Immediate 3D Skull Changes Following 3D-Guided Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE: Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
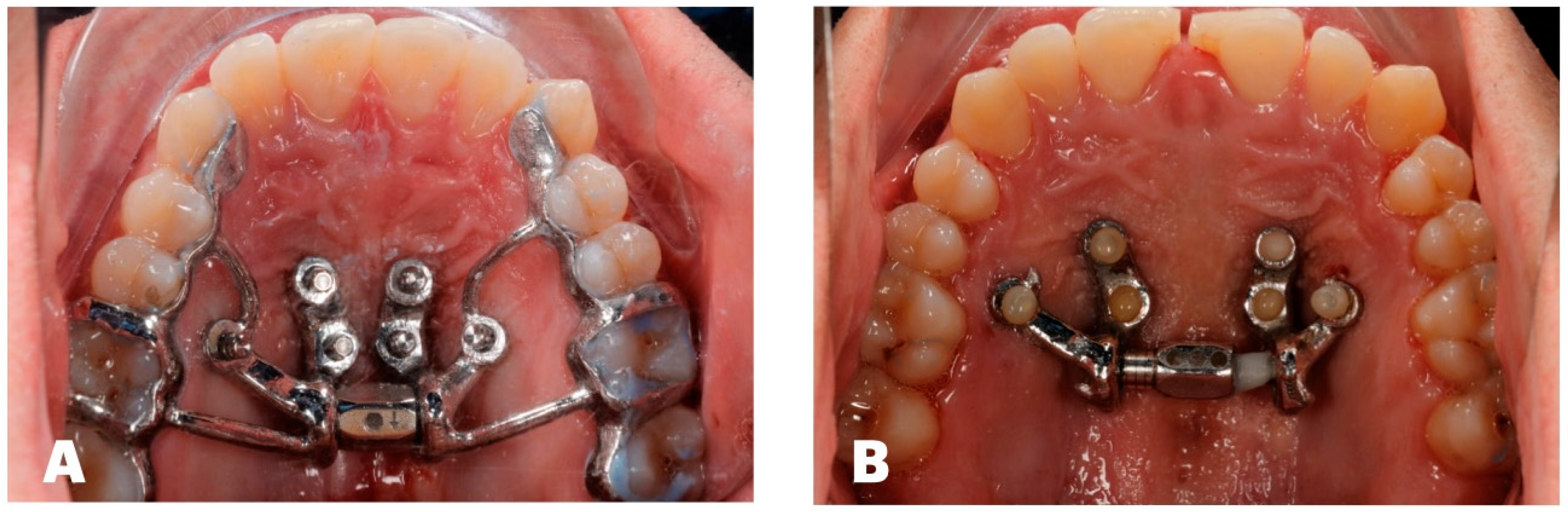
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- i.
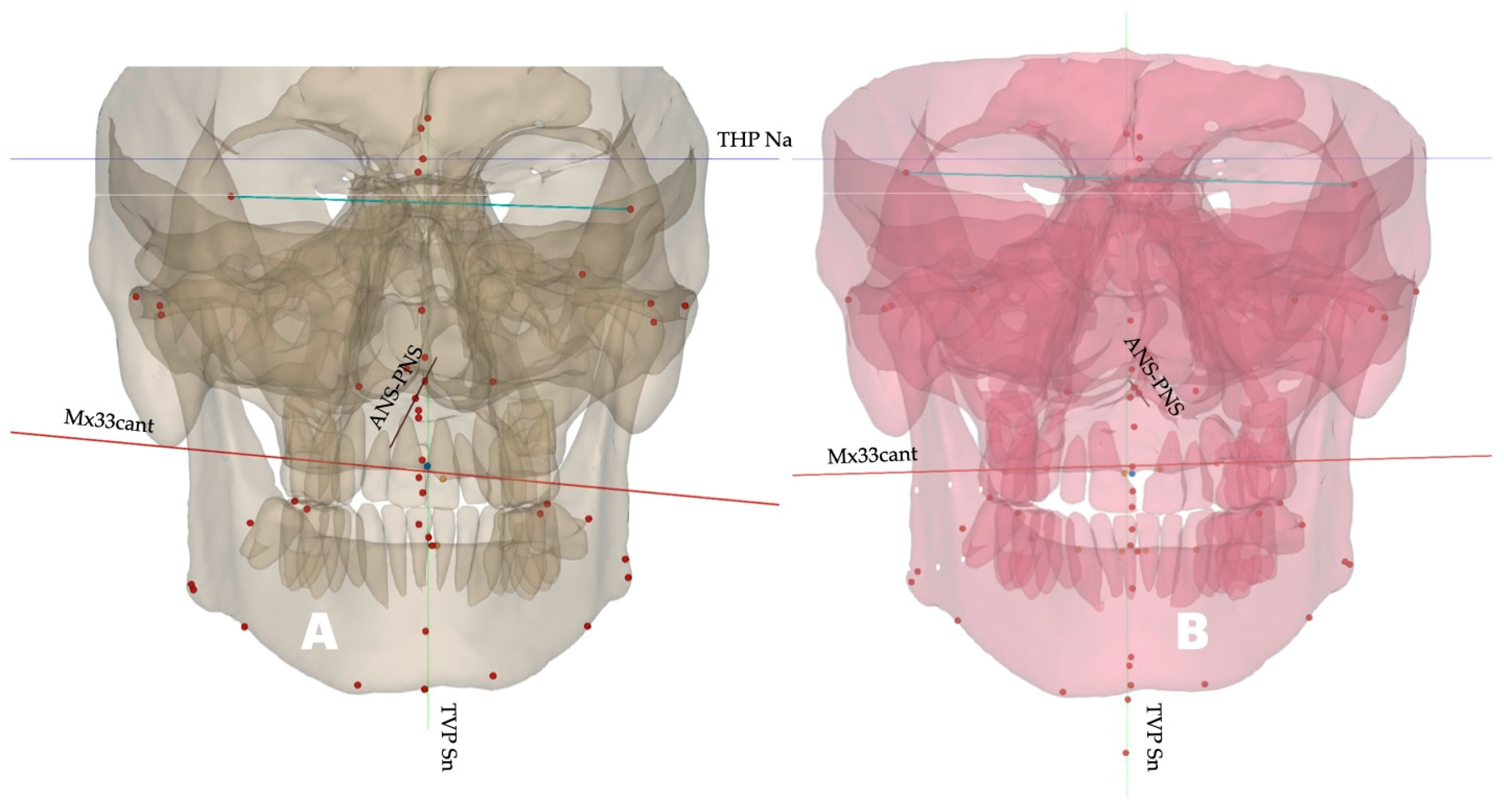
- Sagittal: ANS to TVL; Mx incisor R to TVL; Mx incisor L to TVL; upper-right canine to TVL; upper-left canine to TVL; upper-right molar to TVL; upper-left molar to TVL; pogonion to TVL; B-point to TVL; PNS to TVL (Table 1).
- ii.
- Canting: Mx33 cant.
- iii.
- Width difference: width difference, Mx molar; width difference, Zyg arch; width difference, Lat Orb rim.
- iv.
- Transverse: Mx molar R width; Mx molar L width; Zyg arch R width; Zyg arch L width; Lat Orb rim R width; Lat Orb rim L width.
- v.
- Vertical: Mx incisor height; Mx canine R height; Mx canine L height; Mx molar R height; Mx molar L height; pogonion height; PNS height, menton height.
- vi.
- Soft tissue: RChkbone; LChkbone; Rnasalbase; Lnasalabase.
