Immunopathology and Immunosenescence
A topical collection in International Journal of Molecular Sciences (ISSN 1422-0067). This collection belongs to the section "Molecular Pathology, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics".
Submission Status: Closed (31 October 2025) | Viewed by 139352Editors
Interests: ageing; age-related diseases; centenarians; immunogenetics; immunosenescence; inflammation; longevity; successful ageing; unsuccessful ageing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: autoimmunity; immune response; immunogenetics; immunosenescence; inflammaging; immunopathology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: inflamm-aging; immunogenetics; nutritional interventions; positive biology; viral infections
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: aging; nutrition; inflammation nutraceuticals; longevity; centenarians
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
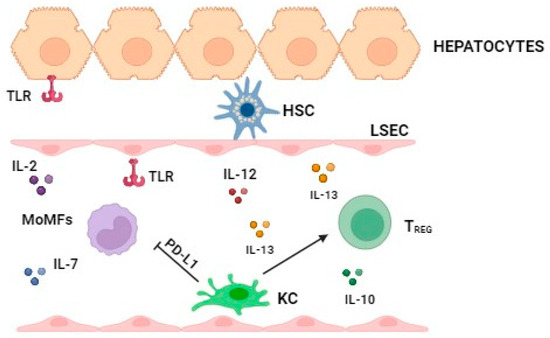
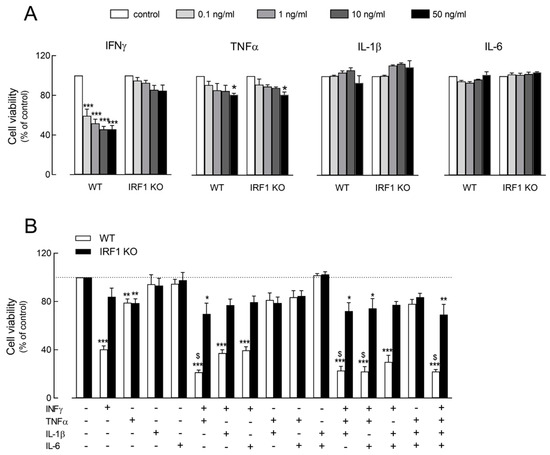
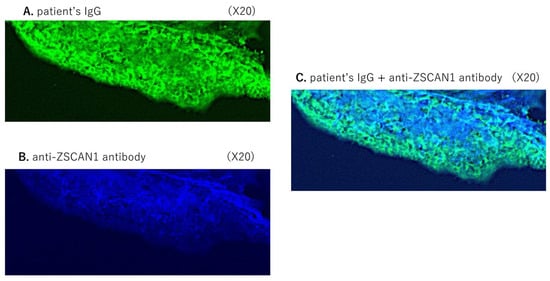
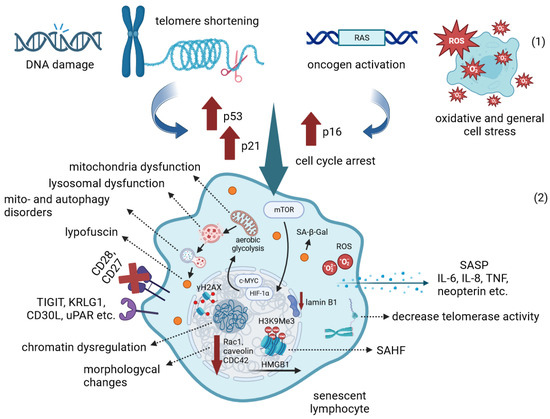
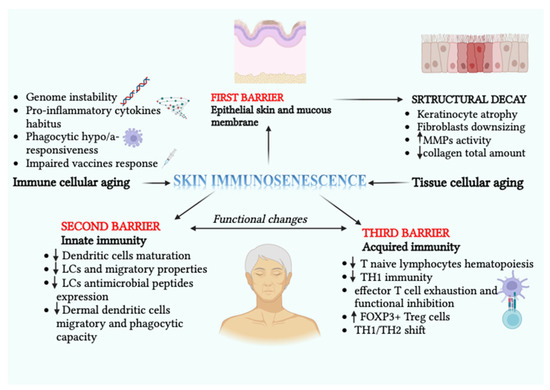
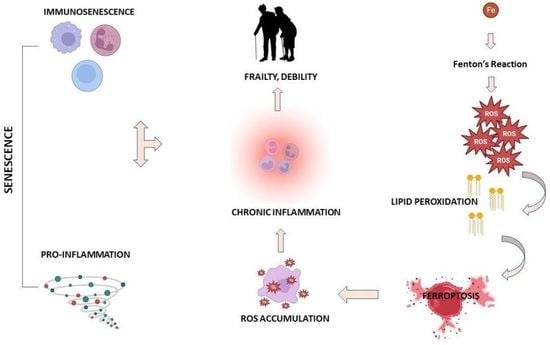
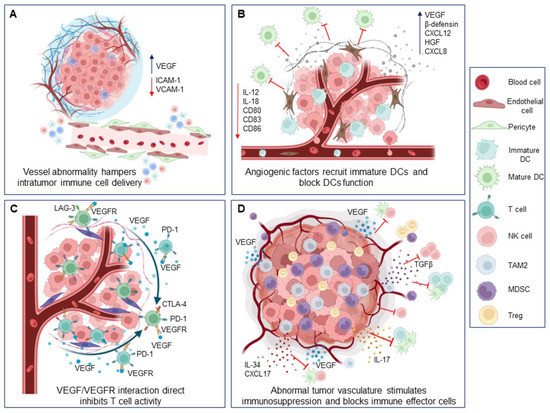
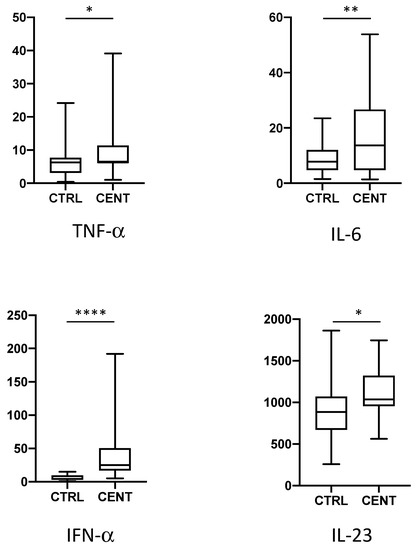
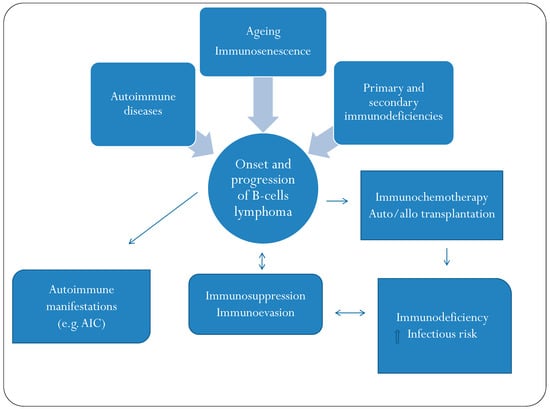
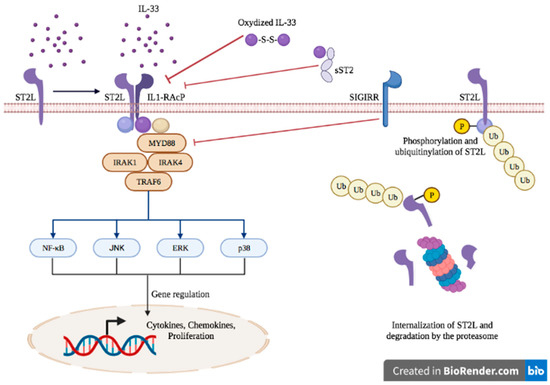
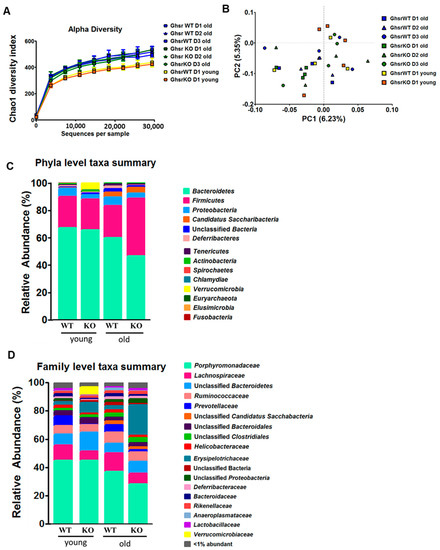
Advances in immunology have led to a greater understanding of the human immune response, and of its role in health and disease, although some aspects still need to be clarified. Two concern immunopathology and immunosenescence. Immunopathology refers to the damage to the self, caused by a hyper-reactive immune system in response to normal stimuli, and contributes to the mechanisms of various human diseases. Conversely, the reduction in the ability to trigger immune responses effective