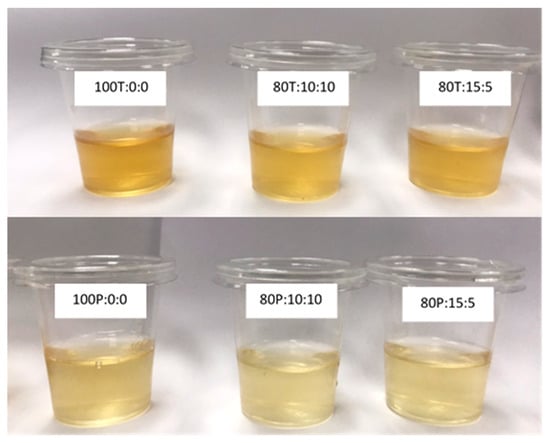
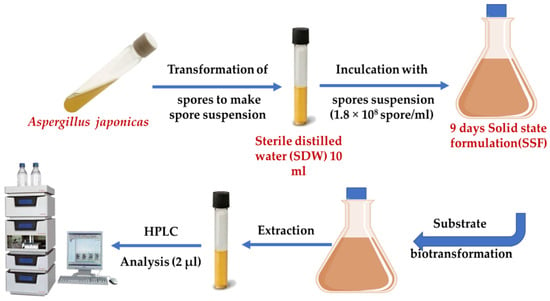
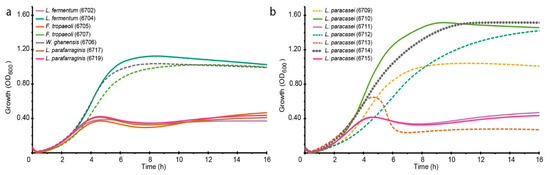
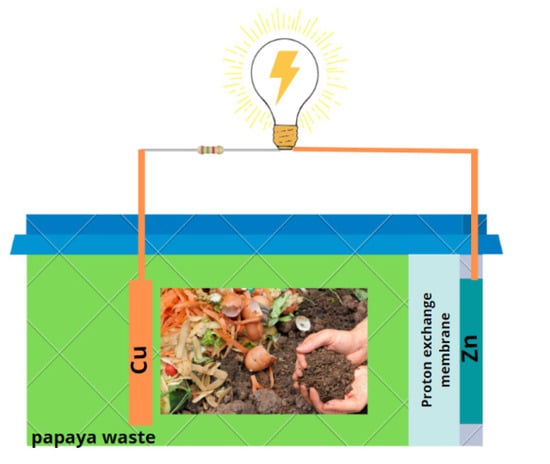
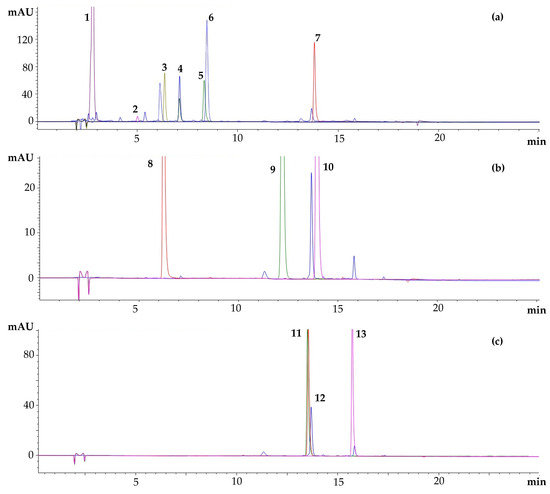
Food Waste Valorization
A topical collection in Fermentation (ISSN 2311-5637). This collection belongs to the section "Industrial Fermentation".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 106297Editor
Interests: microbial fermentation; fermentation process management; biofuel; biorefinery; value-added products; microbial pigments production; microbial carotenoids; functional food
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
During the industrial processing of agricultural or animal products, large amounts of wastes are produced. All these wastes, generated in large amounts throughout the different seasons of the year, can be considered the most abundant renewable resources on earth.
Due to the large availability and richness in components of these raw materials, a great interest is focused on their reuse, both from an economical and environmental points of view.
The economical interest is based on the fact that many of such wastes could be used as low-cost raw materials for the production of new value-added compounds, with a further production costs reduction. The environmental concern comes from their composition, especially the agro-industrial wastes that can contain potentially toxic compounds, which may cause deterioration of the environment when uncontrolled wastes are either burned or left on the soil to decay naturally or buried under the ground. Moreover, these materials exhibit both high biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) values, and give rise to serious pollution problems if not properly disposed of.
Recycling and transformation of food wastes represent a great opportunity in supporting a sustainable development by their conversion into value-added products, through fermentation process.
The Topic Collection will be focused on new food waste fermentation technologies and add value products resulting from food waste fermentation. The main topics include, but are not limited to the following:
- New fermentation process
- New food or feed production
- SCP production
- Biofuel production
- Biomolecules production
- Upstream and downstream optimization
- Fermentation products characterization
This is linked with the collection "Food Waste Valorization" and you can check it from here:
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/fermentation/special_issues/waste_valorization
Dr. Alessia Tropea
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Fermentation is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2100 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.