Journal Description
AppliedChem
AppliedChem
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of applied chemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review and reviewer names are published annually in the journal.
- AppliedChem is a companion journal of Applied Sciences.
Latest Articles
Hydrothermal Synthesis of FAU-Type Zeolite NaX Using Ladle Slag and Waste Aluminum Cans
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010012 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study explores a sustainable synthesis route for FAU-type zeolite X using acid-treated ladle slag as a silicon source and waste aluminum cans as an alternative aluminum precursor. Conventional zeolite synthesis relies on high-purity reagents, which are costly and environmentally intensive to produce.
[...] Read more.
This study explores a sustainable synthesis route for FAU-type zeolite X using acid-treated ladle slag as a silicon source and waste aluminum cans as an alternative aluminum precursor. Conventional zeolite synthesis relies on high-purity reagents, which are costly and environmentally intensive to produce. Previous research has rarely addressed the valorization of ladle slag and metallic aluminum waste for zeolite formation, leaving their potential largely unexplored. The study focuses on the effective utilization of industrial and post-consumer wastes—acid-treated ladle slag and aluminum cans—as precursors for FAU-type NaX zeolite, demonstrating their feasibility as alternative silicon and aluminum sources. Here, zeolite X was synthesized hydrothermally from treated slag combined with either dissolved aluminum cans and commercial sodium aluminate at 90 °C for 6 h. FAU-type zeolite X was successfully synthesized using both aluminum sources, with a SiO2/Al2O3 ratio of approximately 1.4. The results demonstrate that waste-derived precursors can effectively replace conventional chemicals, yielding predominantly NaX zeolite with high crystallinity and minor NaA impurity (as observed by XRD), with experimental yields of 1.47 g for aluminum cans and 1.266 g for sodium aluminate. The obtained zeolite X samples were structurally and texturally characterized by XRD, FTIR, XRF, BET surface area analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis (TG).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in AppliedChem, 2nd Edition)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Lavender Paper: A Sustainable Alternative for Pulp Production
by
Kateřina Hájková, Josef Bárta, Tomáš Holeček, Michaela Filipi and Jiří Synek
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010011 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This research investigates the potential of secondary lavender biomass (Lavandula officinalis) as a raw material for paper production within the context of the circular economy and its practical applications. Lavender stems, a by-product of essential oil extraction, were processed using the
[...] Read more.
This research investigates the potential of secondary lavender biomass (Lavandula officinalis) as a raw material for paper production within the context of the circular economy and its practical applications. Lavender stems, a by-product of essential oil extraction, were processed using the nitrate–alkali pulping method. The chemical composition of the raw material was analysed according to TAPPI standards, and the resulting pulp was characterised in terms of its mechanical and physical properties, including tensile strength and air permeability. Lavender stems contained 29.43% cellulose and 24.10% lignin, indicating moderate delignification efficiency under the applied conditions. The pulp yield was 24.2% with a Kappa number of 15.9. Of the prepared sheets, the paper with a weight of 80 g·m−2 showed the best mechanical properties, with a breaking length of 1.71 km and a tensile strength index of 16.76 N·m·g−1. In addition, lavender-based paper demonstrated measurable repellent activity against Tineola bisselliella, reducing insect presence by 70% compared to control samples, as determined by controlled laboratory exposure tests. This bioactivity is attributed to residual volatile compounds such as linalool and linalyl acetate, originating from lavender biomass. Overall, lavender secondary biomass represents a promising non-wood fibre for the production of biodegradable, functional paper materials that combine structural integrity with natural repellent properties.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Selection of Optimal Drying and Grinding Techniques to Maximize Polyphenol Yield from Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Powder Extracts
by
Tea Bilušić, Zoran Zorić, Ivana Šola, Zvonimir Marijanović, Marita Hvizdak, Kristijan Čalić, Ivana Bočina, Zdenka Pelaić, Danica Sinovčić and Marija Ćosić
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010010 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
This study investigated the influence of drying techniques such as convection hot-air drying, vacuum drying, and freeze drying with slow and flash pre-freezing on the total phenolic content and the profile of dominant phenolic compounds in cultivated blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Although
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the influence of drying techniques such as convection hot-air drying, vacuum drying, and freeze drying with slow and flash pre-freezing on the total phenolic content and the profile of dominant phenolic compounds in cultivated blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Although fresh blueberries exhibited higher total phenolic content (1350.85 mg GAE/100 g), total flavonol glycosides (66.20 mg/100 g), and total anthocyanins (218.23 mg/100 g) compared with dried samples, freeze-dried samples, particularly those subjected to flash pre-freezing, retained higher contents of these components in the dried material compared to other drying techniques. This could be attributed to the microstructural preservation of plant tissue during freeze drying. Furthermore, the study demonstrated that subsequent milling of freeze-dried samples, whether using a knife mill or a ball mill, also affects the availability of bioactive compounds in freeze-dried blueberry powders. The combination of flash pre-freezing followed by ball milling yielded the highest availability of bioactive components in the processed blueberry powder.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Women’s Special Issue Series: AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Decolorization and Mineralization of Acid Violet 19 Dye by Potassium Ferrate (VI)
by
Bimo Tri Goutomo, Seong Yeop Han, Dian Majid and Il-Kyu Kim
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010009 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
Acid violet 19 (AV19) dye is used in many fields, including photographic film, inks, leather, and textiles. Potassium ferrate (VI) (Fe(VI)) represents a novel oxidant, notable for its strong oxidative capabilities, stability, and environmental sustainability. This research investigates the decolorization and mineralization of
[...] Read more.
