Increase in Electrical Parameters Using Sucrose in Tomato Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
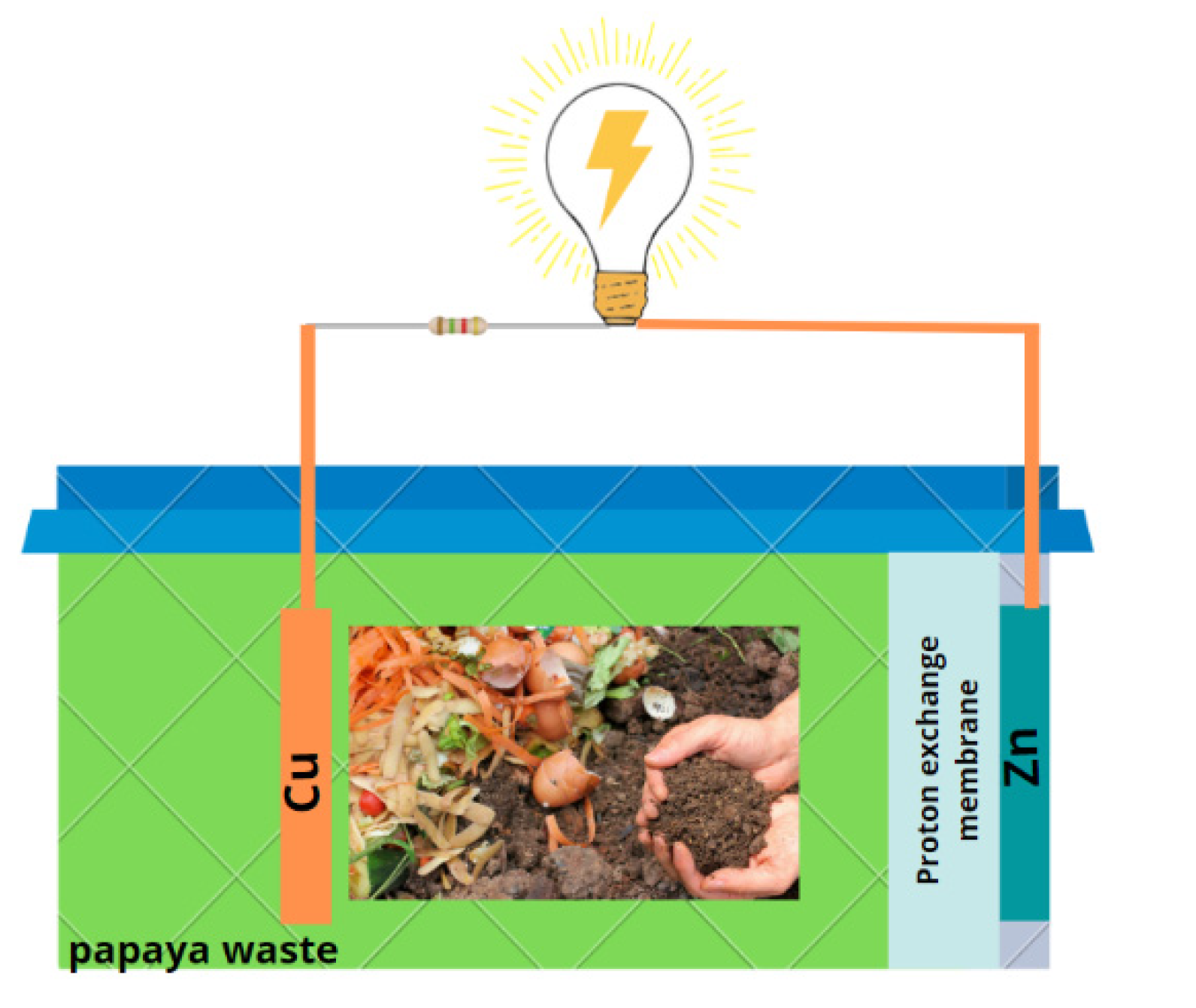
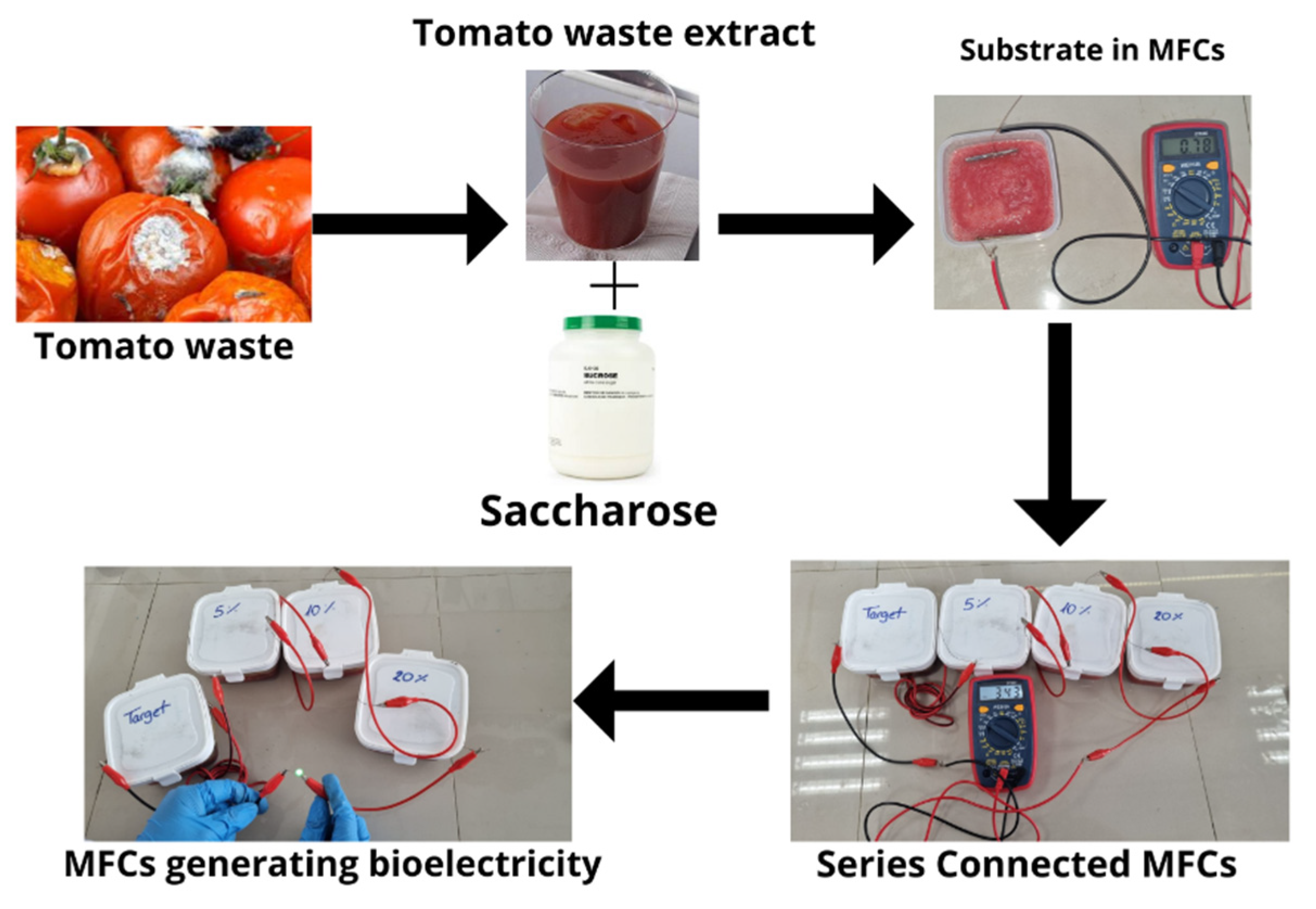
2.1. Fabrication of Microbial Fuel Cells
2.2. Collection of Tomato Waste
2.3. Characterization of Microbial Fuel Cells
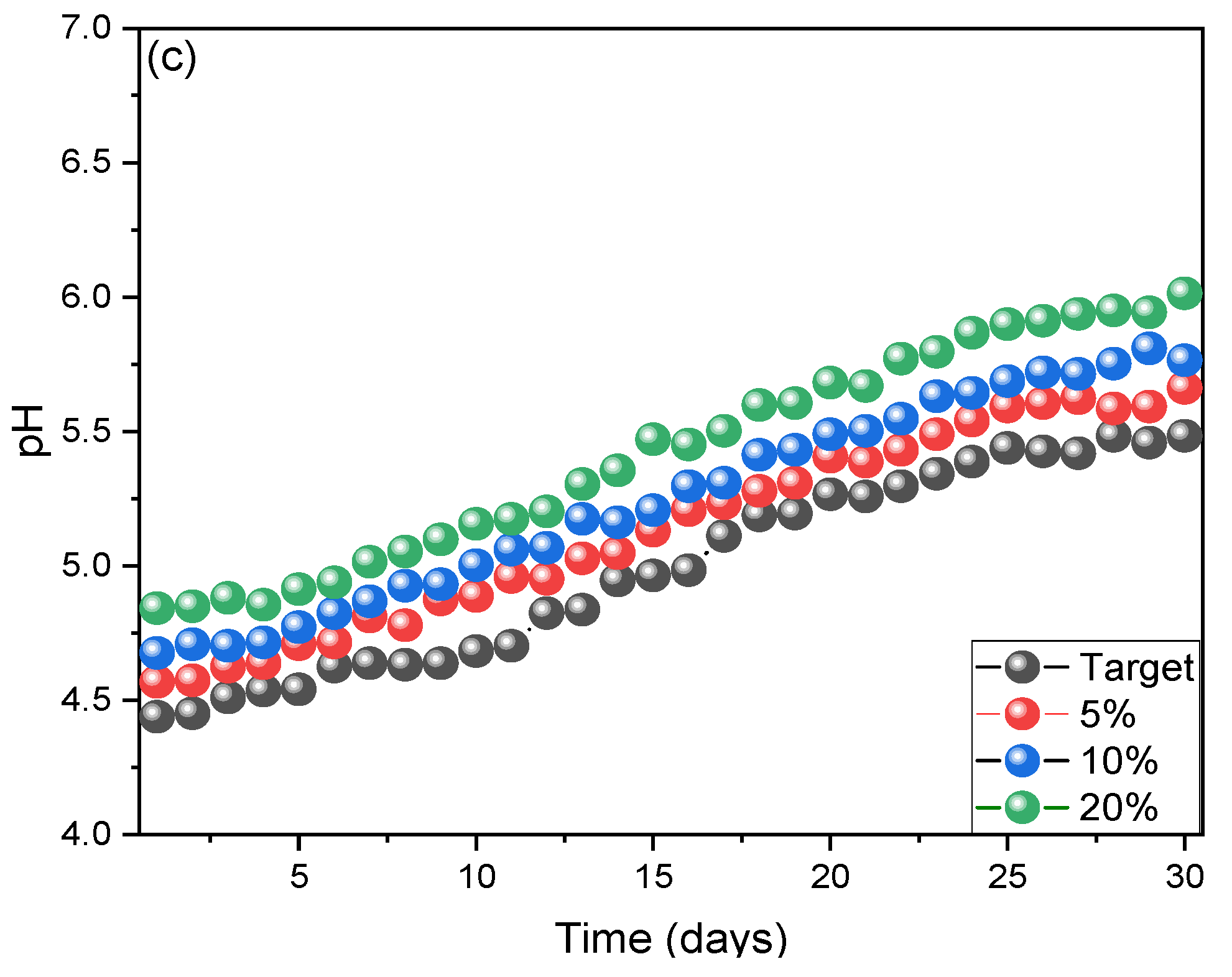
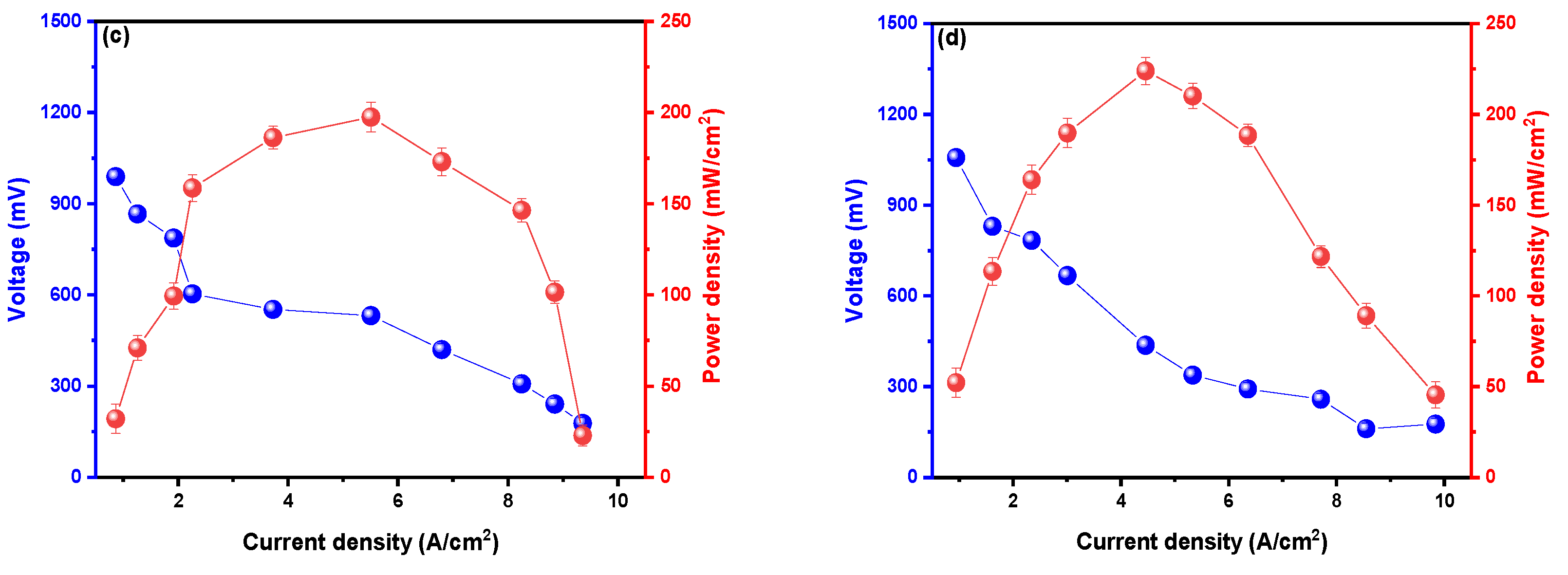
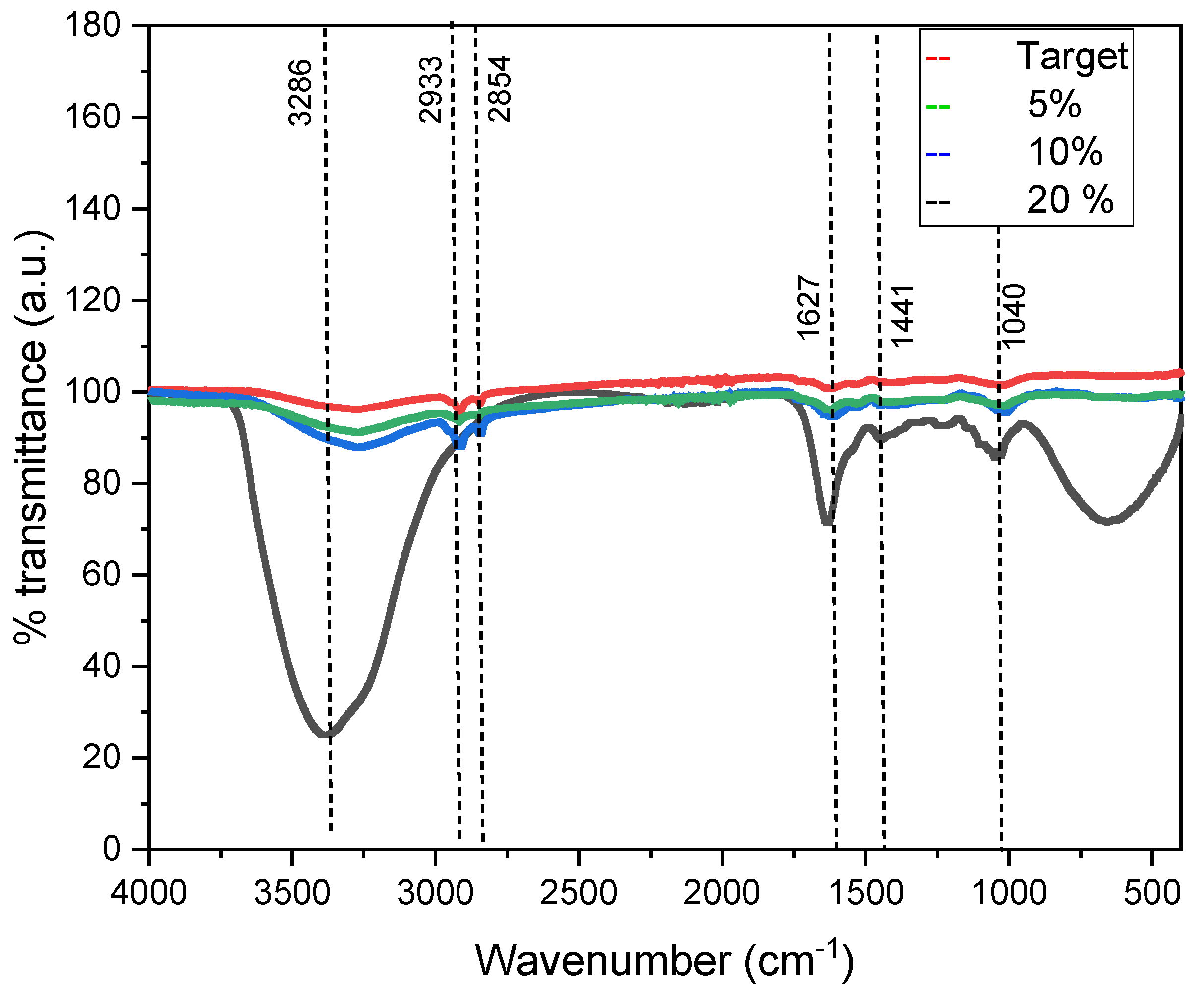
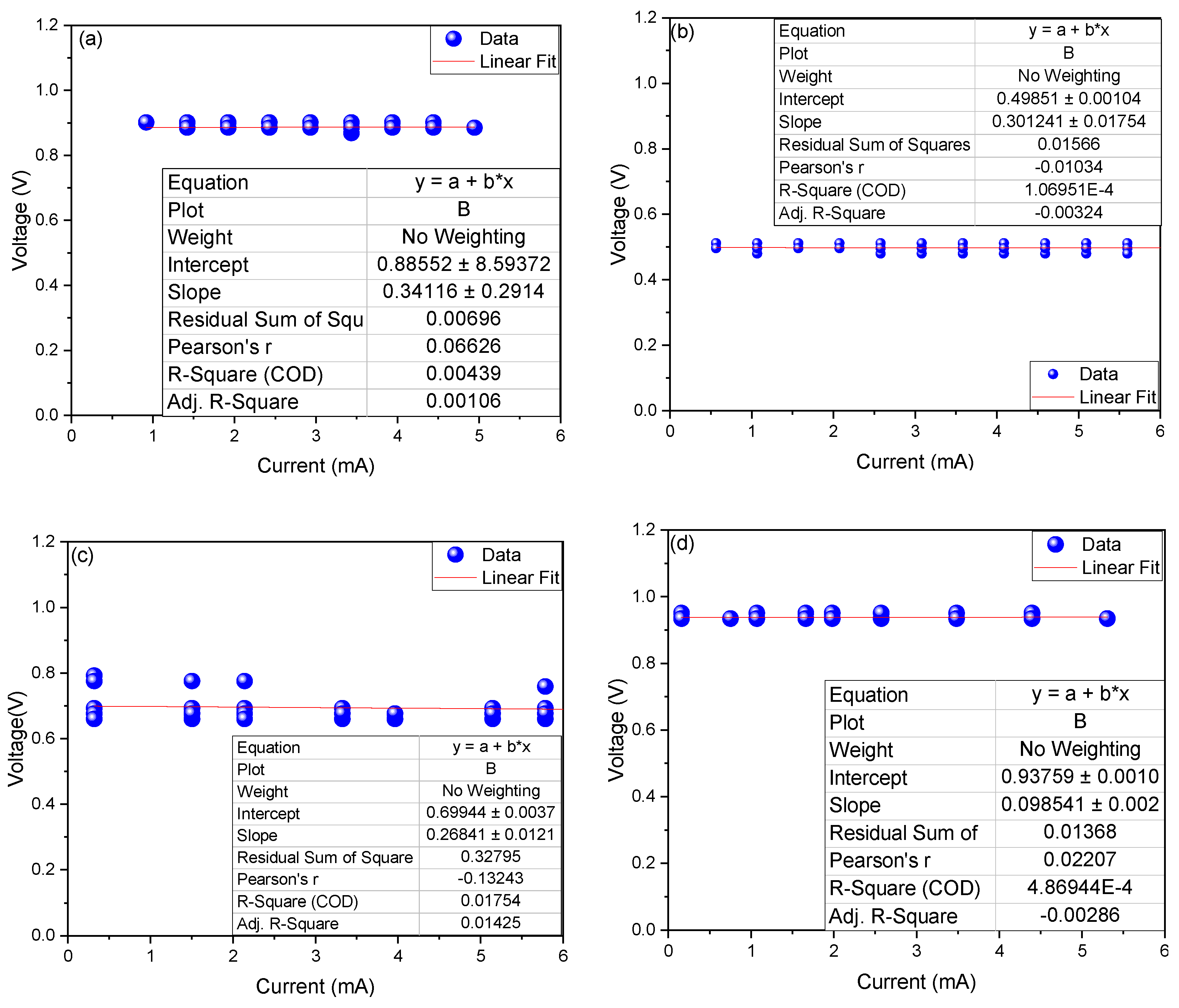
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Bae, J. Urbanization and industrialization impact of CO2 emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.; Carriveau, R. Energy demand curve variables—An overview of individual and systemic effects. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 35, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoro, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. CO2 emission sources, greenhouse gases, and the global warming effect. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Park, Y.K.; Nadda, A.K.; Banerjee, P.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P.; Banat, F.; Bharath, G.; Jeong, S.M.; Lam, S.S. Emerging chemo-biocatalytic routes for val-orization of major greenhouse gases (GHG) into industrial products: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeder, D.J. Fossil Fuels and Climate Change. In Fracking and the Environment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 155–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Qi, J.; Schandl, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Scarcity-weighted fossil fuel footprint of China at the provincial level. