Journal Description
Coatings
Coatings
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on coatings and surface engineering published monthly online by MDPI. The Korean Tribology Society (KTS) is affiliated with Coatings and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Materials Science, Coatings & Films) / CiteScore - Q2 (Surfaces and Interfaces)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 14 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Coatings.
Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Development and Application of Intelligent Coating Technology: A Review
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 597; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050597 (registering DOI) - 9 May 2024
Abstract
Coating technology, as a part of surface engineering, has shown remarkable potential in future industrial applications. With the continuous development and improvement of coating technology, coatings have gradually become an indispensable part of industrial manufacturing, possessing various excellent properties and characteristics, such as
[...] Read more.
Coating technology, as a part of surface engineering, has shown remarkable potential in future industrial applications. With the continuous development and improvement of coating technology, coatings have gradually become an indispensable part of industrial manufacturing, possessing various excellent properties and characteristics, such as superhydrophobicity and self-cleaning, enhanced biological antibacterial properties, and improved corrosion resistance. Intelligent coatings are not only rigid barriers between substrates and the environment but also coatings designed to respond to the environment and improve coating life or achieve certain special functions through this response. Biomimetics is a discipline that studies the structure, function, and behavior of living organisms and applies them to engineering design. Combining bionics with intelligent coating materials can not only improve the performance and functionality of intelligent coatings but also create more intelligent coating materials. This paper includes advanced superhydrophobic intelligent coatings, anticorrosion intelligent coatings, biological antibacterial intelligent coatings, and other intelligent coatings with specific functions. We also provide a detailed overview of the preparation methods and technologies of various representative intelligent coatings, as well as their properties and applications, which will offer some valuable references for the development direction of future intelligent coatings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Review Papers Collection for Smart Coatings)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Carbon Fiber Fabrics with ALD AlxOy Coatings: An Investigation of Thickness Effects on Weight, Morphology, Coloration, and Thermal Properties
by
Vanessa Dias, Nierlly Galvão, Felipe Miranda, Mariana Fraga, Gilberto Petraconi, Homero Maciel and Rodrigo Pessoa
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 596; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050596 (registering DOI) - 9 May 2024
Abstract
This study explores the impact of non-stoichiometric aluminum oxide (AlxOy) coatings applied via thermal atomic layer deposition (ALD) on carbon fiber fabrics (CFFs), emphasizing volume per cycle, FESEM analyses, color transitions, and thermal stability enhancements. Using trimethylaluminum and water
[...] Read more.
This study explores the impact of non-stoichiometric aluminum oxide (AlxOy) coatings applied via thermal atomic layer deposition (ALD) on carbon fiber fabrics (CFFs), emphasizing volume per cycle, FESEM analyses, color transitions, and thermal stability enhancements. Using trimethylaluminum and water at 100 °C, AlxOy was deposited across a range of 1000 to 5000 ALD cycles, with film thicknesses extending up to 500 nm. This notable increase in the volume of material deposited per cycle was observed for the 3D CFFs, highlighting ALD’s capability to coat complex structures effectively. FESEM analyses revealed the morphological evolution of CFF surfaces post-coating, showing a transition from individual grains to a dense, continuous layer as ALD cycles increased. This morphological transformation led to significant color shifts from green to red to blue, attributed to structural coloration effects arising from variations in film thickness and surface morphology. Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA and dTG) indicated that the AlxOy coatings enhanced the thermal stability of CFFs, with a postponement in degradation onset observed in samples subjected to more ALD cycles. In essence, this research highlights the nuanced relationship between ALD processing parameters and their collective influence on both the aesthetic and functional properties of CFFs. This study illustrates ALD’s potential in customizing CFFs for applications requiring specific color and thermal resilience, balancing the discussion between the surface morphological changes and their implications for color and thermal behavior.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Thin Films)
Open AccessArticle
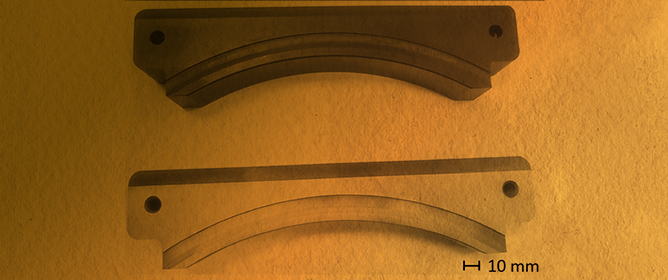
Photocatalytic Activity and Antibacterial Properties of Mixed-Phase Oxides on Titanium Implant Alloy Substrates
by
Haden A. Johnson, Darby Donaho, Aya Ali, Amisha Parekh, Randall S. Williamson, Mary E. Marquart, Joel D. Bumgardner, Amol V. Janorkar and Michael D. Roach
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 595; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050595 (registering DOI) - 9 May 2024
Abstract
Titanium alloys are commonly used for implants, but the naturally forming oxides are bioinert and not ideal for bacterial resistance or osseointegration. Anodization processes are a modification technique that can crystallize the oxides, alter oxide surface topography, and introduce beneficial chemistries. Crystalline titanium
[...] Read more.