Acid violet 19 (AV19) dye is used in many fields, including photographic film, inks, leather, and textiles. Potassium ferrate (VI) (Fe(VI)) represents a novel oxidant, notable for its strong oxidative capabilities, stability, and environmental sustainability. This research investigates the decolorization and mineralization of AV19 through the application of Fe(VI), with a particular emphasis on essential parameters, including pH, molar ratios, and temperature variations. The study ascertained that the optimal conditions for AV19 oxidation are a pH of 7.0, a molar ratio of AV19: Fe(VI) of 1:5, and a temperature of 45 °C with a reaction time of 12 min. The decolorization efficiency achieved was approximately 98%, and the mineralization was 31%. The degradation process yielded intermediates, such as sulfonic acid derivatives, benzoic acid, benzene, and cyclohexane compounds, which were further oxidized into acetic acid, carbon dioxide, and water. Comprehensive computational toxicity evaluations confirmed that both the intermediates and the final products are non-toxic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analytical Chemistry: Fundamentals, Current and Future Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effective Removal of Geosmin from Aqueous Solution Using Bentonite–Alginate–Magnetic Composite
by
Iresha Lakmali Balasooriya and Mudalige Don Hiranya Jayasanka Senavirathna
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010008 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Geosmin contamination in water is a worldwide concern, owing to its strong odor at trace levels and limited removal by typical water treatment methods. In this study, bentonite–alginate–magnetic (Bent-alg-mag) beads were prepared using the ionic gelation method for the removal of
[...] Read more.
Geosmin contamination in water is a worldwide concern, owing to its strong odor at trace levels and limited removal by typical water treatment methods. In this study, bentonite–alginate–magnetic (Bent-alg-mag) beads were prepared using the ionic gelation method for the removal of geosmin from aqueous solutions. The adsorbent’s physicochemical properties were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. The influence of factors such as contact time, solution pH, initial geosmin concentration, and adsorbent dosage on adsorption performance was systematically investigated. Under optimal conditions, over 96% of geosmin was removed within 480 min. The adsorption kinetics were best described by the pseudo-first-order model (R2 = 0.9918), indicating that the process is primarily controlled by surface adsorption. Adsorption equilibrium data were well fitted by the Langmuir isotherm model (R2 = 0.9705) and a maximum monolayer capacity of 16.064 ng/g. The adsorbent exhibited 70% removal efficiency after three adsorption–desorption cycles, showing good regeneration potential, though long-term stability may be limited. Overall, the Bent-alg-mag beads proved to be an effective and promising material for the removal of geosmin from water.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Photocatalytic Degradation of Ibuprofen Using Se-Doped SnO2 Nanoparticles Under UV–Visible Irradiation
by
Luis Alamo-Nole and Cristhian Castro-Cedeño
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010007 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing presence of pharmaceutical residues such as ibuprofen in aquatic environments represents a growing concern due to their persistence and limited biodegradability. In this study, selenium-doped tin oxide (SnO2:Se) nanoparticles covered with glycerol were synthesized via a microwave-assisted method to
[...] Read more.
