Journal Description
Dermatopathology
Dermatopathology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on dermatopathology, published quarterly online. It is the official journal of the European Society of Dermatopathology (ESDP).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 32.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Unusual Invader in a Patient with Long-Standing Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case of Leishmania major Colonization of Rheumatoid Nodules
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010008 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Rheumatoid nodules are the most common extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Long-term immunomodulatory therapies, including corticosteroids, used in the management of rheumatoid arthritis are associated with a higher risk of infections. Leishmaniasis is a neglected protozoal infection that may arise in these patients.
[...] Read more.
Rheumatoid nodules are the most common extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Long-term immunomodulatory therapies, including corticosteroids, used in the management of rheumatoid arthritis are associated with a higher risk of infections. Leishmaniasis is a neglected protozoal infection that may arise in these patients. Cutaneous presentation is the most common and is characterized by a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations and courses, depending on the interplay between species involved and the host’s immune response. Here, we report the rare and intriguing case of a patient with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis, chronically treated with systemic prednisone, whose rheumatoid nodules were colonized by Leishmania major. In this context, therapeutic strategies must be tailored to species and patient factors. This report expands the differential diagnosis of rheumatoid nodule, highlighting the importance of considering opportunistic infections in exuberant presentations, particularly in immunosuppressed patients coming from or travelling in endemic regions. Intracellular pathogens may exploit the localized immunological niche represented by the rheumatoid nodule of an immunocompromised host to survive and replicate undisturbed. It also underscores the value of the clinico-pathological correlation and the importance of integrating molecular analyses to identify unexpected microorganisms that can be hidden by concomitant disease, avoiding misdiagnosis, ensuring timely treatment, and improving patients outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinico-Pathological Correlation in Dermatopathology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Behçet-like Syndromes: A Comprehensive Review
by
Gaia Mancuso, Igor Salvadè, Adam Ogna, Brenno Balestra and Helmut Beltraminelli
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010007 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Behçet-like syndrome (BLS) refers to the presence of Behçet’s disease (BD) features occurring in association with distinct clinical–pathological conditions such as inborn errors of immunity, myeloproliferative disorders, infections, or drug exposure. BLS may differ clinically from BD and is increasingly recognized as
[...] Read more.
Background: Behçet-like syndrome (BLS) refers to the presence of Behçet’s disease (BD) features occurring in association with distinct clinical–pathological conditions such as inborn errors of immunity, myeloproliferative disorders, infections, or drug exposure. BLS may differ clinically from BD and is increasingly recognized as a separate entity. Distinguishing BLS from primary BD is essential for appropriate management, and studying BLS may provide insights into BD pathogenesis. Objectives: To summarize clinical features, treatments, and genetic abnormalities reported in BLS, we reviewed all published cases up to January 2024. Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Scopus, and Embase was performed using the terms “Behçet-like syndrome”, “Behçet-like disease”, and “Pseudo-Behçet disease”. We included English-language reports of patients > 12 years old with a defined underlying etiology and Behçet-like manifestations, defined by ≥2 ICBD criteria and/or gastrointestinal involvement, mucosal ulcers, thrombosis, or non-recurrent disease. Epidemiological, clinical, laboratory, histological, and treatment data were extracted and analyzed descriptively. Results: Of 679 publications, 53 met inclusion criteria, comprising 100 patients with BLS. The median age was 44 years (IQR 22–52), with a female predominance (1:2). Fifty-three percent were from non-European countries. A genetic disorder was identified in 70% of cases, while HLA-B51 was present in 10%. Frequent manifestations included skin lesions (68%), fever (56%), intestinal involvement (43%), and joint symptoms (43%). Treatments included glucocorticoids (65%), conventional DMARDs (32%), and biologics (22%), mainly anti-TNF agents. Antiviral/antibiotic therapy was used in 9% and chemotherapy in 15%. Two patients with trisomy-8 MDS underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Conclusions: Diverse conditions—including monogenic diseases, immune defects, myeloproliferative disorders, infections, and drug-related reactions—can produce Behçet-like features. Our findings highlight differences in clinical expression and treatment response across BLS etiologies. Recognizing BLS is essential for appropriate management and may contribute to a deeper understanding of BD pathogenesis and future targeted therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinico-Pathological Correlation in Dermatopathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma—A Systematic Review
