Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood
Abstract
1. Introduction
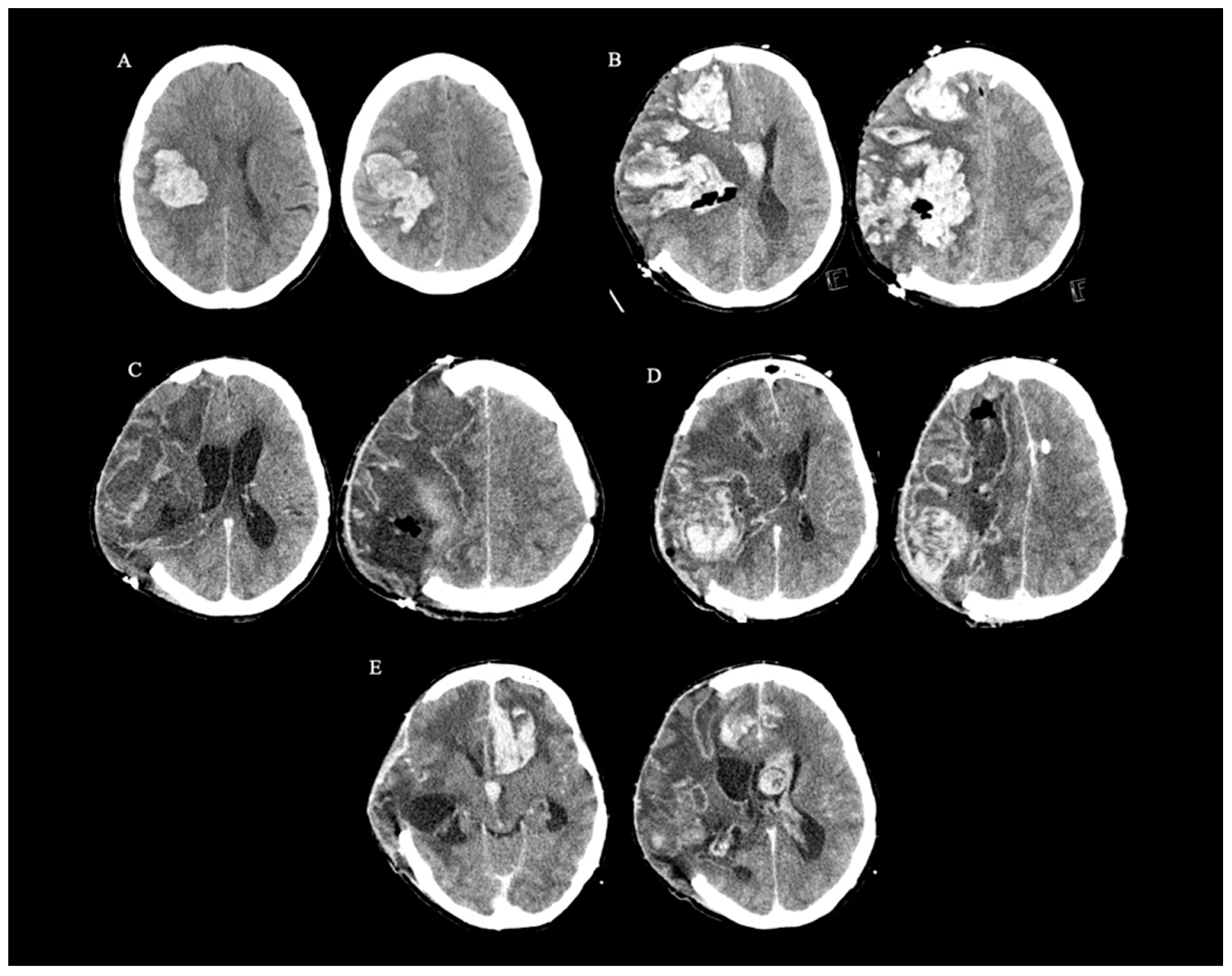
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, S.A.; Patel, R.K.; Lutsep, H.L. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Diagnosis and potential therapies. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Thomas, M.M.; Sipe, A.L.; Benzinger, T.L.; McConathy, J.; Connolly, S.; Schwetye, K.E. Multimodality Review of Amyloid-related Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Radiographics 2016, 36, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, G.; Collinge, J.; Fox, N.C.; Lashley, T.; Mead, S.; Schott, J.M.; Werring, D.J.; Ryan, N.S. Clinical considerations in early-onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 2023, 146, 3991–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikija, S.; Pretnar-Oblak, J.; Frol, S.; Malojcic, B.; Gattringer, T.; Rak-Frattner, K.; Staykov, D.; Salmaggi, A.; Milani, R.; Magdic, J.; et al. Iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: A multinational case series and individual patient data analysis of the literature. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 29, 17474930231203133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblak, J.P.; Jurečič, A.; Writzl, K.; Frol, S. Preceding Head Trauma in Four Cases of Sporadic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy—Case Report Series. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Samarasekera, N.; Lerpiniere, C.; Humphreys, C.; McCarron, M.O.; White, P.M.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Cordonnier, C.; Wardlaw, J.M.; et al. The Edinburgh CT and genetic diagnostic criteria for lobar intracerebral haemorrhage associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: Model development and diagnostic test accuracy study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Charidimou, A. Diagnosis of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: Evolution of the Boston Criteria. Stroke 2018, 49, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Mead, S.; Ellis, M.; Wadsworth, J.D.; Nicoll, A.J.; Kenny, J.; Launchbury, F.; Linehan, J.; Richard-Loendt, A.; Walker, A.S.; et al. Evidence for human transmission of amyloid-β pathology and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nature 2015, 10, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Samra, K.; Adams, M.E.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Parry-Jones, A.R.; Grieve, J.; Toma, A.K.; Farmer, S.F.; Sylvester, R.; Houlden, H.; et al. Iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy: An emerging clinical phenomenon. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 16, jnnp-2022-328792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Adams, M.E.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Alistar Lammie, G.; Turner, B.; Wani, M.; Sawhney, I.M.S.; Mead, S.; Brandner, S.; Werring, D.J. Early onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy following childhood exposure to cadaveric dura. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Quaegebeur, A.; Taipa, R.; Viana-Baptista, M.; Barbosa, R.; Koriath, C.; Sciot, R.; Mead, S.; Brandner, S. Evidence of amyloid-β cerebral amyloid angiopathy transmission through neurosurgery. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C. Case report of iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy after exposure to Lyodura: An Australian perspective. