Journal Description
Neurology International
Neurology International
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal which provides an advanced forum for studies related to all aspects of neurology and neuroscience, published bimonthly online by MDPI (from Volume 12 issue 3 - 2020).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration: Insights and Therapeutic Strategies for Parkinson’s Disease
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(3), 502-517; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030037 - 29 Apr 2024
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by the gradual deterioration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Oxidative stress has been identified as a key player in the development of PD in recent studies. In the first part, we
[...] Read more.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition marked by the gradual deterioration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Oxidative stress has been identified as a key player in the development of PD in recent studies. In the first part, we discuss the sources of oxidative stress in PD, including mitochondrial dysfunction, dopamine metabolism, and neuroinflammation. This paper delves into the possibility of mitigating oxidative stress as a potential treatment approach for PD. In addition, we examine the hurdles and potential of antioxidant therapy, including the challenge of delivering antioxidants to the brain and the requirement for biomarkers to track oxidative stress in PD patients. However, even if antioxidant therapy holds promise, further investigation is needed to determine its efficacy and safety in PD treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Advances in Neurodegenerative Diseases)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Pain Catastrophizing: How Far Have We Come
by
Katarina Simic, Boris Savic and Nebojsa Nick Knezevic
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(3), 483-501; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030036 - 26 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The perception of pain is strongly influenced by various social, emotional, and cognitive factors. A psychological variable which has consistently been shown to exert its influence on pain is a cognitive process referred to as pain catastrophizing. Numerous studies have found it to
[...] Read more.
The perception of pain is strongly influenced by various social, emotional, and cognitive factors. A psychological variable which has consistently been shown to exert its influence on pain is a cognitive process referred to as pain catastrophizing. Numerous studies have found it to be a strong predictor of pain intensity and disability across different clinical populations. It signifies a maladaptive response to pain marked by an exaggerated negative assessment, magnification of symptoms related to pain, and, in general, a tendency to experience marked pain-related worry, as well as experiencing feelings of helplessness when it comes to dealing with pain. Pain catastrophizing has been correlated to many adverse pain-related outcomes, including poor treatment response, unsatisfactory quality of life, and high disability related to both acute and chronic pain. Furthermore, there has been consistent evidence in support of a correlation between pain catastrophizing and mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression. In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge regarding pain catastrophizing, with special emphasis on its clinical significance, and emerging treatment modalities which target it.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Extensive Study Regarding the Microscopic Anatomy of the Early Fetal Human Optic Nerve
by
Mihai Alin Publik, Florin Mihail Filipoiu, Adrian Vasile Dumitru, Andrei Precup, Ioan-Andrei Petrescu, Iulian Slavu, Raluca Florentina Tulin, Adrian Tulin, Andra Ioana Baloiu, Monica Mihaela Cirstoiu and Octavian Munteanu
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(3), 470-482; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16030035 - 24 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The development of the optic nerve and its surrounding tissues during the early fetal period is a convoluted period because it spans both the organogenesis period and the fetal period. This study details the microscopic anatomy and histoembryology of the optic nerve in
[...] Read more.
The development of the optic nerve and its surrounding tissues during the early fetal period is a convoluted period because it spans both the organogenesis period and the fetal period. This study details the microscopic anatomy and histoembryology of the optic nerve in embryos during the early fetal period, including the second half of the first trimester of pregnancy. Serial sections through the orbit of variously aged embryos allowed us to analyze the nerve in both longitudinal and transverse aspects. A histological assessment and description of the structures surrounding and inside the nerve were performed, highlighting the cellular subtypes involved. By employing immunohistochemical techniques, we could characterize the presence and distribution of astrocytes within the optic nerve. Our findings suggest that by the 8th gestational week (WG) the structures are homologs to all the adult ones but with an early appearance so that maturation processes take place afterward. By this age, the axons forming the nerve are definitive adult axons. The glial cells do not yet exhibit adult phenotype, but their aspect becomes adult toward the 13th week. During its development the optic nerve increases in size then, at 14 weeks, it shrinks considerably, possibly through its neural maturation process. The morphological primordium of the blood–nerve barrier can be first noted at 10 WG and at 13 WG the morphological blood–nerve barrier is definitive. The meningeal primordium can be first noted as a layer of agglomerated fibroblasts, later toward 13 WG splitting in pachymeninx and leptomeninges and leaving space for intrinsic blood vessels.
Full article
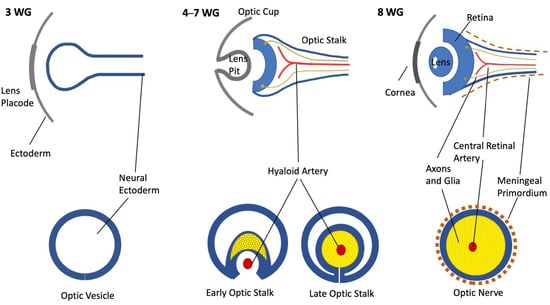
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Acute Postoperative Pain in Developing Chronic Pain after Total Knee Arthroplasty
by
Nebojsa Nick Knezevic, Osman Syed, Christopher Kabir, Aisha Patel, Isabel Rao Shuai and Antony R. Tharian
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 459-469; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020034 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
While total knee arthroplasties (TKAs) are performed with the intent to reduce pain, chronic postsurgical pain (CPSP) is one of the most well-documented complications that can occur following surgery. This study aimed to assess whether perioperative factors, focusing on acute postsurgical pain and
[...] Read more.