The increasing presence of pharmaceutical residues such as ibuprofen in aquatic environments represents a growing concern due to their persistence and limited biodegradability. In this study, selenium-doped tin oxide (SnO2:Se) nanoparticles covered with glycerol were synthesized via a microwave-assisted method to evaluate their photocatalytic performance in the degradation of ibuprofen under ultraviolet (UV) and visible light. Optimal synthesis parameters were determined at pH 7.5–8.0 and 130 °C, yielding stable, dark-brown colloidal suspensions. HRTEM analysis revealed a coexistence of one-dimensional (1D) nanowires and zero-dimensional (0D) quantum dots, confirming nanoscale morphology with crystallite sizes between 8 and 100 nm. EDS analysis confirmed the presence of Sn, O, and trace Se (0.1 wt%), indicating Se incorporation as a dopant. UV–Vis spectroscopy showed strong absorption near 324 nm and slight band-gap narrowing in the Se-doped samples, suggesting enhanced visible-light responsiveness. Photocatalytic experiments demonstrated an ibuprofen degradation efficiency of ~60% under visible light and 80% under UV irradiation with aeration, compared to only 5% removal using commercial SnO2. The enhanced performance was attributed to Se-induced band-gap modulation, effective charge-carrier separation, and singlet oxygen generation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Short-Term Olive Fruit Storage Conditions on the Quality of Virgin Olive Oil: A Case Study of Three Cultivars (‘Kalinjot’, ‘Leccino’, and ‘Frantoio’) in Albania
by
Onejda Kyçyk, Angjelina Vuksani, Gjoke Vuksani, Florina Pazari and Tokli Thomaj
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010006 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study examined the influence of short-term olive fruit storage on the quality of virgin olive oil (VOO) from three cultivars (‘Kalinjot’, ‘Leccino’, and ‘Frantoio’) grown in southwest Albania. Olive fruits were processed immediately after harvest, or after 10 days of storage under
[...] Read more.
This study examined the influence of short-term olive fruit storage on the quality of virgin olive oil (VOO) from three cultivars (‘Kalinjot’, ‘Leccino’, and ‘Frantoio’) grown in southwest Albania. Olive fruits were processed immediately after harvest, or after 10 days of storage under ambient conditions (20–22 °C) and refrigeration (5 °C). Oils were evaluated for physicochemical quality parameters (free acidity, peroxide value, and UV absorption indices), as well as bioactive and sensory-related compounds (bitterness index, chlorophylls, carotenoids, and total phenolic content). Results showed that immediate processing yielded the highest quality oils, with low free acidity (0.28–0.35%) and preserved bioactive compounds. Ambient storage led to marked deterioration, including significant increases in free acidity and peroxide values, loss of pigments, and 20–70% reduction in phenolic content, accompanied by decreased bitterness. In contrast, cold storage mitigated these effects, maintaining values closer to baseline and preserving sensory and functional attributes. ANOVA confirmed significant effects of storage duration, temperature, and cultivar on most parameters, with ‘Kalinjot’ exhibiting greater stability compared to ‘Frantoio’ and ‘Lecino’. These findings highlight that minimizing the interval between harvest and milling is critical for ensuring oil quality, while refrigerated storage offers a practical strategy to safeguard chemical and sensory characteristics when immediate processing is not feasible.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Enthalpy of Formation of Acetylenes and Aromatic Nitro Compounds for a Group Contribution Method with “Chemical Accuracy”
by
Robert J. Meier and Paul R. Rablen
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010005 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
In this paper we provide the Group Contribution parameters for acetylenes and aromatic nitro compounds fitting with a recently developed Group Contribution method with chemical accuracy (1 kcal/mol) for the heat of formation of organics. These additional parameters widen the applicability of the
[...] Read more.
In this paper we provide the Group Contribution parameters for acetylenes and aromatic nitro compounds fitting with a recently developed Group Contribution method with chemical accuracy (1 kcal/mol) for the heat of formation of organics. These additional parameters widen the applicability of the Group Contribution method. We also provide further G4 quantum calculated values as reference when no experimental data are available and compare to previously reported G4 data.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Nutritional Value and Bioactive Lipid Constituents in Seeds of Phaseolus Bean Cultivated in Bulgaria
by
Ginka Antova, Tsvetelina Stoilova and Petar Chavdarov
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010004 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Seeds from four landraces of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus coccineus L.) from the National Collection of Bulgaria were analyzed for their chemical and lipid composition. The chemical analysis revealed that protein ranged from 24.4% to 31.5%, carbohydrates from 53.1%
[...] Read more.
