Surface and Interface Science and Engineering for the Society of the Future
A topical collection in Coatings (ISSN 2079-6412).
Submission Status:
Closed
|
Viewed by 222237
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
 Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Istituto di Chimica dei Composti OrganoMetallici (ICCOM-CNR), Via Madonna del Piano 10, 50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Firenze, Italy
Interests: electrodeposition of materials for renewable energy production; surface engineering; corrosion and corrosion protection; thermal barriers coatings; electron microscopy (SEM, TEM); X-ray techniques for surface structure and composition (XPS, XRF, XRD); electroless deposition of metals and cermet’s; simulation and modelling of complex electrochemical systems
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Surface and interface science and engineering have a central role in addressing major societal challenges that, without being exhaustive, include the transition to renewable energy, pollution mitigation and remediation, saving of critical raw materials, food security and health science. Accordingly, we launch this new Special Issue of Coatings that will collect original research articles and review papers. Contributions will focus on the fundamentals and application of surface and interface science and engineering and will emphasize the potential of the covered subject in addressing these important societal challenges.
We look forward to receiving your contribution.
Dr. Alessandro Lavacchi
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Coatings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (26 papers)
Open AccessArticle
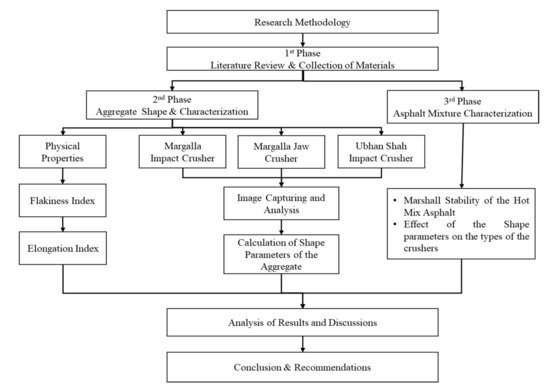
Shape Characterizing of Aggregates Produced through Different Crushing Techniques
by
Ghulam Yaseen, Wesam Salah Alaloul, Imran Hafeez and Abdul Hannan Qureshi
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4615
Abstract
The aggregate shape properties produced from the different crushing techniques influence the performance properties of the asphalt mixtures. The objective of this study was to classify the aggregates into spherical, flat, elongated and flat, and elongated shapes, collected from impact crusher and jaw
[...] Read more.
The aggregate shape properties produced from the different crushing techniques influence the performance properties of the asphalt mixtures. The objective of this study was to classify the aggregates into spherical, flat, elongated and flat, and elongated shapes, collected from impact crusher and jaw crusher of two sources, and to calculate the shape parameters, such as aspect ratio, shape factor, form factor, sphericity, roundness, and angularity index. In addition, this study also investigated the effects of this classification on the Marshall stability and volumetric properties of asphalt mixtures prepared from the respective shape of aggregates. The results showed that the aggregate of different fractions (passing 37.5 mm and retained on 4.75 mm) produced from the jaw crusher of Margalla quarry showed better shape parameters. The spherical aggregates collected from all crushers showed 20–30% higher Marshall stability of the blends by improving the mechanical and volumetric properties of the asphalt mixtures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
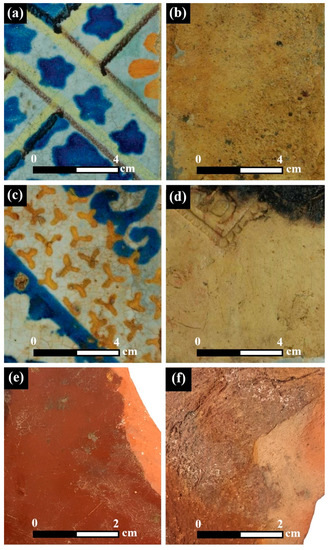
A Tale of Two Tiles: Characterization of Floor Tiles from the Nineteenth-Century Akko Tower Shipwreck (Israel)
by
Alexandra Inberg, Dana Ashkenazi, Yishai Feldman, Omri Dvir and Deborah Cvikel
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 4328
Abstract
Fragments of decorated floor tiles were retrieved from the Akko Tower shipwreck, Israel. Most tiles were made of bright brown fired clay with a white glaze decorated with colored stenciled motifs (Type A); and others consisted of a red-brown fired clay body, coated
[...] Read more.