While total knee arthroplasties (TKAs) are performed with the intent to reduce pain, chronic postsurgical pain (CPSP) is one of the most well-documented complications that can occur following surgery. This study aimed to assess whether perioperative factors, focusing on acute postsurgical pain and perioperative opioid consumption, were associated with the development of chronic postsurgical pain. Under general anesthesia, 108 patients underwent TKA and were treated postoperatively with a multimodal analgesia approach. Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) pain scores at rest and with movement were recorded on postoperative days 0–3, 7, 14, and 30. Patients were sent a survey to assess chronic pain at months 22–66, which was examined as a single-group post hoc analysis. Based on the responses, patients were either classified into the CPSP or non-CPSP patient group. Chronic postsurgical pain was defined as an NRS score ≥ 4 with movement and the presence of resting pain. The primary outcome was a change in NRS. There were no differences in NRS pain scores with movement in the first 30 days postoperatively between patients with CPSP and without CPSP. Each unit increase in resting pain on postoperative days 3 and 14 was associated with significantly greater odds of CPSP presence (OR = 1.52; OR = 1.61, respectively), with a trend towards greater odds of CPSP at days 7 and 30 (OR = 1.33; OR = 1.43, respectively). We found that very intense pain in the initial phase seems to be related to the development of CPSP after TKA.
Full article
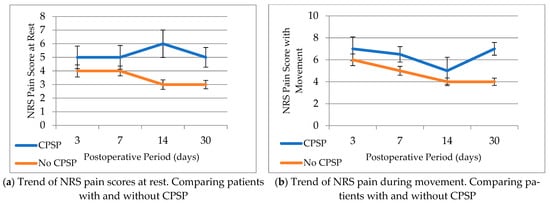
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Thecaloscopy Reduces the Risk of Recurrent Perineural (Tarlov) Cysts after Microsurgical Resection
by
Michael Luchtmann, Angelika Klammer, Mircea-Alin Iova, André Roth, Vijay Kumar Chanamolu, Christian Mawrin and Jan-Peter Warnke
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 450-458; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020033 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sacral Tarlov cysts (TCs), often asymptomatic, can cause significant pain and severe neurological dysfunction. Conventional treatments are generally associated with high recurrence and complication rates. Specifically, the substantial recurrence rates, which can reach as high as 50%, significantly impact long-term outcomes. Recent evidence
[...] Read more.
Sacral Tarlov cysts (TCs), often asymptomatic, can cause significant pain and severe neurological dysfunction. Conventional treatments are generally associated with high recurrence and complication rates. Specifically, the substantial recurrence rates, which can reach as high as 50%, significantly impact long-term outcomes. Recent evidence increasingly supports the hypothesis that the formation of Tarlov cysts (TCs) may be associated with inflammatory processes within the nerve root sheath, further exacerbated by elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure. This retrospective study explores thecaloscopy, combined with surgical techniques, as a more effective alternative. We observed a total of 78 patients, 48 of whom underwent endoscopic fenestration of the arachnoid sheath in addition to microsurgical resection of the TC. We found that the fenestration of the arachnoid sheath at the level of lumbosacral spinal nerve root entry led to a significantly decreased risk of developing recurrent TCs (5/48 vs. 9/30). Only one of the patients suffered from a persistent new bladder dysfunction after microsurgical resection. This presented technique provides a promising treatment path for the future management of TCs, offering a safe and more effective treatment option compared to previous methods. Additionally, the advantages of the thecaloscopy provide pathophysiological implications regarding the development of perineural cysts.
Full article
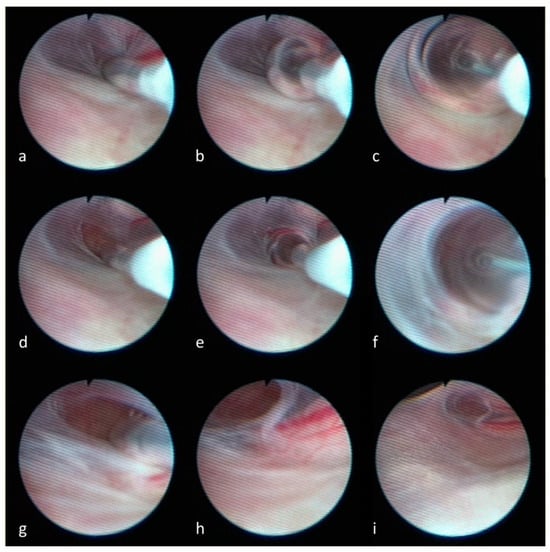
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neurocognitive Impairment and Social Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease Patients
by
Triantafyllos Doskas, Konstantinos Vadikolias, Konstantinos Ntoskas, George D. Vavougios, Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Polyxeni Stamati, Ioannis Liampas, Vasileios Siokas, Lambros Messinis, Grigorios Nasios and Efthimios Dardiotis
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 432-449; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020032 - 16 Apr 2024
Abstract
In addition to motor symptoms, neurocognitive impairment (NCI) affects patients with prodromal Parkinson’s disease (PD). NCI in PD ranges from subjective cognitive complaints to dementia. The purpose of this review is to present the available evidence of NCI in PD and highlight the
[...] Read more.