by
Li Yang Loo, Shi Huan Tay and Choon Chiat Oh
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010006 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is an immunogenic malignancy with variable immune infiltration and inconsistent responses to checkpoint blockade. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) influence tumor progression and therapeutic outcome, yet their phenotypic and functional diversity across disease contexts remains incompletely understood. This review systematically
[...] Read more.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is an immunogenic malignancy with variable immune infiltration and inconsistent responses to checkpoint blockade. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) influence tumor progression and therapeutic outcome, yet their phenotypic and functional diversity across disease contexts remains incompletely understood. This review systematically characterizes the TIL landscape in human cSCC. Following PRISMA 2020 guidelines, PubMed and Embase were searched up to May 2025 and restricted to studies evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in human cSCC, using the modified Newcatle–Ottawa score to assess risk of bias. Data were synthesized qualitatively given methodological heterogeneity. 48 studies met inclusion criteria. cSCCs exhibited dense CD3+ infiltrates composed of cytotoxic (CD8+GzmB+, Ki-67+, CD69+) and regulatory (FOXP3+, CCR4+) subsets. Higher CD8+ activity correlated with smaller tumors and longer disease-free survival, whereas FOXP3+ enrichment and TGF-β2 signaling promoted immune evasion. Immunosuppressed patients demonstrated diminished CD8+ density and clonality. Immune modulation with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, imiquimod, HPV vaccination, or OX40 stimulation enhanced effector function. The cSCC immune microenvironment reflects a balance between cytotoxic and suppressive factors. Harmonizing multimodal immune profiling and integrating spatial context with systemic immune status may advance both prognostic stratification and therapeutic design.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Need for Standardization of PRAME Immunohistochemistry in Melanocytic Neoplasms
by
Calla M. Sullivan, Dominick DiMaio, Scott Lauer, Dinesh Pradhan, Julie Youngs, Kaeli Samson and Corey J. Georgesen
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010005 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Accurate diagnosis of melanomas is crucial for proper evaluation and treatment. One immunohistochemical stain frequently utilized is PRAME (PReferentially expressed Antigen in MElanoma), a tumor-associated antigen expressed in most melanomas. This study aims to evaluate the reproducibility of PRAME scoring performed by dermatopathologists
[...] Read more.
Accurate diagnosis of melanomas is crucial for proper evaluation and treatment. One immunohistochemical stain frequently utilized is PRAME (PReferentially expressed Antigen in MElanoma), a tumor-associated antigen expressed in most melanomas. This study aims to evaluate the reproducibility of PRAME scoring performed by dermatopathologists at an academic tertiary referral medical center. A blinded survey was designed featuring 21 melanocytic neoplasms stained with PRAME and H&E. For each case, five dermatopathologists provided a PRAME score from 0–4+, percent PRAME positivity, values for H-score, and a descriptive interpretation. Absolute agreement across raters was assessed using a Kappa statistic for PRAME score and intraclass correlations (ICCs) for H-score and PRAME percentage. Statistical analysis indicated poor inter-rater reliability for PRAME score (Kappa = 0.16), percent PRAME positivity (ICC = 0.31), and H-score (ICC = 0.40). Reporting language varied among pathologists. Our study demonstrated that the interpretation of PRAME immunohistochemistry lacks reproducibility, especially for challenging lesions. This suggests that a more rigorous, defined, and reproducible scoring method should be investigated for equivocal cases. Future studies may explore the utility of artificial intelligence software in the interpretation of PRAME for borderline lesions to improve reliability and standardize scoring.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Deeply Pigmented Reticulated Acanthoma with Sebaceous Differentiation Mimicking Cutaneous Malignancy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
by
Padol Chamninawakul, Xiaotian Wu and Joyce S. S. Lee
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010004 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Reticulated acanthoma with sebaceous differentiation (RASD) is a rare, benign cutaneous neoplasm. Its variable clinical presentation frequently mimics both benign and malignant entities, posing a significant diagnostic challenge. We report a case of pigmented RASD in a 78-year-old Malay male of Fitzpatrick skin
[...] Read more.