Fragments of decorated floor tiles were retrieved from the Akko Tower shipwreck, Israel. Most tiles were made of bright brown fired clay with a white glaze decorated with colored stenciled motifs (Type A); and others consisted of a red-brown fired clay body, coated with a brown pigment covered with transparent brown glaze (Type B). This study aimed to characterize the two tile types; to reveal information concerning the manufacturing process; and to determine the origin of their raw material. A multidisciplinary approach was used, including light microscopy, SEM-EDS, electron probe microanalysis with wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EPMA-WDS), XRD, Raman spectroscopy, and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) analyses. The characterization of both tile types demonstrated the use of different raw materials. The Type A tiles were covered with tin-opacified majolica glaze and colored with various mixtures of pigments. The blue color was due to pigment rich in cobalt; the yellow color was due to Naples yellow and lead-tin yellow I minerals; and the green, orange, and brown colors were all prepared by mixing the Naples yellow pigment with different minerals. These majolica glaze tiles were probably manufactured in Sicily. The brown coating of the Type B tiles was due to pigment rich in lead and iron minerals. These tiles were produced with different manufacturing processes, and apparently made in France.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
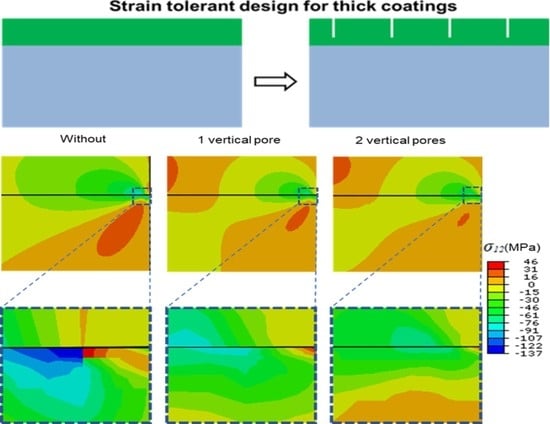
Strain-Induced Cracking Behavior of Coating/Substrate Systems and Strain Tolerant Design for Thick Coatings
by
Ghazanfar Mehboob, Tong Xu, Guang-Rong Li, Shahnwaz Hussain, Gohar Mehboob and Adnan Tahir
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4736
Abstract
The life span for a coating attached to its substrate is basic support for their desired protective function. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the causes responsible for the failure of coatings during service. This paper developed a finite element model to
[...] Read more.
The life span for a coating attached to its substrate is basic support for their desired protective function. Therefore, it is necessary to find out the causes responsible for the failure of coatings during service. This paper developed a finite element model to investigate the cracking behavior of plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings induced by the mismatch strain of thermal expansion between coating and substrate. Crack propagation affected by coating thicknesses was realized by the virtual crack closure technique (VCCT). The residual stresses (σ
22 and σ
12) and the strain energy release rate (SERR) induced at the tip of pre-crack in ceramic coatings are calculated. Results show that the σ
22 and σ
12 at the tip of the pre-crack increases continuously with the thickening ceramic coatings. The SERRs at the tip of the pre-crack in top-coat (TC) were increased with the thickness of ceramic coatings, resulting in the propagation of cracks. The crack length increases with the thickening of ceramic coatings. The crack propagation and coalescence lead to coating spallation, which is one of the main failure modes for plasma sprayed ceramic coatings during service. Given that, strain tolerant design was developed by inserting vertical pores in coatings. It was found that the SERRs were decreased with the increase in the number of vertical pores, as well as their depth. Moreover, the coatings with vertical pores appear to be crack-resistant, in particular for the thicker coatings. This suggests that the strain tolerant design is helpful to extend the life span of thick coatings, which makes a fundamental contribution to the design and preparation of advanced protective coatings in future applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
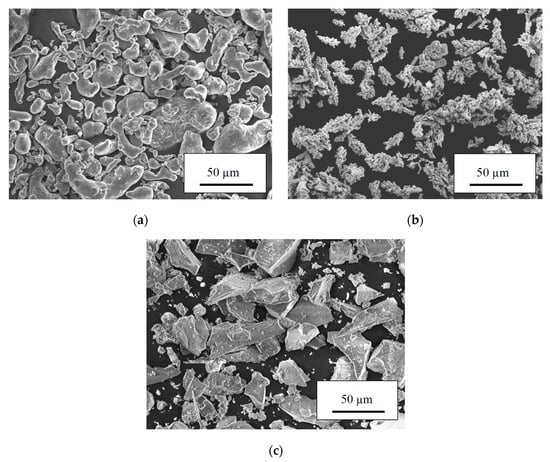
Heat-Treatment of Aluminium-Nickel Composite Cold Sprayed Coating
by
Marcin Winnicki, Marek Jasiorski, Agnieszka Baszczuk and Marcin Korzeniowski
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4805
Abstract
