Journal Description
Hydrobiology
Hydrobiology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on freshwater and marine biology, limnology, fisheries, oceanography, and aquatic ecology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus and other databasaes.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Agricultural and Biological Sciences (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 7.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Hydrobiology is a companion journal of Life.
Latest Articles
Water Temperature as the Main Cause of Failure to Meet the Requirements of the European Water Framework Directive in the Fish Fauna Quality Element: Comparison of Two Low Mountain Rivers in Bavaria, Germany
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010006 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
This study addresses a long-term failure to achieve the good ecological status for fish fauna required by the European Water Framework Directive (WFD) in the salmonid–rhithral zone in Bavaria, Germany. To identify the causes, we compared extensive fish population data from the Eger
[...] Read more.
This study addresses a long-term failure to achieve the good ecological status for fish fauna required by the European Water Framework Directive (WFD) in the salmonid–rhithral zone in Bavaria, Germany. To identify the causes, we compared extensive fish population data from the Eger River with data from its twin river, the Röslau. The proportion of autochthonous cold, oligo-stenothermic fish species is significantly lower in the Eger (4.97% vs. 37.31%). In addition, continuous water temperature measurements were taken at five locations from spring to early autumn in 2023. The Eger showed significantly higher water temperatures throughout the measurement period. In midsummer, differences in daily maximum temperatures exceeded 10 °C at the same altitude. The proportion of cold-water fish in the population appeared to be negatively related to the mean of summer water temperature peaks (MWTP) (R = 0.95, p < 0.01). Accordingly, restoration measures in the Eger would need to reduce the MWTP from the current 19.1–20.5 °C to at least 16–16.5 °C, which requires more detailed data on the thermal footprint of individual hydraulic structures. The anthropogenic thermal impact on the Eger was overlooked as the root cause of the problem for many years, which largely explains the ineffectiveness of previous restoration measures. At least within the salmonid–rhithral zone, we consider the ability of the standardized fish-based assessment tool (fiBS) to detect thermal deterioration to be sufficient, provided it is applied with due care.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Blood Biochemical Parameters in Non-Native Armored Catfishes (Loricariidae) from Highland Rivers of Central Vietnam
by
Tran Duc Dien, Ekaterina V. Ganzha and Efim D. Pavlov
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010005 - 1 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the past decade, non-native suckermouth armored catfish, Pterygoplichthys spp., have spread throughout the highland rivers of Lam Dong province, Vietnam. We examined spatial and temporal variation in endocrine and biochemical profiles across different river reaches, river systems, and between two sampling years
[...] Read more.
In the past decade, non-native suckermouth armored catfish, Pterygoplichthys spp., have spread throughout the highland rivers of Lam Dong province, Vietnam. We examined spatial and temporal variation in endocrine and biochemical profiles across different river reaches, river systems, and between two sampling years (2020 and 2022). Seven blood parameters related to metabolism and energy balance were measured: total and free triiodothyronine, cholesterol, triglycerides, total protein, creatinine, and direct bilirubin. Concentrations of thyroid hormones and cholesterol did not differ significantly across sites or years. Multivariate analyses indicated that thyroid-related pathways were only weakly influenced by the environmental variation, suggesting preserved thyroid homeostasis. In contrast, triglycerides, total protein, creatinine, and direct bilirubin varied among rivers and between years at the same site, likely reflecting differences in food availability and energy balance. These results suggest that biochemical variation in non-native armored catfish is primarily expressed through lipid metabolism and protein turnover, while thyroid function remains comparatively conserved across invaded river habitats.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Carassius gibelio from Lakes of Varying Ecological Quality
by
Dimitra Petrocheilou, Olga Petriki, Martha Kaloyianni and Dimitra C. Bobori
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010004 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC requires the assessment of the ecological quality in all surface waters using biological indices, yet the effective application of these indices often demands extensive and long-term monitoring data. Oxidative stress biomarkers offer a promising complementary approach, as they
[...] Read more.
The Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC requires the assessment of the ecological quality in all surface waters using biological indices, yet the effective application of these indices often demands extensive and long-term monitoring data. Oxidative stress biomarkers offer a promising complementary approach, as they can detect early biochemical responses of organisms to environmental degradation. In this study, we evaluated the suitability of two oxidative stress biomarkers—malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and DNA damage—in the gonads of a freshwater fish species, the Prussian carp Carassius gibelio (Bloch, 1782) as indicators of ecological condition in lakes of differing environmental quality. Fish were sampled from four lakes (Doirani, Vegoritida, Volvi, Petron; Northern Greece) representing a gradient of physicochemical and ecological quality. Both MDA concentrations and DNA damage showed significant (p < 0.05) differences among lakes. However, only DNA damage in the gonads was significantly (p < 0.05) associated with lake ecological quality as determined by the Greek Lake Fish Index (GLFI), with higher biomarker responses observed in lakes of poorer status. These findings demonstrate that oxidative stress biomarkers in C. gibelio reflect variations in lake ecological quality and may serve as sensitive, early-warning tools for biomonitoring and pollution assessment in freshwater ecosystems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Juvenile Sardine Production in Ecological Culture System: Opportunities for Restocking and Coastal Sustainability
by
Ángel Urzúa, Fabián Guzmán-Rivas and Ana Aguilera-Macías
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010003 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Small pelagic fish, including sardines, are essential to global fisheries and aquaculture feed production. However, these species are increasingly exposed to intense exploitation. In Chile, the common sardine (Strangomera bentincki), endemic to the Humboldt Current System, supports major industrial and artisanal
[...] Read more.