Reticulated acanthoma with sebaceous differentiation (RASD) is a rare, benign cutaneous neoplasm. Its variable clinical presentation frequently mimics both benign and malignant entities, posing a significant diagnostic challenge. We report a case of pigmented RASD in a 78-year-old Malay male of Fitzpatrick skin type IV who presented with a 5-year history of an 8 × 5 mm deeply pigmented, asymmetrical nodule on the left upper back, with a 2 mm central raised area showing less pigmentation. The lesion was clinically suspicious for malignant melanoma. Histopathological examination revealed characteristic features of RASD: a broad, plate-like, reticulated and pigmented epidermal proliferation with clusters of mature sebocytes at the bases of anastomosing rete ridges. Following biopsy confirmation, the residual lesion is being managed conservatively with observation. This case demonstrates an unusual heavily pigmented clinical presentation that completely obscured the typical yellowish hue associated with sebaceous differentiation, highlighting pigmented RASD as an important diagnostic pitfall in patients with skin of color. In conclusion, RASD should be included in the differential diagnosis of pigmented cutaneous lesions, especially in patients with skin of color. Recognition of this benign entity can prevent unnecessary aggressive surgical intervention.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hypothetical Abductive Reasoning in Dermatology and Dermatopathology
by
Carlo Francesco Tomasini and Lorenzo Magnani
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010003 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Abductive reasoning, or abduction, is a key process in scientific discovery and medical diagnosis. In everyday dermatology and dermatopathology, however, it functions as the practical engine behind differential diagnosis, clinicopathologic correlation, and disciplined pattern recognition. In this paper, we retain the epistemological
[...] Read more.
Abductive reasoning, or abduction, is a key process in scientific discovery and medical diagnosis. In everyday dermatology and dermatopathology, however, it functions as the practical engine behind differential diagnosis, clinicopathologic correlation, and disciplined pattern recognition. In this paper, we retain the epistemological foundation of abduction but translate it into usable steps for clinicians and dermatopathologists. We distinguish abduction from deduction and induction; separate creative abduction (which generates new concepts) from selective abduction (daily diagnostic choice); and show how both operate within a simple Select-and-Test (ST) Model: select a hypothesis, deduce what else should be true, test against data, and then update. We then reinterpret Ackerman’s algorithmic method of pattern analysis as an operationalization of the ST-Model. Through a couple of concise case vignettes, we illustrate visual and manipulative abduction, nonmonotonic updates, and the role of artifacts (dermoscopy, DIF, stains) as so-called epistemic mediators. Finally, we map contemporary AI tools to selective abduction and propose practical guardrails for fairness, transparency, and accountability. The result is a pragmatic framework that preserves philosophical depth while addressing the daily needs of dermatologists and dermatopathologists in the clinic and at the microscope.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Increased Expression of Angiopoietin 2 and Tie2 in Rosacea
by
Aysin Kaya, Jean-Hilaire Saurat, Nathalie Satta and Gürkan Kaya
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010002 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study we evaluated the expression of Angiopoietin 1, Angiopoietin 2, and Tie2 by immunohistochemistry in the skin of 10 patients with erythemato telangiectatic and papulopustular rosacea. Significantly increased expression of Tie2 and Angiopoietin 2 in the endothelial cells of the dermal
[...] Read more.
In this study we evaluated the expression of Angiopoietin 1, Angiopoietin 2, and Tie2 by immunohistochemistry in the skin of 10 patients with erythemato telangiectatic and papulopustular rosacea. Significantly increased expression of Tie2 and Angiopoietin 2 in the endothelial cells of the dermal vessels in rosacea skin vs. non-lesional skin (100% and 33.3% for Tie2, and 100% and 50% for Angiopoietin 2) was observed. There was no difference in the expression of Angiopoietin 1 and phosphorylated Tie2 (pTie2) between the lesional skin of rosacea and non-lesional skin.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Intelligence for Lentigo Maligna: Automated Margin Assessment via Sox-10-Based Melanocyte Density Mapping
by
Rieke Löper, Lennart Abels, Daniel Otero Baguer, Felix Bremmer, Michael P. Schön and Christina Mitteldorf
Dermatopathology 2026, 13(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology13010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Lentigo maligna (LM) is a melanoma in situ with high cumulative sun damage. Histological evaluation of resection margins is difficult and time-consuming. Melanocyte density (MD) is a suitable, quantifiable, and reproducible diagnostic criterion. In this retrospective single-centre study, we investigated whether an artificial
[...] Read more.
