Abstract
Bisphenol A, BPA, is a small molecule frequently used in large-scale plastic production. The chemical has garnered a reputation for its association with harmful human health effects, and numerous animal studies have contributed to its classification as an endocrine disruptor. Prior research has investigated the impact of the chemical on echinoderms, including seven species of sea urchin. Our project investigated the toxic effects of this chemical on two uninvestigated species: Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata. We exposed embryos to a range of environmentally relevant BPA concentrations (1 µg/L, 10 µg/L, 100 µg/L, and 1000 µg/L) for 48 h, until the pluteus stage. Larvae were classified according to the type of abnormality they exhibited, using a light microscope, and the EC50 was determined through probit analysis and dose–response curves. We also examined isolated plutei skeletons under a scanning electron microscope to assess changes to the skeletal structure under increasing concentrations of BPA. Our results suggest BPA induces embryotoxicity and soft tissue abnormalities more severely in L. variegatus, whereas A. punctulata exhibits more resistance to these effects. The EC50 values, over 1000 µg/L for A. punctulata and approximately 260 µg/L for L. variegatus, support this. These relative values also agree with our hypothesis that sea urchin embryos in a single genus have a similar level of BPA embryotoxicity. Interestingly, under SEM examination, the A. punctulata skeletal microstructure appears to be altered as a result of BPA exposure. While the EC50s are below what has been documented in many, but not all, marine environments, longer and consistent exposure may have a more deleterious impact. These findings suggest BPA’s effects on echinoderms should be further explored with multiple forms of analysis and over the long term.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a monomeric compound that was initially synthesized in the 1890s and later investigated in the 1930s for its potential use as a synthetic estrogen analog [1]. In the following decades, its use as a synthetic estrogen analog subsided when more potent alternatives were discovered. Since the 1950s, it has been used in plastic production, namely polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins that comprise everyday goods, including water bottles, food packaging, and dental materials [2]. Production of the compound is widespread, with the global output estimated at over 8 million metric tons as of 2018, making its presence difficult to avoid [3]. Since its debut in the plastic industry, BPA has become infamous for being an endocrine disruptor in both vertebrates and invertebrates, thus earning its classification as a nonsteroidal xenoestrogen. In 1993, Krishnan et al. [4] were the first to discover BPA could leach from polycarbonate flasks when yeast that were incubated in the flasks appeared to falsely express endogenous estrogen. This discovery sparked interest in BPA’s capability to interfere with the endocrine system and led to increased awareness regarding its ability to leach from plastic material. Subsequent testing on mice and rats in the 1990s confirmed physiological changes occurred even below the accepted safety standard for BPA ingestion [5,6,7].
We now know BPA contaminates food and drink ingested by humans through leaching from plastic containers [8]. BPA exposure in human adults has been associated with a decrease in fertility rates and embryo quality [9], decreased sperm quality [10], miscarriage [11], premature delivery [12], abnormal sex and thyroid hormone levels [13,14], immune interference [15], cardiovascular diseases [16], inflammation and oxidative stress [17,18], and abnormal gene expression [19]. BPA exposure prior to birth has been associated with decreased birth weight, childhood obesity, disrupted neurodevelopment, and a further likelihood of developing childhood asthma [20]. BPA has been attributed to a wide array of adverse human health effects at all stages of life.
BPA gains access to marine and freshwater ecosystems through plastic trash leaching, plastic burning in landfills, and effluent from wastewater treatment plants [21]. Worldwide, BPA concentrations in both freshwater and marine environments range from tens to thousands of ng/L [22]. For example, BPA concentrations in Japanese surface waters were 3.1 to 120 ng/L, with higher concentrations detected downstream of urban and industrial zones [23], while China’s and Turkey’s freshwater BPA levels were as high as 7480 ng/L [24] and 29,920 ng/L, respectively [25]. Although freshwater experiences the highest levels of BPA, the chemical eventually reaches the ocean and has been shown to persist there longer than in freshwater river ecosystems, potentially leading to a greater level of ocean contamination [21]. Like freshwater, a wide range of BPA levels have been observed in ocean water, from 23 ng/L in the East China Sea [26] to 4160 ng/L and 16,920 ng/L in, respectively, surface and deep seawater around Turkey [25].
Once in the environment, aquatic organisms are exposed to BPA, which can potentially modify their endocrine-related processes, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. However, as the literature from the past three decades has demonstrated, specific effects vary between different species. For example, in the fish Pimephales promelas, only 16 µg/L of BPA exposure caused decreased spermatocyte production, leading to reduced numbers of mature spermatozoa [27]. More recently, Han et al. [28] exposed the crustacean Litopenaeus vannamei to 2 µg/L BPA and observed delays in the gonad development, reduced rates of oxygen consumption, reduced metabolism-related gene expression, and increased gonad hormone levels.
Echinoderms, specifically sea urchins, have been utilized in many toxicology studies as they share many physiological and biochemical processes with vertebrates [29]. Sea urchin embryos are a useful model system for examining toxicity on early development because of their transparent nature and relatively rapid growth [30,31]. The physiological effects of bisphenol A on early-stage embryonic development have been reported on seven sea urchin species, including Strongylocentrotus purpuratus and Lytechinus anamesus [32], Strongylocentrotus nudus and Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus [33], Paracentrotus lividus [34], Echinometra lucunter [35], and Arbacia lixula [36]. Several of these studies have examined the detrimental effects on embryonic development by classifying developmental abnormalities and delays and performing sperm bioassays. Reported effective concentrations (EC50s) for embryonic development range from less than 1.56 µg/L in Echinometra lucunter [35] to 1210 µg/L in Paracentrotus lividus [37], suggesting differential, species-specific responses to BPA. Additionally, only one sea urchin species, Paracentrotus lividus, has a reported BPA EC50 above 1000 µg/L.