Small pelagic fish, including sardines, are essential to global fisheries and aquaculture feed production. However, these species are increasingly exposed to intense exploitation. In Chile, the common sardine (Strangomera bentincki), endemic to the Humboldt Current System, supports major industrial and artisanal fisheries. Landings are expected to reach 300,000 tons by 2025, mostly for fishmeal production. As a keystone species, S. bentincki is highly sensitive to environmental variability during early development, which can reduce recruitment and threaten long-term population sustainability. This interdisciplinary approach integrates ecological and biotechnological perspectives to assess the feasibility of controlled juvenile sardine production in land-based Ecological Aquaculture (EA) systems, including Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) and Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA), which are designed to reduce environmental impacts. These systems enable precise control of temperature, feeding regimes, and water quality, facilitating investigations into larval and juvenile survival, growth performance, and physiological responses under variable thermal and nutritional conditions. Emphasis is placed on fatty acid metabolism during ontogeny, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), which are essential for somatic growth, reproductive development, and thermal tolerance. Developing standardized protocols for juvenile S. bentincki culture addresses key gaps in husbandry and physiology (temperature threshold, nutrient density, larval growth rate, etc.) while introducing a novel ecological–aquaculture integration framework. This approach links early-life ecology with applied rearing techniques to support stock enhancement, strengthen artisanal fisheries, and promote sustainable aquaculture diversification under increasing environmental variability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Valve Gape Movement of an Endangered Freshwater Mussel During Burrowing
by
Alan Cottingham, Jake Daviot, James R. Tweedley and Stephen Beatty
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010002 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Understanding the behavioral strategies that allow freshwater mussels to persist under environmental stress is essential for their conservation, yet burrowing behavior remains poorly quantified. We tested whether valve movement data could be used to detect and characterize burrowing in the endangered Westralunio carteri
[...] Read more.
Understanding the behavioral strategies that allow freshwater mussels to persist under environmental stress is essential for their conservation, yet burrowing behavior remains poorly quantified. We tested whether valve movement data could be used to detect and characterize burrowing in the endangered Westralunio carteri; a species endemic to a region undergoing severe climatic drying. Mussels from multiple populations were monitored individually under laboratory conditions using Hall effect sensors, and valve movement patterns were analyzed to distinguish between burrowing and non-burrowing behaviors. Burrowing was associated with rapid, high-amplitude valve movements that lengthened as burial progressed, while non-burrowing behaviors showed distinct, slower patterns. These differences indicate that valvometry can reliably identify burrowing behavior, providing a non-invasive method for monitoring mussel activity. This approach has broad applications for ecological research, conservation assessment, and early-warning biomonitoring of imperiled freshwater mussel populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Systematic Review on the Reproductive Aspects of the Chelidae Family
by
Lucas Maia Garcês, Fernanda Victoria Nery Dias, Paulo Henrique Rocha Aride and Adriano Teixeira de Oliveira
Hydrobiology 2026, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology5010001 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Austro-American Side-necked Turtles originated in Gondwana and are found only in South America and Australasia. This paper aimed to review the reproductive aspects of the Chelidae family systematically. The searches were conducted in several databases, resulting in 86 studies, of which only
[...] Read more.
The Austro-American Side-necked Turtles originated in Gondwana and are found only in South America and Australasia. This paper aimed to review the reproductive aspects of the Chelidae family systematically. The searches were conducted in several databases, resulting in 86 studies, of which only 21 were considered adequate. The research was mainly conducted in Australia and Brazil, in both natural and laboratory settings, across different ontogenetic stages among the sixteen species studied. The analyzed publications focused on different aspects of the reproductive biology of the Chelidae family, including ecology, anatomy, morphology, behavior, and other perspectives. Thus, this study aimed to answer questions related to reproduction and the factors that can affect the preparation, mating, sexual activity, and oviposition phases, highlighting the most researched areas and those that still require attention for the conservation of these species.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hydrogeochemical and Biological Attributes of Chiuchiu Pond, a Pre-Andean Wetland in Northern Chile: Bases for Its Protection and Conservation
by
Benito Gómez-Silva, Luis Cáceres, Milton Urrutia and Alexandra Galetović
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040034 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Chiuchiu Pond (CCP) is an inland brackish water body in a pre-Andean scenery in the Atacama Desert, northern Chile. Presently unprotected, the CCP is attractive for tourism and a notable geosite for wildlife characterized by maintaining a fixed water level and chemical
[...] Read more.