Lentigo maligna (LM) is a melanoma in situ with high cumulative sun damage. Histological evaluation of resection margins is difficult and time-consuming. Melanocyte density (MD) is a suitable, quantifiable, and reproducible diagnostic criterion. In this retrospective single-centre study, we investigated whether an artificial intelligence (AI) tool can support the assessment of LM. Training and evaluation were based on MD in Sox-10-stained digitalised slides. In total, 86 whole slide images (WSIs) from LM patients were annotated and used as a training set. The test set consisted of 177 slides. The tool was trained to detect the epidermis, measure its length, and determine the MD. A cut-off of ≥30 melanocytes per 0.5 mm of epidermis length was defined as positive. Our AI model automatically recognises the epidermis and measures the MD. The model was trained on nuclear immunohistochemical signals and can also be applied to other nuclear stains, such as PRAME or MITF. The WSI is automatically visualised by a three-colour heat map with a subdivision into low, borderline, and high melanocyte density. The cut-offs can be adjusted individually. Compared to manually counted ground truth MD, the AI model achieved high sensitivity (87.84%), specificity (72.82%), and accuracy (79.10%), and an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.818 in the test set. This automated tool can assist (dermato) pathologists by providing a quick overview of the WSI at first glance and making the time-consuming assessment of resection margins more efficient and more reproducible. The AI model can provide significant benefits in the daily routine workflow.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence in Dermatopathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Is Radiotherapy a Risk Factor for Melanoma?
by
Sumeyye Ozer, Priya Agarwal, Noah Musolff, Brendan Plann-Curley, Gizem Cosgun, Helen Yanyu Sun and Babar Rao
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040043 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
Melanoma is a highly aggressive skin cancer primarily linked to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, the potential role of ionizing radiation from radiotherapy in melanoma development remains unclear. This review synthesizes data from epidemiologic studies and case reports on melanoma after radiation exposure. Evidence
[...] Read more.
Melanoma is a highly aggressive skin cancer primarily linked to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, the potential role of ionizing radiation from radiotherapy in melanoma development remains unclear. This review synthesizes data from epidemiologic studies and case reports on melanoma after radiation exposure. Evidence indicates that childhood radiotherapy, even at low doses, is associated with an increased melanoma risk, plausibly reflecting the heightened radiosensitivity of developing melanocytes. Occupational radiation exposure, particularly in earlier eras with insufficient shielding, also appears to elevate risk. In patients exposed to radiation in adulthood, findings are mixed: large population datasets suggest a modest increase in melanoma following therapeutic radiation, whereas some case–control analyses do not demonstrate a clear dose–response relationship. UV radiation promotes melanomagenesis through direct DNA photoproducts driving characteristic C>T transitions at dipyrimidine sites, alongside oxidative stress and local immune modulation that facilitate malignant transformation. Collectively, individuals with prior radiotherapy, especially those irradiated in childhood, should be considered at increased melanoma risk and may benefit from long-term, targeted surveillance of irradiated fields. Awareness of this association between radiation exposure and melanoma may also support clinicopathologic correlation during the diagnostic evaluation of melanocytic lesions. Future work should define dose–response relationships in contemporary radiotherapy methods, characterize molecular signatures of ionizing radiation-associated melanomas, and establish evidence-based surveillance strategies for high-risk cohorts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Experimental Dermatopathology)
Open AccessReview
Translating Features to Findings: Deep Learning for Melanoma Subtype Prediction
by
Dorra Guermazi, Sarina Khemchandani, Samer Wahood, Cuong Nguyen and Elie Saliba
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040042 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Melanoma subtyping plays a vital role in histopathological diagnosis, informing prognosis and, in some cases, guiding targeted therapy. However, conventional histologic classification is constrained by inter-rater reliability, morphologic overlap, and the underrepresentation of rare subtypes. Deep learning (DL)—particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs)—presents a
[...] Read more.