Seeds from four landraces of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus coccineus L.) from the National Collection of Bulgaria were analyzed for their chemical and lipid composition. The chemical analysis revealed that protein ranged from 24.4% to 31.5%, carbohydrates from 53.1% to 56.1%, fat from 0.9% to 1.4%, fiber from 2.6% to 2.8%, and ash from 3.9% to 4.7%, indicating their high nutritional and caloric value. The seed oils contained significant levels of bioactive compounds, including tocopherols (3483–3809 mg/kg), carotenoids (1664–2049 mg/kg), and phospholipids (24.6–62.2%), which contribute to their health-promoting properties. In the Phaseolus vulgaris accessions, the oil was primarily composed of linolenic (n-3) and linoleic acids (n-6), followed by palmitic and oleic acids, whereas in the Phaseolus coccineus accession, linoleic acid (n-6) predominated, followed by linolenic (n-3) acid. β-Sitosterol was the major sterol, followed by stigmasterol, while the tocopherol fraction was mainly composed of γ-tocopherol (88.2–95.0%), with δ-tocopherol as a secondary component. Phosphatidylcholine was the predominant phospholipid, accounting for 33.1–51.7%. These findings underscore the potential of Bulgarian bean landraces as functional ingredients in health-oriented food products due to their balanced nutritional profile and presence of bioactive lipids.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Metabolomic Profile and Antioxidant Capacity of Methanolic Extracts of Mentha pulegium L. and Lavandula stoechas L. from the Portuguese Flora
by
Carmo Serrano, Violeta Lopes, Octávio Serra, Carlos Gaspar, Ana Maria Barata, Andreia Soares and M. Conceição Oliveira
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010003 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study assessed the phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and phytochemical composition of methanolic extracts from Portuguese Mentha pulegium L. and Lavandula stoechas L. Through spectrophotometric methods (TPC, FRAP, and DPPH), high-resolution techniques (HPLC-ESI(-)-HRMS/MS), along with multivariate techniques (PCA and cluster analysis). A total
[...] Read more.
This study assessed the phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and phytochemical composition of methanolic extracts from Portuguese Mentha pulegium L. and Lavandula stoechas L. Through spectrophotometric methods (TPC, FRAP, and DPPH), high-resolution techniques (HPLC-ESI(-)-HRMS/MS), along with multivariate techniques (PCA and cluster analysis). A total of 24 to 26 metabolites were identified across the analyzed plant species, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, terpenoids, jasmonates, and fatty acids. M. pulegium was primarily composed of diosmin and hesperidin, whereas L. stoechas exhibited amounts of rosmarinic acid and associated phenolic compounds. Multivariate and correlation analyses demonstrated variability within species and emphasized connections among metabolite categories, biosynthetic routes and environmental influences like altitude. Inland accessions of M. pulegium from Beja, Portalegre and Évora showed elevated TPC and FRAP levels while DPPH activity fluctuated according to distinct metabolite profiles. Despite these variations, phytochemical diversity did not adhere to a geographic trend, indicating that genetic and biosynthetic elements are more influential. The interplay between flavonoids and phenolic acids seemed crucial in determining antioxidant activity. Overall, the Portuguese germplasm of both species demonstrates substantial bioactive potential and chemical diversity, underscoring its value for food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical applications. These findings provide a scientific basis for selecting promising accessions and developing future biotechnological strategies.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Microwave-Assisted Chemical Recycling of a Polyurethane Foam for Pipe Pre-Insulation and Reusability of Recyclates in the Original Foam Formulation
by
Liudmyla Gryshchuk, Sergiy Grishchuk, Gregor Grun and Wael Almustafa
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010002 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Considering the high demand for efficient chemical recycling and reusability of polyurethane foams (PUFs), combined microwave-assisted solvolysis routes have been applied to a widely used commercial PUF for pipe pre-insulation, and the reusability of as-received recycled products in the original formulation was studied.
[...] Read more.
Considering the high demand for efficient chemical recycling and reusability of polyurethane foams (PUFs), combined microwave-assisted solvolysis routes have been applied to a widely used commercial PUF for pipe pre-insulation, and the reusability of as-received recycled products in the original formulation was studied. The influence of the type and amount of recyclate on the main foaming parameters, shrinkage behavior, density, compression properties, morphology, thermal stability, and humidity uptake was determined. Based on shrinkage as the main exclusion criterion, recycling products of two routes have been evaluated as suitable for reuse in the original formulation without any purification or fractionation. However, a maximum of 5 wt.% of the original polyol compound could be replaced by these recycled products to fulfill the requirement of ≤5% shrinkage, which also resulted in foam performance that is well acceptable for use in pre-insulated pipes. The most beneficial property profiles were achieved by replacing 3 wt.% of the original polyol component.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Solvent Extraction Method for Stilbenoid and Phenanthrene Compounds in Orchidaceae Species
by
David J. Machate, Teresinha Gonçalves da Silva, António B. Mapossa and Maria A. M. Maciel
AppliedChem 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem6010001 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study introduces an optimized and selective extraction methodology using dichloromethane/methanol (DCM/MeOH, 95:5, v/v) in combination with accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) for the targeted stilbenoid and phenanthrene derivatives from five orchid species: Cattleya nobilior (root), Cymbidium defoliatum (root and bulb),
[...] Read more.