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Sharma, S.; Yahia, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible Utilization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Rodríguez-Couto, S. Development and modification of materials to build cost-effective anodes for microbial fuel cells (MFCs): An overview. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 164, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.H.; Kim, E.; Jung, S.P. Anode biofilm maturation time, stable cell performance time, and time-course electrochemistry in a single-chamber microbial fuel cell with a brush-anode. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 106, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Kundu, P.P. Introduction to Microbial Fuel Cells. In Progress and Recent Trends in Microbial Fuel Cells; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, A.; Kundu, P.P. Configurations of Microbial Fuel Cells. In Progress and Recent Trends in Microbial Fuel Cells; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathiba, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Recent advancements in microbial fuel cells: A review on its electron transfer mechanisms, microbial community, types of substrates and design for bio-electrochemical treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, R.; Tamuly, A.; Kakati, B.K. Recent developments in electricity generation by Microbial Fuel Cell using different substrates. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Y.; Ibn Sina, A.A.; Khandker, S.S.; Neesa, L.; Tanvir, E.M.; Kabir, A.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds in Tomatoes and Their Impact on Human Health and Disease: A Review. Foods 2020, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, T.; Yu, J.; He, H.; Shi, W.; Ma, J. Enhancement of the electro-Fenton degradation of organic contaminant by accelerat-ing Fe3+/Fe2+ cycle using hydroxylamine. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 105, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagbor, A.; Azunda, B.; Igwe, C.; Akpan, J. Electricity Generation from Waste Tomatoes, Banana, Pineapple Fruits and Peels Using Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells (SMFC). Open Access J. Waste Manag. Xenobiotics 2020, 3, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.; Naveda, R.N.; Paredes, E.A.; Orbegoso, J.A.; Céspedes, T.C.; Salvatierra, A.R.; Rodríguez, M.S. Agricultural Wastes for Electricity Generation Using Microbial Fuel Cells. Open Biotechnol. J. 2020, 14, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, J. Influence of Substrate Proximate Properties on Voltage Production in Microbial Fuel Cells. J. Sustain. Bioenergy Syst. 2020, 10, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Microbial Fuel Cell: Recent Developments in Organic Substrate Use and Bacterial Electrode Interaction. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4570388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, W.; Yusup, S.; Mohammad, S.N.A.A. Screening of fruit waste as substrate for microbial fuel cell (MFC). AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2332, 020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Jiang, Y.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Treu, L.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhang, Y. Electricity generation and microbial communities in microbial fuel cell powered by macroalgal biomass. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 123, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelekshmy, B.R.; Basheer, R.; Sivaraman, S.; Vasudevan, V.; Elias, L.; Shibli, S.M.A. Sustainable electric power generation from live anaerobic digestion of sugar industry effluents using microbial fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 6041–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Sweet Drinks as Fuels for an Alkaline Fuel Cell with Nonprecious Catalysts. Energies 2021, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andayani, D.G.S.; Andini, D.G.T. Utilization of tofu wastewater and sugar industry by-products as a medium for the production of antifungal metabolites by Paecylomyces Marquand StrainTP4. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 623, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segundo, R.-F.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Nazario-Naveda, R.; Benites, S.M.; Delfín-Narciso, D.; Angelats-Silva, L.; Díaz, F. Golden Berry Waste for Electricity Generation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, O.; Granot, D. An Overview of Sucrose Synthases in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Lu, J. Investigation and evaluation of membrane fouling in a microbial fuel cell-membrane bioreactor systems (MFC-MBR). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Flores, S.; Benites, S.M.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Cabanillas-Chirinos, L.; Valdiviezo-Dominguez, F.; Quezada Álvarez, M.A.; Vega-Ybañez, V.; Angelats-Silva, L. Bioelectricity production from blueberry waste. Processes 2021, 9, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveenkumar, M.; Senthilkumar, K. Microbial fuel cell for harvesting bio-energy from tannery effluent using metal mixed biochar electrodes. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 149, 106082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, G.; Chen, J.; Bi, L.; Dai, L.; Wen, Z. N-doped porous carbon nanosheets as pH-universal ORR electrocatalyst in vari-ous fuel cell devices. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, D.A.; Carmona-Martínez, A.A.; Chendake, A.D.; Pandit, S.; Pant, D. Modeling and optimization strategies towards per-formance enhancement of microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Flores, S.; De La Cruz-Noriega, M.; Nazario-Naveda, R.; Benites, S.M.; Delfín-Narciso, D.; Angelats-Silva, L.; Murga-Torres, E. Use