There is little documentation regarding the precise skeletal defects induced by BPA on developing urchin embryos and larvae. A few studies have observed skeletal malformations in light microscope images but have not defined these abnormalities in a detailed manner [32,36,38]. Gambardella et al. [39] have provided the most comprehensive categorization of larval skeletal abnormalities caused by environmental stressors, including BPA. Their analysis of light micrograph data, compiled from the available literature on P. lividus, identifies the most common malformations. However, to date, alterations to the ultrastructure of the larval skeleton in response to BPA exposure have not been explored.
We chose to examine BPA sensitivity and impact on the larval development and skeletal ultrastructure of the two species, Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata. These two species were chosen for several reasons. Foremost, both have been recognized for their utility in prior embryotoxicity assays [40,41,42,43]. They also belong to genera that have been previously investigated to determine BPA’s impact on embryonic and larval development [32,36]. Each species develops in similar temperature ranges in the wild and reaches the pluteus stage within the same time frame [44]. More specifically, L. variegatus and A. punctulata skeletons have distinct differences from each other. The skeleton of L. variegatus has two single body rods containing small spines [45]. A. punctulata is smaller in comparison, with multiple body rods that are connected through small fenestrations down the length of each arm [46]. We utilized a light microscope (LM) to determine BPA-induced developmental abnormalities and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to determine how BPA may be impacting the microstructure of the pluteus skeleton. This study is the first of its kind to utilize both approaches in order to gain an understanding of BPA’s influence on both the soft tissue and skeletal development of sea urchin embryos.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sea Urchin Fertilization Procedure
Adult Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata were obtained from Gulf Specimen Marine Lab (Panacea, FL, USA). Spawning was induced by injecting 0.5 M KCl close to the oral cavity, followed by vigorous shaking [47]. Eggs were collected in artificial seawater (pH 8.2, 32 ppt), and sperm were collected dry. Fertilization was accomplished by adding approximately five drops of the diluted sperm solution to the large volume of washed and suspended eggs. Sperm were added until 90% fertilization was observed. The beaker of zygotes was periodically swirled until they reached the two-cell stage; this took 90 min for L. variegatus and 120 min for A. punctulata.
2.2. Exposure of Embryos to Bisphenol A Solutions
Test concentrations of bisphenol A (BPA) were prepared by dissolving 0.05 g of BPA in 5 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) [34]. It has been previously shown that DMSO has no independent impact on sea urchin development [38,48,49,50]. Five µL of the BPA-DMSO solution was added to 50 mL of seawater (32 ppt) to create a 1000 µg/L stock solution. The stock solution was utilized to create 1.0, 10, and 100 µg/L BPA with seawater, with the 1000 µg/L stock serving as the highest concentration. Seawater served as the control.
Six-well plates were used for incubating the embryos at 21 degrees Celsius. Embryos for the light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) data collection were raised in separate 6-well plates, and each well contained 10 mL of test solution [36]. Three wells of each test concentration were prepared for SEM data collection, and one well of each test concentration was prepared for light microscope data collection.
When the embryos reached the 2-cell stage, 120–800 µL of concentrated embryo solution was added to each well to form an even single layer of noncontiguous embryos. The 6-well plates were covered and left undisturbed for 48 h to allow for embryos to develop to the early pluteus stage.
2.3. Light Microscopy Procedure and Data Collection
The plutei of each well were fixed with 40 µL of fresh 20% formalin [33] and a sample of approximately 100 plutei was photographed with a Nikon E200 compound microscope (Tokyo, Japan) at 40×. From these images, each embryo/pluteus was classified as either normal or abnormal, with specific distinctions being made for certain common abnormalities. The abnormal classifications included the embryos that did not reach the blastula stage and only appeared as a ball of cells, embryos that only reached the prism stage of development, underdeveloped plutei that appeared distinctly smaller than mature plutei, fully grown plutei with shortened limbs or incomplete/missing limbs, and fully grown plutei with a deteriorated epithelium that was pulled back at the tips of the skeleton. These categories are more detailed representations of the P1, P2, and D classifications used by Rezg et al. [36] and Arslan et al. [38] in their analyses of BPA’s impact on sea urchin embryonic development.
Two approaches were taken to determine the EC50. Each set of measurements was plotted and determined to have a normal distribution prior to analysis. The normal versus abnormal classification data were analyzed via Probit analysis [34] with R, and dose–response curves with GraphPad Prism (San Diego, CA, USA).
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Procedure and Data Collection
The contents from all three wells within an individual BPA treatment group were transferred into a 50 mL tube to start the soft tissue-removal and skeleton-isolation process, according to Clark et al. [51]. A 4.8% Clorox bleach solution was added to each 50 mL tube in a 1:3 ratio (10 mL of bleach solution for 30 mL of plutei). Each tube was set horizontally to minimize plutei settling at the bottom of the tube. The plutei were examined under the dissecting microscope for 15 min, 30 min, and then every 5 min after bleach was added until only the skeletons were visible in the solution.
The bleach and dissolved tissue were gradually removed from the skeletons using distilled water. Once the skeletons settled to the bottom of the upright tube, 40–45 mL of the bleach solution was removed, and 10–20 mL of distilled water was added. This process was repeated six times until the liquid was clear. The top 40–45 mL of liquid was removed from each tube, leaving the skeletons at the bottom [51].
The stripped skeletons were resuspended in the remaining distilled water. Four to five drops of skeleton solution were transferred onto each SEM stub, which had been previously covered with Scotch® brand (Hutchinson, MN, USA) double-sided tape. The prepared SEM stubs were placed in a gravity convection oven (Binder, Tuttlingen, Germany) at 30 °C for 24 h to allow the water to evaporate and the skeletons to adhere to the tape [51].