Titanium alloys are commonly used for implants, but the naturally forming oxides are bioinert and not ideal for bacterial resistance or osseointegration. Anodization processes are a modification technique that can crystallize the oxides, alter oxide surface topography, and introduce beneficial chemistries. Crystalline titanium oxides are known to exhibit photocatalytic activity (PCA) under UVA light. Anodization was used to create mixed-phase oxides on six titanium alloys including commercially pure titanium (CPTi), Ti-6Al-4V (TAV), Ti-6Al-7Nb (TAN), two forms of Ti-15Mo (TiMo-β and TiMo-αβ), and Ti-35Nb-7Zr-5Ta (TNZT). Combined EDS and XPS analyses showed uptake of the electrolyte and substrate alloying elements into the oxides. The relative oxide PCA was measured using methylene blue degradation assays. CPTi and TAN oxides exhibited increased PCA compared to other alloys. Combined XRD and EBSD oxide phase analyses revealed an unfavorable arrangement of anatase and rutile phases near the outermost surfaces, which may have reduced PCA for other oxides. The relative Staphylococcus aureus attachment to each oxide was also assessed. The CPTi and TiMo-αβ oxides showed significantly reduced S. aureus attachment after 1 h of UVA compared to un-anodized CPTi. Cell culture results verified that the UVA irradiation did not negatively influence the MC3T3-E1 attachment or proliferation on the mixed-phase oxides.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Trends in Coatings and Surface Technology, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
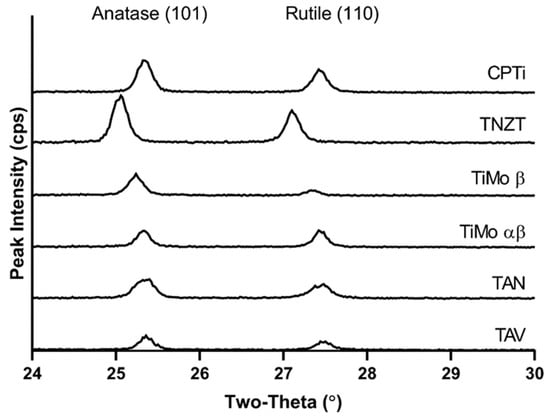
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Beam Mode on Hole Properties in Laser Processing
by
Tingzhong Zhang, Hui Li, Chengguang Zhang and Aili Zhang
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 594; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050594 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
The laser beam mode affects the power density distribution on the irradiated target, directly influencing the product quality in laser processing, especially the hole quality in laser drilling. The Gaussian beam shape, Mexican-Hat beam shape, Double-Hump beam shape, and Top-Hat beam shape are
[...] Read more.
The laser beam mode affects the power density distribution on the irradiated target, directly influencing the product quality in laser processing, especially the hole quality in laser drilling. The Gaussian beam shape, Mexican-Hat beam shape, Double-Hump beam shape, and Top-Hat beam shape are four typical laser beam modes used as a laser heat source and introduced into our proficient laser-drilling model, which involves complex physical phenomena such as heat and mass transfer, solid/liquid/gas phase changes, and two-phase flow. Simulations were conducted on an aluminum target, and the accuracy was verified using experimental data. The results of the simulations for the fundamental understanding of this laser–material interaction are presented in this paper; in particular, the hole shape, including the depth–diameter ratio and the angle of the cone, as well as spatter phenomena and, thus, the formed recast layer, are compared and analyzed in detail in this paper. This study can provide a reference for the optimization of the laser-drilling process, especially the selection of laser beam mode.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Development in Post-processing for Additive Manufacturing)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Determination of Fe3O4 Content and Total Nonhydraulic Minerals in Steel Slag
by
Xinkai Hou, Jiaoyang Sun, Xiangfeng Wang, Xiaoqi Fan and Ying Wang
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 593; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050593 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
The nonhydraulic minerals (Fe3O4, RO phase, Fe) in slag are important indicators for evaluating the pozzolanic activity and detecting the quality of the slag activation processing technology. Fe3O4 is an important characteristic mineral among the nonhydraulic
[...] Read more.