In addition to motor symptoms, neurocognitive impairment (NCI) affects patients with prodromal Parkinson’s disease (PD). NCI in PD ranges from subjective cognitive complaints to dementia. The purpose of this review is to present the available evidence of NCI in PD and highlight the heterogeneity of NCI phenotypes as well as the range of factors that contribute to NCI onset and progression. A review of publications related to NCI in PD up to March 2023 was performed using PubMed/Medline. There is an interconnection between the neurocognitive and motor symptoms of the disease, suggesting a common underlying pathophysiology as well as an interconnection between NCI and non-motor symptoms, such as mood disorders, which may contribute to confounding NCI. Motor and non-motor symptom evaluation could be used prognostically for NCI onset and progression in combination with imaging, laboratory, and genetic data. Additionally, the implications of NCI on the social cognition of afflicted patients warrant its prompt management. The etiology of NCI onset and its progression in PD is multifactorial and its effects are equally grave as the motor effects. This review highlights the importance of the prompt identification of subjective cognitive complaints in PD patients and NCI management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Papers from the Editorial Board Members (EBMs) and Invited Scholars of Neurology International)
Open AccessArticle
[125I]IPC-Lecanemab: Synthesis and Evaluation of Aβ-Plaque-Binding Antibody and Comparison with Small-Molecule [18F]Flotaza and [125I]IBETA in Postmortem Human Alzheimer’s Disease
by
Christopher Liang, Cayz G. Paclibar, Noresa L. Gonzaga, Stephanie A. Sison, Harman S. Bath, Agnes P. Biju and Jogeshwar Mukherjee
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 419-431; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020031 - 08 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Therapeutic antibodies for reducing Aβ plaque load in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is currently making rapid progress. The diagnostic imaging of Aβ plaque load in AD has been underway and is now used in clinical studies. Here, we report our preliminary findings on imaging
[...] Read more.
Therapeutic antibodies for reducing Aβ plaque load in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is currently making rapid progress. The diagnostic imaging of Aβ plaque load in AD has been underway and is now used in clinical studies. Here, we report our preliminary findings on imaging a therapeutic antibody, Lecanemab, in a postmortem AD brain anterior cingulate. [125I]5-iodo-3-pyridinecarboxamido-Lecanemab ([125I]IPC-Lecanemab) was prepared by coupling N-succinimidyl-5-([125I]iodo)-3-pyridinecarboxylate with Lecanemab in modest yields. The distinct binding of [125I]IPC-Lecanemab to Aβ-rich regions in postmortem human AD brains was higher in grey matter (GM) containing Aβ plaques compared to white matter (WM) (GM/WM was 1.6). Anti-Aβ immunostaining was correlated with [125I]IPC-Lecanemab regional binding in the postmortem AD human brains. [125I]IPC-Lecanemab binding was consistent with the binding of Aβ small molecules, [18F]flotaza and [125I]IBETA, in the same subjects. [18F]Flotaza and [125I]IBETA, however, exhibited significantly higher GM/WM ratios (>20) compared to [125I]IPC-Lecanemab. Our results suggest that radiolabeled [125I]IPC-Lecanemab retains the ability to bind to Aβ in human AD and may therefore be useful as a PET imaging radiotracer when labeled as [124I]IPC-Lecanemab. The ability to directly visualize in vivo a promising therapeutic antibody for AD may be useful in treatment planning and dosing and could be complimentary to small-molecule diagnostic imaging to assess outcomes of therapeutic interventions.
Full article
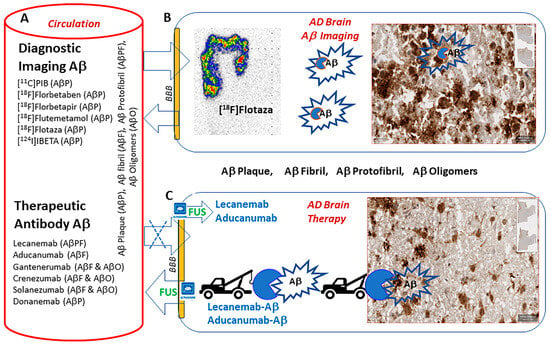
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mortality Predictors for Adult Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury: A Literature Review
by
Ansam Eghzawi, Alameen Alsabbah, Shatha Gharaibeh, Iktimal Alwan, Abeer Gharaibeh and Anita V. Goyal
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 406-418; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020030 - 05 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) represent a significant public health concern, with mild-to-moderate cases comprising a substantial portion of incidents. Understanding the predictors of mortality among adult patients with mild-to-moderate TBIs is crucial for optimizing clinical management and improving outcomes. This literature review examines
[...] Read more.
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) represent a significant public health concern, with mild-to-moderate cases comprising a substantial portion of incidents. Understanding the predictors of mortality among adult patients with mild-to-moderate TBIs is crucial for optimizing clinical management and improving outcomes. This literature review examines the existing research to identify and analyze the mortality predictors in this patient population. Through a comprehensive review of peer-reviewed articles and clinical studies, key prognostic factors, such as age, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, the presence of intracranial hemorrhage, pupillary reactivity, and coexisting medical conditions, are explored. Additionally, this review investigates the role of advanced imaging modalities, biomarkers, and scoring systems in predicting mortality following a mild-to-moderate TBI. By synthesizing the findings from diverse studies, this review aims to provide clinicians and researchers with valuable insights into the factors influencing mortality outcomes in adult patients with a mild-to-moderate TBI, thus facilitating more informed decision making and targeted interventions in clinical practice.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Utilization of Ocrelizumab within Different Treatment Strategies for Multiple Sclerosis: A 5-Year Population-Based Study
by
Marcello Moccia, Giuseppina Affinito, Giuseppina Marrazzo, Tiziana Ciarambino, Paolo Di Procolo, Licia Confalonieri, Antonio Carotenuto, Maria Petracca, Roberta Lanzillo, Maria Triassi, Vincenzo Brescia Morra and Raffaele Palladino
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 394-405; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020029 - 29 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: We aim to provide up-to-date real-world evidence on the persistence, adherence, healthcare resource utilization, and costs of multiple sclerosis (MS) by comparing ocrelizumab to other disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) and within different DMT sequences. Methods: We included 3371 people with MS who first
[...] Read more.