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1185267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purrucker, J.C.; Röcken, C.; Reuss, D. Iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy rather than sporadic CAA in younger adults with lobar intracerebral haemorrhage. Amyloid 2023, 30, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, K.; van Etten, E.S.; Siegerink, B.; Kappelle, L.J.; Lemstra, A.W.; Schreuder, F.B.M.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Peul, W.C.; Terwindt, G.M.; van Walderveen, M.A.A.; et al. Iatrogenic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Post Neurosurgery: Frequency, Clinical Profile, Radiological Features, and Outcome. Stroke 2023, 54, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro Romero, A.; Moreno Loscertales, C.; Marta Moreno, E. Unilateral cerebral amyloid angiopathy after neurointervention. Neurologia (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 37, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellie, J.F.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Watson, R.; Praeger, A.J.; Nair, G.; Murugasu, A.; Rowe, C.C.; Masters, C.L.; Collins, S.; McLean, C.; et al. Amyloid-β (Aβ)-Related Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Causing Lobar Hemorrhage Decades After Childhood Neurosurgery. Stroke 2022, 53, e369–e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limpo, H.; Andrés, A.; Fortes, J.; García, M.A.; Presti, A.L. Early-onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy, a prion-like disease: Case report and literature review. J. Neurosurg. Res. Rev. 2021, 4, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiki, K.; Hirose, G.; Kumahashi, K.; Kohda, Y.; Ido, K.; Shioya, A.; Misaki, K.; Kasuga, K. Follow-up study of a patient with early onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy following childhood cadaveric dural graft. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2021, 163, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, G.; Maderna, E.; Marucci, G.; Catania, M.; Erbetta, A.; Chiapparini, L.; Indaco, A.; Caroppo, P.; Bersano, A.; Parati, E.; et al. Iatrogenic early onset cerebral amyloid angiopathy 30 years after cerebral trauma with neurosurgery: Vascular amyloid deposits are made up of both Aβ40 and Aβ42. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunmuktane, Z.; Banerjee, G.; Paine, S.; Parry-Jones, A.; Rudge, P.; Grieve, J.; Toma, A.K.; Farmer, S.F.; Mead, S.; Houlden, H.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease neuropathological change three decades after iatrogenic amyloid-β transmission. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, D.; Porché, M.; Cabrejo, L.; Guidoux, C.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Nicolas, G.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Plu, I.; Chabriat, H.; Duyckaerts, C. Fatal Aβ cerebral amyloid angiopathy 4 decades after a dural graft at the age of 2 years. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Mineharu, Y.; Arawaka, Y.; Nishida, S.; Tsuji, H.; Miyake, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Minamiguchi, S.; Takagi, Y.; Miyamoto, S.; et al. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a young man with a history of traumatic brain injury: A case report and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2017, 159, 15–18, Erratum in: Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2017, 159, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, P.; Marucci, G.; Maccagnano, E.; Gobbo, C.L.; Bizzozero, I.; Tiraboschi, P.; Redaelli, V.; Catania, M.; Di Fede, G.; Caputi, L.; et al. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a 51-year-old patient with embolization by dura mater extract and surgery for nasopharyngeal angiofibroma at age 17. Amyloid 2021, 28, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Komatsu, J.; Sakai, K.; Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Aoki, S.; Ikeuchi, T.; Yamada, M. Cerebral hemorrhagic stroke associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy in young adults about 3 decades after neurosurgeries in their infancy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 399, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling, R.; Helbok, R.; Beer, R.; Lackner, P.; Broessner, G.; Pfausler, B.; Röckenb, C.; Aguzzic, A.; Chemellid, A.; Schmutzharda, E. Recurrent intracerebral haemorrhage after coitus: A case report of sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a younger patient. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, L.; Van Weehaeghe, D.; Vandenberghe, R.; Demeestere, J.; Van Laere, K.; Lemmens, R. The Role of Amyloid PET in Diagnosing Possible Transmissible Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy in Young Adults with a History of Neurosurgery: A Case Series. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 50, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, N.; Planton, M.; Siegfried, A.; Calviere, L.; Payoux, P.; Albucher, J.F.; Viguier, A.; Delisle, M.-B.; Uro-Coste, E.; Chollet, F.; et al. Amyloid-β transmission through cardiac surgery using cadaveric dura mater patch. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachiyama, K.; Kajikawa, S.; Nakamori, M.; Matsushima, H.; Imamura, E.; Wakabajashi, S.; Urakami, K. Infant critical head injury could be a remote cause of middle-aged cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Res. Sq. 2020, 22, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomzig, A.; Wagenführ, K.; Daus, M.L.; Joncic, M.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Thanheiser, M.; Mielke, M.; Beekes, M. Decontamination of medical devices from pathological amyloid-β-, tau- and α-synuclein aggregates. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 25, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eisele, Y.S.; Bolmont, T.; Heikenwalder, M.; Langer, F.; Jacobson, L.H.; Yan, Z.X.; Roth, K.; Aguzzi, A.; Staufenbiel, M.; Walker, L.C.; et al. Induction of cerebral beta-amyloidosis: Intracerebral versus systemic Abeta inoculation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12926–12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purrucker, J.C.; Hund, E.; Ringleb, P.A.; Hartmann, C.; Rohde, S.; Schönland, S.; Steiner, T. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy—An underdiagnosed entity in younger adults with lobar intracerebral hemorrhage? Amyloid 2013, 20, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.M.; Bruins, S.; Vogel, H.; Shuer, L.M.; Wijman, C.A. Intracerebral hemorrhage caused by cerebral amyloid angiopathy in a 53-year-old man. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabjan, M.; Jurečič, A.; Jerala, M.; Oblak, J.P.; Frol, S. Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 327-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020023
Fabjan M, Jurečič A, Jerala M, Oblak JP, Frol S. Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood. Neurology International. 2024; 16(2):327-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabjan, Maša, Ana Jurečič, Miha Jerala, Janja Pretnar Oblak, and Senta Frol. 2024. "Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood" Neurology International 16, no. 2: 327-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020023
APA StyleFabjan, M., Jurečič, A., Jerala, M., Oblak, J. P., & Frol, S. (2024). Recurrent Intracerebral Haematomas Due to Amyloid Angyopathy after Lyodura Transplantation in Childhood. Neurology International, 16(2), 327-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16020023





