Effects of Cumulative Municipal Wastewater Exposure on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages: An Experimental Stream Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
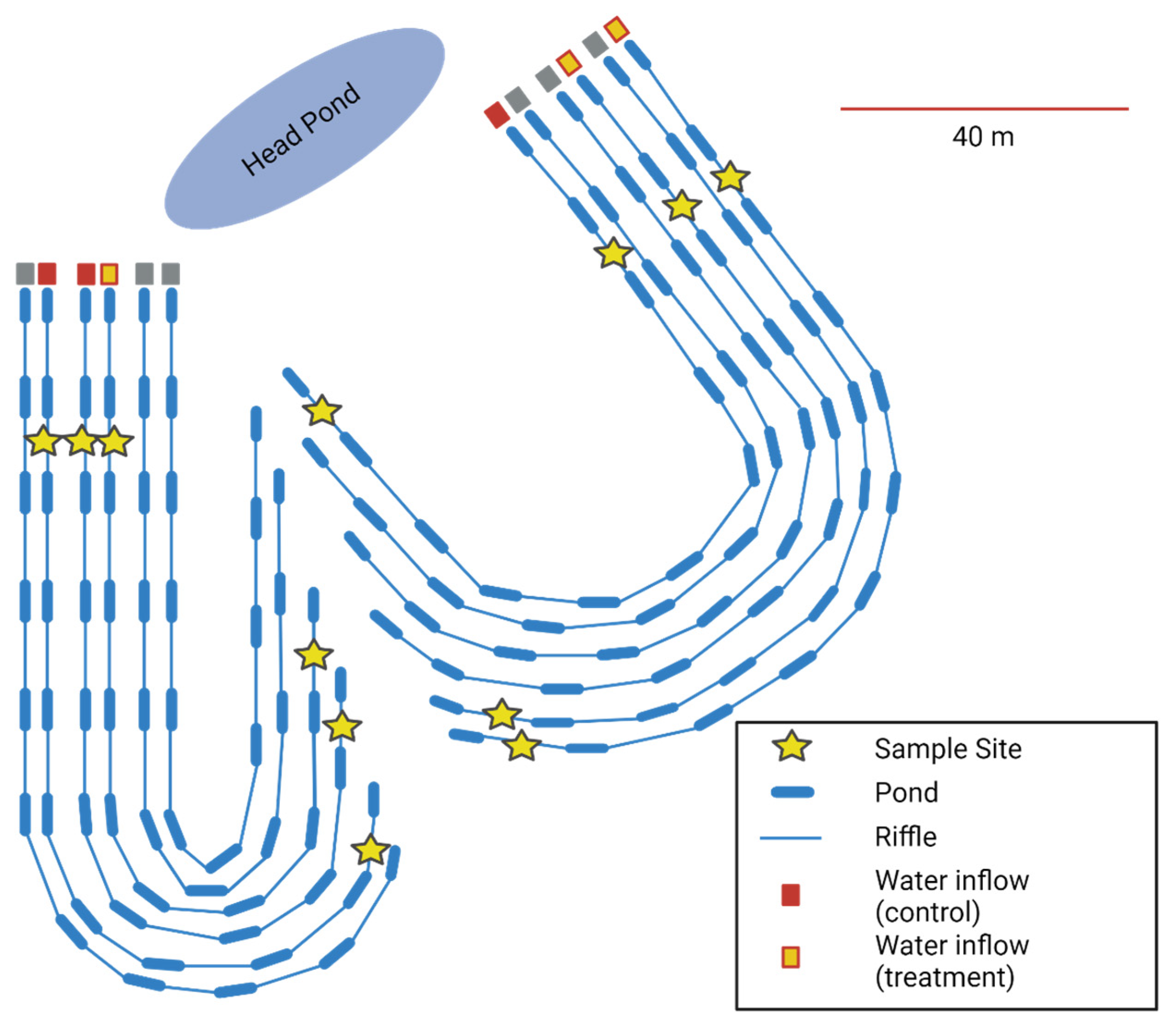
2.1. The Advancing Canadian Water Assets Experimental Streams
2.2. Field and Laboratory Methods
2.3. Ecological Methods and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of Artificial Streams
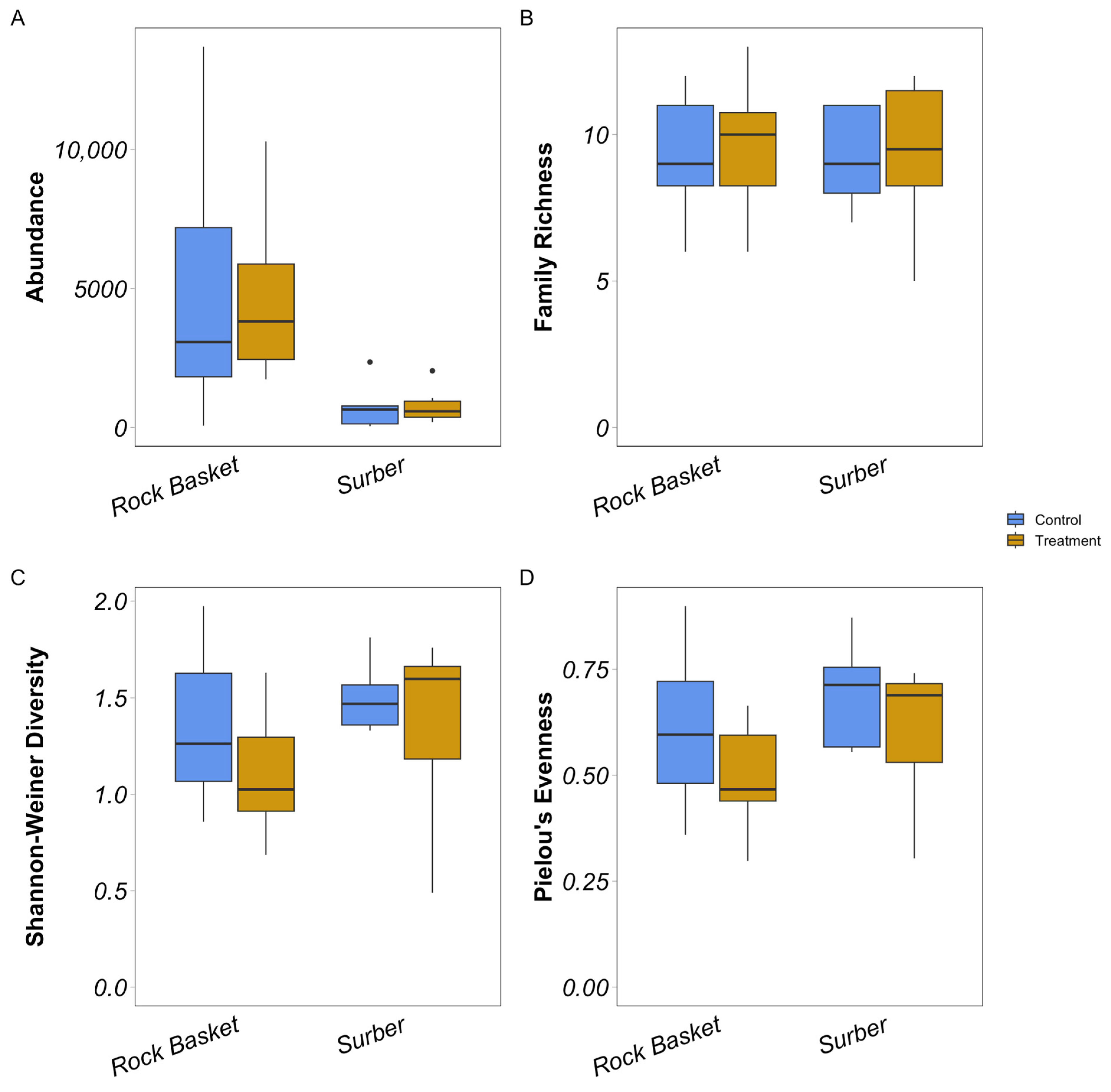
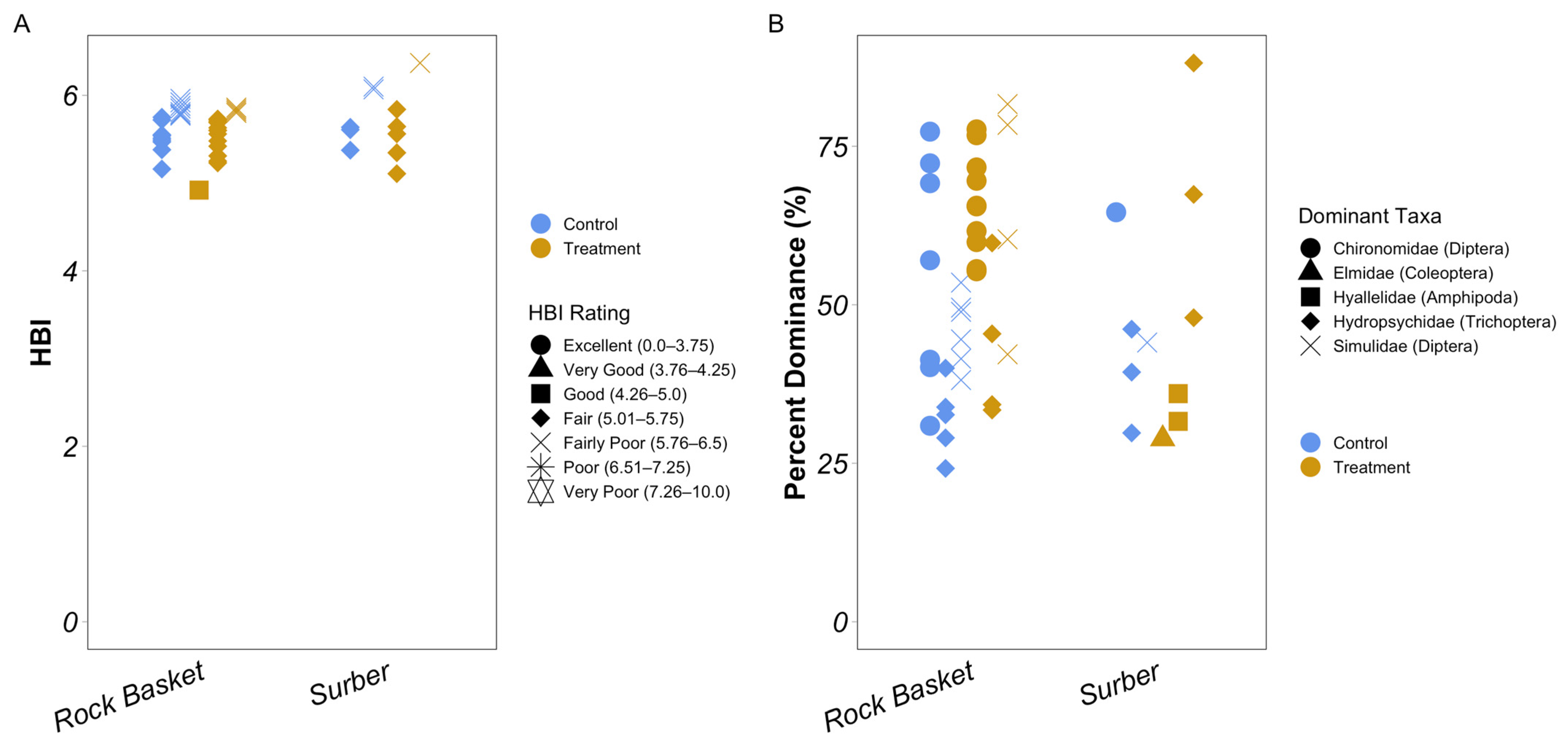
3.2. Diversity Metrics
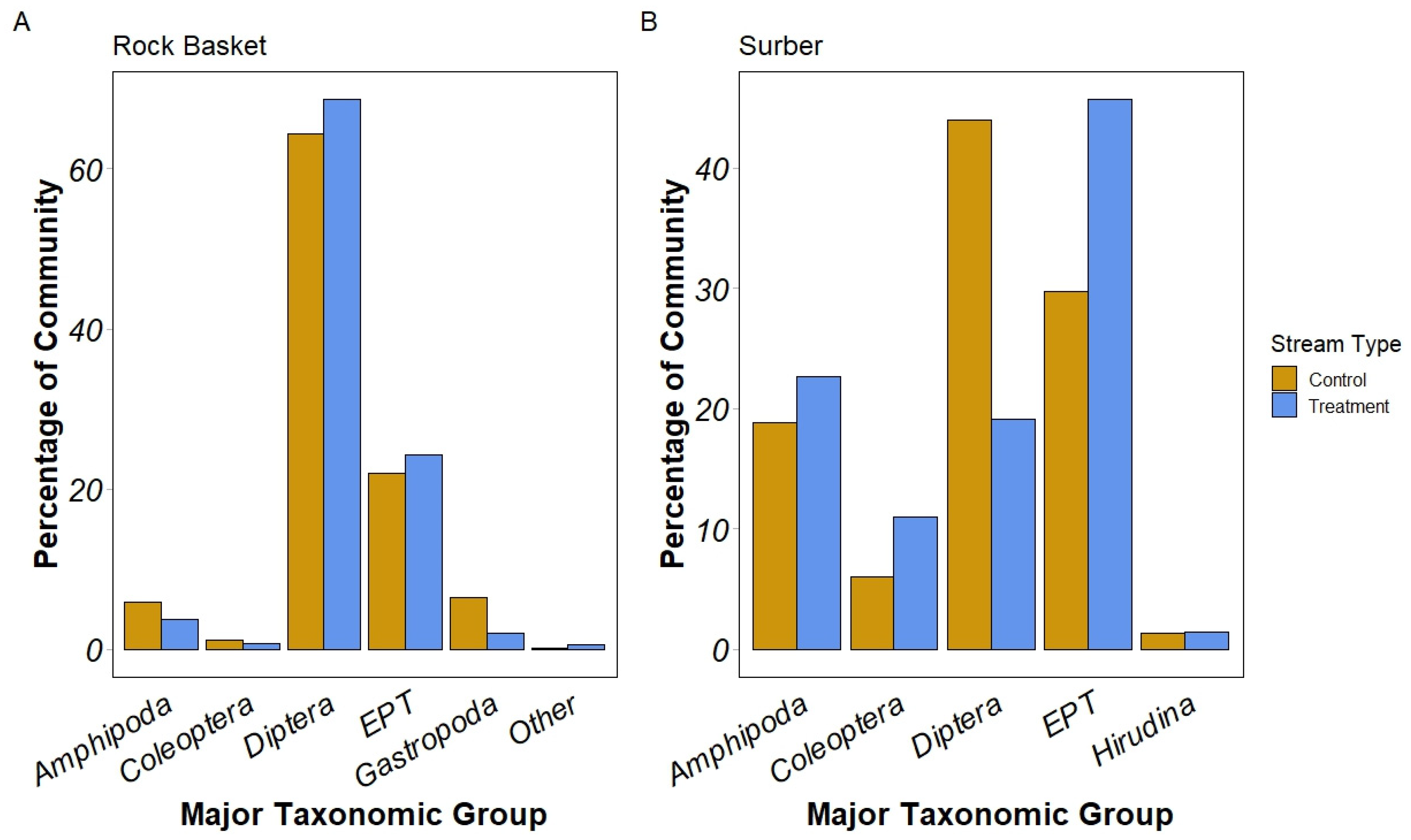
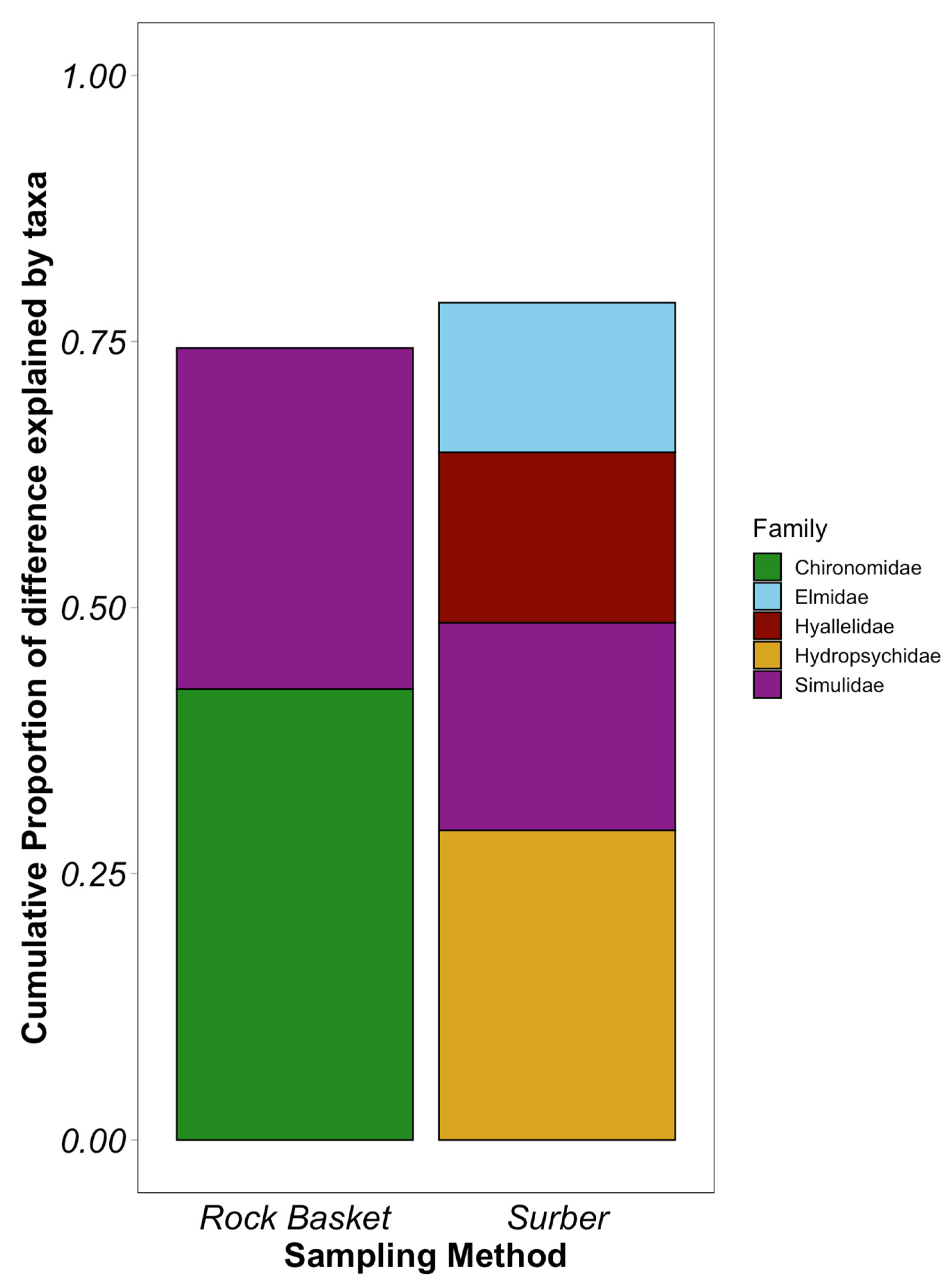
3.3. Major Taxonomic Group Distribution
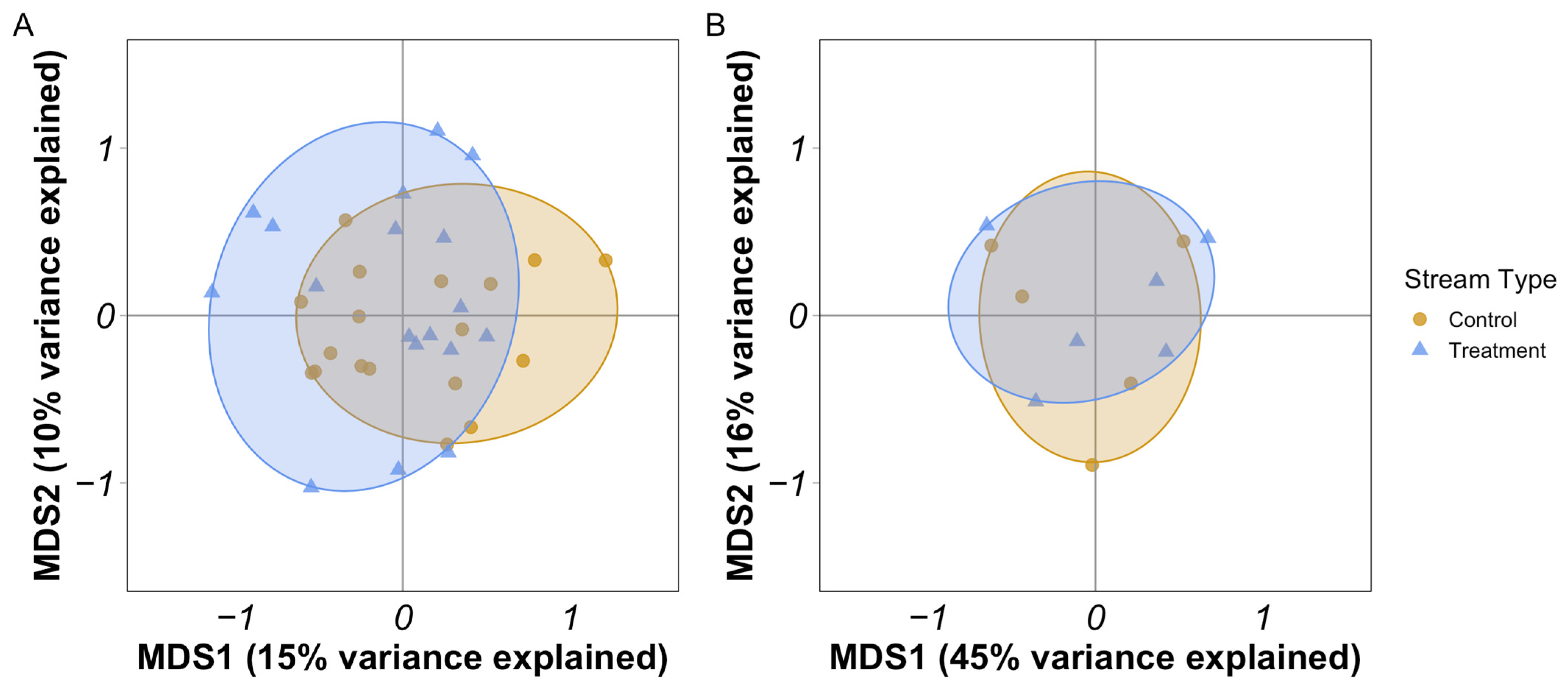
3.4. Multivariate Comparisons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MWWE | Municipal Wastewater Effluent |
| ESOC | Emerging Substance of Concern |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
| ACWA | Advancing Canadian Water Assets |
| CABiN | Canadian Aquatic Biomonitoring Network |
| HBI | Hilsenhoff Biotic Index |
| SIMPER | Similarity Percentages |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinates Analysis |
| EPT | Ephemeroptera Plecoptera Trichoptera |
References
- Beltrán de Heredia, I.; González-Gaya, B.; Zuloaga, O.; Garrido, I.; Acosta, T.; Etxebarria, N.; Ruiz-Romera, E. Occurrence of emerging contaminants in three river basins impacted by wastewater treatment plant effluents: Spatio-seasonal patterns and environmental risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P. Emerging pollutants in wastewater: A review of the literature. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, E.; Hornek-Gausterer, R.; Türker Saçan, M. Single and mixture toxicity of pharmaceuticals and chlorophenols to freshwater algae Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 129, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeton, C.; Chambers, P.A.; Grace, L. Wastewater release and its impacts on Canadian waters. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1836–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, D.; Gujer, W. Evolution of a wastewater treatment plant challenges traditional design concepts—ScienceDirect. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culp, J.M.; Cash, K.J.; Glozier, N.E.; Brua, R.B. Effects of pulp mill effluent on benthic assemblages in mesocosms along the Saint John River, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2916–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.M.; Latimer, H.A.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Thornton, K.W.; Bartell, S.M.; Kidd, K.A. Prioritizing contaminants of emerging concern for ecological screening assessments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, W.; Aissa, S.A.; Backhaus, T.; Dulio, V.; Escher, B.I.; Faust, M.; Hilscherova, K.; Hollender, J.; Hollert, H.; Müller, C.; et al. Effect-based methods are key. The European Collaborative Project SOLUTIONS recommends integrating effect-based methods for diagnosis and monitoring of water quality. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, B.W.; Dubé, M.G.; Hedley, K.; Portt, C.B.; Munkittrick, K.R. Aquatic Environmental Effects Monitoring Guidance for Environmental Assessment Practitioners. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, D.F.; Carlisle, D.M.; Chon, T.-S.; Culp, J.; Harding, J.S.; Keizer-Vlek, H.E.; Robinson, W.A.; Strachan, S.; Thirion, C.; Hughes, R.M. Stream biomonitoring using macroinvertebrates around the globe: A comparison of large-scale programs. Environ. Monit Assess 2014, 187, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hroch, M.; Brabec, K. Analysis of multiple-pressure pattern in rivers and its effects on the structure of macroinvertebrate communities. Limnologica 