The Chiuchiu Pond (CCP) is an inland brackish water body in a pre-Andean scenery in the Atacama Desert, northern Chile. Presently unprotected, the CCP is attractive for tourism and a notable geosite for wildlife characterized by maintaining a fixed water level and chemical composition without surface inlets/outlets. This paper aims to characterize factors accounting for its perennial character by gathering climatic, hydrogeochemical, and morphometric information and microbiological and functional characterization. The CCP is an isolated U-shaped doline with a maximum depth of 17.5 m and vertical walls with more than 80% of soluble salts (halite and calcite) under arid conditions characterized by constant seasonal variation patterns. This is a unique case in that no similar conditions among reported wetlands or ponds have been found in the world. From our studies, it was characterized as an oligotrophic, lentic oligomictic, well-mixed water body, without thermal stratification, stable water level and hydrochemical composition, with water balance conditions from underground flows. Analysis of the microbial community revealed a core composition dominated by Proteobacteria (43.1%), Bacteroidetes (23.5%), and Cyanobacteria (10%). We provide a multidisciplinary contribution to justify urgent actions for the CCP’s conservation, representing a model for other unprotected coastal and inland wetlands in northern Chile and drylands elsewhere.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Food, Growth and Biological Production of the European Eel, Anguilla anguilla, in a Small Stream in Jutland, Denmark
by
Gorm Rasmussen, Birgit M. Therkildsen and Michael I. Pedersen
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040033 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Yellow eels were sampled by electrofishing in 1979, 1980, and 1981 in Vester Vedsted Stream, Denmark, which has as its outlet to the North Sea. Yellow eels were aged by burning the otoliths. The gender of the eels was not specified, and they
[...] Read more.
Yellow eels were sampled by electrofishing in 1979, 1980, and 1981 in Vester Vedsted Stream, Denmark, which has as its outlet to the North Sea. Yellow eels were aged by burning the otoliths. The gender of the eels was not specified, and they varied from 6.5 to 48.5 cm in length. The ages varied from 0+ to 10+ years. The annual growth rate Δ varied from 3.4 cm for the youngest eels to 2.2 cm for eels over 10 years old, with a mean of 3.1 cm. Body mass wet weight was correlated to energy content (kcal), with an annual mean growth rate Δ of 5.33 kcal. In contrast to body length, the annual growth rate Δ of energy content (kcal) increased with age. Von Bertalanffy growth trajectory (cm) of length-at-age was calculated, and L∞ = 118.4 cm. Annual natural mortality M was calculated, and M was significantly dependent on body mass, i.e., high M at low body mass vs. low M at high body mass. The biological production was calculated to be 13.5 g wet weight m−2 per year. A total of 780 eel stomachs were analyzed, 287 (37%) of which were empty. Mass (wet weight, g) of food content increased more than proportionally with eel body mass. Chironomid larvae, Ephemeroptera nymphs, Simulium larvae, and Gammarus pulex were the dominant food taxa, followed by Trichoptera larvae. The size of Chironomid larvae, Ephemeroptera nymphs, and Simulium larvae prey was independent of the length of the eel, whereas the size of Gammarus pulex increased with increased eel length.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Ohrid Trout: A “Living Fossil” Endemic to Lake Ohrid Left Behind by Science
by
Tânia Vieira Madureira, Maria João Rocha, Eduardo Rocha and Maja Jordanova
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040032 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Ohrid trout (Salmo letnica) is a species endemic to Lake Ohrid (shared by Albania and North Macedonia), which is internationally recognized for its geological longevity and unique natural features. Given that the species has distinctive biological, ecological, and evolutionary characteristics,
[...] Read more.
The Ohrid trout (Salmo letnica) is a species endemic to Lake Ohrid (shared by Albania and North Macedonia), which is internationally recognized for its geological longevity and unique natural features. Given that the species has distinctive biological, ecological, and evolutionary characteristics, as well as significant economic value, the decline in this trout’s population is a serious and urgent problem, deserving continuous, scientifically based management. Yet, although it is considered a “Fossil Trout”, research on this species remains limited in relation to science and conservation. To understand the current state of the art, we conducted a systematic review in Web of Science, analyzing 31 indexed articles about the Ohrid trout. These studies primarily focused on the seasonal morphological characteristics of specific organs, phylogenetics, and, to a lesser extent, the impacts of environmental contamination. However, notable gaps exist in understanding sex- and stage-specific physiology, morphotype diversity, and pollutant bioaccumulation. To address these limitations, integrative strategies that combine multi-omics biomarker development, genetic screening of broodstock, and systematic monitoring of pollution and climate-related stressors are crucial. Regional authorities should work with international organizations to establish long-term monitoring of S. letnica. This review aims to provide a critical foundation for overcoming the “Living Fossil Left Behind by Science” paradigm and to foster global initiatives to preserve the long-term survival and evolutionary legacy of this endangered species.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Meiofaunal Abundance, Vertical Distribution, and Secondary Production from an Upwelling Coastal Area in Southern Peru (~14°16′ S)
by
Víctor Aramayo
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040031 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Meiofaunal assemblages are crucial components of benthic ecosystems, significantly contributing to organic matter cycling and energy transfer. However, baseline quantitative data from some upwelling systems remain limited. This study characterizes the abundance, vertical distribution, and secondary production of meiofauna at a coastal upwelling
[...] Read more.