The stubs were sputter coated in silver or gold using the Cressington 108 auto sputter coater (Watford, England). The skeletons on the stubs were viewed and photographed with the Topcon ABT-60 Scanning Electron Microscope (Tokyo, Japan) at 15 kV. ImageJ (version 1.53) was used to obtain measurements for the full length, aboral arm length, cross bridge length, aboral arm width, and cross bridge width of each pluteus skeleton. A t-test was used to compare experimental groups for each measurement. Statistically significant differences were determined with a p-value of less than 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Light Microscope Analysis
The effects of BPA on the early embryological development of two sea urchin species, Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata, were investigated. Embryos were grown for 48 h in a 1.0, 10.0, 100, or 1000 µg/L BPA solution alongside a control and then examined for abnormalities in pluteal development. Additionally, we categorized the observed abnormalities into six distinct categories: underdeveloped pluteus, deteriorated epithelium, shortened arms, incomplete/missing arms, prism (delayed development), and a ball of cells (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
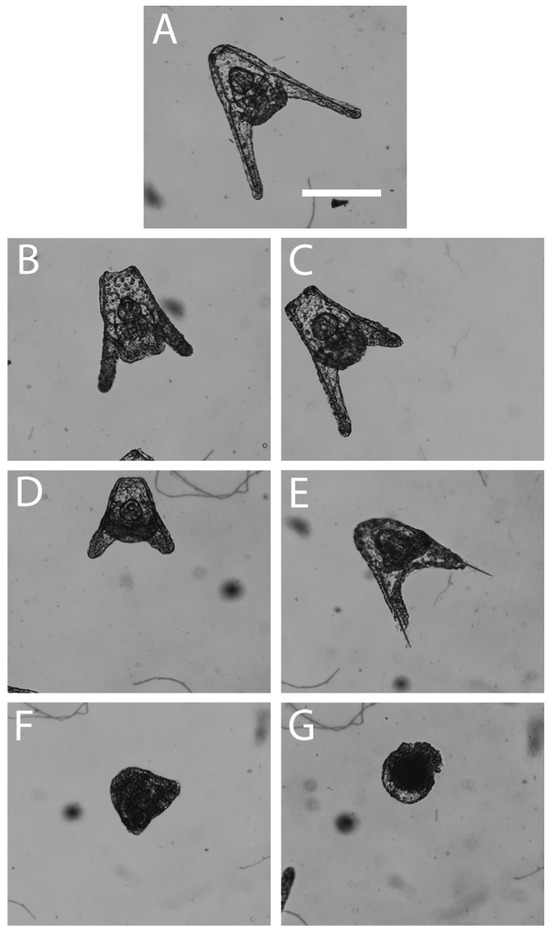
Figure 1.
Observed embryonic malformations in Lytechinus variegatus 48 h post-fertilization. (A) Normal pluteus, (B) shortened arms, (C) incomplete/missing arm(s), (D) underdeveloped pluteus, (E) deteriorated epithelium of a pluteus, (F) prism, and (G) ball of cells. Scale bar represents 10 µm.
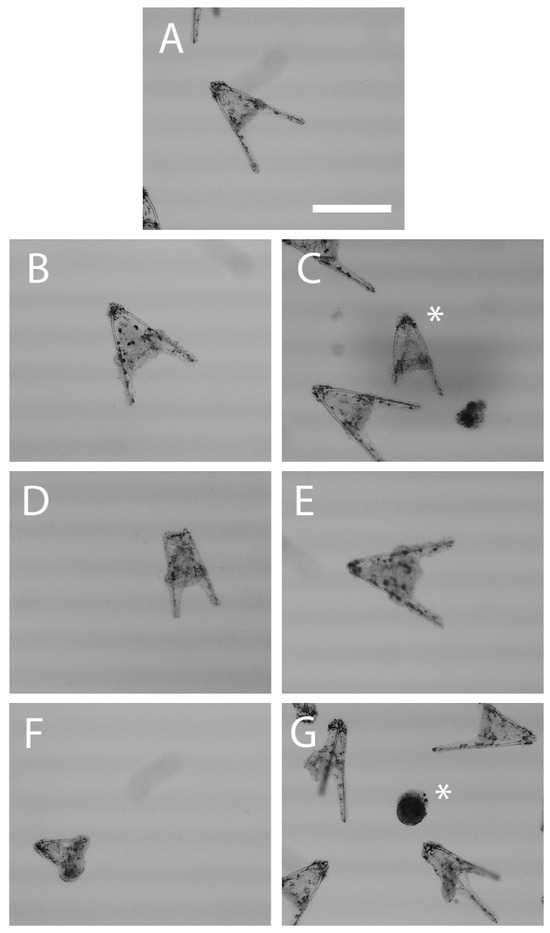
Figure 2.
Observed embryonic malformations in Arbacia punctulata 48 h post-fertilization. Asterisk indicates pluteus of interest. (A) Normal pluteus, (B) shortened arms, (C) incomplete/missing arm(s), (D) underdeveloped pluteus, (E) deteriorated epithelium of a pluteus, (F) prism, and (G) ball of cells. Scale bar represents 10 µm.
In A. punctulata, the control, 1.0 µg/L treatment, and 10 µg/L treatment groups all contained approximately 10% abnormal embryos. The percentage of abnormal plutei rose at BPA concentrations of 100 and 1000 µg/L compared to lower concentrations and the control (Figure 3A). The most prominent type of abnormality observed in A. punctulata across all concentrations was the ball of cells category (51.5%), followed by underdeveloped plutei (23.6%), plutei with shortened arms (17.9%), plutei with incomplete/missing arms (3.06%), plutei with a deteriorated epithelium (2.18%), and finally embryos in the prism stage (1.75%) (Figure 3C). There was no significant pattern of prevalent abnormalities as the BPA concentration increased.Because less than fifty percent of the A. punctulata embryos were impacted by the highest BPA concentration, 1000 µg/L, a dose–response curve could not provide an EC50. Probit analysis, however, calculated a predictive value for the EC50 of A. punctulata that was outside of the range of 1000 µg/L, at 1368 µg/L.
