Innovative Bioreactor Design and Advanced Optimization Strategies for Biorefineries and Bioprocessing
A special issue of Processes (ISSN 2227-9717). This special issue belongs to the section "Biological Processes and Systems".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 5 July 2026 | Viewed by 46822
Special Issue Editors
2. Chemical Process and Energy Resources Institute—CPERI/LPRE, Centre for Research and Technology Hellas—CERTH, 57001 Thessaloniki, Greece
Interests: photobioreactors; fermentation; microalgae; biopolymers; biorefinery; biofuels; nanocellulose; bioprocess modeling; techno-economic analysis; biomass
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: microalgae; photobioreactors; CO2 capture; techno-economic analysis; biopolymers; biomolecules; nanomaterials; agro-industrial wastes; colloids; emulsifying agents
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
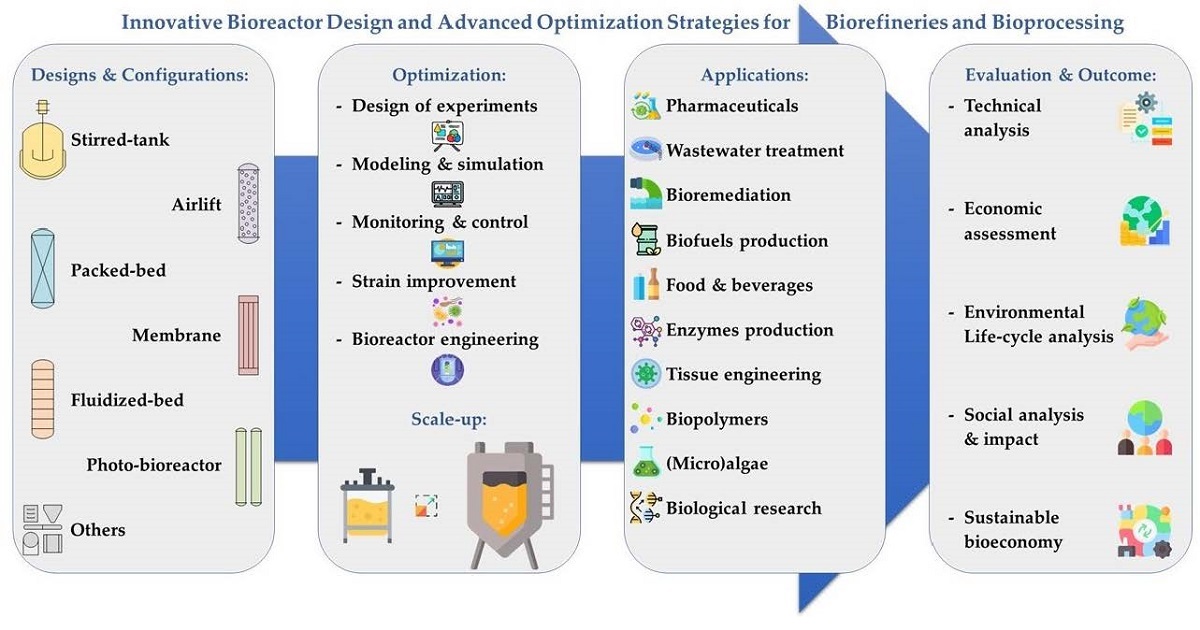
Bioreactors are increasingly essential for various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, agriculture, environmental remediation, and bioenergy. Specifically, novel design and optimization of bioreactors are critical for enhancing efficiency and productivity within biorefineries and bioprocessing systems, addressing contemporary challenges in the bioeconomy. This entails consideration of parameters such as reactor type, agitation, aeration, temperature, pH control, and nutrient supply. Optimization techniques, including mathematical modeling and statistical analysis, aid in maximizing product yield, minimizing production costs, and ensuring process robustness.
In biorefineries, where multiple products are derived from biomass and wastes, integrated bioreactor systems are indispensable. These systems should be adaptable to various feedstocks and capable of handling complex microbial communities. Advanced monitoring and control strategies enable real-time adjustments to optimize performance. Furthermore, the integration of downstream processing units enhances product purification and recovery. Beyond technical advancements in bioreactors, ensuring their economic and environmental sustainability is of paramount importance.
In this context, the aim of this Special Issue of Processes is to attract high-quality original research contributions and review articles in the field of “Innovative Bioreactor Design and Advanced Optimization Strategies for Biorefineries and Bioprocessing”. This could include individual experimental and theoretical studies or combined approaches.
Specific topics for the Special Issue include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Design of innovative bioreactor configurations, including photo-bioreactors.
- 2G and 3G biorefineries for energy, fuels and materials.
- Fermentative production of biofuels, biochemicals, and biopolymers.
- Hybrid (photo-)bioreactor systems for bioremediation and wastewater treatment.
- Microbial activity towards bioprocessing and downstream processing.
- Experimental and model-based intensification and scale-up of bioproduction systems.
- Advanced multi-scale modeling and simulation of complex bioreactor phenomena.
- Versatile monitoring and efficient control systems for bioreactors.
- Techno-economic assessment and Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) of multi-purpose bioreactors.
Dr. Giannis Penloglou
Guest Editor
Dr. Alexandros Pavlou
Guest Editor Assistant
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Processes is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- bioreactor
- photobioreactor
- fermentation
- biorefinery
- bioprocessing
- microbial production
- monitoring and control
- mathematical modeling and simulation
- techno-economic assessment
- life cycle analysis
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