The nonhydraulic minerals (Fe3O4, RO phase, Fe) in slag are important indicators for evaluating the pozzolanic activity and detecting the quality of the slag activation processing technology. Fe3O4 is an important characteristic mineral among the nonhydraulic minerals. In order to accurately assess the pozzolanic activity of steel slag powder and to monitor the quality of the activation process of steel slag powder for separate nonhydraulic minerals, it is imperative to precisely determine the nonhydraulic mineral content within the steel slag. Further refinement and enhancement are required for both the HNO3 dissolution method used in determining Fe3O4 content in steel slag, as well as for the EDTA-DEA-TEA (ethylenediamine tetraacetate sodium-diethylamine-triethanolamine) dissolution method employed in determining total nonhydraulic minerals, due to potential deviations caused by challenging impurity separations. The results show that the content of Fe3O4 is determined by 10%HNO3-20%NaOH-chemical analysis method, which solves the problem that the impurities of refractory materials (quartz, corundum, mullite) and amorphous phase affects the content determination in HNO3 dissolution method. The total amount of nonhydraulic minerals (Fe3O4, RO phase, Fe) was determined by the EDTA-NaOH-TEA dissolution method, which solved the problem that the incomplete dissolution of C2F in the EDTA-DEA-TEA dissolution method affected the content determination. The maximum error between the content determination value and the theoretical calculation value of the two methods is less than 0.50%. The improved Fe3O4 and total nonhydraulic mineral quantification methods are feasible and reliable.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Laser-Assisted Processes and Thermal Treatments of Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
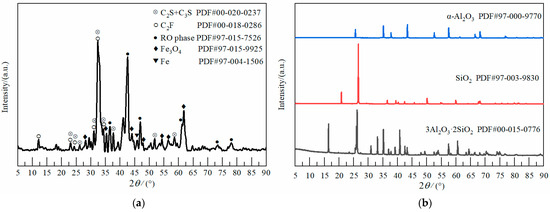
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dual-Function Hybrid Coatings Based on Polytetrafluoroethylene and Cu2O for Anti-Biocorrosion and Anti-Wear Applications
by
Guohui Li, Huan Li, Yongkun Xu, Ren He, Ga Zhang and Zongzhu Liu
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 592; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050592 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
Corrosion and wear issues of motion components exposed to water-based corrosion mediums, e.g., naval vessels and oil extraction equipment, pose challenges for the lifespan and reliability of the motion systems. In this work, epoxy-based coatings modified with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and cuprous oxide (Cu
[...] Read more.
Corrosion and wear issues of motion components exposed to water-based corrosion mediums, e.g., naval vessels and oil extraction equipment, pose challenges for the lifespan and reliability of the motion systems. In this work, epoxy-based coatings modified with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles were prepared. The anti-corrosion performance of the coatings was comparatively investigated by electrical impedance spectroscopy and Tafel tests in sterile and sulphate-reducing bacteria (SRB) mediums. Moreover, the tribological behaviors of the coatings were examined under water lubrication conditions. Our results demonstrate that the epoxy coatings lower significantly the corrosion current density icorr and the charge transfer resistance of the electrical double layer Rct of the carbon steel substrate. Interestingly, the hybrid coatings filled with both PTFE and Cu2O exhibit excellent anti-corrosion and anti-wear performance. After being immersed in the SRB medium for 18 days, the icorr of the pure EP coating and hybrid coatings are 1.10 × 10−7 Amp/cm2 and 0.3 × 10−7 Amp/cm2, and the Rct values are 1.04 × 103 Ω·cm2 and 3.87 × 103 Ω·cm2, respectively. A solid tribofilm forms on the stainless steel counterface sliding against the hybrid coating, which is surmised to be essential for the low friction coefficients and wear. The present work paves a route for formulating the dual-function coatings of anti-biocorrosion and anti-wear.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Tribological Behavior and Mechanical Performance of Coatings and Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Feasibility Analysis of Resource Application of Dry Flue Gas Desulfurization Ash in Asphalt Pavement Materials
by
Kai Li, Zhigang Zhou, Yinghui Zhang and Ronghua Ying
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 591; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050591 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
To verify the feasibility of applying dry flue gas desulfurization ash (DFGDA) to asphalt pavement materials, the asphalt mastic (filler and asphalt composition) prepared by adding different proportions of DFGDA and LSP (limestone powder) into 70# matrix asphalt was studied experimentally. The asphalt
[...] Read more.
To verify the feasibility of applying dry flue gas desulfurization ash (DFGDA) to asphalt pavement materials, the asphalt mastic (filler and asphalt composition) prepared by adding different proportions of DFGDA and LSP (limestone powder) into 70# matrix asphalt was studied experimentally. The asphalt mastics were subjected to the penetration test, the softening point test, and the ductility test. Moreover, the rheological properties of asphalt mastic were evaluated with dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) tests and bending beam rheometer (BBR) tests. An interaction ability index C-value based on the Palierne model was proposed to evaluate the interaction ability between DFGDA and asphalt. The influence of DFGDA asphalt on the interaction ability of matrix asphalt was observed and evaluated using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that with the increasing proportion of DFGDA, the penetration of asphalt mastic gradually decreased, the softening point increased, and the ductility slightly decreased. At the same temperature, the dynamic shear modulus G* of the asphalt mortar significantly increased with increasing DFGDA content. The incorporation of DFGDA negatively affected the low-temperature plastic deformation resistance of asphalt, but the impact was weakened with the growing DFGDA amount and the powder mastic ratio. The combination mode of DFGDA and matrix asphalt depends on the physical blending, and their interaction ability mainly depends on the miscibility between DFGDA and matrix asphalt. In conclusion, DFGDA can be utilized as a novel filler in asphalt pavement materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Cleaner Materials for Pavements)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evolution of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Biomedical Ti-20Zr-40Ta Alloy during Aging Treatment
by
Xueqing Wu, Kun Yang, Jun Cheng and Jianguo Lin
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 590; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050590 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
The research focus in the field of medical titanium alloys has recently shifted towards the development of low-modulus and high-strength titanium alloys. In this study, the influence of aging temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a β-type Ti-20Zr-40Ta alloy (TZT) was
[...] Read more.
