- Article
Geographical Variations in Polycystic Ovarian Morphology: Comparison of India- and United States-Based Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Hilary Zhang,
- Abbey Kalay and
- Marla E. Lujan
- + 6 authors
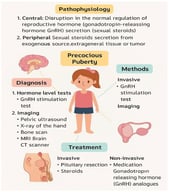
Background/Objectives: Geographical differences exist in the clinical presentation of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The degree to which ovarian morphology contributes to this variability is unknown. Methods: This study compared ovarian ultrasound features between women with PCOS residing in two geographical regions (India and the United States) using stored de-identified ultrasound scans from 331 women with PCOS. Sonographic markers of interest included follicle number per ovary (FNPO), follicle number per cross-section (FNPS), ovarian volume (OV), ovarian area (OA), stromal area (SA), and stromal-to-ovarian area ratio (S/A). Results: Most participants in both regions met the accepted criteria for polycystic ovarian morphology (India 87% vs. U.S. 83%). The U.S.-based group had a higher prevalence of follicle excess (41% in U.S. vs. 29% in India; p = 0.037), whereas the prevalence of ovarian enlargement was similar across groups (India 37% vs. U.S. 31%, p = 0.252). FNPS was higher in the U.S.-based group (p = 0.046), while the India-based group had higher OV (p = 0.010). SA and S/A did not differ between groups, albeit OA was slightly larger in women with PCOS from India (p = 0.022). Associations between ovarian morphology and menstrual cycle length (ρ = 0.16–0.25), hirsutism score (ρ = 0.19–0.23), and total testosterone (ρ = −0.33–0.42) were noted in both groups (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Some variation in ovarian morphology may exist across geographic regions. However, the degree of variability is unlikely to warrant regional definitions for polycystic ovarian morphology at this time.
21 February 2026



![Comparison of conventional and nonconventional markers of polycystic ovarian morphology across India and United States-based women with PCOS. A comparison of conventional [(A) FNPO, (B) FNPS, (C) OV] and nonconventional [(D) OA, (E) SA, (F) S/A] markers in women with PCOS in India and the U.S. Box-and-whisker diagrams of conventional and unconventional markers are presented for women with PCOS in India (N = 119) and the U.S. (N = 212). Boxes represent the 25th and 75th percentile, and the horizontal band within the box represents the median. The 5th–95th percentile range is denoted by the vertical bars. p-values from Wilcoxon two sample t-tests (unadjusted comparison).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=470,h=317/https://mdpi-res.com/reprodmed/reprodmed-07-00010/article_deploy/html/images/reprodmed-07-00010-g001-550.jpg)