Melanoma subtyping plays a vital role in histopathological diagnosis, informing prognosis and, in some cases, guiding targeted therapy. However, conventional histologic classification is constrained by inter-rater reliability, morphologic overlap, and the underrepresentation of rare subtypes. Deep learning (DL)—particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs)—presents a compelling opportunity to enhance diagnostic precision and reproducibility through automated analysis of histopathologic slides. This review examines the clinical importance and diagnostic challenges of melanoma subtyping, outlines core DL methodologies in dermatopathology, and synthesizes current advances in applying DL to subtype classification. Pertinent limitations including dataset imbalance, a lack of interpretability, and domain generalizability are discussed. Additionally, emerging directions such as multimodal integration, synthetic data generation, federated learning, and explainable AI are highlighted as potential solutions. As these technologies mature, DL holds considerable promise in advancing melanoma diagnostics and supporting more personalized, accurate, and equitable patient care.
Full article
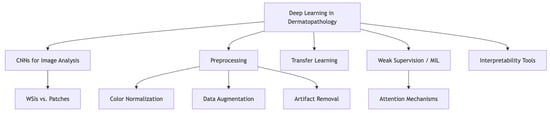
Figure 1
Open AccessClinicopathological Challenge
Asymmetric Lip Hyperpigmentation in a Transplant Patient
by
Vincent Kimpe, David Alvarez Martinez, Sébastien Menzinger and Gürkan Kaya
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040041 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A 56-year-old patient presented to our dermatology clinic with asymmetric hyperpigmentation on her lower lip, which had developed over the previous six to twelve months. Her medical history included kidney and pancreas transplants, requiring chronic immunosuppression, and two lip filler injections with hyaluronic
[...] Read more.
A 56-year-old patient presented to our dermatology clinic with asymmetric hyperpigmentation on her lower lip, which had developed over the previous six to twelve months. Her medical history included kidney and pancreas transplants, requiring chronic immunosuppression, and two lip filler injections with hyaluronic acid (HA). Clinical examination revealed irregular pigmented macules limited strictly to the lower lip. Histological analysis showed epidermal melanosis, pigmentary incontinence, solar elastosis, and amorphous dermal HA deposits, without evidence of melanocytic hyperplasia or granulomatous inflammation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Indeterminate Subcutaneous Lesion of the Nasal Dorsum in an Adolescent: A Multidisciplinary Approach to a Rare Case of Spindle Cell Lipoma
by
Alessandro Serrone, Chiara Rustichelli, Gian Luca Fadda, Giuseppe Riva, Massimo Rizzo and Giovanni Cavallo
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040040 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We report the case of a 16-year-old girl presenting with a painless, clinically stable subcutaneous swelling of the nasal dorsum with a three-year history. Despite an extensive multidisciplinary diagnostic work-up—including dermatological, otorhinolaryngological, and radiological evaluations (ultrasound, CT, and MRI)—the nature of the lesion
[...] Read more.
We report the case of a 16-year-old girl presenting with a painless, clinically stable subcutaneous swelling of the nasal dorsum with a three-year history. Despite an extensive multidisciplinary diagnostic work-up—including dermatological, otorhinolaryngological, and radiological evaluations (ultrasound, CT, and MRI)—the nature of the lesion remained indeterminate. In order to achieve a definitive diagnosis while preserving the nasal profile aesthetics, the mass was entirely excised via an endoscope-assisted closed rhinoseptoplasty approach. Histopathological analysis revealed a spindle cell lipoma characterized by CD34 positivity and a Ki-67 proliferation index of less than 1%. This finding is extremely rare in terms of both anatomical location and patient age. The present case highlights the crucial role of histopathological examination in establishing the correct diagnosis, supported by a multidisciplinary assessment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Histopathologic Features and Molecular Markers of Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis (ECCL)
by
Siddharth Venigalla, Tanvir K. Dhaliwal, Anvita Anumolu, Lena Rafey, Arturo P. Saavedra and David D. Limbrick
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040039 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (ECCL) is a rare congenital neurocutaneous disorder characterized by ocular, skin, and central nervous system manifestations. Despite its recognizable clinical features, such as nevus psiloliparus, histopathologic characterization of ECCL remains limited in the dermatopathology literature, and diagnosis is often clinical. This
[...] Read more.
Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (ECCL) is a rare congenital neurocutaneous disorder characterized by ocular, skin, and central nervous system manifestations. Despite its recognizable clinical features, such as nevus psiloliparus, histopathologic characterization of ECCL remains limited in the dermatopathology literature, and diagnosis is often clinical. This scarcity of published histopathological descriptions makes diagnostic confirmation challenging and underscores the value of synthesizing the available evidence. This comprehensive review synthesizes reported histopathological findings across cutaneous manifestations highlighting key tissue-level features that may aid diagnostic confirmation. Additionally, we review the emerging role of molecular diagnostics, particularly the identification of mosaic activating mutations in FGFR-1 and KRAS, which have been implicated in ECCL pathogenesis. By integrating clinicopathologic correlations with molecular insights, this review aims to enhance our dermatopathological understanding of ECCL, bolstering diagnostic reasoning and clinical decision making for this rare neurocutaneous condition.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Clinicopathological Analysis of Oral Focal Mucinosis and Solitary Cutaneous Focal Mucinosis: A Case Series and Literature-Based Analysis
by
Wickramasinghe Mudiyanselage Sithma Nilochana Wickramasinghe, Primali Rukmal Jayasooriya, Balapuwaduge Ranjit Rigobert Nihal Mendis and Tommaso Lombardi
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040038 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Oral focal mucinosis (OFM) and solitary cutaneous focal mucinosis (SCFM) are rare, benign lesions characterized by localized mucin deposition in the stromal connective tissue. While both share similar histological features, they occur in distinct anatomical sites and clinical contexts and have not
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Oral focal mucinosis (OFM) and solitary cutaneous focal mucinosis (SCFM) are rare, benign lesions characterized by localized mucin deposition in the stromal connective tissue. While both share similar histological features, they occur in distinct anatomical sites and clinical contexts and have not been directly compared in the literature. Method: This study presents a case series of 39 OFM cases diagnosed over 25 years, supplemented by a literature review of previously reported OFM cases, and compares the combined data with published cases of SCFM. The literature-based analysis included 116 OFM cases published in four articles and 138 cases of SCFM published in five articles. Demographic and clinical data were extracted and analyzed, including age, sex, lesion location, size, duration, symptoms, clinical impression, treatment, and recurrence. Results: The mean age of OFM patients was 41 years, with a slight female predominance, most commonly affecting the gingiva. SCFM cases were more common in males, with a higher mean age of 52 years and frequent occurrence on the extremities and trunk. Both lesions were predominantly asymptomatic and managed by conservative excision. Due to its rare occurrence and nonspecific clinical presentation, both entities were frequently clinically misdiagnosed. Conclusions: In conclusion, this is the first study to directly compare OFM with SCFM and represents the largest series of OFM reported to date. The study provides new comparative insights into SCFM and OFM, highlighting differences in age, gender, lesion site, size, and symptomatology. SCFM predominantly affects older males on the extremities, whereas OFM occurs in younger females, mainly in the gingiva, with larger, sometimes symptomatic lesions, and with a very low recurrence rate.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Cutaneous Neufibroma in the Absence of Classical NF1 Features: A Case Report and Literature Review
by
Christine Suryani Novelita Sutrisno, Desy Hinda Pramita and Ita Puspita Dewi
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040037 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a prevalent neurocutaneous illness resulting from mutations in the NF1 gene, usually diagnosed according to clinical criteria set by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). These encompass café-au-lait macules, axillary freckling, Lisch nodules, ocular gliomas, osseous lesions, neurofibromas,
[...] Read more.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a prevalent neurocutaneous illness resulting from mutations in the NF1 gene, usually diagnosed according to clinical criteria set by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). These encompass café-au-lait macules, axillary freckling, Lisch nodules, ocular gliomas, osseous lesions, neurofibromas, and familial history. Atypical instances exhibiting partial or isolated characteristics, such as numerous cutaneous neurofibromas (cNFs) absent other classical manifestations, provide a diagnostic difficulty and may be little acknowledged in clinical environments. We describe a 47-year-old male with several soft, non-tender, pinkish-red papules and nodules dispersed throughout the face, torso, limbs, and back. A solitary café-au-lait macule measuring 3 x 2 cm was seen below the right breast, no axillary or inguinal freckling was observed, Lisch nodules were absent during ophthalmologic examination, and there was no pertinent family history. The histopathological examination