Intermetallic compounds, especially aluminides, show good high-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, high melting points, and thus have received considerable attention as potential substitutes for superalloys in high-temperature applications. Aluminides are especially interesting because they are stable up to the critical temperature of ordering, which
[...] Read more.
Intermetallic compounds, especially aluminides, show good high-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, high melting points, and thus have received considerable attention as potential substitutes for superalloys in high-temperature applications. Aluminides are especially interesting because they are stable up to the critical temperature of ordering, which is close to the melting temperature. In the Al-Ni system, the most studied intermetallics are Ni
3Al, NiAl and NiAl
3. In the presented study, Al and Ni powders were mixed together with Al
2O
3 in various proportions to produce dense coatings by low-temperature cold spraying. Two types of post-deposition treatments were applied to produce aluminides, namely furnace heating and resistance spot welding. The former caused a long time diffusion while the latter a self-propagating high temperature synthesis. Both heating methods enabled formations of intermetallic phases. However, the furnace heating provides high porosity. The microstructure of the samples was analyzed by SEM (scanning electron microscope), EDS (energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy) and XRD (X-ray diffraction) together with microhardness measurements.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synergistic Effect of Mica, Glass Frit, and Melamine Cyanurate for Improving Fire Resistance of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber Composites Destined for Ceramizable Coatings
by
Mateusz Imiela, Rafał Anyszka, Dariusz M. Bieliński, Magdalena Lipińska, Przemysław Rybiński and Bartłomiej Syrek
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 6757
Abstract
Synergistic effects of different fillers are widely utilized in polymer technology. The combination of various types of fillers is used to improve various properties of polymer composites. In this paper, a synergistic effect of flame retardants was tested to improve the performance of
[...] Read more.
Synergistic effects of different fillers are widely utilized in polymer technology. The combination of various types of fillers is used to improve various properties of polymer composites. In this paper, a synergistic effect of flame retardants was tested to improve the performance of ceramizable composites. The composites were based of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) used as polymer matrix. Three different types of flame retardants were tested for synergistic effect: Mica (phlogopite) high aspect-ratio platelets, along with low softening point temperature glass frit (featuring ceramization effect), and melamine cyanurate, a commonly used flame retardant promoting carbonaceous char. In order to characterize the properties of the composites, combustibility, thermal stability, viscoelastic properties, micromorphology, and mechanical properties were tested before and after ceramization. The results obtained show that the synergistic effect of ceramization promoting fillers and melamine cyanurate was especially visible with respect to the flame retardant properties resulting in a significant improvement of fire resistance of the composites.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
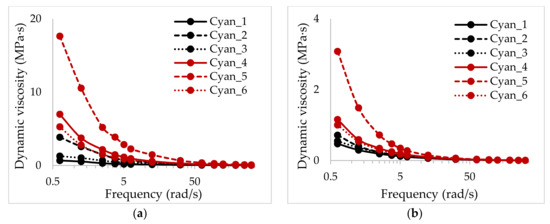
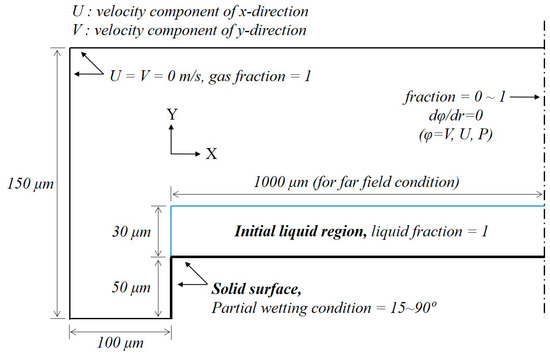
Unevenness of Thin Liquid Layer by Contact Angle Variation of Substrate during Coating Process
by
Na Kyong Kim, Dong Hee Kang and Hyun Wook Kang
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 7202
Abstract
During a thin film application, the surface of the coating liquid applied to the substrate becomes uneven because of the geometry of the substrate, viscosity of the coating liquid, surface tension, and its contact angle with the substrate. The surface is particularly uneven
[...] Read more.