The research focus in the field of medical titanium alloys has recently shifted towards the development of low-modulus and high-strength titanium alloys. In this study, the influence of aging temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a β-type Ti-20Zr-40Ta alloy (TZT) was investigated. It was found that the recovery and the recrystallization occurred in the as-rolled alloy depended on the aging temperature. The periodically distributed Ta-lean phase (β1) and Ta-rich phase (β2) were produced by the spinodal decomposition in all the samples aged at different temperatures. The spinodal decomposition significantly influenced the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of the TZT alloy. Upon aging at 650 °C and 750 °C, the as-rolled alloy exhibited a double-yield phenomenon during tensile testing, indicating a stress-induced martensitic transformation; however, its ductility was limited due to the presence of ω phases. Conversely, aging at 850 °C resulted in an alloy with high strength and good ductility, which was potentially attributed to the enhanced strength resulting from modulated structures introduced with spinodal decomposition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances of Ceramic and Alloy Coatings, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Improved Ability to Resist Corrosion of Selective-Laser-Melted Stainless Steel Based on Microstructure and Passivation Film Characteristics
by
Huimin Tao, Yafang Cai, Zeqi Tong, Yong Huang and Mingming Ding
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 589; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050589 - 9 May 2024
Abstract
The local corrosion resistance of forging and selective laser melting (SLM) 304 steels was explored by intergranular corrosion analysis, double-loop electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation, dynamic polarization experimentation, structural analysis, and passivation film characteristics analysis. The ability to resist sensitization of SLM 304 steel is
[...] Read more.
The local corrosion resistance of forging and selective laser melting (SLM) 304 steels was explored by intergranular corrosion analysis, double-loop electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation, dynamic polarization experimentation, structural analysis, and passivation film characteristics analysis. The ability to resist sensitization of SLM 304 steel is greater than that of forging 304 steel at a temperature of 650 °C for 9 h. Moreover, the pit corrosion resistance of forging and SLM 304 steels is weakened by sensitization, while the pit corrosion resistance of SLM 304 steel is much greater than that of forging steel. Therefore, SLM technology can improve the ability to resist sensitization and pit corrosion of 304 steel. Analysis showed that the ability to resist corrosion of the passivation film of SLM 304 steel is greater than that of forging steel. In addition, corrosion pits are easier to generate at the interface of forging steel and SLM 304 steel. The grain boundary corrosion of SLM 304 steel intensified while the corrosion of the melt pool boundaries weakened after the sensitization treatment, resulting in a decrease in pit corrosion resistance. The coupling effect of these different structures and passivation films decides the pit and sensitization resistance of forging and SLM 304 steels. Clarifying the corrosion mechanism of forging and SLM steels is of great significance for scientific research and the widespread use of SLM technology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Manufacturing and Surface Engineering IV)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Corrosion Behavior of Al2O3-40TiO2 Coating Deposited on 20MnNiMo Steel via Atmospheric Plasma Spraying in Hydrogen Sulfide Seawater Stress Environments
by
Xian Zeng, Xiangxiang Chen, Yongjun Wang, Hao Zhang, Qian Cao and Xudong Cheng
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 588; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050588 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
In this study, an Al2O3-40TiO2 coating was deposited on 20MnNiMo steel via atmospheric plasma spraying. The corrosion behavior of the coating was investigated in both artificial seawater and a simulated environment with hydrogen sulfide and high pressure. Additionally,
[...] Read more.
