- Article
An Improved DTC Scheme Based on Common-Mode Voltage Reduction for Three Level NPC Inverter in Induction Motor Drive Applications
- Salma Jnayah,
- Zouhaira Ben Mahmoud and
- Adel Khedher
- + 1 author
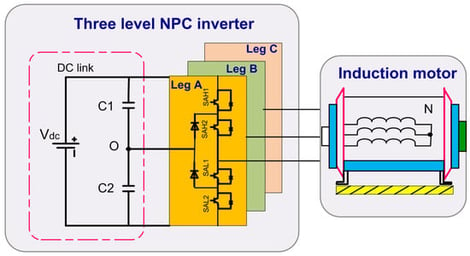
Common-mode voltage (CMV) is a critical concern in motor drive applications employing multilevel inverters, as it can lead to significant issues such as high-frequency noise, electromagnetic interference, and motor bearing degradation. These effects can compromise the reliability, reduce the operational lifespan of electric machines, and introduce safety hazards. In this study, an enhanced Direct Torque Control (DTC) strategy incorporating Space Vector Modulation (SVM) is proposed to specifically address CMV-related challenges in induction motors (IM) driven by a three-level Neutral-Point-Clamped (NPC) inverter. The proposed DTC scheme utilizes a specialized modulation technique that effectively mitigates CMV while also minimizing current harmonic content, and torque and flux ripples with a constant switching frequency. The developed SVM algorithm simplifies the three-level space vector representation into six equivalent two-level diagrams, enabling more efficient control. The zero-voltage vector is synthesized virtually by combining two active vectors within a two-level hexagonal structure. The effectiveness of the proposed DTC approach is validated through both simulation and Hardware-In-the-Loop (HIL) testing. Compared to the conventional DTC method, the proposed solution demonstrates superior performance in CMV minimization and leakage current reduction. Notably, it limits the CMV amplitude to Vdc/6, a significant improvement over the Vdc/2 typically observed with the standard DTC approach.
13 February 2026