During a thin film application, the surface of the coating liquid applied to the substrate becomes uneven because of the geometry of the substrate, viscosity of the coating liquid, surface tension, and its contact angle with the substrate. The surface is particularly uneven at the edge corner portion of the substrate and is thicker than the average coating thickness. This study used the volume-of-fluid (VOF) method to examine the surface unevenness of the coating liquid in terms of the contact angle of the substrate surface and sides. After the coating liquid was evenly applied to the substrate, the maximum height of the uneven region of the coating liquid at the edge of the substrate increased as time passed. The point of maximum height moved away from the edge corner portion of the substrate. The coating liquid applied to the substrate with a contact angle less than 90° exhibited a pinning effect in which the contact point was fixed at the edge. The surface unevenness was more pronounced in the absence of the pinning effect than in its presence, due to the effects of the viscosity of the coating fluid and the surface energy of the substrate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
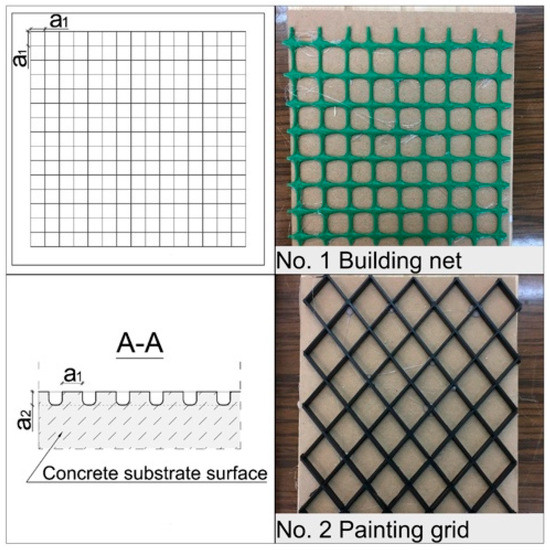
The Effect of Texturing of the Surface of Concrete Substrate on the Pull-Off Strength of Epoxy Resin Coating
by
Kamil Krzywiński and Łukasz Sadowski
Cited by 39 | Viewed by 7352
Abstract
This paper describes a study conducted to evaluate the effect of texturing of the surface of concrete substrate on the pull-off strength (
fb) of epoxy resin coating. The paper investigates a total of seventeen types of textures: after grooving, imprinting,
[...] Read more.