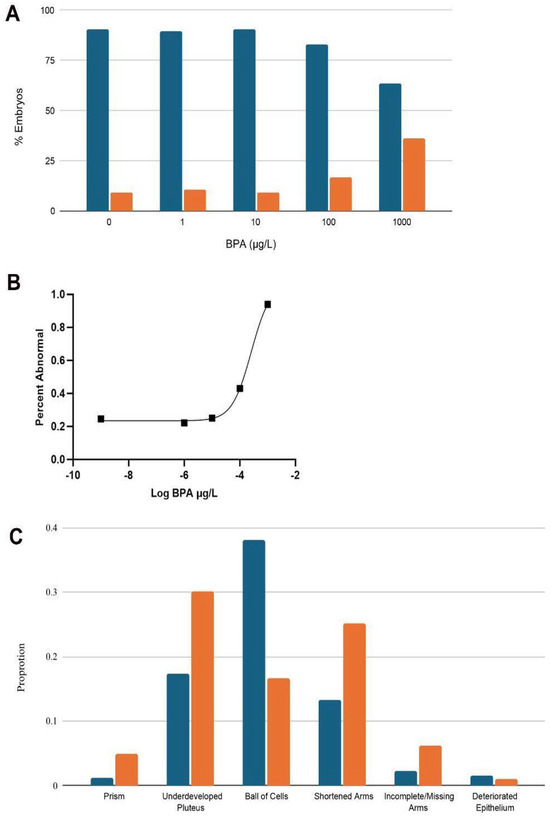
Figure 3.
Percentage of total normal (dots) and abnormal (horizontal lines) embryos in different BPA concentrations within (A) Arbacia punctulata (n = approximately 200). (B) Dose–response curve for L. variegatus embryos/larvae exposed to seawater (control) or one of four concentrations of BPA for 48 h. (C) The total prevalence of each abnormality across all BPA samples combined, not including controls. Blue bars indicate A. punctulata abnormalities while orange bars indicate L. variegatus abnormalities.
For L. variegatus, similarly to the other species, the control, 1.0 µg/L treatment, and 10 µg/L treatment groups did not significantly vary in percentage of abnormal plutei, with all three groups falling closely to 25% abnormal (Figure 3B). The percentage of abnormal plutei rose in the two highest BPA concentrations and reached close to 100% in the 1000 µg/L treatment (Figure 3B). Probit analysis determined the EC50 for L. variegatus was 277 µg/L, and the dose–response curve generated an EC50 of 257 µg/L (Figure 3B).
The most prominent type of abnormality recorded for Lytechinus variegatus across all concentration samples was underdeveloped pluteus (35.9%), followed by shortened arms (30.0%), ball of cells (19.9%), incomplete/missing arms (7.29%), prism (5.83%), and deteriorated epithelium (1.17%) (Figure 3C).
3.2. SEM Analysis
We carried out a quantitative analysis of the effects of BPA on the L. variegatus and A. punctulata skeletal microstructure, as observed with SEM. The full length of the pluteus skeleton, the aboral arm length, the aboral arm width, the cross bridge length, and the cross bridge width of the pluteus skeleton were each measured (Figure 4), and each experimental group was compared to one another, as well as to the controls, to determine statistical significance.
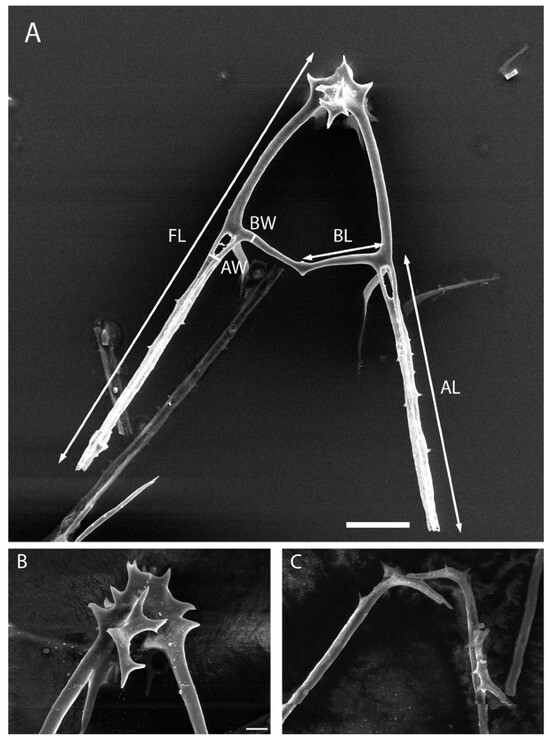
Figure 4.
Depictions of measurements performed on sea urchin plutei and visual differences in sea urchin basket structure between Arbacia punctulata and Lytechinus variegatus. (A) Demonstration of the measurement parameters for full length (FL), arm length (AL), bridge length (BL), arm width (AW), and bridge width (BW) on an A. punctulata pluteus. (A) Scale bar represents 33.3 µm. Differences in basket structure can be observed between A. punctulata (B) and L. variegatus (C). (B,C) scale bars are 5 µm.
In Arbacia punctulata, the larvae’s full lengths in all BPA treatments were significantly less than the control’s full lengths (all p < 0.05) (Figure 5). However, pairwise comparisons between each BPA treatment group for the full length were not significantly different. A similar pattern was seen when the aboral arm length measurements from all treatment groups were compared to the control group, with p-values less than 0.05, except for the 100 µg/L group (p = 0.0521) (Figure 5). In addition, there was no difference between the treatment groups for aboral arm length. For the cross-bridge length, all BPA treatments were significantly less than the controls (all p < 0.5) (Figure 5). Additionally, significant differences between cross bridge lengths were observed between 1 µg/L and 10 µg/L (p = 0.0424), as well as 10 µg/L and 1000 µg/L (p = 0.0331). For arm width, a significant decrease in width was only observed when the control group was compared to the 1000 µg/L group (p = 0.0264) (Figure 5). All other comparisons were not statistically significant for this measurement type. For the cross-bridge width, a significant decrease was observed in the 1000 µg/L concentration compared with the other concentrations and the control (p < 0.05) (Figure 5). No other significant differences were observed for the cross-bridge width measurements.