Meiofaunal assemblages are crucial components of benthic ecosystems, significantly contributing to organic matter cycling and energy transfer. However, baseline quantitative data from some upwelling systems remain limited. This study characterizes the abundance, vertical distribution, and secondary production of meiofauna at a coastal upwelling station off southern Peru (14°16′ S) for July 2006 (Neutral conditions) and May 2007 (moderate La Niña, LN), using four-replicated sediment cores sectioned into 0–1, 1–2, 2–5, and 5–10 cm layers. While Nematoda (families Desmodoridae, Chromadoridae, Monhysteridae, Oxystominidae, Comesomatidae) dominated the community (>79% in all layers, both years), the total taxonomic richness did not differ substantially between study periods nor across the sediment column for 2006 or for 2007. Total density (0–10 cm) fluctuated between 3916 ± 2202 Ind 10 cm−2 in 2006 and 4203 ± 2274 Ind 10 cm−2 in 2007, with non-significant changes. Biomass (µgC 10 cm−2) in 2006 ranged from 80 ± 24 in the 5–10 cm section to 455 ± 134 in the 2–5 cm section. The uppermost 0–1 cm layer showed 238 ± 155, while the 1–2 cm section reached 302 ± 69. In 2007, biomass was consistently higher in the surface layers, with maximum values in the 1–2 cm section (500 ± 534), followed by the 0–1 cm section (376 ± 34). Hierarchical clustering produced depth-ordered groups with high within-depth similarity (>80–90%). SIMPER results identified Desmodora, Comesomatidae, and Chromadoridae among the top contributors to within-depth similarity and to the dissimilarity observed between surface and subsurface assemblages. A depth-related gradient of community composition was detected, suggesting vertical habitat heterogeneity modulated by several environmental factors; however, PERMANOVA analysis residuals (96.73%) indicate a high variation not explained by ENSO phase, sediment section, or their interaction, suggesting other unmeasured factors explaining meiofaunal community structure. Meiofauna’s production ranged from 2.836 ± 0.049 gC m−2 y−1 in 2006 to 3.106 ± 1.566 gC m−2 y−1 in 2007. These findings expand the limited knowledge on meiofaunal abundance and metabolic demands in this ocean region, fostering future efforts for comparative analyses across latitudes, depth gradients, and oceanographic regimes.
Full article
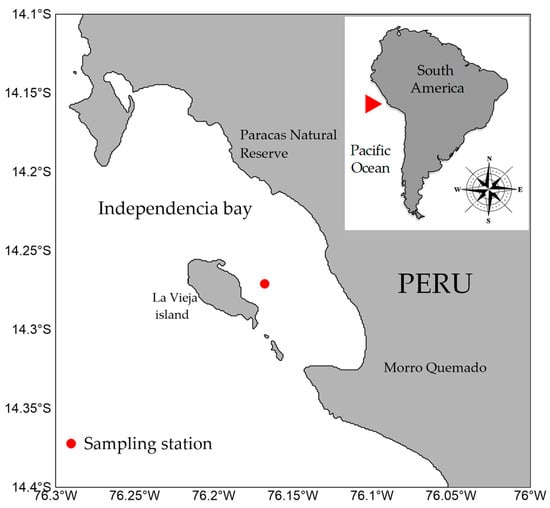
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation and Economic Analysis of Totally Replacing Soybean Oil with Fish By-Product Oil in Diets for Colossoma macropomum: Effects on Growth, Physiology, and Meat Composition
by
Pedro Alves de Oliveira Filho, João Paulo Ferreira Rufino, Paula Ribeiro dos Santos, Ariany Rabello da Silva Liebl, Harison Santos de Oliveira, Diany Bastos Bezerra, Manoel Pio Nonato Neto, Ana Paula Nunes de Sena, Pedro de Queiroz Costa Neto, Jesaías Ismael da Costa, Jackson Pantoja-Lima, Thyssia Bonfim Araújo da Silva and Adriano Teixeira de Oliveira
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040030 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Aquaculture faces challenges in reducing feed costs while promoting sustainable use of by-products. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of totally replacing soybean oil (SBO) with fish by-product oil (FBO) in the diet of Colossoma macropomum, focusing on growth performance, physiological
[...] Read more.