- vii.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MARPE | Mini-Screw-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion |
| ANS | Anterior Nasal Spine |
| PNS | Posterior Nasal Spine |
| CBCT | Cone-Beam Computed Tomography |
| MSE | Maxillary Skeletal Expander |
References
- Zeng, W.; Yan, S.; Yi, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Long-term efficacy and stability of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion in mid to late adolescents and adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaqrami, B.S.; Al-Somairi, M.A.A.; Al-Gumaei, W.S.; Al-Tayar, B.; Abdulghani, E.A.; Alhammadi, M.S.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, H.; He, H. Degree and pattern of expansion of commercially available and custom-fabricated miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion systems in young adult patients: A retrospective comparative analysis. Int. Orthod. 2025, 23, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Suh, H.; Bianchi, J.; Yoon, A.; Oh, H. Treatment outcomes of 3D-printed custom and conventional mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expanders (MARPE). Prog. Orthod. 2025, 26, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bud, E.S.; Bică, C.I.; Păcurar, M.; Vaida, P.; Vlasa, A.; Martha, K.; Bud, A. Observational Study Regarding Possible Side Effects of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expander (MARPE) with or without the Use of Corticopuncture Therapy. Biology 2021, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, S.; Kolesnyk, V.; Chepanova, D. Applications of the Novel Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy Guide for MARPE Midfacial Skeletal Expansion. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Gandhi, V.; Vich, M.L.; Allareddy, V.; Tadinada, A.; Yadav, S. Long-term assessment of conventional and mini-screw-assisted rapid palatal expansion on the nasal cavity. Angle Orthod. 2022, 92, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Arqub, S.; Mehta, S.; Iverson, M.G.; Yadav, S.; Upadhyay, M.; Almuzian, M. Does Mini Screw Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) have an influence on airway and breathing in middle-aged children and adolescents? A systematic review. Int. Orthod. 2021, 19, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, M.; Montresor, L.; Cantarella, D.; Zerman, N.; Spinas, E. Does Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion Influence Upper Airway in Adult Patients? A Scoping Review. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAskar, S.; Jamal, M.; Khamis, A.H.; Ghoneima, A. Comparative Assessment of Pharyngeal Airway Dimensions in Skeletal Class I, II, and III Emirati Subjects: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Fu, Q.-M.; Xu, X.-Y. Relationships among tongue volume, hyoid position, airway volume and maxillofacial form in paediatric patients with Class Ⅰ, Class Ⅱ and Class Ⅲ malocclusions. Shanghai J. Stomatol. 2020, 29, 632–637. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, W.; Wang, M.; Cai, M.; Li, Z.; Hou, B.; Pan, X. Correlation between craniocervical posture and upper airway dimension in patients with bilateral anterior disc displacement. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, N.; Colak, O.; Sfogliano, L.; Elkenawy, I.; Fijany, L.; Fraser, A.; Zhang, B.; Moon, W. Differential assessment of skeletal, alveolar, and dental components induced by microimplant-supported midfacial skeletal expander (MSE), utilizing novel angular measurements from the fulcrum. Prog. Orthod. 