Background: We aim to provide up-to-date real-world evidence on the persistence, adherence, healthcare resource utilization, and costs of multiple sclerosis (MS) by comparing ocrelizumab to other disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) and within different DMT sequences. Methods: We included 3371 people with MS who first received or switched DMT prescriptions from January 2018 to December 2022; they were identified through hospital discharge records, drug prescriptions, and exemption codes from the Campania Region (South Italy). We calculated persistence (time from the first prescription to discontinuation or switching to another DMT), adherence (proportion of days covered (PDC)), DMT costs, and MS hospital admissions and related costs. Results: The most frequently prescribed DMT was dimethyl fumarate (n = 815; age 38.90 ± 11.91 years; 69.5% females), followed by ocrelizumab (n = 682; age 46.46 ± 11.29 years; 56.3%); 28.8% of the patients treated with ocrelizumab were naïve to DMTs. Using ocrelizumab as a statistical reference, the risk of discontinuation was higher for other highly active (HR = 6.32; 95%CI = 3.16, 12.63; p < 0.01) and low-/medium-efficacy DMTs (HR = 10.10; 95%CI = 5.10, 19.77; p < 0.01); adherence was lower for other highly active DMTs (Coeff = −0.07; 95%CI = −0.10, −0.04; p < 0.01) and low-/medium-efficacy DMTs (Coeff = −0.16; 95%CI = −0.19, −0.14; p < 0.01). monthly DMT costs were higher for other highly active DMTs (Coeff = 77.45; 95%CI = 29.36, 125.53; p < 0.01) but lower for low-/medium-efficacy DMTs (Coeff = −772.31; 95%CI = −816.95, −727.66; p < 0.01). The hospital admissions and related costs of MS were similar between ocrelizumab, other highly active DMTs, and other low-/medium-efficacy DMTs, and with ocrelizumab as the first-line DMT after other highly active DMTs and after low-/medium-efficacy DMTs, which was possibly due to the low number of observations. Conclusions: From 2018 to 2022, ocrelizumab was among the most frequently prescribed DMTs, with 28.8% prescriptions to incident MS patients, confirming its relevance in clinical practice. Ocrelizumab was associated with the highest persistence and adherence, pointing towards its favorable benefit–risk profile. The costs of ocrelizumab were lower than those of other highly active DMTs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Papers from the Editorial Board Members (EBMs) and Invited Scholars of Neurology International)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Decoding Post-Viral Fatigue: The Basal Ganglia’s Complex Role in Long-COVID
by
Thorsten Rudroff
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 380-393; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020028 - 28 Mar 2024
Abstract
Long-COVID afflicts millions with relentless fatigue, disrupting daily life. The objective of this narrative review is to synthesize current evidence on the role of the basal ganglia in long-COVID fatigue, discuss potential mechanisms, and highlight promising therapeutic interventions. A comprehensive literature search was
[...] Read more.
Long-COVID afflicts millions with relentless fatigue, disrupting daily life. The objective of this narrative review is to synthesize current evidence on the role of the basal ganglia in long-COVID fatigue, discuss potential mechanisms, and highlight promising therapeutic interventions. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases. Mounting evidence from PET, MRI, and functional connectivity data reveals basal ganglia disturbances in long-COVID exhaustion, including inflammation, metabolic disruption, volume changes, and network alterations focused on striatal dopamine circuitry regulating motivation. Theories suggest inflammation-induced signaling disturbances could impede effort/reward valuation, disrupt cortical–subcortical motivational pathways, or diminish excitatory input to arousal centers, attenuating drive initiation. Recent therapeutic pilots targeting basal ganglia abnormalities show provisional efficacy. However, heterogeneous outcomes, inconsistent metrics, and perceived versus objective fatigue discrepancies temper insights. Despite the growing research, gaps remain in understanding the precise pathways linking basal ganglia dysfunction to fatigue and validating treatment efficacy. Further research is needed to advance understanding of the basal ganglia’s contribution to long-COVID neurological sequelae and offer hope for improving function across the expanding affected population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue COVID-19, Neuroinflammation and Therapeutics, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
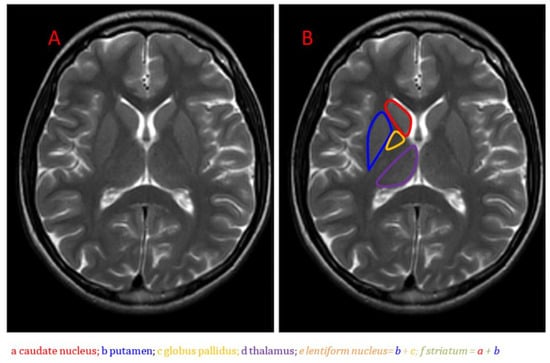
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Hyperglycaemia Aggravates Oxidised Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Schwann Cell Death via Hyperactivation of Toll-like Receptor 4
by
Wataru Nihei, Ayako Kato, Tatsuhito Himeno, Masaki Kondo, Jiro Nakamura, Hideki Kamiya, Kazunori Sango and Koichi Kato
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 370-379; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020027 - 19 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Increased low-density lipoprotein levels are risk factors for diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes mellitus is associated with elevated metabolic stress, leading to oxidised low-density lipoprotein formation. Therefore, it is important to investigate the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy in diabetes complicated by dyslipidaemia
[...] Read more.
Increased low-density lipoprotein levels are risk factors for diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes mellitus is associated with elevated metabolic stress, leading to oxidised low-density lipoprotein formation. Therefore, it is important to investigate the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy in diabetes complicated by dyslipidaemia with increased levels of oxidised low-density lipoprotein. Here, we examined the effects of hyperglycaemia and oxidised low-density lipoprotein treatment on Schwann cell death and its underlying mechanisms. Immortalised mouse Schwann cells were treated with oxidised low-density lipoprotein under normo- or hyperglycaemic conditions. We observed that oxidised low-density lipoprotein-induced cell death increased under hyperglycaemic conditions compared with normoglycaemic conditions. Moreover, hyperglycaemia and oxidised low-density lipoprotein treatment synergistically upregulated the gene and protein expression of toll-like receptor 4. Pre-treatment with TAK-242, a selective toll-like receptor 4 signalling inhibitor, attenuated hyperglycaemia- and oxidised low-density lipoprotein-induced cell death and apoptotic caspase-3 pathway. Our findings suggest that the hyperactivation of toll-like receptor 4 signalling by hyperglycaemia and elevated oxidised low-density lipoprotein levels synergistically exacerbated diabetic neuropathy; thus, it can be a potential therapeutic target for diabetic neuropathy.