This study introduces an optimized and selective extraction methodology using dichloromethane/methanol (DCM/MeOH, 95:5, v/v) in combination with accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) for the targeted stilbenoid and phenanthrene derivatives from five orchid species: Cattleya nobilior (root), Cymbidium defoliatum (root and bulb), Dendrobium phalaenopsis (stem), Encyclia linearifolioides (leaf), and Phalaenopsis aphrodite (root). Sequential extraction was performed with hexane, followed by DCM/MeOH (95:5 and 1:1, v/v) under controlled temperatures (70 °C for hexane, 100 °C for DCM/MeOH), using three static cycles per stage. Chemical profiling by high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode-array-detector and tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-MS/MS) enabled the identification of twenty specialized metabolites—seven stilbenoids and thirteen phenanthrenes—several reported here for the first time, including crepidatuol B, dendrosinen D, and coeloginanthridin. The analytical method showed excellent separation of structurally related phenolic compounds, demonstrating the efficiency of the extraction protocol and the selectivity of the solvent system. Many of the identification metabolites are known for cytotoxic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic regulatory properties, while newly detected compounds remain unexplored and present promising candidates for future biological evaluation. The broad distribution of these metabolites across the studied orchids enhances the current understanding of their phytochemical diversity and suggests chemotaxonomic relevance within the Orchidaceae family. Importantly, the extraction strategy requires minimal plant material, offering ecological advantages when working with rare or endangered species. Overall, this environmentally conscious extraction approach provides a robust platform for metabolic discovery and supports future research in natural products chemistry, plant ecology, drug discovery, structure–activity relationships studies and biotechnological applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spectroscopic Investigations of Diethanolamine-Modified Nucleic Acids
by
Tabea Lenz and Marian Hebenbrock
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040040 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To develop a modifier based on diethanolamine, a corresponding phosphoramidite for automated solid-phase deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis was synthesized. The influence of this modifier on the thermal stability of the terminally modified nucleic acids showed a dependence on the neighboring nucleobases and could be
[...] Read more.
To develop a modifier based on diethanolamine, a corresponding phosphoramidite for automated solid-phase deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis was synthesized. The influence of this modifier on the thermal stability of the terminally modified nucleic acids showed a dependence on the neighboring nucleobases and could be attributed to the fraying of the DNA ends. The potential for modification with dioxazaborocanes was first investigated using a small molecule model, and the formation of the dioxazaborocane was confirmed both in solution and in the solid state. Such a modification could expand the scope of xenonucleic acids in the future and modulate the properties of nucleic acids in solution. The influence on the thermal stability of the modified nucleic acids was minimal. In the future, this modification will be extended to internal incorporation and the potential of dioxazaborocanes in the nucleic acid context will be further exploited.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Plant Extracts as Natural Inhibitors of Non-Enzymatic Browning: A Case of Fruits and Fruit-Based Products
by
Lusani Norah Vhangani and Jessy Van Wyk
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040039 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Heat processing in fruit and fruit-based food products is aimed at producing nutritious, shelf-stable, and consumer- appealing food products. However, the processing and prolonged storage conditions employed favour non-enzymatic browning (NEB) reactions. Recent research is aimed at finding natural products to inhibit deleterious
[...] Read more.
Heat processing in fruit and fruit-based food products is aimed at producing nutritious, shelf-stable, and consumer- appealing food products. However, the processing and prolonged storage conditions employed favour non-enzymatic browning (NEB) reactions. Recent research is aimed at finding natural products to inhibit deleterious food reactions, with NEB being one of them. This review discusses the role of plant extracts in inhibiting NEB reactions during the processing and storage of fruit and fruit-based products. The review follows a traditional narrative approach, where approximately 100 articles were reviewed by summarising the role of vegetables, fruits, and fruit-based products in the diet, followed by the chemical reactions taking place during processing and storage, with emphasis on the pathways of three types of NEB reactions. We evaluate the prevention of NEB reactions using plant and plant extracts with a focus on the inhibitory mechanisms, as well as limitations, thereof. Encapsulation was also discussed as a possible intervention for the limitations posed by plant extracts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Women’s Special Issue Series: AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Copper Recovery from a Refractory Sulfide Mineral by Ferric Leaching and Regeneration of the Leaching Medium Through Catalytic Oxidation with Carbon for Recirculation
by
Verónica Cascante-Alvarado, Ernesto de la Torre and Carlos F. Aragón-Tobar
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040038 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Optimizing copper recovery from sulfide minerals such as chalcopyrite, which constitutes over 70% of global copper reserves, is essential due to the depletion of conventional copper oxide resources. This study aimed to establish optimal ferric leaching conditions for a chalcopyrite-rich concentrate to maximize
[...] Read more.