2020, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, D.; Savio, G.; Grigolato, L.; Zanata, P.; Berveglieri, C.; Lo Giudice, A.; Isola, G.; Del Fabbro, M.; Moon, W. A New Methodology for the Digital Planning of Micro-Implant-Supported Maxillary Skeletal Expansion. Med. Devices 2020, 13, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, S.; Kolesnyk, V.; Chepanova, D. Asymmetry Management During 3D-Guided Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE Treatment with Direct Printed Aligners: Case Report. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, G.W.; Jelic, J.S.; Kim, J.; Cummings, D.R.; Beress, A.; Worley, C.M.; Chung, B.; Bergman, R. Soft tissue cephalometric analysis: Diagnosis and treatment planning of dentofacial deformity. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1999, 116, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, G.W.; Bergman, R.T. Facial keys to orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Part I. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1993, 103, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echarri-Nicolás, J.; González-Olmo, M.J.; Echarri-Labiondo, P.; Romero, M. Short-term outcomes in the upper airway with tooth-bone-borne vs bone-borne rapid maxillary expanders. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mozany, S.A.; Dalci, O.; Almuzian, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Tarraf, N.E.; Ali Darendeliler, M. A novel method for treatment of Class III malocclusion in growing patients. Prog. Orthod. 2017, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Yu, H.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Ahn, H.-W.; Kang, Y.-G.; Park, J.J. Comparison of treatment effects with or without miniscrews for maxillary protraction in growing patients with Class III malocclusion. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2025, 168, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, P.T.H.; Trang, P.T.; Hang, P.T.T.; Viet, H. Clinical and cone-beam computed tomography outcomes of miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion in the treatment of maxillary transverse deficiency: A prospective study. Medicine 2025, 104, e44684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanović, A.; Theodorou, C.I.; Bergé, S.J.; Schols, J.G.J.H.; Xi, T. Efficacy of Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE) in late adolescents and adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, N.; Seker, E.D.; Yücesoy, T. Comparison of the effects of different rapid maxillary expansion techniques on craniofacial structures: A finite element analysis study. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.J. The Treatment of Maxillary Deficiency by Opening the Midpalatal Suture. Angle Orthod. 1965, 35, 200–217. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, W.M.; Kronman, J.H. Anatomical changes induced by splitting of the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1969, 39, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Filho, O.G.; Montes, L.A.; Torelly, L.F. Rapid maxillary expansion in the deciduous and mixed dentition evaluated through posteroanterior cephalometric analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1995, 107, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertz, R.; Dreskin, M. Midpalatal suture opening: A normative study. Am. J. Orthod. 1977, 71, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Liu, S.; Lei, L.; Liu, O.