Aquaculture faces challenges in reducing feed costs while promoting sustainable use of by-products. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of totally replacing soybean oil (SBO) with fish by-product oil (FBO) in the diet of Colossoma macropomum, focusing on growth performance, physiological and hepatic responses, meat composition, and economic viability. A total of 360 juveniles (9.1 ± 0.59) were distributed in a randomized design with six treatments (0–100% SBO replacement) and six replicates each, and fed to apparent satiation for 91 days. Growth performance did not differ significantly among treatments (p > 0.05), although fish receiving 40% FBO achieved the best feed conversion ratio among treatments. Hematological and biochemical analyses indicated that higher FBO levels (particularly 100%) indicating subtle yet adaptive physiological adjustments, such as moderate modulations in lipid metabolism and erythropoietic activity. Liver weight and hepatosomatic index decreased linearly with increasing FBO levels. In meat composition, FBO inclusion enhanced protein and reduced lipid contents. Although economic indicators were not statistically different (p > 0.05), offered the most favorable trade-off between biological performance and economic efficiency. These findings demonstrate that partial replacement of SBO with FBO, particularly at 40%, represents a sustainable and economically viable alternative for C. macropomum farming.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nutrition–Physiology Interactions in Aquatic Species)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Asymptotic Sigmoidal Curve Obtained Through the Multi-Model Approach Provides the Best Description of Growth in Panulirus inflatus Juveniles (Decapoda: Palinuridae)
by
Juan Francisco Arzola-González, Jesús Audomar Landeros-Armenta, José Adán Félix-Ortiz, Yecenia Gutiérrez-Rubio, Martín Ignacio Borrego, Raúl Pérez-González, Jorge Payán-Alejo and Eugenio Alberto Aragón-Noriega
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040029 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A mark–recapture experiment was conducted off Mazatlán in the entrance of the Gulf of California to evaluate the growth of juvenile spiny lobsters (Panulirus inflatus). A total of 40 post larvae of spiny lobster were captured, marked, and maintained in plastic
[...] Read more.
A mark–recapture experiment was conducted off Mazatlán in the entrance of the Gulf of California to evaluate the growth of juvenile spiny lobsters (Panulirus inflatus). A total of 40 post larvae of spiny lobster were captured, marked, and maintained in plastic cages for 180 days in seawater off Mazatlán, Sinaloa, Mexico (23°12′32.4″ N 106°25′33.2″ W). Carapace length (CL in mm) was measured. Growth was estimated using the Schnute model, which encompasses four primary cases. In this study, two additional variants equivalent to the von Bertalanffy and Logistic models were also incorporated. These six models were parametrized using normal and log-normal distributions of errors. The selection of the best distribution and best model was based on the Akaike information criterion (AIC). The AIC selected the normal distribution of error and sigmoid-shaped curve as best representative of the growth pattern of juvenile spiny lobster P. inflatus. By identifying the asymptotic sigmoidal curve as the best descriptor of juvenile growth, this study offers a reliable foundation for subsequent assessments of population dynamics, resource management, and aquaculture development of P. inflatus.
Full article
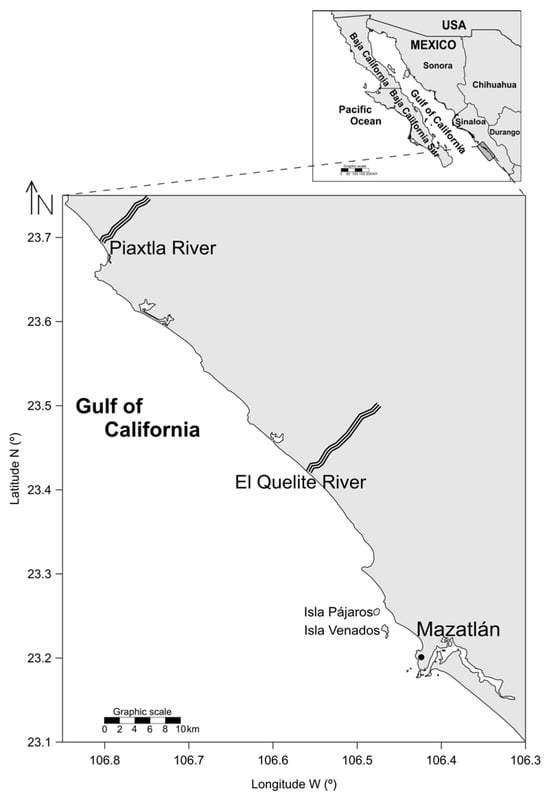
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microalgal Diversity in the Ecuadorian Tropical Andes and Its Association with Abiotic Factors
by
María Cristina Guamán-Burneo, Nory González-Romero and Alex Santillán-Sarmiento
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040028 - 17 Oct 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Ecuadorian Tropical Andes serve as vital biodiversity hotspots, crucial for hosting and preserving unique endemic species. While numerous taxonomic groups within these hotspots have been extensively studied, microalgae remain relatively unknown. This study aimed to document the microalgal diversity of Tropical Andean
[...] Read more.
The Ecuadorian Tropical Andes serve as vital biodiversity hotspots, crucial for hosting and preserving unique endemic species. While numerous taxonomic groups within these hotspots have been extensively studied, microalgae remain relatively unknown. This study aimed to document the microalgal diversity of Tropical Andean lakes in Ecuador and its relationship with abiotic environmental factors. Water samples were collected from 28 lakes throughout 10 conservation areas, spanning different altitudes in the Ecuadorian Tropical Andes, along with water physical/chemical data. A total of 92 microalgal genera were identified, spanning Bacillariophyta, Chlorophyta, Glaucophyta, Ocrophyta, Cyanophyta, and Euglenophyta. Lakes such as Rodeococha, Anteojos, Chinchillas, Toreadora, Magdalena, and La Mica exhibited the highest richness of microalgal genera. A positive association between temperature and the majority of microalgal phyla, except Glaucophyta, was observed. On the other hand, negative correlations were observed between total dissolved solids and water conductivity with microalgal biodiversity. Additionally, all groups displayed negative associations with pH, except Glaucophyta. The Jaccard similarity index was low among lake communities in agreement with the uniqueness of genera found in some lakes. This study represents a fundamental baseline for future investigations into Ecuador’s microalgal diversity and its relationship with abiotic environmental factors in the delicate freshwater ecosystems of Tropical Andean lakes.