Optimizing copper recovery from sulfide minerals such as chalcopyrite, which constitutes over 70% of global copper reserves, is essential due to the depletion of conventional copper oxide resources. This study aimed to establish optimal ferric leaching conditions for a chalcopyrite-rich concentrate to maximize copper recovery and to evaluate the regeneration of the oxidizing potential in the residual leaching solution for reuse. Ferric sulfate (Fe2(SO4)3), as a ferric ion (Fe3+) carrier, was used as oxidizing agents at a concentration of [0.1 M] in sulfuric acid ([0.5 M] H2SO4), using a CuFeS2 concentrate (75% chalcopyrite) leached over 80 h. Copper was recovered through cementation with metallic iron, while the residual leaching solution, containing ferrous ions, was analyzed to determine total iron content via atomic absorption spectroscopy and to assess the presence of ferrous ions through KMnO4 titration. This step was crucial, as an excess of ferrous ions would indicate a loss of oxidizing potential of the ferric ion (Fe3+). Catalytic oxidation was conducted with microporous activated carbon (30 g/L) to regenerate Fe3+ for a second leaching cycle, achieving 90.7% Fe2+ oxidation. Optimal leaching conditions resulted in 95% soluble copper recovery at 1% solids, d80: 74 μm, pH < 2, Eh > 450 mV, 92 °C, [0.5 M] H2SO4, and [0.1 M] Fe2(SO4)3. In the second cycle, the regenerated solution reached 75% copper recovery. These findings highlight temperature as a critical factor for copper recovery and demonstrate catalytic oxidation as a viable method for regenerating ferric solutions in industrial applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design and Synthesis of Ferulic Acid Derivatives with Enhanced Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Activities: Discovery of Dual Antioxidant Agent
by
Koichi Shikama, Jun Takayama, Meiyan Xuan, Hirokazu Matsuzaki, Bo Yuan, Hiroyuki Teramae, Mari Okazaki and Takeshi Sakamoto
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040037 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ferulic acid (FA) is well known for its antioxidant properties and neuroprotective effects. To enhance these biological activities, we designed a novel series of FA derivatives by introducing a phenyl group at the α-position of the carboxyl moiety. Further structural modifications were achieved
[...] Read more.
Ferulic acid (FA) is well known for its antioxidant properties and neuroprotective effects. To enhance these biological activities, we designed a novel series of FA derivatives by introducing a phenyl group at the α-position of the carboxyl moiety. Further structural modifications were achieved by incorporating hydroxy or alkoxy substituents at various positions on the two aromatic rings. A series of these derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their antioxidant capacity using the DPPH radical scavenging assay, as well as their cytoprotective effects against oxidative stress in Neuro-2a cells. Among the synthesized compounds, one derivative exhibited significantly enhanced activity in both assays. Mechanistic studies indicated that this heightened efficacy is attributable to a unique reaction pathway involving dual antioxidant mechanisms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Advances in Paper Spray Mass Spectrometry (PS-MS) for On-Site Harm Reduction Drug Checking and Illicit Supply Surveillance
by
Taelor M. Zarkovic, Lucas R. Abruzzi, Collin Kielty, Bruce Wallace, Dennis K. Hore and Chris G. Gill
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040036 - 1 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Harm reduction drug checking utilizing paper spray mass spectrometry (PS-MS) has been the focus of ongoing research since 2017 and has seen many refinements. The presented work is the result of this research and has led to the public-facing PS-MS use for on-site
[...] Read more.