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Q.; Lu, Y. Changes of the upper airway and bone in microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion: A cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhiz, A.; Schepers, S.; Lambrichts, I.; Vrielinck, L.; Sun, Y.; Politis, C. Lateral cephalometry changes after SARPE. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarella, D.; Dominguez-Mompell, R.; Moschik, C.; Mallya, S.M.; Pan, H.C.; Alkahtani, M.R.; Elkenawy, I.; Moon, W. Midfacial changes in the coronal plane induced by microimplant-supported skeletal expander, studied with cone-beam computed tomography images. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alan, A.; Kaya, Y.; Sancak, K. Mid-facial skeletal and soft tissue changes after maxillary skeletal expander application: A retrospective CBCT study. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
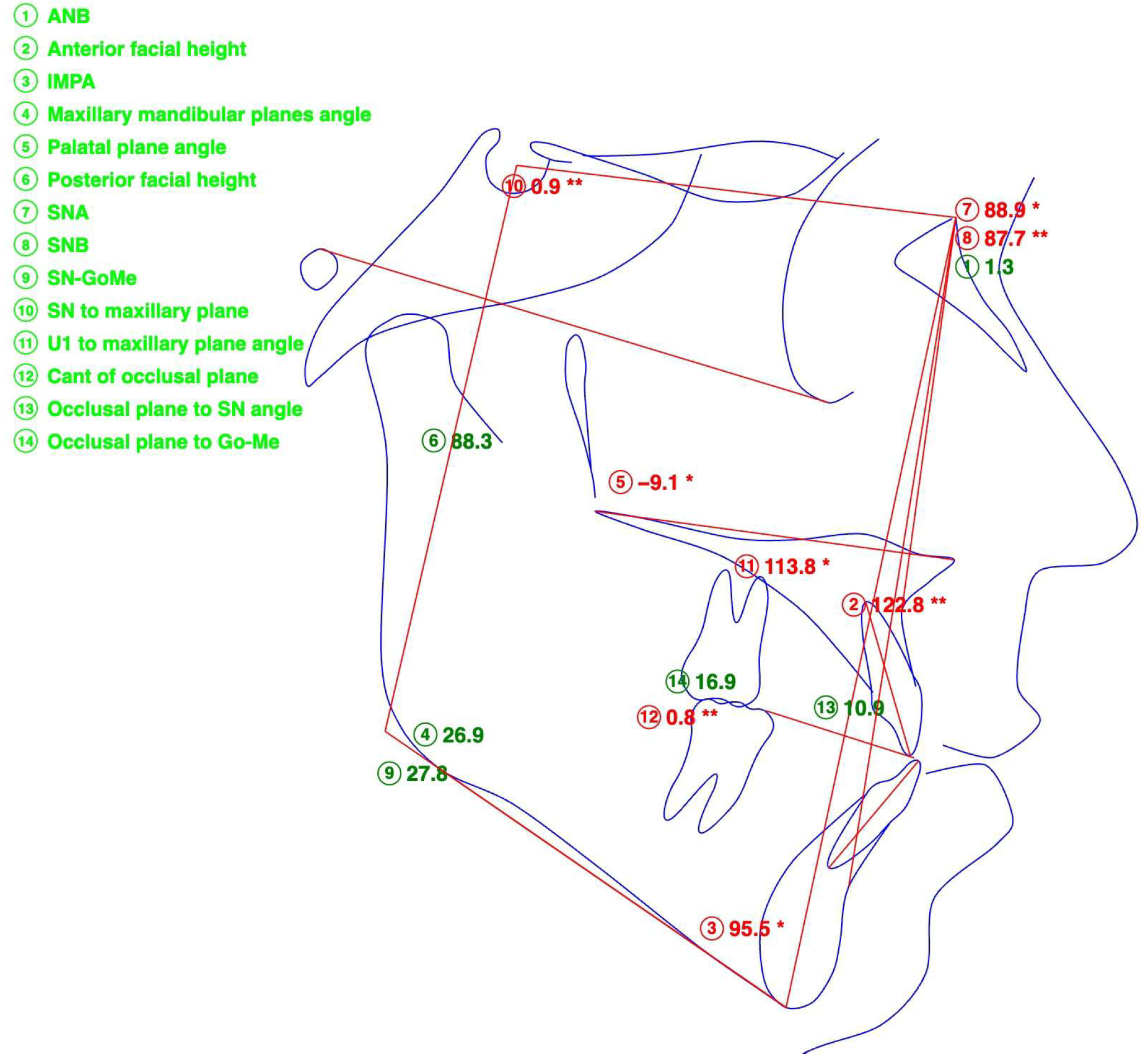







| Measurement | Value, Degrees |
|---|---|
| SNA | 88.9 |
| SNB | 87.7 |
| ANB | 1.3 |
| SN-ANS-PNS | 0.9 |
| FH-ANS-PNS | −9.1 |
| SN-GoMe | 27.8 |
| ANS-PNS-GoMe | 26.9 |
| U1 to Palatal Plane | 113.8 |
| Measurement | Value, Degrees |
|---|---|
| SNA | 88.4 |
| SNB | 85.6 |
| ANB | 2.8 |
| SN-ANS-PNS | 3.1 |
| FH-ANS-PNS | −8.5 |
| SN-GoMe | 28.3 |
| ANS-PNS-GoMe | 25.2 |
| U1 to Palatal Plane | 114.2 |
| Measurement | Description |
|---|---|
| ANS to TVL | Distance from ANS to True Vertical Plane (TVL) Through Sn (Subnasal) |
| Mx Incisor R to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Right Central Incisor Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Mx Incisor L to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Left Central Incisor Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Upper-Right Canine to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Right Canine Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Upper-Left Canine to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Left Canine Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Upper-Right Molar to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Right First Molar Mesiofacial Cusp Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Upper-Left Molar to TVL | Distance from Maxillary Left First Molar Mesiofacial Cusp Tip to TVL (Sn) |
| Pogonion to TVL | Distance from Pogonion to TVL (Sn) |
| B-Point to TVL | Distance from Point B to TVL (Sn) |
| PNS to TVL | Distance from PNS to TVL (Sn) |
| Mx33 Cant | Cant of the Maxillary Canine Plane (Positive—Right-Side Down; Negative—Left-Side Down) |
| Width Difference Mx Molar | Width Difference Between Right and Left Measurements of Maxillary Molar Width |
| Width Difference Zyg Arch | Width Difference Between Right and Left Measurements of Zygomatic Arch Width |
| Width Difference Lat Orb Rim | Width Difference Between Right and Left Measurements of Lateral Orbital Rim Width |
| Mx Molar R Width | Distance Between Distofacial Cusp of Maxillary Right First Molar and Midfacial Plane |
| Mx Molar L Width | Distance Between Distofacial Cusp of Maxillary Left First Molar and Midfacial Plane |
| Zyg Arch R Width | Distance Between Right Zygomatic Arch and Midfacial Plane |
| Zyg Arch L Width | Distance Between Left Zygomatic Arch and Midfacial Plane |
| Lat Orb Rim R Width | Distance Between Right Frontozygomatic Suture and Midfacial Plane |
| Lat Orb Rim L Width | Distance Between Left Frontozygomatic Suture and Midfacial Plane |
| Mx Incisor Height | Distance Between THP (Na) and Maxillary Central Incisor Tip |
| Max Canine R Height | Distance Between THP (Na) and Maxillary Right Canine Tip |
| Mx Canine L Height | Distance Between THP (Na) and Maxillary Left Canine Tip |