This paper describes a study conducted to evaluate the effect of texturing of the surface of concrete substrate on the pull-off strength (
fb) of epoxy resin coating. The paper investigates a total of seventeen types of textures: after grooving, imprinting, patch grabbing and brushing. The texture of the surface of the concrete substrate was prepared during the first 15 min after pouring fresh concrete into molds. The epoxy resin coating was laid after 28 days on hardened concrete substrates. To investigate the pull-off strength of the epoxy resin coating to the concrete substrate, the pull-off method was used. The results were compared with the results obtained for a sample prepared by grinding, normative minimal pull-off strength values and the values declared by the manufacturer. During this study twelve out of fifteen tested samples achieved a pull-off strength higher than 1.50 MPa. It was found that one of the imprinting texturing methods was especially beneficial.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
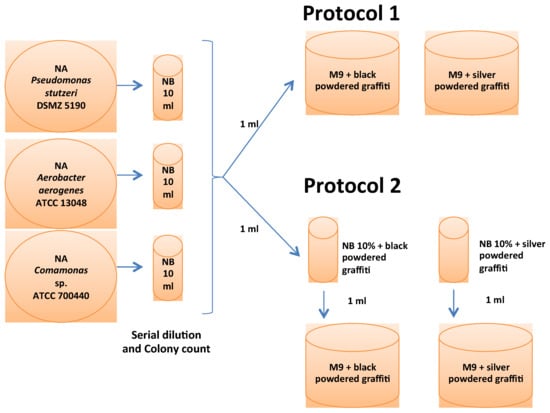
Biocleaning to Remove Graffiti: A Real Possibility? Advances towards a Complete Protocol of Action
by
Patricia Sanmartín and Pilar Bosch-Roig
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 6725
Abstract
The first academic studies on the use of microorganisms in cleaning procedures appeared in the late 1980s/early 1990s. In the past thirty years, most of such studies have addressed the removal of nitrate and sulphate salts and organic matter from surfaces by using
[...] Read more.
The first academic studies on the use of microorganisms in cleaning procedures appeared in the late 1980s/early 1990s. In the past thirty years, most of such studies have addressed the removal of nitrate and sulphate salts and organic matter from surfaces by using non-pathogenic anaerobic microorganisms, mainly sulphate-reducing bacteria. The successful use of microbes in the removal of graffiti paint remains, however, a work in progress. Biocleaning surfaces to remove graffiti is not a simple task, because of the complex chemical composition of graffiti paints. This study looks at ways of improving the bioremoval of graffiti and presents the latest findings regarding different methodological aspects of cleaning natural and man-made stone. Granite and concrete substrates were coated with silver and black graffiti spray paints for comparison of the efficacy of the biocleaning method on these different materials. Visual and microscopic examination along with colour and infrared measurements made after application of the bacterial strains tested (previously shown to be suitable candidates for bioremoval of graffiti) revealed remarkably successful results. The findings presented thus represent progress in the development of a biocleaning protocol applicable to the in-situ removal of graffiti. Important improvements have been made regarding the time of treatment, which has been reduced by up to 20 days, and the use of a culture medium enriched with powdered graffiti, which facilitates and accelerates the adaptation of the microorganisms to the target surface.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Expanding Plasma Process for Nitriding Mo–Ti Bilayer Thin Films
by
Isabelle Jauberteau, Richard Mayet, Julie Cornette, Pierre Carles, Denis Mangin, Annie Bessaudou, Jean Louis Jauberteau and Armand Passelergue
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 4643
Abstract
Owing to the reducing effect of NH
x radicals and H species produced in (Ar-N
2-H
2) expanding plasma, chemical reactions are promoted in thin metal films in contrast with other plasma treatments where the impinging energetic ions play the main
[...] Read more.
Owing to the reducing effect of NH
x radicals and H species produced in (Ar-N
2-H
2) expanding plasma, chemical reactions are promoted in thin metal films in contrast with other plasma treatments where the impinging energetic ions play the main role. Multi layers of Mo, Ti, and their nitrides are used in very recent applications such as supercapacitors or solar cells. They combine the interesting properties of the constituents. This work reports on the formation and the structure of Ti nitrides and Mo silicides in Mo–Ti bilayer films coated on Si wafers exposed to (Ar-N
2-H
2) plasma for 1 to 3 h. Nitrogen diffuses into the surface layers from 400 °C and TiN starts to crystallize from 600 °C. Interdiffusion of Mo, Ti, and Si through Mo–Ti bilayer films gives rise to the formation of Mo–Ti alloys and MoSi
2 of hexagonal structure, which transforms into MoSi
2 of tetragonal structure at longer treatment durations. A 1 h 30 min plasma exposure at 800 °C leads to the formation of three layers of nearly equal thickness with clear interfaces, which consist of TiN and MoSi
2 of nanometric size in the vicinity of the Mo–Ti bilayer film surface.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Calcium Ethoxide as Consolidant for Porous Limestones: Influence of the Solvent
by
Martina Zuena, Elisabetta Zendri, Dória Costa, José Delgado-Rodrigues, Naida El Habra and Patrizia Tomasin
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5267
Abstract
Calcium ethoxide nanosuspension, a consolidating product developed during the European Nanomatch project, is here modified by adding two different solvents, 2-butanol and n-butylacetate, chosen for their different boiling points with respect to ethanol, the solvent employed in a previous work to dilute the
[...] Read more.
