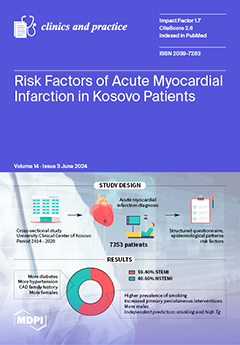
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI), presented as ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI), is influenced by atherosclerosis risk factors. Aim: The aim of this study was to assess the patterns of presentation of patients with acute MI in Kosovo. Methods: This
[...] Read more.
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI), presented as ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI), is influenced by atherosclerosis risk factors. Aim: The aim of this study was to assess the patterns of presentation of patients with acute MI in Kosovo. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study conducted at the University Clinical Center of Kosovo, which included all patients hospitalized with acute MI over a period of 7 years. Results: Among the 7353 patients admitted with acute MI (age 63 ± 12 years, 29% female), 59.4% had STEMI and 40.6% had NSTEMI. The patients with NSTEMI patients less (48.3% vs. 54%,
p < 0.001), but more of them had diabetes (37.8% vs. 33.6%,
p < 0.001), hypertension (69.6% vs. 63%,
p < 0.001), frequently had a family history of coronary artery disease (CAD) (40% vs. 38%,
p = 0.009), and had more females compared to the patients with STEMI (32% vs. 27%,
p < 0.001). The patients with NSTEMI underwent less primary percutaneous interventions compared with the patients with STEMI (43.6% vs. 55.2%,
p < 0.001). Smoking [1.277 (1.117–1.459),
p ˂ 0.001] and high triglycerides [0.791 (0.714–0.878),
p = 0.02] were independent predictors of STEMI. Conclusions: In Kosovo, patients with STEMI are more common than those with NSTEMI, and they were mostly males and more likely to have diabetes, hypertension, and a family history of CAD compared to those with NSTEMI. Smoking and high triglycerides proved to be the strongest predictors of acute STEMI in Kosovo, thus highlighting the urgent need for optimum atherosclerosis risk control and education strategies.
Full article