of Banana Waste as a Source for Bioelectricity Generation. Processes 2022, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, A.; Colombo, A.; Cossettini, A.; Goglio, A.; D’Ardes, V.; Trasatti, S.; Cristiani, P. Single-chamber microbial fuel cells as on-line shock-sensors for volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digesters. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Electric energy production from food waste: Microbial fuel cells versus anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, P.; Ray, R.N.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Basak, B.; Muthuraj, M.; Bhunia, B. Process engineering for stable power recovery from dairy wastewater using microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 46, 3171–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Duan, C.; Duan, W.; Sun, F.; Cui, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Role of electrode materials on performance and microbial characteristics in the constructed wetland coupled microbial fuel cell (CW-MFC): A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 301, 126951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Bautista, Y.; Ramírez-Morales, E.; Pérez-Hernández, B.; Ojeda-Morales, M.E.; López-Lázaro, J.S.; Martínez-Pereyra, G. Electricity Production and Bioremediation from Synthetic Sugar Industry Wastewater by Using Microbial Isolate in Microbial Fuel Cell. Sugar Tech 2020, 22, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Khajuria, Y.; Singh, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Lee, Y.; Rai, P.K.; Singh, V.K. Study of molecular and elemental changes in nem-atode-infested roots in papaya plant using FTIR, LIBS and WDXRF spectroscopy. At. Spectrosc. 2020, 41, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, J.; Kumar, V.; Gopinath, P. Carica papaya loaded poly (vinyl alcohol)-gelatin nanofibrous scaffold for potential applica-tion in wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.; Barwar, S.; Kane, P.; More, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using papaya seed and its characterization. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedbavna, P.; Rolfe, S.A.; Huang, W.E.; Thornton, S.F. Biodegradation of phenolic compounds and their metabolites in contami-nated groundwater using microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Du, Z.; Li, J.; Cheng, F. Co-metabolism for enhanced phenol degradation and bioelectricity generation in microbial fuel cell. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 134, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Santos, P.; Zanuso, E.; Genisheva, Z.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Teixeira, J.A. Green and Sustainable Valorization of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Pinus By-Products. Molecules 2020, 25, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrykus, S.; León-Fernández, L.F.; Nieznański, J.; Karkosiński, D.; Fernandez-Morales, F.J. The