Calcium ethoxide nanosuspension, a consolidating product developed during the European Nanomatch project, is here modified by adding two different solvents, 2-butanol and n-butylacetate, chosen for their different boiling points with respect to ethanol, the solvent employed in a previous work to dilute the original product. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (µFT-IR) was used to understand how the presence of these new solvents can influence the kinetics of the carbonation process and the pathway reaction. Furthermore, coatings derived from nanosuspensions were maintained for specific time intervals at controlled relative humidity conditions (RH = 50% and RH = 90%); the formed mineralogical phases were characterized by µFT-IR and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Results indicate that the used solvents can influence the kinetic and reaction pathways, while the phases formed at the end of the carbonation process are influenced by both solvents and RH conditions. The effectiveness of calcium ethoxide based product diluted in 2-butanol and n-butylacetate as limestone consolidants was evaluated with drilling resistance measurement system (DRMS) and ultrasound pulse velocity (UPV). The impact on color coordinates was also assessed. The results were compared with those obtained with the same product diluted in ethanol and a commercial nanolime. The use of these solvents gave different and better results in terms of efficacy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
A Micro-Tomographic Insight into the Coating Systems of Historical Bowed String Instruments
by
Giacomo Fiocco, Tommaso Rovetta, Claudia Invernizzi, Michela Albano, Marco Malagodi, Maurizio Licchelli, Alessandro Re, Alessandro Lo Giudice, Gabriele N. Lanzafame, Franco Zanini, Magdalena Iwanicka, Piotr Targowski and Monica Gulmini
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 5976
Abstract
Musical instruments are tools for playing music, but for some of them—made by the most important historical violin makers—the myths hide the physical artwork. Ancient violin-making Masters developed peculiar construction methods and defined aesthetic canons that are still recognizable in their musical instruments.
[...] Read more.
Musical instruments are tools for playing music, but for some of them—made by the most important historical violin makers—the myths hide the physical artwork. Ancient violin-making Masters developed peculiar construction methods and defined aesthetic canons that are still recognizable in their musical instruments. Recently, the focus of scientific investigations has been set on the characterization of materials and methods used by the ancient violin makers by means of several scientific approaches. In this work, the merits of synchrotron radiation micro-computed tomography and optical coherence tomography (OCT) for the investigation of complex coatings systems on historical bowed string musical instruments are discussed. Five large fragments removed during past restorations from instruments produced by Jacobus Stainer, Gasparo da Salò, Giovanni Paolo Maggini, and Lorenzo Guadagnini have been considered for a non-invasive insight by tomographic techniques and the results are discussed considering previous micro-invasive investigations. The tomographic approach allows to highlight the micro-morphology of the coating systems and offers preliminary information on the methods that were employed by the ancient Masters to treat the wood and finish the musical instrument.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Influence of ALD Coating Layers on the Optical Properties of Nanoporous Alumina-Based Structures
by
Ana L. Cuevas, María del Valle Martínez de Yuso, Víctor Vega, Ana Silvia González, Víctor M. Prida and Juana Benavente
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 6174
Abstract
Optical changes associated with the surface coating of different metal oxides and nanolayers by the ALD technique of a nanoporous alumina structure (NPAS) obtained by the two-step anodization method were analyzed. The NPASs were coated with: (i) a single layer (SiO
2 or
[...] Read more.