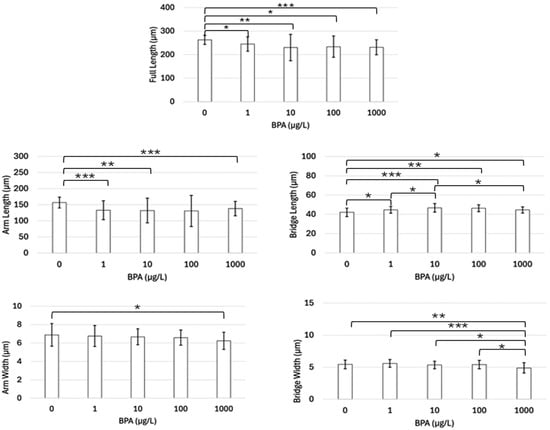
Figure 5.
Average length (µm) of each skeletal measurement performed in each treatment group (n = 30) of Arbacia punctulata. Horizontal brackets indicate which pairs are being statistically compared. One star (*) denotes p-value < 0.05, two stars (**) denotes p-value < 0.01, and three stars (***) denotes p-value < 0.001.
A similar procedure was utilized to assess BPA’s impact on the skeletal ultrastructure of L. variegatus. Arm length (Figure 6) and bridge width (Figure 6) were the only two skeletal elements that revealed significant differences between any of the treatment groups. Pluteus arm length was significantly smaller in the 100 µg/L and 1000 µg/L groups compared to the controls (p < 0.05) (Figure 6). Bridge width of the 1000 was significantly less than the control (p = 0.0002). Additionally, the bridge width of the plutei in the 1000 µg/L sample was significantly smaller in comparison to the plutei of the 1.0 µg/L, 10 µg/L, and 100 µg/L samples (all p < 0.05). There were no significant differences between any treatment groups or the control and treatment groups of full length (Figure 6), bridge length (Figure 6), and arm width (Figure 6).
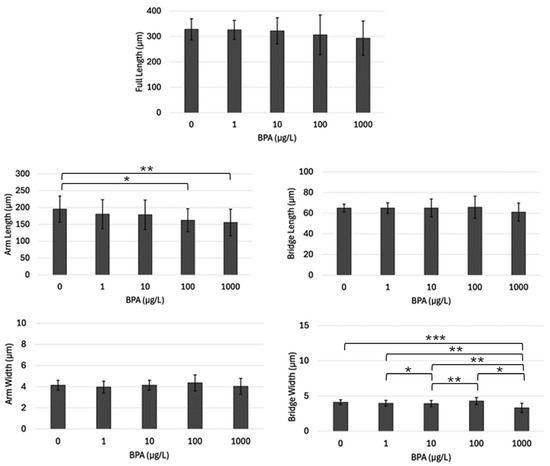
Figure 6.
Average length (µm) of each skeletal measurement performed in each treatment group (n = 30) of Lytechinus variegatus. Horizontal brackets indicate which pairs are being statistically compared. One star (*) denotes p-value < 0.05, two stars (**) denotes p-value < 0.01, and three stars (***) denotes p-value < 0.001.
The base of the pluteus skeleton for L. variegatus is simple in structure and has minimal attachments between both sides. A. punctulata skeletons were observed to have a basket-like structure at the base of the pluteus that consisted of several connections between both sides of the skeleton. After transferring the L. variegatus skeletons onto the SEM stubs to collect measurements, it was observed that the left and right sides of the pluteus skeleton became separated. It was also observed that A. punctulata skeletons consistently remained full plutei when transferred to stubs and did not separate (Figure 4).
4. Discussion
It has been long documented that BPA poses a toxicological risk to both vertebrate and invertebrate aquatic species by impacting their reproductive systems, endocrine systems, metabolism, immune functions, and other physiological pathways [52]. Impacts have been observed in multiple species of insects, fish, amphibians, angiosperms, crustaceans, mollusks, annelids, platyhelminthes, ascidians, cnidarians, rotifers, porifera, macroalgae, phytoplankton, and echinoderms [53]. As echinoderms are present in most regions of the ocean, sea urchins are one of the key model organisms used to study the effects of BPA on early development. Additionally, their rapid early development enables studies to be performed on a much smaller time scale rather than necessitating longitudinal experimental designs. As of this paper, seven species have been examined toxicologically [32,34,35,36]. Because there were differences in how these species responded, we determined it would be useful to investigate two additional species: Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata.
Prior approaches to studying BPA’s effects have focused on classifying embryological abnormalities and calculating EC50s. We incorporated these prior methods and additionally hypothesized that BPA induces alterations in the sea urchin skeleton on the microscale, investigating these alterations utilizing a scanning electron microscope. Prior studies have also often utilized BPA concentrations far above typical environmental concentrations in their testing samples [38]. The range of BPA concentrations we used (1–1000 µg/L) reflects environmentally relevant values, which allows us to better understand BPA’s impact on aquatic ecosystems [22]. With dosages that are accurate to the environment, we can draw stronger comparisons between our own species and other sea urchins of different species and genera.
