- Systematic Review
Sperm Microbiota and Its Potential Impact on Male Fertility: A Systematic Review
- Raghda Youssef,
- Caroline Aimone-Vianna and
- Anne Julie Fattet
- + 2 authors
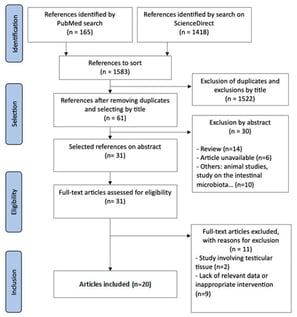
Background/Objectives: Infertility is a major public health concern, affecting one in six individuals worldwide and nearly one-quarter of couples in France. While a male, female, or combined factor can be identified in approximately 75% of cases, infertility remains unexplained in 10–25%. Genital tract infections account for roughly 15% of male infertility cases and are often asymptomatic, being detected incidentally during routine evaluation prior to assisted reproductive technology (ART). Emerging evidence suggests that the seminal microbiota may contribute to sperm quality and male reproductive health. This systematic review aims to evaluate whether specific microbial profiles are associated with alterations in semen parameters. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed and ScienceDirect, yielding 165 and 1418 records, respectively. In the end, 20 articles were included in this systematic review. Results: Men with normal semen parameters commonly exhibited a higher abundance of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, whereas Prevotella was more frequently observed in individuals with impaired semen quality. Several taxa—such as Gardnerella, Corynebacterium, and Staphylococcus spp.—were detected in both normal and altered semen profiles, suggesting that their impact on sperm quality may depend on reaching a pathogenic threshold. Conclusions: Current evidence supports an association between seminal microbiota composition and sperm quality. However, the heterogeneity of available studies and the lack of standardized methodologies limit the ability to draw firm conclusions. Further well-designed studies are required to clarify causal relationships and to determine the clinical relevance of seminal microbiota assessment in male infertility.
5 February 2026