2022, 97, 126027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, P.A.; Allard, M.; Walker, S.L.; Marsalek, J.; Lawrence, J.; Servos, M.; Busnarda, J.; Munger, K.S.; Adare, K.; Jefferson, C.; et al. Impacts of Municipal Wastewater Effluents on Canadian Waters: A Review. Water Qual. Res. J. 1997, 32, 659–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Paterson, M.J.; Rennie, M.D.; Podemski, C.L.; Findlay, D.L.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Liber, K. Direct and indirect responses of a freshwater food web to a potent synthetic oestrogen. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nietch, C.T.; Quinlan, E.L.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Impellitteri, C.A.; Raikow, D.; Walters, D. Effects of a chronic lower range of triclosan exposure on a stream mesocosm community. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2874–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S.; Covaci, A.; Xia, X. Urban sewage discharge of neonicotinoids and their transformation products threatens aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhorpe, D.P.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Growns, I.O.; Hadwen, W.L.; Rees, G.N. Disruption in water quality patterns along the river continuum by a large bottom release dam. Australas. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 22, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.S.C.; Challis, J.K.; Ji, X.; Giesy, J.P.; Brinkmann, M. Impacts of wastewater effluents and seasonal trends on levels of antipsychotic pharmaceuticals in water and sediments from two cold-region rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Lutz, A.; Carroll, R.; Keteles, K.; Dahlin, K.; Murphy, M.; Nguyen, D. Occurrence, distribution, and seasonality of emerging contaminants in urban watersheds. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvigny-Khenafou, N.P.D.; Piggott, J.J.; Atkinson, D.; Zhang, Y.; Macaulay, S.J.; Wu, N.; Matthaei, C.D. Impacts of multiple anthropogenic stressors on stream macroinvertebrate community composition and functional diversity. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, G.R.; Brown, C.J.; Bennett, C.J.; Oakes, K.D.; McMaster, M.E.; Servos, M.R. Fish community responses to multiple municipal wastewater inputs in a watershed. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2013, 9, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunzel, K.; Kattwinkel, M.; Liess, M. Effects of organic pollutants from wastewater treatment plants on aquatic invertebrate communities. Water Res. 2013, 47, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, M.G.; Culp, J.M.; Cash, K.J.; Glozier, N.E.; MacLatchy, D.L.; Podemski, C.L.; Lowell, R.B. Artificial Streams for Environmental Effects Monitoring (EEM): Development and Application in Canada over the Past Decade. Water Qual. Res. J. 2002, 37, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.J. Advancing Canadian Wastewater Assets (ACWA) bridges laboratory-scale testing of wastewater technologies and effects on receiving environments. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 47, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.M.L.; Armitage, P.D.; Milner, A.M.; Ledger, M.E. Replicability of physicochemistry and macroinvertebrate assemblages in stream mesocosms: Implications for experimental research. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liber, K.; Goodfellow, W.; den Besten, P.; Clements, W.; Galloway, T.; Gerhardt, A.; Green, A.; Simpson, S. In situ-based effects measures: Considerations for improving methods and approaches. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2009, 3, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffran, K.A.; Anderson, A.M. Review of Benthic Invertebrates and Epilithic Algae at Long-Term Monitoring Sites in the Bow River; Alberta Environment: Edmonton, AL, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sosiak, A. Long-term response of periphyton and macrophytes to reduced municipal nutrient loading to the Bow River (Alberta, Canada). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlos, M.J.; Arnold, V.I.; Bumagat, J.S.; Zhou, J.; Cereno, K.M.; Deas, A.; Dai, K.; Ruecker, N.J.; Munkittrick, K.R. Combining chemical, bioanalytical and predictive tools to assess persistence, seasonality, and sporadic releases of organic micropollutants within the urban water cycle. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada Water: CABIN. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/canadian-aquatic-biomonitoring-network.html (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Tronstad, L.M.; Tronstad, B.P. Assessing Methods to Monitor Aquatic Invertebrates in a Large River: Comparing Rock Baskets and Hess Samplers in the Snake River, Wyoming, USA. Hydrobiology 2024, 3, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letovsky, E.; Myers, I.E.; Canepa, A.; McCabe, D.J. Differences between kick sampling techniques and short-term Hester-Dendy sampling for stream macroinvertebrates. BIOS 2012, 83, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeardley, R.; Jacobs, S.; Fritz, K.; Thoeny, W. Comparison of Three Macroinvertebrate Sampling Methods for Use in Assessment of Water Quality Changes in Flashy Urban Streams. J. Environ. Prot. 2020, 11, 585–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzanne, C.L. Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Non-Point Source Disturbances on the Structure and Function of Tributary Ecosystems in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Master’s Thesis, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1828/6102 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Wrona, F.J.; Culp, J.M.; Davies, R.W. Macroinvertebrate Subsampling: A Simplified Apparatus and Approach. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickley, P. An Apparatus for Subdividing Benthos Samples. Oikos 1975, 26, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, H.F. Aquatic Invertebrates of Alberta; University of Alberta Press: Edmonton, AL, Canada, 1991; ISBN 978-0-88864-233-2. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Arnold, T.B.; Emerson, J.W. Nonparametric Goodness-of-Fit Tests for Discrete Null Distributions. R J. 2011, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.S.; Lento, J.; Culp, J.M.; Lacelle, D.; Kokelj, S.V. Permafrost thaw and intense thermokarst activity decreases abundance of stream benthic macroinvertebrates. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, W.; Yan, N.D.; Somers, K.M.; Heneberry, J.H. Crustacean zooplankton communities in lakes recovering from acidification. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Perrée, I.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. A mesocosm approach for detecting stream invertebrate community responses to treated wastewater effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enns, D.; Cunze, S.; Baker, N.J.; Oehlmann, J.; Jourdan, J. Flushing away the future: The effects of wastewater treatment plants on aquatic invertebrates. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams-Subiza, E.A.; Brand, C.; Miserendino, M.L. Compositional shifts in freshwater macroinvertebrate communities over 30 years of urbanization. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 183, 106738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, M.F.; Chambers, P.A.; Schindler, D.W. Constraints on benthic algal response to nutrient addition in oligotrophic mountain rivers. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 858–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, L.A.; Clements, W.H. Assessing the influence of water and substratum quality on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in a metal-polluted stream: An experimental approach. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, R.J. Colonization by Lotic Macroinvertebrates: A Review of Processes and Patterns. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.J. Colonizing macroinvertebrates in the Upper Mississippi River with a comparison of basket and multiplate samplers. Freshw. Biol. 1982, 12, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.V.; Barnes, J.R. Patterns of Macroinvertebrate Colonization in an Intermittent Rocky Mountain Stream in Utah. Great Basin Nat. 1985, 45, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Marwein, I.; Gupta, S. Colonization Pattern of Aquatic Insects at Two Small Streams of Shillong, Meghalaya, North-East India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 91, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, R.S.; Armitage, P.D.; Aston, K.; Blackburn, J.H.; Hamburger, M.; Woodward, C.A. Colonization and emergence of midges (Chironomidae: Diptera) in slow sand filter beds. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1992, 26, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, P.S. Disturbance, patchiness, and diversity in streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2000, 19, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, N.M.; Auro, M.E.; Hagen, T.; Dumont, K.L. How Colonization Time Influences Macroinvertebrate Community Measures on Artificial Substrates. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2005, 20, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, E.C.; Harrel, R.C. Sequences of colonization, diversity, biomass, and productivity of macroinvertebrates on artificial substrates in a freshwater canal. Hydrobiologia 1978, 59, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and Riverscapes: The Influence of Land Use on Stream Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Temperature (°C) | pH | Total Organic Carbon (mg/L) | Total Nitrogen (mg/L) | Total Phosphorus (mg/L) |
| Head pond (September) | 13.75 | 8.03 | 1.65 | 0.85 | 0.03 |
| Head pond (October) | 7.55 | 8.19 | 1.4 | 0.75 | 0.015 |
| Site | Flow (L/s) | Mean Width (cm) | Mean Depth (cm) | Mean Substrate Size (mm) | Mean Specific Conductivity (µS/cm) |
| Control Streams | 13.4 | 143.53 | 8.28 | 60.6 | 299.4 |
| Treatment Streams | 13.4 | 145.10 | 8.05 | 59.0 | 286.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutherland, A.M.; Wrona, F.J.; Barrett, D.C. Effects of Cumulative Municipal Wastewater Exposure on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages: An Experimental Stream Approach. Hydrobiology 2025, 4, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4020017
Sutherland AM, Wrona FJ, Barrett DC. Effects of Cumulative Municipal Wastewater Exposure on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages: An Experimental Stream Approach. Hydrobiology. 2025; 4(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutherland, Aphra M., Frederick J. Wrona, and David C. Barrett. 2025. "Effects of Cumulative Municipal Wastewater Exposure on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages: An Experimental Stream Approach" Hydrobiology 4, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4020017
APA StyleSutherland, A. M., Wrona, F. J., & Barrett, D. C. (2025). Effects of Cumulative Municipal Wastewater Exposure on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Assemblages: An Experimental Stream Approach. Hydrobiology, 4(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology4020017