Full article
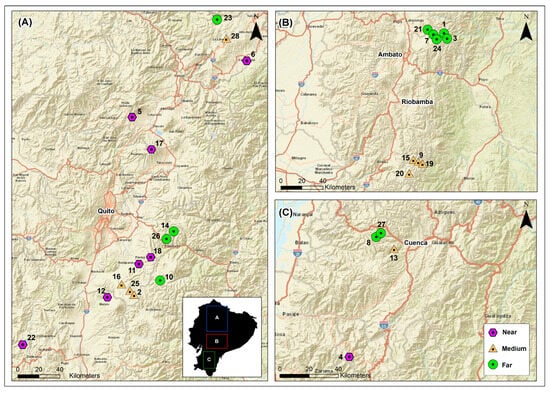
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Morphological and Meristic Feature Studies and Marketing Status of Peregrine Crab Varuna litterata from a Coastal Estuary in Sundarbans Mangrove Forest, Bangladesh
by
Joyanta Bir, Prianka Paul, Wasim Sabbir, Khirujjaman Sumon and Rimu Das
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040027 - 12 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Varuna litterata is an estuarine crab species widely distributed across the Indo-Pacific region, commonly dwelling in brackish waters, mangrove forests, and tidal estuaries. In Bangladesh, while four Scylla species dominate the commercial crab market, the locally consumed V. litterata remains a biologically overlooked
[...] Read more.
Varuna litterata is an estuarine crab species widely distributed across the Indo-Pacific region, commonly dwelling in brackish waters, mangrove forests, and tidal estuaries. In Bangladesh, while four Scylla species dominate the commercial crab market, the locally consumed V. litterata remains a biologically overlooked gem of the coastal waters. These crabs are frequently captured as a byproduct during shrimp fry collection from coastal estuaries. In this context, the current study investigates the reproductive biology, morphometric dynamics, and market potential of V. litterata collected from the Pasur River, a coastal mangrove forest-adjacent estuary of southern Bangladesh. A total of 75 individuals were collected from March to April 2023, comprising 35 males and 40 females, resulting in a sex ratio of 1:1.14 (♂:♀), with a predominance of females. A visual observation of ovary development revealed four distinct maturation stages, with Stage IV (fully mature) being the most prevalent (43%), indicating peak reproductive activity during the sampling period. Morphometric analysis revealed that the average carapace width (CW) was 31.2 ± 5.7 mm and 31.9 ± 5.8 mm and the mean carapace length (CL) was 29.3 ± 4.7 mm and 30.1 ± 4.9 mm in males and females, respectively. However, the mean body weight (BW) was 13.1 ± 4.3 g in males and 12.7 ± 3.8 g in female crabs. The dominant CW class ranges from 33 to 33.99 mm (males) and 28.99–29.99 mm (females), appear to be the most vulnerable to fishing pressure. BW-CW and CL-CW relationships demonstrated negative allometric growth, with high correlations in both sexes. Significant sexual dimorphism was observed, with males having larger cheliped dimensions, while females had broader abdomens, likely supporting reproductive functions that are essential to their conservation. The marketing of this crab remains largely informal, yet rising local demand and prices highlight its emerging commercial potential. Therefore, incorporation into aquaculture and coastal fishery development of this crab species could enhance food security, support livelihoods, and contribute to sustainable blue economy initiatives in Bangladesh.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Environmental DNA (eDNA) Surveillance of Zebra Mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in Lake Lanier, Georgia: A Model for Early Detection and Public Engagement
by
Larry L. Bowman, Jr., Amy L. Rodriguez, Hannah Fontenot and Margi Flood
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040026 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Environmental DNA (eDNA) detection has emerged as a powerful, non-invasive tool for identifying aquatic organisms, particularly those that are rare, elusive, or invasive. Dreissena polymorpha (zebra mussel) is an invasive bivalve posing ecological and economic threats to North American freshwater systems. In April
[...] Read more.
Environmental DNA (eDNA) detection has emerged as a powerful, non-invasive tool for identifying aquatic organisms, particularly those that are rare, elusive, or invasive. Dreissena polymorpha (zebra mussel) is an invasive bivalve posing ecological and economic threats to North American freshwater systems. In April 2021, zebra mussels were discovered attached to a boat destined for Lake Sidney Lanier in North Georgia—a high-use recreational reservoir with no prior reports of infestation. To determine whether D. polymorpha had been introduced, we implemented a biomonitoring protocol leveraging eDNA collection and PCR-based detection. Sampling was conducted during summer 2022 across high-risk marina sites and potential habitats. Positive controls from the Tennessee River yielded expected results, while Lake Lanier samples showed no evidence of zebra mussel DNA. Our results validate using eDNA methodology for proactive biomonitoring and highlight the importance of molecular surveillance and community outreach to prevent the establishment of invasive species in vulnerable aquatic systems. This study demonstrates the utility of a scalable, replicable early detection framework that can be adopted by educational institutions, natural resource agencies, and community groups to mitigate the risk of biological invasions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
No Nets, No Shocks, No Problem: Assessing Replicability and Disturbance Effects in Fish Monitoring Using Remote Video Cameras in Low Order Streams
by
Abigail Archi, Jaclyn M. H. Cockburn and Paul V. Villard
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4040025 - 24 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Conventional fish population sampling methods such as electrofishing and netting, pose risks to fish and are often restricted to small, shallow headwater streams—especially where endangered species may be present. Additionally, non-capture surveying (e.g., snorkelling) can disturb fish and make observation more challenging. This
[...] Read more.