In this study, an Al2O3-40TiO2 coating was deposited on 20MnNiMo steel via atmospheric plasma spraying. The corrosion behavior of the coating was investigated in both artificial seawater and a simulated environment with hydrogen sulfide and high pressure. Additionally, ion dissolution experiments were conducted to evaluate the coating’s bio-friendliness. In artificial seawater, the corrosion rate (based on the corrosion current) of the Al2O3-40TiO2 coating initially decreased before increasing. It was speculated that the blocking of corrosion products in the defect channels was helpful in delaying the progress of corrosion in the early stage. The coating had a corrosion current on the order of 10−6 A/cm2 in artificial seawater, suggesting good protection in conventional seawater environments. In the simulated environment, the corrosion rate (based on the weight loss) of the Al2O3-40TiO2 coating showed a continuously declining trend. It was deduced that, unlike corrosion products in artificial seawater, the corrosion products in the simulated environment (e.g., metal sulfide) might be more chemically stable, leading to a longer blocking effect. Therefore, a minimal corrosion rate of 0.0030 mm/a was obtained after the coating was immersed for 30 days. The amount of dissolved coated elements was negligible and there were only small amounts of dissolved non-coated elements such as Ni and Mo. The developed coating can be considered to be highly biofriendly if the non-coated area of the specimen is well sealed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Corrosion and Anticorrosion of Alloys/Metals)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preparation of a Consolidation Material of Organosilica-Modified Acrylate Emulsion for Earthen Sites and the Evaluation of Its Effectiveness
by
Xin Du, Qian Wu, Gui Fu, Qingwen Ma, Guopeng Shen and Hua Li
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 587; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050587 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
In this paper, a new consolidation material for earthen sites with silicone-modified acrylic emulsion was synthesized and applied to the consolidation test of soil samples of the site. The effectiveness was tested through the properties of soil samples on the changes in weight,
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a new consolidation material for earthen sites with silicone-modified acrylic emulsion was synthesized and applied to the consolidation test of soil samples of the site. The effectiveness was tested through the properties of soil samples on the changes in weight, color, permeability test, air permeability, hydrolysis resistance, water resistance, and salt resistance. The results show that the samples treated with the new material have an outstanding effect on hydrolysis resistance, water resistance, and salt resistance without the change in color and gas permeability. After being soaked in Na2SO4 and sodium chloride solution for half a month, the reinforced soil sample did not crack, and it could undergo 15 days of water resistance test and five cycles of sodium sulfate resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Multifunctional Polymer Coatings and Films: Exploring Innovations Across Industries)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Preparation and Properties of Environmentally Friendly, Hydrophobic, Corrosion-Resistant, Multifunctional Composite Coatings
by
Zhenhua Chu, Zhixin Zhang, Wan Tang, Jiahao Lu and Jingxiang Xu
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 586; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050586 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
With the continuous exploitation of the marine resources, the equipment should meet the marine complex working environment. In this study, a type of environmentally friendly coating was prepared. Based on low surface energy environmental protection and anti-fouling, a film forming material with water-based
[...] Read more.
With the continuous exploitation of the marine resources, the equipment should meet the marine complex working environment. In this study, a type of environmentally friendly coating was prepared. Based on low surface energy environmental protection and anti-fouling, a film forming material with water-based epoxy-modified silicone resin emulsion was prepared. And industrial fillers were added to give it both inorganic and organic properties. Meanwhile, various contents of graphene oxide (GO) were added in the coating system. The coating properties were comprehensively analyzed, and the optimal GO content was obtained as 0.1 wt. %. The composite coating was studied by seawater immersion experiments, and the failure process of the coating in was proposed. The composite coating prepared in the present study has both environmental protection and hydrophobic anti-fouling characteristics, and its comprehensive performance is excellent through various performance evaluations, i.e., it meets the requirements of long-term coating, environmental friendliness and anti-fouling and corrosion resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Alloys and Composites Corrosion and Mechanical Properties)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Selection of Crosslinking Agents for Acrylic Resin Used in External Coatings for Aluminum Packaging in the Beverage Industry
by
Michelli Santarelli, Baltus Cornelius Bonse and Joao Guilherme Rocha Poço
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 585; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050585 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
Paints and coatings are widely used in various applications such as walls, cars, packaging, and food products. The quality of food packaging is essential due to its direct or indirect contact with food. The demand for high-quality food packaging is increasing due to
[...] Read more.
Paints and coatings are widely used in various applications such as walls, cars, packaging, and food products. The quality of food packaging is essential due to its direct or indirect contact with food. The demand for high-quality food packaging is increasing due to the higher production and consumption rates. However, containers used in the beverage industry often face problems like scratches and abrasions during transportation. This study aimed to investigate different formulations of external coatings for beverage cans to improve their physical resistance properties and prevent corrosion and surface damage problems. The study involved reacting an acrylic resin with six different amino resins, including methylated melamine, butylated melamine, glycoluril, methylated urea, butylated urea, and benzoguanamine, in various proportions. The results of 25 formulated samples were compared based on properties such as adhesion, durability, and chemical resistance. The outcomes of the study showed significant differences among the crosslinking agents. Among all the crosslinking agents, methylated melamine showed the most favorable results in the analyses, proving to be effective in almost all tests.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Advances in Food Contact Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preparation and Capacitive Properties of Ni-Doped Zinc Cobaltate/Carbon Fiber Composite Porous Mesh Materials
by
Donghua Chen, Yang Liu, Jun Wang, Tenghao Ma, Hui Zhi, Wei Xiao, Yabin Wang and Jing Wang
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 584; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050584 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
Nickel-element-doped zinc cobaltate/carbon fiber composites (Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF) were prepared on carbon cloth (made of a combination of carbon fibers) conductive substrates using a simple ambient stirring method combined with heat treatment. Characterization tests of the materials revealed that the prepared
[...] Read more.