Full article
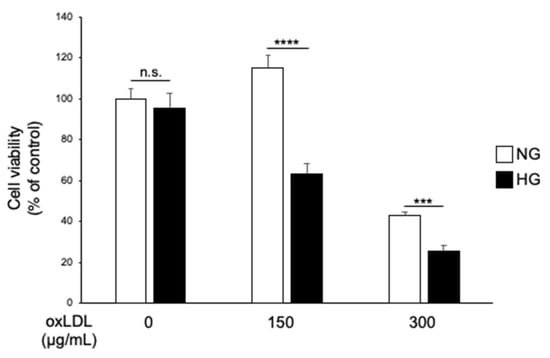
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Headache Disorders: An Observational, Cross-Sectional Study
by
Leonidas Mantonakis, Ioanna Belesioti, Christina I. Deligianni, Vasilis Natsis, Euthimia Mitropoulou, Elina Kasioti, Maria Lypiridou and Dimos D. Mitsikostas
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 356-369; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020026 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Headache disorders have been associated with anxiety and depressive disorders. The aim of this study was to assess symptoms of anxiety and depression in a large sample of individuals with different headache disorders (HDs) in order to determine whether their frequency differs
[...] Read more.
Background: Headache disorders have been associated with anxiety and depressive disorders. The aim of this study was to assess symptoms of anxiety and depression in a large sample of individuals with different headache disorders (HDs) in order to determine whether their frequency differs by headache type. Methods: Consecutive individuals with headache attending a headache outpatient clinic were interviewed with the HAM-D and HAM-A, along with age, sex, and education matched non-headache individuals. Results: Individuals numbering 2673 with headache (females 71.2%) and 464 non-headache individuals (females 70.9%) were interviewed (with participation rates of 98.3% and 91.0%, respectively). Migraine was diagnosed in 49.7%, tension-type headache in 38%, cluster headache 5.2%, and medication overuse (MO) in 21.8%. Participants with HD scored more in HAM-A (OR = 4.741, CI95%: 3.855–5.831, p < 0.001) and HAM-D scales (OR = 2.319, CI95%: 1.892–2.842, p < 0.001) than non-headache individuals. Participants with chronic HDs (≥15 days with headache for ≥3 consecutive months; 52.5%) scored higher for both HAM-A (OR = 1.944, CI95%: 1.640–2.303, p < 0.001) and HAM-D (OR = 1.625, CI95%: 1.359–1.944, p < 0.001) than those with episodic HDs (33.1%), as did participants with MO vs. participants without MO (OR = 3.418, CI95%: 2.655–4.399, p < 0.001 for HAM-A, OR = 3.043, CI95%: 2.322–3.986, p < 0.001 for HAM-D). Female and low-educated participants scored higher on both scales. Conclusion: Because symptoms of anxiety and depression are substantial in people with HD, the treating physicians should look out for such symptoms and manage them appropriately.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Migraines and Beyond: Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Headache Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
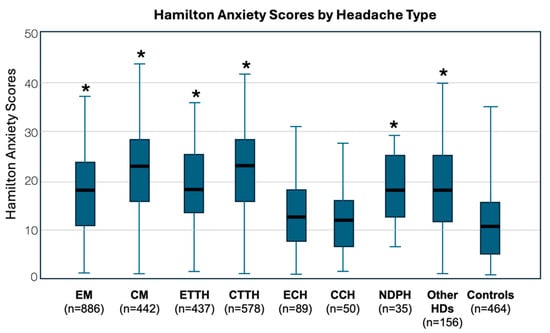
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Pulsed Radiofrequency for Auriculotemporal Neuralgia: A Case Report
by
Yan Tereshko, Enrico Belgrado, Christian Lettieri, Simone Dal Bello, Giovanni Merlino, Gian Luigi Gigli and Mariarosaria Valente
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 349-355; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020025 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
Auriculotemporal neuralgia is a rare facial pain disorder with no therapeutic evidence for refractory cases. We described a male patient with right auriculotemporal neuralgia, refractory to anesthetic nerve blocks and botulinum toxin type A injections, who was successfully treated with pulsed radiofrequency without
[...] Read more.
Auriculotemporal neuralgia is a rare facial pain disorder with no therapeutic evidence for refractory cases. We described a male patient with right auriculotemporal neuralgia, refractory to anesthetic nerve blocks and botulinum toxin type A injections, who was successfully treated with pulsed radiofrequency without adverse events. Pulsed radiofrequency may be an effective and safe treatment for refractory auriculotemporal neuralgia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Migraines and Beyond: Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Headache Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
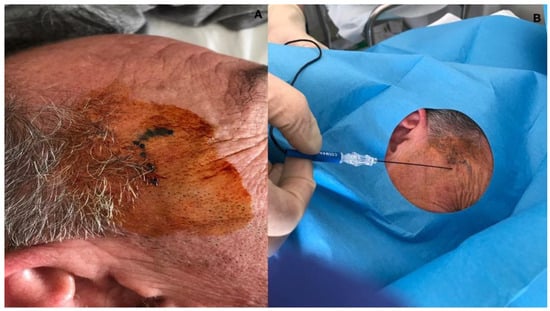
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Emerging Evidence of Golgi Stress Signaling for Neuropathies
by
Remina Shirai and Junji Yamauchi
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 334-348; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020024 - 07 Mar 2024
Abstract
The Golgi apparatus is an intracellular organelle that modifies cargo, which is transported extracellularly through the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and plasma membrane in order. First, the general function of the Golgi is reviewed and, then, Golgi stress signaling is discussed. In addition to
[...] Read more.
