- Article
Neuroprotective Effects of Herbal Formula Yookgong-Dan on Oxidative Stress-Induced Tau Hyperphosphorylation in Rat Primary Hippocampal Neurons
- Hyunseong Kim,
- Jin Young Hong and
- In-Hyuk Ha
- + 5 authors
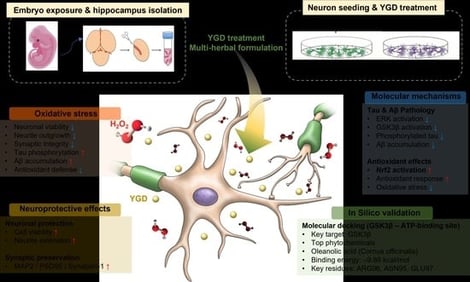
This study sought to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of YGD in an oxidative stress-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like cellular model and to elucidate the underlying molecular pathways, with a focus on tau phosphorylation, Aβ accumulation, and antioxidant defense mechanisms. Rat primary hippocampal neurons were exposed to hydrogen peroxide to induce oxidative stress. The effects of YGD on neuronal viability, neurite outgrowth, and synaptic integrity were assessed using the immunodetection of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95), and synapsin-1. Levels of phosphorylated tau and Aβ were quantified, and the involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), and nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) pathways was examined. Additionally, in silico molecular docking studies targeting the ATP-binding site of GSK3β were conducted to screen major phytochemicals from the ten medicinal herbs constituting YGD. YGD markedly enhanced neuronal viability under oxidative stress, promoted neurite extension, and increased synaptic marker expression (MAP2, PSD-95, and synapsin-1). Treatment reduced phosphorylated tau by suppressing ERK and GSK3β activation and significantly decreased Aβ accumulation. YGD also upregulated antioxidant defenses via the activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Docking simulations identified oleanolic acid (from Cornus officinalis) as the most potent GSK3β binder (−9.86 ± 0.40 kcal/mol), forming stable interactions with ARG96, ASN95, and GLU97. Additional compounds, including alisol C, drypemolundein B, and friedelin, demonstrated favorable binding energies and engaged key ATP-binding site residues. YGD confers neuroprotection through the integrated modulation of tau phosphorylation, Aβ pathology, and oxidative stress, partly via the multi-target engagement of GSK3β by its constituent phytochemicals. These findings support that YGD attenuates oxidative stress-induced AD-like cellular alterations.
6 February 2026