Nickel-element-doped zinc cobaltate/carbon fiber composites (Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF) were prepared on carbon cloth (made of a combination of carbon fibers) conductive substrates using a simple ambient stirring method combined with heat treatment. Characterization tests of the materials revealed that the prepared products were porous Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF mesh structures. This porous network structure increases the surface area of the material and helps shorten the diffusion path of ions and electrons. The samples were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods to investigate the effect of Ni elemental doping on the stability of the materials. The results show that there are no other impurity peaks and no other impurity elements in the Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF electrode material, which indicates that the sample purity is high. Meanwhile, the electrochemical properties of Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF electrode materials were studied. Under the condition of 15 A·g−1, the specific capacitance of Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF electrode material is 1470 F·g−1, and after 100 cycles, its specific capacity reaches 1456 F·g−1, which is 99.0% of the specific capacity of 1470 F·g−1, indicating that the electrode material has good stability. In addition, we assembled asymmetric supercapacitors (Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF//CNTs) with Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF as the positive material and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as the negative material. In the cyclic stability experiment of Ni-ZnCo2O4/CF/CNTs devices, when the current density was 1 A·g−1, the specific capacitance was 182 F·g−1. After 10,000 cyclic charge–discharge tests, the specific capacity became 167 F·g−1, which was basically unchanged compared with the initial specific capacity, reaching 91.8%. It shows that it has higher charge–discharge performance and higher cycle stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Surface Modification of Advanced Transition Metal-Based Materials for Electrochemical Energy Storage)
►▼
Show Figures
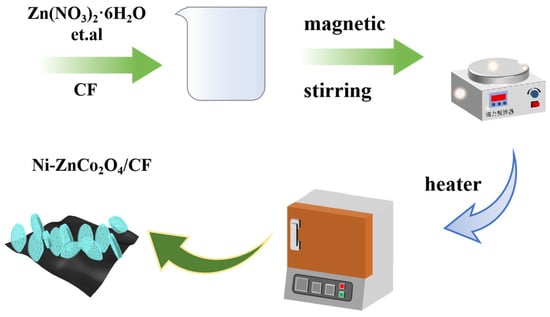
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Surface Wear Monitoring System of Industrial Transformer Tap-Changer Contacts by Using Voice Signal
by
Xiangyu Tan, Fangrong Zhou, Wenyun Li, Gang Ao, Xiaowei Xu and Le Yang
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 583; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050583 - 8 May 2024
Abstract
Surface wear of the tap-changer contacts of industrial transformers (due to frequent switching times) easily leads to operation failure of industrial transformers, which affects the safety and stability of the transmission network. In this paper, an intelligent voice signal monitoring system was proposed
[...] Read more.
Surface wear of the tap-changer contacts of industrial transformers (due to frequent switching times) easily leads to operation failure of industrial transformers, which affects the safety and stability of the transmission network. In this paper, an intelligent voice signal monitoring system was proposed for the abnormal condition (surface wear) of tap-changer contacts. This monitoring system was composed of a voice signal acquisition system, voice analysis system and voice processing system. First, the voice signal of the tap-changer contacts was collected, and the collected voice signal was analyzed in the time domain and the frequency domain. Secondly, the characteristic curve of the voice signal was proposed, and the voice curve was compared with that of the normal operation state. In this case, the running state and surface wear abnormal situation of the tap changer could be monitored and determined, and the cause of the abnormal state could also be further analyzed. This method solved the surface wear problem of the tap changer in industrial transformers, which could be not monitored effectively in real time. This method improved the operational reliability of industrial transformers and had high economic and social benefits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Trends and Advances in Anti-wear Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thermal-Mechanical Coupling Analysis of Permeable Asphalt Pavements
by
Yuekun Li, Xulong Wang, Hailong Zhang, Zhenxia Li and Tengteng Guo
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 582; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050582 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
In order to clarify the mechanical response of permeable asphalt pavements under a temperature effect, the mechanical responses of different types of permeable asphalt pavements, which were based on a self-developed drainage SBS-modified asphalt mixture with fiber, were simulated using ANSYS finite element
[...] Read more.