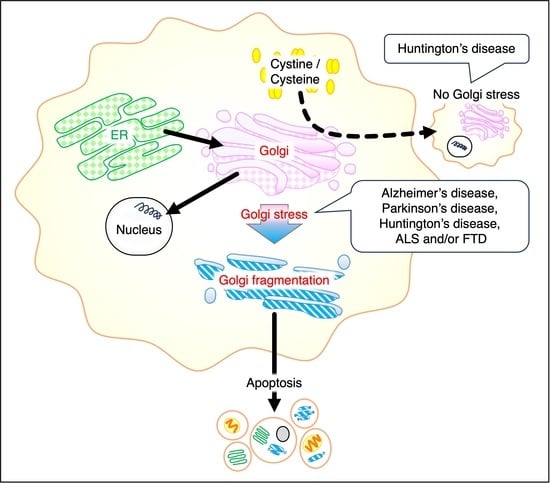
The Golgi apparatus is an intracellular organelle that modifies cargo, which is transported extracellularly through the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and plasma membrane in order. First, the general function of the Golgi is reviewed and, then, Golgi stress signaling is discussed. In addition to the six main Golgi signaling pathways, two pathways that have been increasingly reported in recent years are described in this review. The focus then shifts to neurological disorders, examining Golgi stress reported in major neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease. The review also encompasses findings related to other diseases, including hypomyelinating leukodystrophy, frontotemporal spectrum disorder/amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, microcephaly, Wilson’s disease, and prion disease. Most of these neurological disorders cause Golgi fragmentation and Golgi stress. As a result, strong signals may act to induce apoptosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Papers from the Editorial Board Members (EBMs) and Invited Scholars of Neurology International)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessCase Report
Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood
by
Maša Fabjan, Ana Jurečič, Miha Jerala, Janja Pretnar Oblak and Senta Frol
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 327-333; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020023 - 04 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The number of published cases of presumed iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy (iCAA) due to the transmission of amyloid β during neurosurgery is slowly rising. One of the potential ways of transmission is through a cadaveric dura mater graft (LYODURA) exposure during neurosurgery. This
[...] Read more.
The number of published cases of presumed iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy (iCAA) due to the transmission of amyloid β during neurosurgery is slowly rising. One of the potential ways of transmission is through a cadaveric dura mater graft (LYODURA) exposure during neurosurgery. This is a case of a 46-year-old female patient with no chronic conditions who presented with recurrent intracerebral haemorrhages (ICHs) without underlying vessel pathology. Four decades prior, the patient had a neurosurgical procedure with documented LYODURA transplantation. Brain biopsy confirmed CAA. This is a rare case of histologically proven iCAA after a documented LYODURA transplantation in childhood. Our case and already published iCAA cases emphasize the need for considering neurosurgery procedure history as important data in patients who present with ICH possibly related to CAA.
Full article
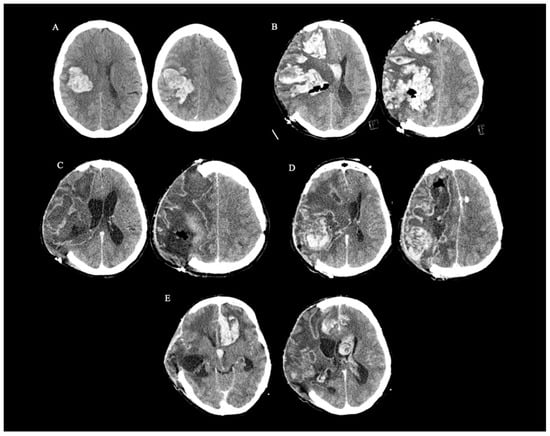
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Visuo-Attentional and Phonological Deficits Explored in French Students with Dyslexia: Eye Movements Recorded during a Phonological Lexical Decision Task
by
Aikaterini Premeti, Frédéric Isel and Maria Pia Bucci
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 312-326; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020022 - 01 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Whether dyslexia is caused by phonological or attentional dysfunction remains a widely debated issue. To enrich this debate, we compared the eye movements of 32 French university students with (14 students) and without (18 students) dyslexia while performing a delayed phonological lexical decision
[...] Read more.
Whether dyslexia is caused by phonological or attentional dysfunction remains a widely debated issue. To enrich this debate, we compared the eye movements of 32 French university students with (14 students) and without (18 students) dyslexia while performing a delayed phonological lexical decision task on 300 visually presented stimuli. The processing stimuli involved either a lexical (i.e., words) or a non-lexical route relying on a grapheme-phoneme correspondence (pseudohomophones and pseudowords), while other stimuli involved only a visual search (consonant and symbol sequences). We recorded the number of fixations, the duration of the first fixation and the amplitude of saccades made on the stimuli. Compared to the controls, the participants with dyslexia made more fixations while reading regardless of the type of stimulus (lexical and non-lexical). Crucially, the participants with dyslexia exhibited longer first fixations in particular while reading phonologically challenging stimuli such as pseudohomophones and pseudowords compared to stimuli involving a simple visual search (consonants, symbols). Taken together, these results suggest that both visual and phonological impairments may be implicated in dyslexia, supporting the hypothesis that dyslexia is a multifactorial deficit.