Previous work has shown that there are common developmental responses to increasing doses of BPA. Many of these abnormalities correlate with ours. While some authors simply described the abnormalities, others constructed classification schemes [32,39]. For example, Rezg et al. [36] reported abnormalities in Arbacia lixula under three distinct classifications: P1 (pluteus with skeletal abnormalities), P2 (blockage at pre-pluteus stages), and D (early embryonic death). Arslan et al. [38] adopted a similar classification system in Paracentrotus lividus with P1, P2, and D, as well as an additional classification with R (plutei at half the size of a normal pluteus). This classification system was useful, but we felt that it did not include the level of detail necessary to highlight the abnormalities that surfaced in the species we analyzed. In comparing our categorizations, P1 plutei share similarities with our underdeveloped pluteus classification, while P2 seems to correspond to both our ball of cells and prism classifications. Plutei classified as R embryos also share features emblematic of the plutei we documented as shortened arms. We identified fully grown plutei with epithelial degradation along the skeletal rods to be in our deteriorated epithelium category, and this appears nearly identical to the early embryonic death category. Considering that embryos are consistently fixed with formalin prior to examination, we determined that using “early embryonic death” as a method of categorization was not an accurate use of the term. Incidences of plutei with similar features to that of our incomplete/missing arms classification were not described in either article, suggesting that this may be a unique malformation found within the two species we analyzed.
In toxicological studies, EC50s serve as invaluable standardized measures of the potency of certain chemicals, establishing safe exposure levels, and evaluating the biological risk that certain substances pose. Across all of the current literature, BPA EC50s in sea urchin embryos range from 1.56 µg/L in Echinometra lucunter [35] up to 1210 µg/L in Paracentrotus lividus [37]. Our research has shown that BPA induces embryotoxicity in both Arbacia punctulata and Lytechinus variegatus. However, L. variegatus demonstrated significantly more sensitivity to the effects of BPA upon embryological analysis. Developmental abnormalities in 50% of our L. variegatus samples were correlated with an EC50 of approximately 260 µg/L, according to the two statistical tests we employed. This value does fall within the lower end of the range of recorded EC50s for other species, suggesting that L. variegatus is one of the more vulnerable species and is at a greater immediate threat to increasing BPA concentrations in aquatic environments. At the other end of the embryotoxicity spectrum, A. punctulata appears to be more resistant to BPA’s impacts on early embryonic development.
We sought to investigate whether or not species belonging to the same genus demonstrate a similar resistance or sensitivity to BPA, and this appears to be the case. A study by Rezg et al. followed a very similar experimental procedure to our own, evaluating the development of Arbacia lixula and generating an EC50 of 794 µg/L [36]. We determined the EC50 of Arbacia punctulata was even higher, over 1000 µg/L, which may be one of the highest reported EC50s for any studied sea urchin species. Though these values are different from each other by several hundred µg/L, they are both on the higher range of BPA EC50 values that have been recorded in sea urchins. This suggests that the Arbacia genera may possess a greater resiliency to the chemical compared to others. The two species in the Lytechinus genus, L. anamesus [32] and L. variegatus, also show BPA EC50s in a similar, but much lower, range of 230 to 270 µg/L, respectively.
While our range of BPA concentrations was chosen because they represented levels seen in nature, in the future a more accurate A. punctulata EC50 could be obtained by extending the range of test concentrations above 1000 µg/L. However, since higher concentrations would lie far outside the range of what is environmentally relevant, we cannot expect that this species would be exposed to concentrations in their natural environment high enough to induce developmental abnormalities in 50% of the population.
Prior studies did not assess BPA’s impact on the sea urchin plutei’s skeletal microstructure, which could only be detected with the scanning electron microscope. Since the pluteus skeleton is a major feature that is developed within the first 48 h following urchin fertilization, we prioritized investigating potential micro-alterations in order to elucidate how and where the chemical is inducing larval malformations. We have that between our two species of interest, Arbacia punctulata skeletal structure appears to be more sensitive to the effects of BPA. We reported significant impacts to the skeleton within each category of measurement and generally observed a decrease in length and width with increasing BPA concentrations. In Lytechinus variegatus, the impact was much less significant. There were very few notable decreases in length or width with increasing concentrations of BPA. This suggests that the skeleton of L. variegatus possesses an increased resistance to the chemical alterations that BPA induces in skeletal development.
In preparing stubs for SEM analysis, we observed that L. variegatus larval skeletons would often separate down the midline during the preparation process, whereas A. punctulata skeletons remained intact. L. variegatus pluteal skeletons are larger than that of A. punctulata skeletons but also were thinner on average. Additionally, the basket skeletal structure located on the apical end of the pluteus is thinner in L. variegatus. We hypothesize the thicker and more substantial basket structure on the apical end of A. punctulata pluteus held together the two halves of the skeleton during SEM preparation. The separation of the skeletons in L. variegatus leads to clumping that prevents measurement of fully intact skeletons and interferes with the ability to record significant changes to the skeleton with increasing concentrations. It could also lead to duplicate measurements on the two halves of the same organism.
In comparing our two forms of analysis, it becomes evident that the impact of BPA cannot be observed through only one method. Between our two species, the overall embryological development of A. punctulata appeared more resistant to the effects of BPA, while L. variegatus samples demonstrated a greater number of embryological abnormalities. However, we also show that A. punctulata experiences greater skeletal alterations when exposed to BPA compared to L. variegatus skeletons. This could suggest that the chemical interferes with separate developmental pathways in each species, instigating unique changes. Future research examining the important regulatory pathways that induce skeletogenesis and other aspects of embryological development would be pertinent in explaining this differential impact we observed. Additionally, examining more sea urchin species through this two-pronged analysis would be vital in not only furthering our understanding of BPA’s impact but also discovering potential mechanisms for BPA resistance. Considering the similarities in early development between sea urchin species and humans, we believe that this would be worth pursuing.
