- Article
Sterol Endoperoxides and Their Antileishmanial Effects: Influence on Viability, Oxygen Metabolism and Sterol Synthesis
- Deblina Sarkar,
- Azra Aleta and
- Lars Gille
- + 9 authors
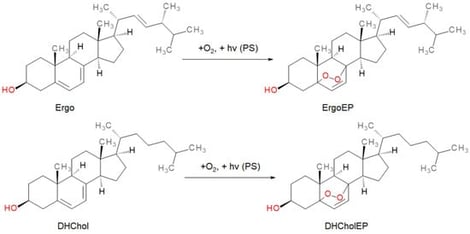
Leishmaniasis is a global health issue, especially in tropical and subtropical areas, with treatment challenges due to the development of resistance to current drugs. This has prompted the search for new antileishmanial compounds. Endoperoxides, due to parasites’ reliance on external iron and susceptibility to oxidative stress, are promising antileishmanial compounds. This study evaluated two sterol endoperoxides—ergosterol endoperoxide (ErgoEP) and dehydrocholesterol endoperoxide (DHCholEP)—for their antileishmanial activity and mechanism in vitro. Cell viability assays with Leishmania donovani and Leishmania tarentolae promastigotes showed IC50 values in the low micromolar range (from 2.0 to 4.5 µM, respectively) with low toxicity to murine and J774A.1 macrophages. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy confirmed radical generation in the presence of low-molecular-weight iron compounds. However, this did not trigger the antileishmanial effect, as neither N-acetylcysteine nor pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone altered activity. Mitochondrial function(s) and superoxide production in Leishmania remained unaffected. Both endoperoxides significantly inhibited synthesis of 5-dehydroepisterol, the major sterol in Leishmania tarentolae, suggesting targeting of the sterol biosynthesis pathway. Their limited toxicity to mammalian macrophages makes ergosterol and dehydrocholesterol endoperoxides promising candidates for future antileishmanial drug development.
14 March 2026