Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Metallurgical Processes: Towards Carbon Neutrality and Zero Waste
A special issue of Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This special issue belongs to the section "A: Sustainable Energy".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 20 April 2026 | Viewed by 1774
Special Issue Editors
Interests: metallurgical thermodynamics; extractive metallurgy; recycling; energy materials; circular economy; electrochemistry; chalcogenide and intermetallic materials; sulfosalts and sulfates characterizations; metallurgical engineering; metals; renewable energy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: thermodynamic modeling; process simulation of pyrometallurgical process; hydrogen reduction kinetics; steelmaking process; recycling of industrial waste
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: metallurgical thermodynamics; extractive metallurgy; recycling; energy materials; circular economy; electrochemistry; chalcogenide and intermetallic materials; sulfosalts and sulfates characterizations; metallurgical engineering; metals; renewable energy
Interests: biomass valorisation; lignin; wet oxidation; catalysis; biorefinery; chemical engineering; nanotechnology; polymers
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
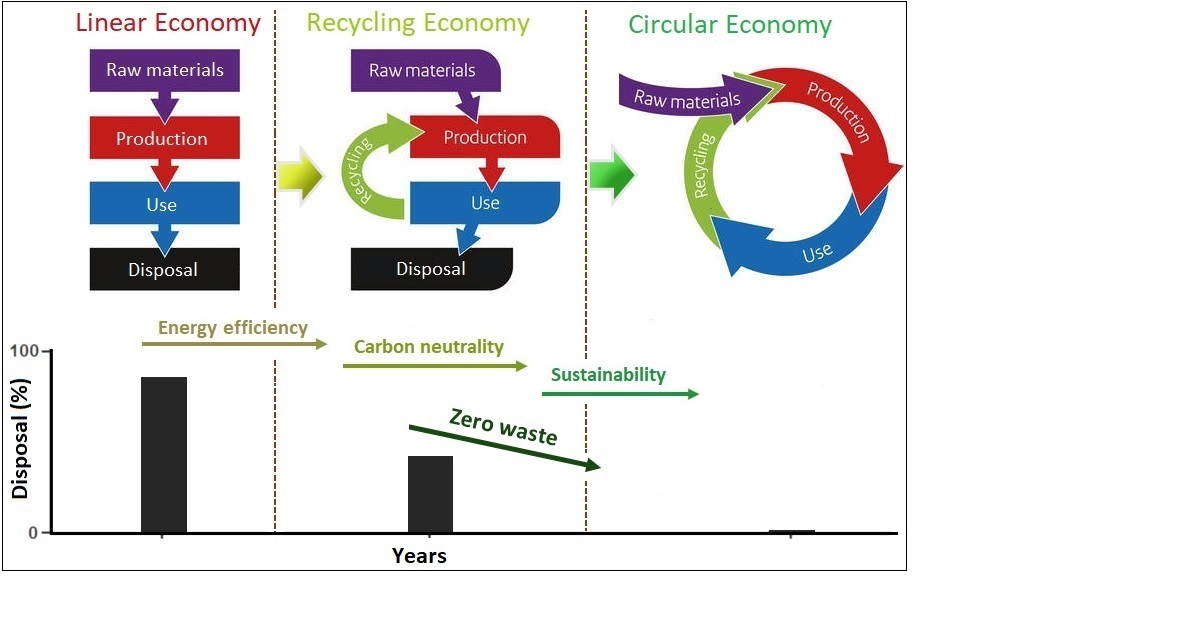
Metals are the backbone of modern society and are present in everything from infrastructure to electronics. However, their extraction and processing come at a significant environmental cost, generating carbon emissions and large volumes of waste. As the world moves towards a sustainable future, achieving "zero carbon" and "zero waste" in the metals sector is crucial.
This Special Issue requests submissions that address industry-specific challenges and propose solutions that drastically reduce energy- and/or process-related carbon emissions, as well as waste from metal extraction and processing. Original research and reviews in areas such as carbon-neutral extraction, waste minimization and valorization, perspectives on technical challenges and broader inorganic material-related technological challenges preventing the achievement of energy sustainability are also welcome.
Dr. Fiseha Tesfaye
Dr. Minkyu Paek
Dr. Mykola Moroz
Dr. Abayneh Getachew Demesa
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy efficiency
- extraction and processing
- recycling and secondary recovery
- sustainable metals
- zero carbon emissions
- zero waste
- recycling and circular production
- thermodynamic modeling and phase diagrams
- pyrometallurgical solutions for sustainability
- heat recovery in the metals industry
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.