influence of external load on the performance of microbial fuel cells. Energies 2021, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Yong, Y.C.; Chang, F.X. Anode materials for soil microbial fuel cells: Recent advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segundo, R.-F.; Magaly, D.L.C.-N.; Benites, S.M.; Daniel, D.-N.; Angelats-Silva, L.; Díaz, F.; Luis, C.-C.; Fernanda, S.-P. Increase in Electrical Parameters Using Sucrose in Tomato Waste. Fermentation 2022, 8, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8070335
Segundo R-F, Magaly DLC-N, Benites SM, Daniel D-N, Angelats-Silva L, Díaz F, Luis C-C, Fernanda S-P. Increase in Electrical Parameters Using Sucrose in Tomato Waste. Fermentation. 2022; 8(7):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8070335
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegundo, Rojas-Flores, De La Cruz-Noriega Magaly, Santiago M. Benites, Delfín-Narciso Daniel, Luis Angelats-Silva, Felix Díaz, Cabanillas-Chirinos Luis, and Silva-Palacios Fernanda. 2022. "Increase in Electrical Parameters Using Sucrose in Tomato Waste" Fermentation 8, no. 7: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8070335
APA StyleSegundo, R.-F., Magaly, D. L. C.-N., Benites, S. M., Daniel, D.-N., Angelats-Silva, L., Díaz, F., Luis, C.-C., & Fernanda, S.-P. (2022). Increase in Electrical Parameters Using Sucrose in Tomato Waste. Fermentation, 8(7), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8070335