In order to clarify the mechanical response of permeable asphalt pavements under a temperature effect, the mechanical responses of different types of permeable asphalt pavements, which were based on a self-developed drainage SBS-modified asphalt mixture with fiber, were simulated using ANSYS finite element software(APDL 19.2). The influence of temperature and temperature change on the mechanical behavior of the permeable asphalt pavements was studied, and the mechanical responses of the pavements at different driving speeds was analyzed. The results show that the extreme values of surface deflection, compressive strain of the soil foundation top surface, and the shear stress and tensile stress of the upper-layer bottom of the three kinds of pavements under dynamic load were about 10% smaller than those under static loads, and the extreme values under different temperature conditions were 28%~50% larger than the values obtained without different temperature conditions. During the 12 h heating process, the mechanical indexes of the three types of pavements with axle loads were consistent with the change law of temperature, and the peak values of the mechanical indexes under dynamic loads were smaller than those under static loads. In addition, the mechanical indexes of the three types of pavements under dynamic loads had the same law of change with speed under the same conditions, and the values were less than the extreme values under static loads, but the degree of influence was different.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Asphalt Materials—Surface Engineering and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
First Results of Nb3Sn Coated Cavity by Vapor Diffusion Method at SARI
by
Qixin Chen, Yue Zong, Zheng Wang, Shuai Xing, Jiani Wu, Pengcheng Dong, Miyimin Zhao, Xiaowei Wu, Jian Rong and Jinfang Chen
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 581; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050581 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Nb3Sn is emerging as one of the focal points in superconducting radio frequency (SRF) research, owing to its excellent superconducting properties. These properties hold significant possibilities for cost reduction and the miniaturization of accelerators. In this paper, we report the recent
[...] Read more.
Nb3Sn is emerging as one of the focal points in superconducting radio frequency (SRF) research, owing to its excellent superconducting properties. These properties hold significant possibilities for cost reduction and the miniaturization of accelerators. In this paper, we report the recent efforts of the Shanghai Advanced Research Institute (SARI) in fabricating high-performance Nb3Sn superconducting cavities using the vapor diffusion method. This includes the construction of a Nb3Sn coating system with dual evaporators and the test results of 1.3 GHz single-cell coated cavities. The coated samples were characterized, and the growth state of the Nb3Sn films was analyzed. The first coated superconducting cavity was tested at both 4.4 K and 2 K, with different cooldown rates passing through the Nb3Sn critical temperatures. The causes of Sn droplet spot defect formation on the surface of the first cavity were analyzed, and such defects were eliminated in the coating of the second cavity by controlling the evaporation rate. This study provides a reference for the preparation of high-performance Nb3Sn-coated cavities using the vapor diffusion method, including the setup of the coating system, the comprehension of the vapor diffusion process, and the test conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Surface Characterization, Deposition and Modification)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Corrosion Inhibition Behavior and Mechanism of 1-Hydroxy-1,1-ethyledine Disodium Phosphonate under an Iron Bacteria System
by
Ping Xu, Yuxuan Zhao and Pengkai Bai
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 580; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050580 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Regenerated water serves as a supplementary source for circulating cooling water systems, but it often fosters microbial growth within pipelines. Given its widespread use as a corrosion inhibitor, understanding HEDP’s efficacy in microbial environments and its impact on microorganisms is imperative. This study
[...] Read more.
Regenerated water serves as a supplementary source for circulating cooling water systems, but it often fosters microbial growth within pipelines. Given its widespread use as a corrosion inhibitor, understanding HEDP’s efficacy in microbial environments and its impact on microorganisms is imperative. This study established an iron bacterial system by isolating and enriching iron bacteria. Through a comprehensive approach incorporating corrosion weight loss analysis, XPS analysis, SEM electron microscopy, as well as microbial and electrochemical testing, the corrosion inhibition behavior and mechanism of HEDP within the iron bacterial system were investigated. The findings reveal that within the iron bacterial system, HEDP achieves a corrosion inhibition rate of 76% following four distinct stages—weakening, strengthening, stabilizing, and further strengthening—underscoring its robust corrosion inhibition capability. Moreover, HEDP enhances the density of biofilms and elevates the activation energy of carbon steel interfaces. It alternates with oxygen to continuously suppress the activity of IRB while gradually inhibiting the activity of IOB. This process culminates in a corrosion inhibition mechanism where cathodic inhibition predominates, supported by anodic inhibition as a complementary mechanism.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Corrosion/Wear Mechanisms and Protective Methods)
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Selected Parameters of Zinc Electroplating on Surface Quality and Layer Thickness
by
Jozef Mascenik, Tomas Coranic, Jiri Kuchar and Zdenek Hazdra
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 579; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050579 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
Surface treatment technologies are pivotal across diverse industrial sectors such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and the automotive industry. Continuous advancements in manufacturing processes are geared towards bolstering efficiency and attaining superior product quality. This study aimed to empirically compare practical outcomes with
[...] Read more.
