- Article
Gain-Enhanced Correlation Fusion for PMSM Inter-Turn Faults Severity Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithms
- Vasileios I. Vlachou,
- Theoklitos S. Karakatsanis and
- Stavros D. Vologiannidis
- + 2 authors
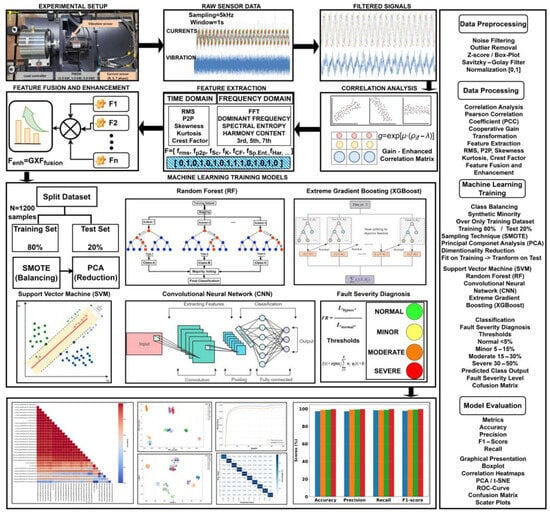
Diagnosing faults in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) is critical for ensuring their reliable operation, particularly in detecting internal short-circuit faults in the stator windings. These faults, such as inter-turn and inter-coil short circuits, can significantly affect motor performance and lead to costly downtime if not detected early. However, detecting these faults accurately, especially in the presence of operational noise and varying load conditions, remains a challenging task. To address this, a novel methodology is proposed for diagnosing and classifying fault severity in PMSMs using vibration and current data. The key innovation of the method is the combination of signal processing for both vibration and current data, to enhance fault detection by applying advanced feature extraction techniques such as root mean square (RMS), peak-to peak values, and spectral entropy in both time and frequency domains. Furthermore, a cooperative gain transformation is applied to amplify weak correlations between vibration and current signals, improving detection sensitivity, especially during early fault progression. In this study, the publicly available dataset on Mendeley, which consists of vibration and current measurements from three PMSMs with different power ratings of 1.0 kW, 1.5 kW, and 3.0 kW, was used. The dataset includes eight different levels of stator fault severity, ranging from 0% up to 37.66%, and covers normal operation, inter-coil short circuit, and inter-turn short circuit. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology, achieving an accuracy of 96.6% in fault classification. The performance values for vibration and current measurements, along with the corresponding fault severities, validate the method’s ability to accurately detect faults across various operating conditions.
22 January 2026