of a skin lesion verified the diagnosis of cutaneous neurofibroma. According to the NIH guidelines, the patient did not satisfy the requirements for a conclusive diagnosis of NF1. This instance underscores the clinical intricacy of NF1 spectrum diseases and suggests the potential for mosaic NF1 or a minor phenotypic variation. The existence of several cNFs without systemic involvement undermines the adequacy of existing diagnostic paradigms, particularly in adults who exhibit no early-life signs. The psychosocial challenges linked to widespread cNF distribution highlight the necessity for a comprehensive assessment. Limitations encompass the lack of genetic testing, which would have facilitated the confirmation of the diagnosis and the assessment of probable mosaicism. Isolated cutaneous neurofibromas, devoid of other conventional NF1 characteristics, are an uncommon yet clinically pertinent manifestation. Clinicians must uphold a heightened level of suspicion for aberrant NF1 phenotypes and contemplate further examination, using molecular diagnostics where feasible. Reevaluating diagnostic criteria to include these polymorphisms is essential for prompt identification, effective care, and enhanced patient outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Basaloid Cell Hyperplasia Overlying Dermatofibroma
by
Pablo Izarra, Marwa Zohdy, Helmut Beltraminelli and Laurence Feldmeyer
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040036 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dermatofibromas (DFs) are benign neoplasms of the dermis typically found on the extremities of young adults. In approximately 3–5% of cases, basaloid cell hyperplasia (BCH) is observed overlying DFs. BCH is characterized by the proliferation of basaloid cells within the epidermis. BCH and
[...] Read more.
Dermatofibromas (DFs) are benign neoplasms of the dermis typically found on the extremities of young adults. In approximately 3–5% of cases, basaloid cell hyperplasia (BCH) is observed overlying DFs. BCH is characterized by the proliferation of basaloid cells within the epidermis. BCH and superficial basal cell carcinoma (BCC) share many histological features, making their differentiation challenging. It is therefore unclear if the proliferation of basaloid cells in DFs represents an inductive process or, conversely, a malignant transformation indicative of BCC. The primary objective of our study was to determine whether BCH can be distinguished from superficial BCC using histology and immunhistological techniques. The histological and immunohistochemical characteristics of 43 DF samples with overlying BCH revealed significant similarities in staining patterns with those of superficial BCC described in the literature. These findings point to the need for innovative methods, such as molecular techniques, to refine diagnostic accuracy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Unilateral Acroangiodermatitis: From Histopathologic Confirmation to Treatment with PDL
by
André Aparício Martins, José Carlos Cardoso and André Pinho
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040035 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Acroangiodermatitis is an uncommon angioproliferative dermatosis, related to chronic circulatory diseases, such as chronic venous insufficiency and arteriovenous malformations. We describe the case of a 32-year-old healthy male presenting with a pruritic, brownish lesion on the dorsal surface of the left foot, evolving
[...] Read more.
Acroangiodermatitis is an uncommon angioproliferative dermatosis, related to chronic circulatory diseases, such as chronic venous insufficiency and arteriovenous malformations. We describe the case of a 32-year-old healthy male presenting with a pruritic, brownish lesion on the dorsal surface of the left foot, evolving for ten years. Physical examination revealed a brown plaque, with a verrucous surface, on the distal dorsum and medial border of the left foot. Histopathology disclosed a marked neovascularization of the upper dermis, associated with erythrocyte extravasation and hemosiderin deposition. Immunochemistry for HHV-8 was negative. CT angiography revealed multiple serpiginous vessels on the dorsum of the left foot, suggestive of a venous malformation. The diagnosis of acroangiodermatitis was established and the patient started topical corticosteroids and compression stockings, without improvement. Although scarcely described in the literature, treatment with PDL was proposed given the vascular proliferation confined to the papillary dermis. After two sessions, a significant improvement was observed. This case emphasises dermatopathology as the gold standard for the differential diagnosis with Kaposi sarcoma. In addition, it highlights PDL as a promising therapeutic option, based on the superficial histopathological location.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Benign Cutaneous Neoplasms with Syndromic Associations
by
Sean Lider, Chanel Mandap and Pavandeep Gill
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040034 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There are many benign skin neoplasms encountered in dermatopathology practice that can be associated with underlying genetic disorders. Although benign themselves, these lesions can offer insight into the potential for development of internal malignancies in patients with these hereditary syndromes. An astute dermatopathologist
[...] Read more.