Surface treatment technologies are pivotal across diverse industrial sectors such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and the automotive industry. Continuous advancements in manufacturing processes are geared towards bolstering efficiency and attaining superior product quality. This study aimed to empirically compare practical outcomes with theoretical insights. Employing galvanic zinc plating under constant voltage with varying plating durations unveiled a correlation between coating thickness and electrolyte composition alongside plating duration. The graphical representation delineated the optimal electrolyte composition conducive to maximal coating thickness. Notably, an evident decrease in leveling ability was noted with prolonged plating durations. The experiment corroborated the notion that theoretical formulas for coating thickness estimation possess limited accuracy, often resulting in measured values surpassing theoretical predictions. These findings underscore the imperative for refined theoretical models to comprehensively grasp galvanic surface treatment processes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Electrodeposited Composite Coatings: Diversity, Applications and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring TMA and H2O Flow Rate Effects on Al2O3 Thin Film Deposition by Thermal ALD: Insights from Zero-Dimensional Modeling
by
Júlia Karnopp, Nilton Azevedo Neto, Thaís Vieira, Mariana Fraga, Argemiro da Silva Sobrinho, Julio Sagás and Rodrigo Pessoa
Coatings 2024, 14(5), 578; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050578 - 7 May 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the impact of vapour-phase precursor flow rates—specifically those of trimethylaluminum (TMA) and deionized water (H2O)—on the deposition of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) thin films through atomic layer deposition (ALD). It explores how these flow rates
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the impact of vapour-phase precursor flow rates—specifically those of trimethylaluminum (TMA) and deionized water (H2O)—on the deposition of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) thin films through atomic layer deposition (ALD). It explores how these flow rates influence film growth kinetics and surface reactions, which are critical components of the ALD process. The research combines experimental techniques with a zero-dimensional theoretical model, designed specifically to simulate the deposition dynamics. This model integrates factors such as surface reactions and gas partial pressures within the ALD chamber. Experimentally, Al2O3 films were deposited at varied TMA and H2O flow rates, with system conductance guiding these rates across different temperature settings. Film properties were rigorously assessed using optical reflectance methods and attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy. The experimental findings revealed a pronounced correlation between precursor flow rates and film growth. Specifically, at 150 °C, film thickness reached saturation at a TMA flow rate of 60 sccm, while at 200 °C, thickness peaked and then declined with increasing TMA flow above this rate. Notably, higher temperatures generally resulted in thinner films due to increased desorption rates, whereas higher water flow rates consistently produced thicker films, emphasizing the critical role of water vapour in facilitating surface reactions. This integrative approach not only deepens the understanding of deposition mechanics, particularly highlighting how variations in precursor flow rates distinctly affect the process, but also significantly advances operational parameters for ALD. These insights are invaluable for enhancing the application of ALD technologies across diverse sectors, including microelectronics, photovoltaics, and biomedical coatings, effectively bridging the gap between theoretical predictions and empirical results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Films/Coatings Processing Technologies: Deposition and Process)
►▼
Show Figures
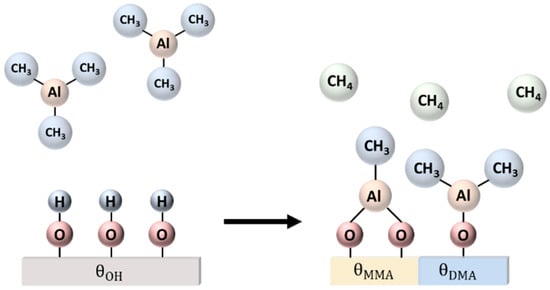
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Coatings Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Batteries, C, Coatings, Energies, Nanomaterials
Advances in Low-Dimensional Materials (LDMs) for Energy Conversion and Storage
Topic Editors: In Soo Kim, Jin Gu KangDeadline: 15 May 2024
Topic in
Coatings, Materials, Metals, JMMP, Machines
Development of Friction Stir Welding and Processing
Topic Editors: Yongxian Huang, Li Zhou, Xiangchen Meng, Yuming XieDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Catalysts, Coatings, Crystals, Energies, Materials, Nanomaterials
Interfacial Bonding Design and Applications in Structural and Functional Materials
Topic Editors: Junlei Qi, Pengcheng Wang, Yaotian YanDeadline: 20 July 2024
Topic in
Coatings, CMD, Materials, Metals, Molecules
Corrosion and Protection of Metallic Materials, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Sebastian Feliú, Jr., Federico R. García-Galván, Lucien VelevaDeadline: 31 July 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Coatings
Surface Treatment for Alloys
Guest Editors: Leszek Klimek, Bartlomiej JanuszewiczDeadline: 10 May 2024
Special Issue in
Coatings
Progresses and Challenges in Experimental Characterization of Coatings
Guest Editors: Giovanni Pappalettera, Claudia BarileDeadline: 15 May 2024
Special Issue in
Coatings
Advances in Deposition and Characterization of Hard Coatings
Guest Editors: Ľubomír Čaplovič, Martin SahulDeadline: 30 May 2024
Special Issue in
Coatings
Effective Coating Barriers for Protection of Reinforced Concrete
Guest Editors: Junjie Wang, Hongwei LinDeadline: 22 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Feature Paper Collection in Plasma Coatings, Surfaces & Interfaces
Collection Editors: Qi Hua Fan, Bocong Zheng
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Surface and Interface Science and Engineering for the Society of the Future
Collection Editor: Alessandro Lavacchi
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Feature Paper Collection in Surface Characterization, Deposition and Modification
Collection Editor: Georgios Skordaris
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Feature Paper Collection in 'Surface Coatings for Biomedicine and Bioengineering'
Collection Editor: Anton Ficai