Full article
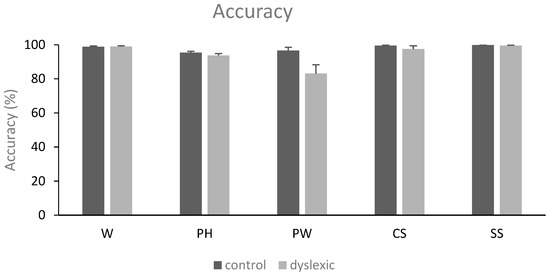
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neurite Damage in Patients with Migraine
by
Yasushi Shibata and Sumire Ishiyama
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 299-311; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020021 - 29 Feb 2024
Abstract
We examined neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging in patients with migraine. We found that patients with medication overuse headache exhibited lower orientation dispersion than those without. Moreover, orientation dispersion in the body of the corpus callosum was statistically negatively correlated with migraine
[...] Read more.
We examined neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging in patients with migraine. We found that patients with medication overuse headache exhibited lower orientation dispersion than those without. Moreover, orientation dispersion in the body of the corpus callosum was statistically negatively correlated with migraine attack frequencies. These findings indicate that neurite dispersion is damaged in patients with chronic migraine. Our study results indicate the orientation preference of neurite damage in migraine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Migraines and Beyond: Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Headache Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
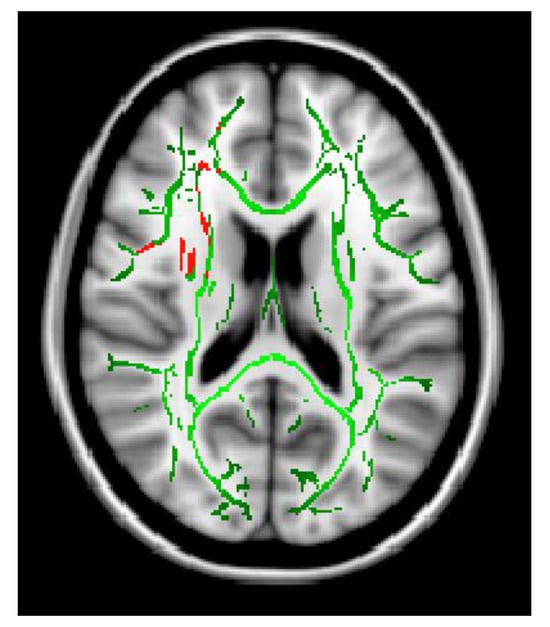
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Acute Anterior Choroidal Artery Territory Infarction: A Case Series Report
by
Antonia Tsika, Polyxeni Stamati, Zisis Tsouris, Antonios Provatas, Alexandra Papa, Dimitrios Tsimoulis, Stylliani Ralli, Vasileios Siokas and Efthimios Dardiotis
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(2), 289-298; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020020 - 29 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Due to the occlusion of the anterior choroidal artery (AChA), ischemic strokes are described with the classic clinical triad, namely hemiplegia, hemianesthesia, and homonymous hemianopsia. The aim of this study is to document the characteristic clinical presentation and course of AChA infract cases.
[...] Read more.
Due to the occlusion of the anterior choroidal artery (AChA), ischemic strokes are described with the classic clinical triad, namely hemiplegia, hemianesthesia, and homonymous hemianopsia. The aim of this study is to document the characteristic clinical presentation and course of AChA infract cases. We describe five cases with acute infarction in the distribution of the AChA, admitted to the Neurological Department of the University General Hospital of Larissa. Results: All cases presented with hemiparesis and lower facial nerve palsy, while four of them had dysarthria, and two patients exhibited ataxia. Two cases underwent intravenous thrombolysis. A notable feature was the worsening of the clinical course, specifically the exacerbation of upper limb weakness within 48 h. Stabilization occurred after the third day, with the final development of a more severe clinical presentation than the initial one. Additionally, muscle weakness was more severe in the upper limb than in the lower limb. The recovery of upper limb function was poor in the three-month follow-up for the four cases. While vascular brain episodes are characterized by sudden onset, in AChA infraction, the clinical onset can be gradually developed over a few days, with a greater burden on the upper limb and poorer recovery.