| Mx Molar R Height | Distance Between THP (Na) and Maxillary Right First Molar Mesiofacial Cusp Tip |
| Mx Molar L Height | Distance Between THP (Na) and Maxillary Left First Molar Mesiofacial Cusp Tip |
| Pogonion Height | Distance Between Pogonion and THP (Na) |
| PNS Height | Distance Between PNS and THP (Na) |
| Menton Height | Distance Between Menton and THP (Na) |
| RChkbone | Soft Tissue Distance from Right Cheekbone to TVP (Sn) |
| LChkbone | Soft Tissue Distance from Left Cheekbone to TVP (Sn) |
| Rnasalbase | Soft Tissue Distance from Right Nasal Base to TVP (Sn) |
| Lnasalabase | Soft Tissue Distance from Left Nasal Base to TVP (Sn) |
| Measurement | Before | After | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANS to TVL | −15.1 mm | −10.7 mm | −4.4 mm |
| Mx Incisor R to TVL | −16.5 mm | −16.0 mm | −0.5 mm |
| Mx Incisor L to TVL | −19.6 mm | −15.7 mm | −3.9 mm |
| Upper-Right Canine to TVL | −21.0 mm | −18.5 mm | −2.5 mm |
| Upper-Left Canine to TVL | −26.2 mm | −21.7 mm | −4.5 mm |
| Upper-Right Molar to TVL | −36.8 mm | −36.2 mm | −0.4 mm |
| Upper-Left Molar to TVL | −41.3 mm | −41.4 mm | 0.1 mm |
| Pogonion to TVL | −14.7 mm | −16.8 mm | 2.1 mm |
| B-Point to TVL | −14.7 mm | −17.0 mm | 2.3 mm |
| PNS to TVL | 70.6 mm | 68.1 mm | −2.5 mm |
| Mx33 Cant | −3.2 degrees | 1.1 degrees | −2.1 degrees |
| Width Difference, Mx Molar | 3.2 mm | −3.7 mm | −0.5 mm |
| Width Difference, Zyg Arch | 3.5 mm | −2.6 mm | 0.9 mm |
| Width Difference, Lat Orb Rim | −1.4 mm | −1.7 mm | 0.3 mm |
| Mx Molar R Width | 30.8 mm | 32.4 mm | 1.6 mm |
| Mx Molar L Width | 27.7 mm | 36.1 mm | 8.4 mm |
| Zyg Arch R Width | 67.6 mm | 67.7 mm | 0.1 mm |
| Zyg Arch L Width | 67.5 mm | 68.3 mm | 0.8 mm |
| Lat Orb Rim R Width | 45.6 mm | 52.0 mm | 6.4 mm |
| Lat Orb Rim L Width | 46.9 mm | 53.6 mm | 6.7 mm |
| Mx Incisor Height | 71.0 mm | 74.2 mm | 3.2 mm |
| Max Canine R Height | 70.9 mm | 73.0 mm | 2.1 mm |
| Mx Canine L Height | 74.1 mm | 72.0 mm | −1.9 mm |
| Mx Molar R Height | 72.7 mm | 73.9 mm | 1.2 mm |
| Mx Molar L Height | 73.8 mm | 73.1 mm | −0.7 mm |
| Pogonion Height | 115.5 mm | 117.6 mm | 2.1 mm |
| PNS Height | 55.5 mm | 55.3 mm | −0.2 mm |
| Menton Height | 121.8 mm | 124.2 mm | 2.4 mm |
| RChkbone | 41.1 mm | 35.4 mm | −5.7 mm |
| LChkbone | 39.0 mm | 37.3 mm | −1.7 mm |
| Rnasalbase | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lnasalabase | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Measurement | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Airway Total Volume, cc | 19.5 | 21.7 |
| Upper Airway Min Cross-Section, mm2 | 253 | 307 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Koval, S.; Kolesnyk, V.; Chepanova, D. Immediate 3D Skull Changes Following 3D-Guided Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE: Case Report. Dent. J. 2026, 14, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14010024
Koval S, Kolesnyk V, Chepanova D. Immediate 3D Skull Changes Following 3D-Guided Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE: Case Report. Dentistry Journal. 2026; 14(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoval, Svitlana, Viktoriia Kolesnyk, and Daria Chepanova. 2026. "Immediate 3D Skull Changes Following 3D-Guided Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE: Case Report" Dentistry Journal 14, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14010024
APA StyleKoval, S., Kolesnyk, V., & Chepanova, D. (2026). Immediate 3D Skull Changes Following 3D-Guided Midpalatal Piezocorticotomy-Assisted MARPE: Case Report. Dentistry Journal, 14(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj14010024