There are many benign skin neoplasms encountered in dermatopathology practice that can be associated with underlying genetic disorders. Although benign themselves, these lesions can offer insight into the potential for development of internal malignancies in patients with these hereditary syndromes. An astute dermatopathologist will recognize clues that suggest a syndromic association of these lesions, such as the presence of multiple lesions, distinct histologic growth patterns, and the results of ancillary immunohistochemical testing. The dermatopathologist can then guide the referring clinician to obtain additional clinical and family history and, if appropriate, pursue further screening and genetic testing. This review article will provide an overview of the clinical and histologic features associated with select common and uncommon benign skin neoplasms with syndromic associations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Diagnostic Challenges in HHV-8-Associated Multicentric Castleman Disease in a Patient with Prior Kaposi Sarcoma
by
Seraphima S. Sidhom, Luke A. Laconi, Christopher A. LaFond and Steven C. Weindorf
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(4), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12040033 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8)-associated multicentric Castleman disease (MCD) is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder with systemic and cutaneous manifestations that can be diagnostically challenging, especially in immunocompromised patients. We report the case of a 68-year-old man with HIV and biopsy-proven Kaposi sarcoma (KS), who developed
[...] Read more.
Human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8)-associated multicentric Castleman disease (MCD) is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder with systemic and cutaneous manifestations that can be diagnostically challenging, especially in immunocompromised patients. We report the case of a 68-year-old man with HIV and biopsy-proven Kaposi sarcoma (KS), who developed progressive fevers, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue, accompanied by diffuse lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and new erythematous and hyperpigmented lesions shortly after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for Guillain–Barré syndrome. A laboratory evaluation revealed that the patient had elevated total protein and polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia, without monoclonality. Imaging demonstrated widespread lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. A core lymph node biopsy showed polytypic plasmacytosis, but was non-diagnostic. Given the ongoing symptoms, an excisional biopsy was performed, revealing regressed germinal centers with increased interfollicular vascularity, mantle zone “onion skinning,” and HHV-8 LANA-1 nuclear positivity, establishing the diagnosis of HHV-8-associated MCD. Rituximab monotherapy was initiated, resulting in clinical improvement, resolution of the constitutional symptoms, and stabilization of ascites. This case highlights the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion for MCD in patients with KS who develop new systemic or cutaneous findings, the limitations of a core biopsy, and the value of a timely excisional biopsy in guiding diagnosis and treatment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessClinicopathological Challenge
Treatment Resistant Acneiform Eruption in a Young Female: A Diagnostic Pitfall
by
Ioannis-Alexios Koumprentziotis, Evdoxia Panou, Antonis Tsimpidakis, Maria Gerochristou, Theodoros Iliakis, Leonidas Marinos, Alexander Stratigos and Vasiliki Nikolaou
Dermatopathology 2025, 12(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12030032 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A 27-year-old female with no significant medical or dermatologic history presented with a persistent acneiform eruption on the face. The patient had been treated with multiple topical and systemic anti-acne treatments with no significant improvement over a period of two years. A punch
[...] Read more.
A 27-year-old female with no significant medical or dermatologic history presented with a persistent acneiform eruption on the face. The patient had been treated with multiple topical and systemic anti-acne treatments with no significant improvement over a period of two years. A punch biopsy was performed on the right cheek lesion showing dense lymphocytic infiltrates of the reticular dermis with peri- and intra-follicular distribution.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Dermatopathology
New Insights in Paediatric Dermatopathology 2025
Guest Editor: Sylvie FraitagDeadline: 31 July 2026
Special Issue in
Dermatopathology
Guidelines for Optimizing Skin Biopsies: Best Practices for Clinicians and Dermatopathologists
Guest Editors: Maria Teresa Fernández Figueras, Angel Fernandez-FloresDeadline: 31 August 2026