Full article
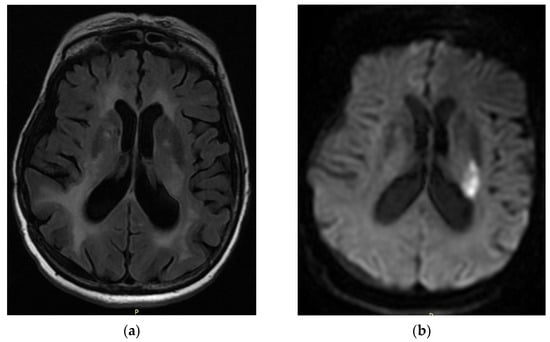
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effectiveness of Switching CGRP Monoclonal Antibodies in Non-Responder Patients in the UAE: A Retrospective Study
by
Reem Suliman, Vanessa Santos, Ibrahim Al Qaisi, Batool Aldaher, Ahmed Al Fardan, Hajir Al Barrawy, Yazan Bader, Jonna Lyn Supena, Kathrina Alejandro and Taoufik Alsaadi
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(1), 274-288; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010019 - 18 Feb 2024
Abstract
Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies (CGRP mAbs) have shown promising effectiveness in migraine management compared to other preventative treatment options. Many questions remain regarding switching between antibody classes as a treatment option in patients with migraine headaches. This preliminary retrospective real-world study explored
[...] Read more.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies (CGRP mAbs) have shown promising effectiveness in migraine management compared to other preventative treatment options. Many questions remain regarding switching between antibody classes as a treatment option in patients with migraine headaches. This preliminary retrospective real-world study explored the treatment response of patients who switched between CGRP mAb classes due to lack of efficacy or poor tolerability. A total of 53 patients with migraine headache switched between three of the CGRP mAbs types due to lack of efficacy of the original prescribed CGRP mAbs, specifically eptinezumab, erenumab, and galcanezumab. Fremanezumab was not included due to unavailability in the UAE. Galcanezumab and eptinezumab target the CGRP ligand (CGRP/L), while erenumab targets CGRP receptors (CGRP/R). The analysis of efficacy demonstrated that some improvements were seen in both class switch cohorts (CGRP/R to CGRP/L and CGRP/L to CGRP/R). The safety of switching between CGRP classes was well observed, as any adverse events presented before the class switch did not lead to the discontinuation of treatment following the later switch. The findings of this study suggest that switching between different classes of CGRP mAbs is a potentially safe and clinically viable practice that may have some applications for those experiencing side effects on their current CGRP mAb or those witnessing suboptimal response.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Migraines and Beyond: Advances in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Chronic Headache Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
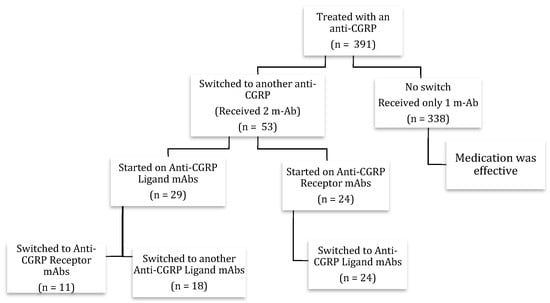
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
The Effects of Intensive Rehabilitation Combined with Thiamine Treatment on Cognitive Recovery in a Case of Non-Alcoholic Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome
by
Cinzia Palmirotta, Gilda Turi, Serena Tagliente, Michele Pansini, Stefania De Trane and Gianvito Lagravinese
Neurol. Int. 2024, 16(1), 263-273; https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010018 - 14 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS) is a severe neurological disorder resulting from thiamine deficiency, commonly associated with alcohol consumption but also stemming from dietary imbalances or other clinical conditions. Cognitive deficits, affecting memory and executive functions, pose a serious concern, with partial recovery often not
[...] Read more.
Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome (WKS) is a severe neurological disorder resulting from thiamine deficiency, commonly associated with alcohol consumption but also stemming from dietary imbalances or other clinical conditions. Cognitive deficits, affecting memory and executive functions, pose a serious concern, with partial recovery often not complete. A 28-year-old woman underwent surgery for acute necrotizing hemorrhagic pancreatitis, leading to admission for post-acute intensive treatment due to prolonged bed rest syndrome. Clinical examinations revealed sensory–motor neuropathy, denervation in the active phase, mammillary body hyperintensity, and cognitive impairment. The patient exhibited poor orientation, lacked awareness of her clinical condition, and experienced impaired nonverbal memory, practical constructive issues, and planning difficulties—consistent with WKS. The patient received high-dose thiamine (300 mg TDS), coupled with daily physiokinesitherapy and occupational therapy. A final neuropsychological evaluation three months later showed substantial remission of executive and memory difficulties, improved spatial–temporal orientation, and enhanced awareness. The complex case required timely multidisciplinary intervention for accurate diagnosis and effective rehabilitation. The patient experienced rapid clinical improvement and cognitive recovery with high-dose thiamine and physiotherapy.
Full article
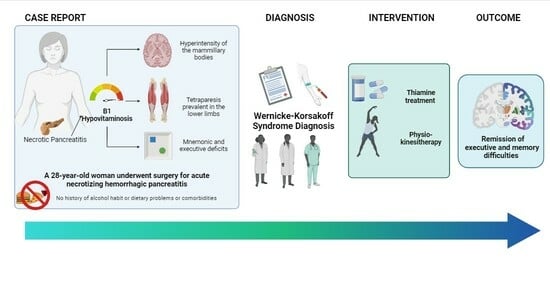
Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Brain Sciences, Geriatrics, Life, Neurology International
Translational Advances in Neurodegenerative Dementias
Topic Editors: Francesco Di Lorenzo, Annibale AntonioniDeadline: 31 October 2024
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, JCM, Medicina, Neurology International
Advances in Exercise-Induced Neurogenesis, Neuronal and Functional Adaptations in Neurorehabilitation
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Cleofas Rodriguez-Blanco, Maria Livia Carrascal MorenoDeadline: 22 December 2024
Topic in
Antioxidants, Biomolecules, JCDD, Metabolites, Neurology International, Pharmaceutics
Tissue-Specific, Disease-Signatured Macrophages in Control of Redox and Antioxidation in Metabolic Diseases
Topic Editors: Xiangwei Xiao, Yingmei Feng, Zhiyong LeiDeadline: 5 July 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Neurology International
Emerging Issues in Vascular Cognitive Impairment
Guest Editors: Dragos Catalin Jianu, Dafin Fior Muresanu, Jean Claude SadikDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Neurology International
Glioblastoma: Mechanics of Development, Progression and New Surgical and Clinical Management
Guest Editor: Nicola MontemurroDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Neurology International
Selected Papers from "Brainstorming Research Assembly for Young Neuroscientists (BraYn)
Guest Editor: Giovanni FerraraDeadline: 1 August 2024
Special Issue in
Neurology International
Treatment Strategy and Mechanism of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Guest Editor: Sonu M. M. BhaskarDeadline: 1 October 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Neurology International
Brain Health Initiative: Advocacy in Global Neurology
Collection Editors: Tissa Wijeratne, Leila Karimi, Dilani Wijeratne
Topical Collection in
Neurology International
Advances in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Collection Editors: Vasileios Siokas, Efthimios Dardiotis
Topical Collection in
Neurology International
Biomarkers in Stroke Prognosis
Collection Editors: Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Konstantinos Vadikolias