Harm reduction drug checking utilizing paper spray mass spectrometry (PS-MS) has been the focus of ongoing research since 2017 and has seen many refinements. The presented work is the result of this research and has led to the public-facing PS-MS use for on-site drug checking in Victoria, BC. Included are the improved methods and approaches required to develop and implement PS-MS as an on-site drug checking technology. Critical details regarding appropriate direct mass spectrometry tune and calibration suites required to avoid isobaric interferences, calibration details, quality control strategies, detailed MS scan approaches to implement rapid drug tests, as well as future work considerations are presented. The PS-MS method presented currently directly quantifies 107 targeted drugs in a two-minute measurement, and can be easily adapted to include additional new targets that appear in the unregulated drug supply that are detected by either low or high resolution PS-MS. The presented methodologies provide a framework to assist those interested in implementing PS-MS to reduce harms from the toxic drug supply, but will have value for those developing rapid, quantitative drug testing for other applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in AppliedChem, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Preanalytical Strategies for Native Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Protein Modifications, Complexes, and Higher-Order Structures
by
Navid J. Ayon
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040035 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Proteins are essential biological macromolecules that play key regulatory roles in all biological processes. Abnormalities in these processes are often reflected in proteins, manifesting as changes in their structure, sequence, folding state, stoichiometry, or spatial and temporal distribution. Proteins serve as biological targets
[...] Read more.
Proteins are essential biological macromolecules that play key regulatory roles in all biological processes. Abnormalities in these processes are often reflected in proteins, manifesting as changes in their structure, sequence, folding state, stoichiometry, or spatial and temporal distribution. Proteins serve as biological targets for drugs and other therapeutics and can also function as therapeutic agents to restore normal biological functions by treating diseases. Hence, it is essential to study native protein species, their modifications, higher-order structures, and complexes, which can be extremely difficult due to the challenges in preserving their native conditions and the instrumental capability required for such analysis. High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) instruments provide advanced technical capabilities to study intact protein species from their gas phase ions after the protein solution is sprayed into the mass spectrometers. However, there are debates about the gas-phase protein structures obtained through mass spectrometry and the resemblance to their biological native state. This review discusses various techniques for isolating, separating, and enriching intact protein species for their native mass spectrometry (nMS) analysis. Emerging technologies, such as automated sample preparation, ion mobility spectrometry, and ambient surface mass spectrometry, are briefly discussed. This review aims to serve as a general guideline for beginners, primarily focusing on the preanalytical strategies and critical instrument parameters for nMS analysis of intact proteins, proteoforms, protein complexes, and higher-order structures.
Full article
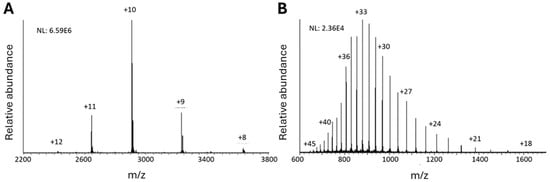
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Potential of Cupriavidus metallidurans and Ochrobactrum anthropi for 241Am Bioaccumulation in Aqueous Solution
by
Leandro Goulart de Araujo, Tania Regina de Borba, Rafael Luan Sehn Canevesi, Sabine Neusatz Guilhen, Edson Antonio da Silva and Júlio Takehiro Marumo
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040034 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study explores, for the first time, the bioaccumulation of americium-241 (241Am) by Cupriavidus metallidurans and Ochrobactrum anthropi, two bacterial strains previously investigated mainly for their interactions with other heavy metals and radionuclides. To the best of our knowledge, no
[...] Read more.
This study explores, for the first time, the bioaccumulation of americium-241 (241Am) by Cupriavidus metallidurans and Ochrobactrum anthropi, two bacterial strains previously investigated mainly for their interactions with other heavy metals and radionuclides. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies have reported the use of these microorganisms for 241Am removal from aqueous solutions. The effects of initial 241Am concentration and solution pH on removal performance were evaluated through batch experiments. Kinetic analyses were performed using pseudo-first-order (PFO) and pseudo-second-order (PSO) models, with the PSO model providing a better fit, suggesting chemisorption as the rate-limiting step in the process. Initial 241Am concentrations ranged from 75 to 300 Bq mL−1, and both bacterial strains demonstrated comparable maximum bioaccumulation capacities of approximately 1.5 × 10−8 mmol g−1. However, O. anthropi exhibited superior resistance to 241Am, maintaining colony growth at activity levels up to 1200 Bq mL−1, compared to a threshold of 400 Bq mL−1 for C. metallidurans. These findings highlight the robustness and efficiency of these bacterial strains—particularly O. anthropic—in removing 241Am from liquid radioactive waste, offering promising implications for bioremediation technologies.
