- 3.2Impact Factor
- 6.4CiteScore
- 16 daysTime to First Decision
Preparation and Applications of Metal and Alloy Powders
This special issue belongs to the section “Metals and Alloys“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
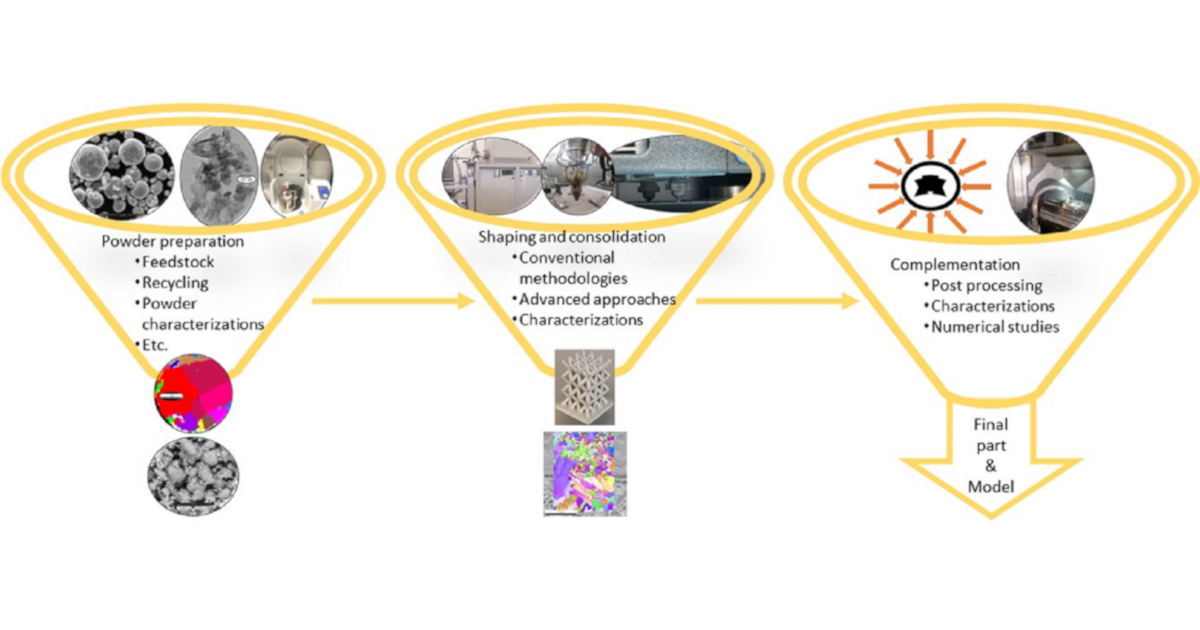
Casting, forging, and machining are conventional manufacturing techniques to produce metallic components. However, energy consumption, geometry, series production, and residues are some critical issues. Powder metallurgy routes seem interesting to produce small parts and semi-complex geometries, leaving fewer residues. Recent techniques such as additive manufacturing provided some advantages including the production of complex geometries and a few numbered products. Thus, the use of metallic powders has become more highlighted than before. However, proper preparations and adequate processing conditions will lead to noteworthy applications in mold, transport, and medical industries. Powder processing can involve single-composition virgin powders, (nano)composite production, mechanical alloying or using rather recent developments such as high entropy alloys or functional materials. Post-processing and/or numerical simulations are complementary steps in order to foster the process and production. The importance of resources and sustainability issues have also led to paying attention to recycling, adding value to residues and creating closed production cycles in the field of powder processing and applications.
Powder preparations can involve different mixing techniques and recycling for additive manufacturing processes. The success of powder applications depends not only on the powder characteristics (shape, size, size distribution, structure, density, and flowability) but also on the optimization of densification or consolidation achieved through sintering or melting approaches. Microstructural characterizations, mechanical and wear analyses, etc. are essential aspects of research and development. Nevertheless, conventional compaction-sintering, powder injection molding, or even advanced techniques such as field-assisted sintering, cold/thermal spraying, cladding, selective laser sintering, filament extrusion printing, powder binder jetting, laser or electron beam melting or binder melting methodologies are welcome for this Special Issue as well, both from academic and industrial researchers.
Prof. Dr. Manuel Vieira
Dr. Ana Rosanete Lourenço Reis
Dr. Omid Emadinia
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- powder characteristics
- mixing and feedstock
- sintering
- melting
- additive manufacturing
- advanced materials
- microstructural and mechanical characterizations
- properties
- numerical modeling
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.

