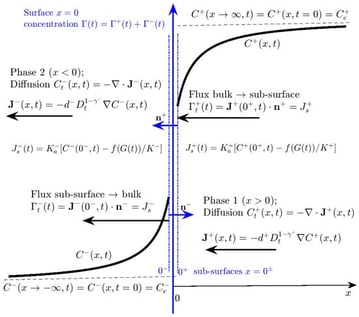
Fractional calculus approach is used to analyze the model of surfactant transport by anomalous diffusion and its adsorption on an interface in a liquid-liquid system. The anomalous diffusion is modeled by time-fractional partial differential equations in the bulk phases. The adsorption of surfactant is described by the corresponding time-fractional Neumann boundary conditions at the interface. The adsorption process is considered under mixed barrier-diffusion control, described by first-order ordinary differential equation, which relates the subsurface concentration with that on the interface. A second relation between these concentrations is derived in terms of a fractional equation by application of Laplace transform technique. By combining both relations the subsurface concentration is eliminated and a single multi-term fractional ordinary differential equation for the surfactant concentration on the interface is derived. Different adsorption kinetic models are considered. In the case of Henry adsorption isotherm the model is linear and possesses analytical solution in terms of multinomial Mittag-Leffler functions. In the cases of Volmer and van der Waals adsorption isotherms nonlinear differential equations of fractional order are obtained. They are reformulated in equivalent integral form, which is used for computer simulation of the process of adsorption. Numerical results are presented and compared with analytical asymptotic predictions.
13 February 2026