Full article
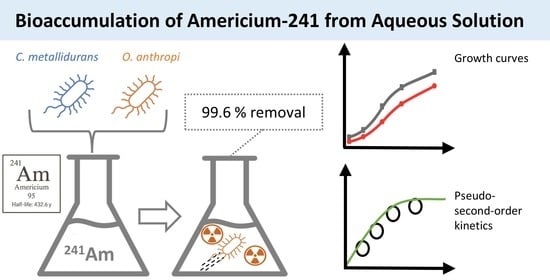
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Processing Water-Based Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Cathodes with CMC Binder: The Impact of Dispersing Methods
by
Leah Jalowy, Henry Lehmann, Patrick Rassek, Olga Fromm, Marc Entenmann and Dominik Nemec
AppliedChem 2025, 5(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5040033 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are vital for modern energy storage applications. Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is a promising cathode material due to its safety, low cost, and environmental friendliness compared to the widely used nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), which contains hazardous nickel and
[...] Read more.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are vital for modern energy storage applications. Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is a promising cathode material due to its safety, low cost, and environmental friendliness compared to the widely used nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), which contains hazardous nickel and cobalt compounds. However, challenges remain in enhancing the performance of LFP cathodes due to their low electronic and ionic conductivity. To improve both the safety and sustainability of the battery, this work presents a water-based LFP cathode utilizing the bio-based binder carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), eliminating the need for polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and the toxic solvent N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP). This study investigates the impact of different dispersing methods—dissolver mixing and wet jet milling—on slurry properties, electrode morphology, and battery performance. Slurries were characterized by rheology, particle size distribution, and sedimentation behavior, while coated and calendered electrodes were examined via thickness measurements and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Electrochemical performance of the electrodes was evaluated by means of C-Rate testing. The results reveal that dispersing methods significantly influence slurry characteristics but marginally affect electrochemical performance. Compared to dissolver mixing, wet jet milling reduced the median particle size by 39% (ΔD50 = 3.1 µm) and lowered viscosity by 96% at 1 s−1, 80% at 105 s−1, and 64% at 1000 s−1. In contrast, the electrochemical performance of the resulting electrodes differed only slightly, with discharge capacity varying by approximately 12.8% at 1.0 C (Δcapacity = 10.7 mAh g−1). This research highlights the importance of optimizing not only material selection but also processing techniques to advance safer and more sustainable energy storage solutions.
Full article
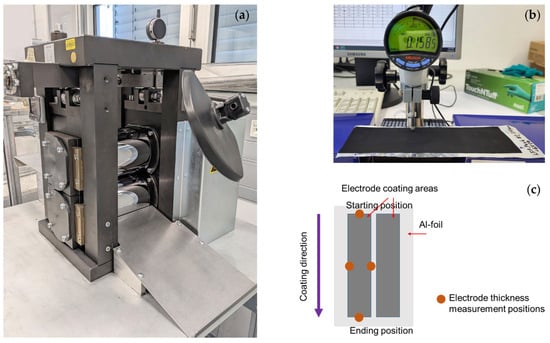
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
6 November 2025
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

2 February 2026
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #31 - MDPI 30 Years, 500 Journals, UK Summit, Z-Forum Conference, APE
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #31 - MDPI 30 Years, 500 Journals, UK Summit, Z-Forum Conference, APE

Topics
Topic in
Catalysts, Materials, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Photochem, Applied Nano, AppliedChem
Fabrication of Hybrid Materials for Catalysis, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Michael Arkas, Jerry J. Wu, Dimitrios GiannakoudakisDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
AppliedChem, Catalysts, Chemistry, Clean Technol., Water
Multifunctional Water Valorization: From Strategies to Mechanisms
Topic Editors: Haiying Jiang, Ying ZhangDeadline: 31 January 2027
Topic in
IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Foods, Antioxidants, AppliedChem
From Food to Medicine: Applications of Natural Bioactive Compounds
Topic Editors: Long Yu, Fan HeDeadline: 31 May 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Women’s Special Issue Series: AppliedChemGuest Editors: Alessandra Biancolillo, Vicky Caponigro, Caterina Durante, Barbara BenedettiDeadline: 20 February 2026
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Analytical Chemistry: Fundamentals, Current and Future Applications
Guest Editor: Antony C. CalokerinosDeadline: 10 March 2026
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Feature Papers in AppliedChem, 2nd Edition
Guest Editor: Jason LoveDeadline: 20 April 2026
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Advances in Medicinal Chemistry for Drug Discovery and Development
Guest Editor: Suresh NarvaDeadline: 31 May 2026