Conventional fish population sampling methods such as electrofishing and netting, pose risks to fish and are often restricted to small, shallow headwater streams—especially where endangered species may be present. Additionally, non-capture surveying (e.g., snorkelling) can disturb fish and make observation more challenging. This study evaluates the effectiveness and reproducibility of remote underwater video (RUV) surveys in a shallow (<0.5 m deep), freshwater stream. Additionally, fish response to disturbances (e.g., shadows, noise, surface disruptions) were characterized. Fish abundance was estimated by maxN (maximum number of individuals observed in a single frame) and used multiple cameras placed in the same habitat (pool). Findings indicated a high consistency in maxN when fish numbers were low (<5 individuals), with increasing variability at higher numbers (>15 individuals). This suggests that single camera setups can reliably detect minimum abundance. Fish responses to four disturbances (e.g., shadows, noise, surface disruptions, mink) were noted throughout. Typically, these responses were short-lived, with fish returning to pre-disturbance maxN values within minutes, with the most significant response to researcher-induced disturbance occurring immediately after RUV deployment. Overall, RUVs proved effective for passive, non-capture fish monitoring in shallow, sensitive habitats, producing replicable data with minimal impact caused by researcher disturbance. This technique can be added to our toolboxes for studying small-bodied fishes in challenging environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ontogenetic Phase Shifts in Metabolism and Intraspecific Scaling in a Non-Teleost Fish, the Sterlet Sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus)
by
Dong In Kim
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4030024 - 10 Sep 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metabolism is fundamental to many biological processes that govern the flow of energy and materials within organisms. Recently, several interspecific studies have suggested that ontogenetic phase shifts in the metabolism of teleost fish coincide with body mass increases during early development. The morphological
[...] Read more.
Metabolism is fundamental to many biological processes that govern the flow of energy and materials within organisms. Recently, several interspecific studies have suggested that ontogenetic phase shifts in the metabolism of teleost fish coincide with body mass increases during early development. The morphological and behavioral changes that accompany these metabolic shifts could explain differences in intraspecific size scaling metabolism, but it remains unclear whether these shifts are widespread in a variety of aquatic organisms, including non-teleost fish. Here, a metabolic study in sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus) was conducted to examine whether the ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism coincide with growth in a non-teleost fish. The results were also compared with previously published metabolic scaling data for the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to explore differences in intraspecific scaling patterns. The present study revealed that ontogenetic phase shifts in metabolism do occur in sterlet sturgeon. These findings indicate that non-teleost fish likely undergo scaling mechanisms in metabolism similar to those of teleost fish.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Long-Term Urban Light Pollution and LED Light Color Temperature on the Behavior of a Holarctic Amphipod Gammarus lacustris Sars, 1863
by
Yana Ermolaeva, Maria Maslennikova, Dmitry Golubets, Arina Lavnikova, Natalia Kulbachnaya, Sofya Biritskaya, Anastasia Solodkova, Ivan Kodatenko, Artem Guliguev, Diana Rechile, Kirill Salovarov, Anastasia Olimova, Darya Kondratieva, Anna Solomka, Alyona Slepchenko, Alexandr Bashkirtsev, Dmitry Karnaukhov and Eugene Silow
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4030023 - 3 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Light pollution is becoming more widespread every year, accompanied by the active use of LED lighting. Currently, the ability of organisms to adapt to this pollution and the potential impact of LED lighting of different color temperatures and intensities on organisms remains poorly
[...] Read more.
Light pollution is becoming more widespread every year, accompanied by the active use of LED lighting. Currently, the ability of organisms to adapt to this pollution and the potential impact of LED lighting of different color temperatures and intensities on organisms remains poorly understood. In this study, we aimed to find out how long-term light pollution affects the behavior of amphipods Gammarus lacustris, and to compare their locomotor activity under different lighting conditions, taking into account the factor of shelter from light. The response of individuals was compared in group and individual experiments under daylight, without light, warm and cold LED light up to 30 lx. The individuals were from two populations: the first is not exposed to light pollution (lake No. 14), while the second is affected (the Angara River within the city of Irkutsk). The locomotor activity of amphipods was assessed in daylight, without light, warm and cold light of 2–2.5 lx and 10–11 lx in the presence and absence of shelters from light. As a result of the experiments, adaptive changes in the reaction of G. lacustris to warm light were identified in individuals from the Angara River. The importance of LED light color temperature and warm light intensity in determining amphipod response to light was also confirmed. It was found that warm and cold light have different effects on the behavior of G. lacustris, and the presence of shelters from light can reduce the negative impact of light pollution in natural conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Working Primers and qPCR Protocols for Rapid eDNA Identification of Four Aquatic Invasive Species Found in the Lower Great Lakes with High Potential for Ballast Transport to Lake Superior
by
Matthew E. Gruwell, Amanda Welsbacher, Noel Moore, Allegra Cangelosi, Abigail Melendez, Ryan Sheehan and Ivor Knight
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4030022 - 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Reliable, timely and economical target organism detection in harbors and ballast water is urgently needed to prevent the spread of aquatic invasive species (AIS) by commercial ships in the North American Great Lakes (NAGL). Inter-Great Lake ships (Lakers) transport large volumes (ca. 52
[...] Read more.