Within the past decade, many industries have shifted towards the utilization of various BPA alternatives such as BPS, BPF, and BPAF in the production of plastics and other materials [38,54]. Many studies in recent years have begun to demonstrate that these chemicals, similar in structure to that of BPA, are inducing effects similar to those of the original compound. These effects are widespread and range from endocrine disruption [55] and reproductive toxicity to developmental damage [56]. As a result, while BPA is still prevalent in our oceans and aquatic environments, further assessment of these chemicals’ impact on sea urchin development may be relevant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.R.M.; methodology, E.R.M.; software, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; validation, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; formal analysis and investigation, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; resources, E.R.M.; data curation, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; writing—review and editing, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; visualization, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S.; supervision, E.R.M.; project administration, E.R.M.; funding acquisition, E.R.M., J.D.K., and M.C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding but was supported by the Muhlenberg College’s Vaughan Summer Research Endowment and the Biology Department.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because sea urchins are invertebrates that do not require state or federal permits.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a publicly accessible repository.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Muhlenberg College Biology Department and the Trexler Library. We greatly appreciate James Russell and Jeremy Teissere of Muhlenberg College, for their assistance with the statistical analyses. We acknowledge prior undergraduate research students, Michael Colasurdo, Laura Gleason, Marissa Mattia, Mehgan McQuade, and G.O.. (in alphabetical order), for their important contributions to the early laboratory work, and Gulf Specimen Marine Lab for their continuous supply of sea urchins. Finally, we are thankful for both reviewers’ valuable and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Vogel, S.A. The politics of plastics: The making and unmaking of bisphenol A “safety”. Am. J. Public Health 2009, 99, S559–S566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hou, J. A critical review of presence, removal and potential impacts of endocrine disruptors bisphenol A. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2002, 254, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Lee, B.P.; Buric, I.; Steele, A.M. Plastics additives and human health: A case study of bisphenol A (BPA). In Plastics and the Environment; Hester, R.E., Harrison, R.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Stathis, P.; Permuth, S.F.; Tokes, L.; Feldman, D. Bisphenol-A: An estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.C.; vom Saal, F.S.; Thayer, K.A.; Dhar, M.G.; Boechler, M.; Welshons, W.V. Relative binding affinity-serum modified access (RBA-SMA) assay predicts the relative in vivo bioactivity of the xenoestrogens bisphenol A and octylphenol. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colerangle, J.B.; Roy, D. Profound effects of the weak environmental estrogen-like chemical bisphenol A on the growth of the mammary gland of Noble rats. J. Steroid Biochem. 1997, 60, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, R.; Mitchner, N.A.; Grant, A.; Allen, D.L.; Bigsby, R.M.; Ben-Jonathan, N. The xenoestrogen bisphenol A induces growth, differentiation, and c-fos gene expression in the female reproductive tract. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food; Anton, R.; Barlow, S.; Boskou, D.; Castle, L.; Crebelli, R.; Dekant, W.; Engel, K.-H.; Forsythe, S.; Grunow, W.; et al. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane bis(2,3-epoxypropyl)ether (Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, BADGE). REF. No 13510 and 39700. EFSA J. 2004, 2, 86–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, M.S.; vom Saal, F.S.; Kim, D.; Taylor, J.A.; Lamb, J.D.; Fujimoto, V.Y. Serum unconjugated bisphenol A concentrations in men may influence embryo quality indicators during in vitro fertilization. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2011, 32, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, J.D.; Ehrlich, S.; Toth, T.L.; Wright, D.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Trisini, A.T.; Ye, X.; Hauser, R. Semen quality and sperm DNA damage in relation to urinary bisphenol A among men from an infertility clinic. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dai, Y.; Luo, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, W.; Shen, Y. Association between serum bisphenol-A and recurrent spontaneous abortion: A 1:2 case-control study, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2012, 33, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cantonwine, D.; Meeker, J.D.; Hu, H.; Sánchez, B.N.; Lamadrid-Figueroa, H.; Mercado-García, A.; Fortenberry, G.Z.; Calafat, A.M.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M. Bisphenol A exposure in Mexico City and risk of prematurity: A pilot nested case control study. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Gao, E.; Yuan, W. Effect of bisphenol A exposure on sex hormone level in occupational women. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2011, 40, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kandaraki, E.; Chatzigeorgiou, A.; Livadas, S.; Palioura, E.; Economou, F.; Koutsilieris, M.; Palimeri, S.; Panidis, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Endocrine disruptors and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Elevated serum levels of bisphenol A in women with PCOS. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2011, 96, E480–E484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees Clayton, E.M.; Todd, M.; Dowd, J.B.; Aiello, A.E. The impact of bisphenol A and triclosan on immune parameters in the U.S. population, NHANES 2003–2006. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, D.; Osborne, N.J.; Henley, W.E.; Cipelli, R.; Young, A.; Money, C.; McCormack, P.; Luben, R.; Khaw, K.-T.; Wareham, N.J.; et al. Urinary bisphenol A concentration and risk of future coronary artery disease in apparently healthy men and women. Circulation 2012, 125, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Hong, Y.-C.; Oh, S.-Y.; Park, M.-S.; Kim, H.; Leem, J.-H.; Ha, E.-H. Bisphenol A exposure is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in postmenopausal women. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Scarlett, A.; Henley, W.E.; Depledge, M.; Wallace, R.B.; Melzer, D. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2008, 300, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, D.; Harries, L.; Cipelli, R.; Henley, W.; Money, C.; McCormack, P.; Young, A.; Guralnik, J.; Ferrucci, L.; Bandinelli, S.; et al. Bisphenol A exposure is associated with in vivo estrogenic gene expression in adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.-H.; Kondo, F. Bisphenol A degradation in seawater is different from that in river water. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrello, J.; Matozzo, V. Bisphenol analogs in aquatic environments and their effects on marine species—A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1271–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Moon, H.-B.; Jeong, Y.; Kannan, P.; Achyuthan, H.; Munuswamy, N.; et al. Bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues including BPS and BPF in surface water samples from Japan, China, Korea and India. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wu, L.-H.; Liu, G.-Q.; Shi, L.; Guo, Y. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of eight endocrine-disrupting chemicals in urban river water and sediments of South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhan, K.; Kocaman, E. Temporal and spatial distributions of bisphenol A in marine and freshwaters in Turkey. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 76, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhao, M.; Jin, H. Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues, triclocarban, and triclosan in sea water and sediment from East China Sea. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohoni, P.; Tyler, C.R.; Hurd, K.; Caunter, J.; Hetheridge, M.; Williams, T.; Woods, C.; Evans, M.; Toy, R.; Gargas, M.; et al. Reproductive effects of long-term exposure to bisphenol A in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2917–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Shi, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Hu, L.; Liu, G. Microplastics and bisphenol A hamper gonadal development of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) by interfering with metabolism and disrupting hormone regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janer, G.G.; LeBlanc, A.; Porte, C. A comparative study on androgen metabolism in three invertebrate species. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2005, 143, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, G.; Cipollaro, M.; Corsale, G.; Esposito, A.; Ragucci, E.; Giordano, G.G.; Trieff, N.M. The sea urchin: Bioassay for the assessment of damage from environmental contaminants. In Community Toxicity Testing, ASTM STP 920; Cairns, J., Ed.; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986; pp. 66–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N. Marine pollution bioassay by using sea urchin eggs in the Tanabe Bay, Wakayama Prefecture, Japan, 1970–1987. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1991, 23, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roepke, T.A.; Snyder, M.J.; Cherr, G.N. Estradiol and endocrine disrupting compounds adversely affect development of sea urchin embryos at environmentally relevant concentrations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 71, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyomoto, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Unuma, T.; Yokota, Y. Effects of ethinyl estradiol and bisphenol A on the development of sea urchin embryos and juveniles. Mar. Biol. 2006, 149, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, Ö.Ç.; Hatice, P. Effects of bisphenol A on the embryonic development of sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus). Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.Q.; de Souza Abessa, D.M. Toxicity of three emerging contaminants to non-target marine organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18354–18364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezg, R.; Oral, R.; Tez, S.; Mornagui, B.; Pagano, G.; Trifu Oggi, T. Cytogenetic and developmental toxicity of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in Arbacia lixula sea urchin embryos. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tato, T.; Salgueiro-González, N.; León, V.M.; González, S.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicological evaluation of the risk posed by bisphenol A, triclosan, and 4-nonylphenol in coastal waters using early life stages of marine organisms (Isochrysis galbana, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Paracentrotus lividus, and Acartia clausi). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, Ö.Ç.; Karaaslan, M.A.; Nalbantlar, B. Developmental effects of bisphenol A and its analogs bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF on sea urchins Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck 1816) and Arbacia lixula (Linnaeus 1758). Res. Sq. 2023, 6, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Marcellini, F.; Falugi, C.; Varrella, S.; Corinaldesi, C. Early-stage anomalies in the sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) as bioindicators of multiple stressors in the marine environment: Overview and future perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, T.J.; Kramer, J.R.; Boeri, R.L.; Gorsuch, J.W. Chronic toxicity of silver to the sea urchin (Arbacia punctulata). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 25, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perina, F.C.; de Souza Abessa, D.M.; Pinho, G.L.L.; Fillmann, G. Comparative toxicity of antifouling compounds on the development of sea urchin. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttger, S.A.; McClintock, J.B. The effects of organic and inorganic phosphates on fertilization and early development in the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2001, 129, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Rittschof, D.; Orihuela, B.; Kwok, K.W.H.; Stafslien, S.; Chisholm, B. The effects of model polysiloxane and fouling-release coatings on embryonic development of a sea urchin (Arbacia punctulata) and a fish (Oryzias latipes). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 110–111, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.K.; Lawrence, J.M. Habitats and characteristics of the sea urchins Lytechinus variegatus and Arbacia punctulata (Echinodermata) on the Florida Gulf-Coast Shelf. Mar. Ecol. 2003, 24, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEdward, L.R.; Herrera, J.C. Body form and skeletal morphometrics during larval development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus Lamarck. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 232, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.B. The growth and metamorphosis of the Arbacia punctulata pluteus, and late development of the white halves of centrifuged eggs. Biol. Bull. 1949, 97, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, P.S. Laboratory culture of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus adults, embryos, and larvae. In Methods in Cell Biology, Volume 27; Schroeder, T.E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Semenova, M.N.; Demchuk, D.V.; Tsyganov, D.V.; Chernysheva, N.B.; Samet, A.V.; Silyanova, E.A.; Kislyi, V.P.; Maksimenko, A.S.; Varakutin, A.E.; Konyushkin, L.D.; et al. Sea urchin embryo model as a reliable in vivo phenotypic screen to characterize selective antimitotic molecules. Comparative evaluation of combretapyrazoles, -isoxazoles, -1,2,3-triazoles, and -pyrroles as tubulin-binding agents. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 700–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenova, M.N.; Kuptsova, T.S.; Semenova, V.V. Toxicity of organic solvents and surfactants to the sea urchin embryos. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellas, J.; Rial, D.; Valdés, J.; Vidal-Liñán, L.; Bertucci, J.I.; Muniategui, S.; León, V.M.; Campillo, J.A. Linking biochemical and individual-level effects of chlorpyrifos, triphenyl phosphate, and bisphenol A on sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larvae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46174–46187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.M.; Lamare, M.; Barker, M. Response of sea urchin pluteus larvae (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) to reduced seawater pH: A comparison among a tropical, temperate, and a polar species. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Fabbri, E. Environmental effects of BPA: Focus on aquatic species. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815598304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.C.; Seebacher, F. Effect of the plastic pollutant bisphenol A on the biology of aquatic organisms: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 3821–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, M.D.; Storch, P.J.; Eck, W.S.; Adams, V.H.; Fedick, P.W.; Harvey, B.G. BPA-free high-performance sustainable polycarbonates derived from non-estrogenic bio-based phenols. Green Chem. 2021, 20, 8016–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y. Bisphenol A alternatives continuously contribute to the endocrine disruption in cetaceans. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Su, S.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Song, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z. Exposure to bisphenol A alternatives bisphenol AF and fluorene-9-bisphenol induces gonadal injuries in male zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).