- Article
Hydrogeochemical and Biological Attributes of Chiuchiu Pond, a Pre-Andean Wetland in Northern Chile: Bases for Its Protection and Conservation
- Benito Gómez-Silva,
- Luis Cáceres and
- Milton Urrutia
- + 1 author
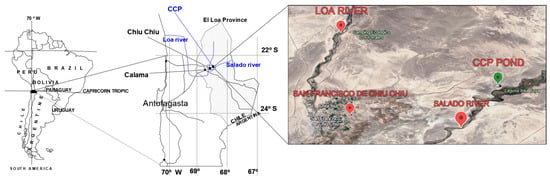
The Chiuchiu Pond (CCP) is an inland brackish water body in a pre-Andean scenery in the Atacama Desert, northern Chile. Presently unprotected, the CCP is attractive for tourism and a notable geosite for wildlife characterized by maintaining a fixed water level and chemical composition without surface inlets/outlets. This paper aims to characterize factors accounting for its perennial character by gathering climatic, hydrogeochemical, and morphometric information and microbiological and functional characterization. The CCP is an isolated U-shaped doline with a maximum depth of 17.5 m and vertical walls with more than 80% of soluble salts (halite and calcite) under arid conditions characterized by constant seasonal variation patterns. This is a unique case in that no similar conditions among reported wetlands or ponds have been found in the world. From our studies, it was characterized as an oligotrophic, lentic oligomictic, well-mixed water body, without thermal stratification, stable water level and hydrochemical composition, with water balance conditions from underground flows. Analysis of the microbial community revealed a core composition dominated by Proteobacteria (43.1%), Bacteroidetes (23.5%), and Cyanobacteria (10%). We provide a multidisciplinary contribution to justify urgent actions for the CCP’s conservation, representing a model for other unprotected coastal and inland wetlands in northern Chile and drylands elsewhere.
18 December 2025