against infections and vaccinations, observed not only in older people, but also during some infections and some therapeutic treatments, is called immunosenescence. The study of immunopathology has been separated from the study of immunosenescence, but it is becoming clear that there might be a close relationship between them. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients are immunocompromised, and several data suggest that premature ageing of the immune system contributes to the pathogenesis of RA. Furthermore, the chronic immune stimulation characteristic of RA can itself age the immune system. On the other hand, the interaction between immunosenescence and its hallmark infllamm-ageing, i.e., an immunopathological response, has been hypothesized to contribute to the cytokine storm in older patients affected by COVID-19 as well as to age-related diseases. This Topical Collection will provide an up-to-date overview, gathering research or review manuscripts addressing processes that mechanistically participate to induce immunopathology and/or immunosenescence. Thus, papers discussing the mechanisms and the molecular pathways able to affect immune cell responses, considering the role of environment and lifestyle, genetics and age, as well as sex and gender as drivers are welcome. Studies on molecular, cellular and blood biomarkers are also welcome.
Prof. Dr. Calogero Caruso
Prof. Dr. Giuseppina Candore
Dr. Anna Aiello
Dr. Giulia Accardi
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Molecular Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. There is an Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal. For details about the APC please see here. Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- age-related diseases
- allergy
- autoimmunity
- gender
- hypersensitivity
- immunogenetics
- immunopathology
- immunosenescence