Reliable, timely and economical target organism detection in harbors and ballast water is urgently needed to prevent the spread of aquatic invasive species (AIS) by commercial ships in the North American Great Lakes (NAGL). Inter-Great Lake ships (Lakers) transport large volumes (ca. 52 million metric tons. annually) of untreated lake water between lakes, with over 50% transported against the natural flow from the lower lakes to Western Lake Superior ports. The transport of ballast water is the number one threat of AIS spread throughout the NAGL. A relatively new tool to fight the spread of AIS is the use of eDNA for rapid detection and identification of target organisms. This technology opens doors for advancing control of ballast-mediated AIS through rapid detection. To that end, we have developed species-specific, reliable eDNA primers to target specific detection of four AIS in water samples along with qPCR protocols. Target organisms were selected based on the following criteria: (1) they are known to be invasive in the lower NAGL, (2) they are established in the lower NAGL but not in Superior, (3) they are biodegradable, and (4) they are obtainable, morphologically distinct and have existing DNA sequence information. Working primers, qPCR protocols and detection limits are provided for three invertebrate species and one alga species. These species are Daphnia lumholtzi (a water flea), Cercopagis pengoi (the fishhook water flea), Echinogammarus ishnus (a scud) and Nitellopsis obtusa (Starry Stonewort).
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
A Library of Microsatellite Markers for Efficiently Characterizing the Aquatic Macrophyte Myriophyllum heterophyllum
by
Lucas E. Bernacki
Hydrobiology 2025, 4(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4030021 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
Myriophyllum heterophyllum is an aquatic macrophyte that is invasive to the northeastern United States and several western European countries. Spreading by vegetative clonal propagation, especially fragmentation, extensive resources are devoted to limiting its growth and spread; however, genetic assessments are not typically included
[...] Read more.
Myriophyllum heterophyllum is an aquatic macrophyte that is invasive to the northeastern United States and several western European countries. Spreading by vegetative clonal propagation, especially fragmentation, extensive resources are devoted to limiting its growth and spread; however, genetic assessments are not typically included in management strategies. Reduction in genetic (clonal) diversity should accompany biomass reduction, yet without genetic assessment, the efficacy of plant removal remains unclear. This paper is the first to describe a microsatellite marker library and its use in the characterization of Myriophyllum heterophyllum. Eighty-seven tissue samples were collected across the invasive distribution of Myriophyllum heterophyllum in Maine, USA. DNA was extracted, and PCR amplification was employed to screen 13 published microsatellites. Sequencing of the amplified loci was performed to characterize repeat motifs and confirm primer binding sites. Fragment sizing of PCR amplicons was employed to determine microsatellite lengths across the 87 samples. A total of 7 of the 13 tested markers were amplified, with six of those seven found to be variable. Polyploidy was evident from allelic diversity within individuals, although precise ploidy could not be determined. Observed heterozygosity ranged from 0.16 to 1.00 across variable markers. This seven-marker library was effective in characterizing the genetic diversity of both newly discovered (<5 years) and older (>50 years) infestations and is expected to be suitable for assessment of genetic diversity in populations within the native range of M. heterophyllum. The marker library also shows potential for use in several other Myriophyllum species.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biology, Data, Diversity, Fishes, Animals, Conservation, Hydrobiology
Intersection Between Macroecology and Data Science
Topic Editors: Paulo Branco, Gonçalo DuarteDeadline: 23 April 2027
Topic in
Toxins, Water, JMSE, Oceans, Hydrobiology, Environments
Recent Advances in Harmful Algal Blooms in Freshwater and Marine Systems
Topic Editors: Patricio A. Díaz, Gonzalo ÁlvarezDeadline: 31 July 2027

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Hydrobiology
Impact of Environmental Changes on Freshwater Ecosystems
Guest Editor: Andrew B.H. ReesDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Hydrobiology
Water Pollution Solutions: From Ecological Risk Assessment to Biological Restoration
Guest Editor: Lei WangDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Hydrobiology
Harmful Algal Bloom Risk: Mechanisms, Prediction, Impacts and Mitigation
Guest Editor: Lixia ShangDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Hydrobiology
Nutrition–Physiology Interactions in Aquatic Species
Guest Editors: Dizhi Xie, Songlin Li, Kangle LuDeadline: 30 September 2026