Optical changes associated with the surface coating of different metal oxides and nanolayers by the ALD technique of a nanoporous alumina structure (NPAS) obtained by the two-step anodization method were analyzed. The NPASs were coated with: (i) a single layer (SiO
2 or TiO
2), and (ii) a double layer of SiO
2 plus Al
2O
3 or aluminum doped ZnO (AZO) to estimate the effect of surface layer coverage material, geometrical parameters (pore-size/porosity), and number of layers on light transmission/reflection. Chemical surface characterization of the different NPASs was carried out by analyzing XPS spectra, which allowed us to obtain an estimation of the coating layer homogeneity. Transmittance and spectroscopic ellipsometry measurements were analyzed in order to detect changes in characteristic optical parameters such as band gap, refractive index, and extinction coefficients associated with the material and the characteristics of the single or double coating layers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
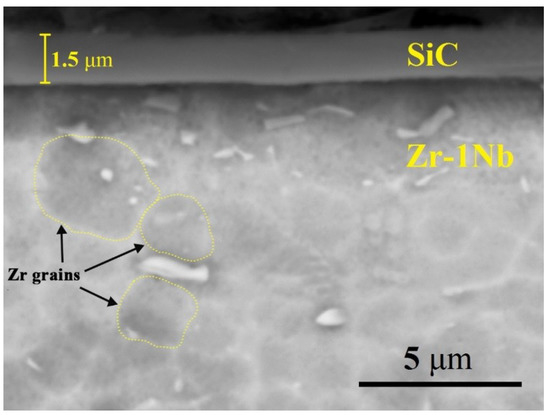
Hydrogen Sorption Kinetics of SiC-Coated Zr-1Nb Alloy
by
Egor B. Kashkarov, Maxim S. Syrtanov, Tatyana L. Murashkina, Alexander V. Kurochkin, Yulia Shanenkova and Aleksei Obrosov
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4815
Abstract
This paper describes the influence of silicon carbide (SiC) coating on hydrogen sorption kinetics of zirconium alloy E110 (Zr-1Nb). Amorphous SiC coating of 1.5-μm thickness was deposited on Zr-1Nb alloy substrate by direct current magnetron sputtering of composite cathode. Hydrogen absorption by SiC-coated
[...] Read more.
This paper describes the influence of silicon carbide (SiC) coating on hydrogen sorption kinetics of zirconium alloy E110 (Zr-1Nb). Amorphous SiC coating of 1.5-μm thickness was deposited on Zr-1Nb alloy substrate by direct current magnetron sputtering of composite cathode. Hydrogen absorption by SiC-coated Zr-1Nb alloy significantly decreased due to low hydrogen permeability of the coating. Hydrogenation tests show that SiC coating provides protective properties against hydrogen permeation in the investigated temperature range of 350–450 °C. It was shown that hydrogenation of uncoated Zr-1Nb leads to formation of δ hydrides at 350 °C and δ and γ hydrides at higher temperatures whereas in the SiC-coated Zr-1Nb alloy only δ hydrides formed. Gradient hydrogen distribution through the SiC coating and H trapping in the carbon-rich interface was observed. The adhesion strength of the coating was ~5 N. Hydrogenation up to 450 °C for 5 h does not degrade the adhesion properties during scratch testing.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Corrosion Behavior and Surface Properties of PVD Coatings for Mold Technology Applications
by
Luigi D'Avico, Ruben Beltrami, Nora Lecis and Stefano P. Trasatti
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 9148
Abstract
Chrome plating is still one of the best solutions to coat martensitic steel used in the molding of plastics and rubbers. However, current stringent regulations on environmental impact call for more sustainable processes. In the present work, some physical vapor deposition (PVD) nitride
[...] Read more.
Chrome plating is still one of the best solutions to coat martensitic steel used in the molding of plastics and rubbers. However, current stringent regulations on environmental impact call for more sustainable processes. In the present work, some physical vapor deposition (PVD) nitride coatings were produced on X155CrMoV12 steel and characterized in terms of both corrosion behavior and surface properties. Results indicated that titanium-based PVD coatings could be a valuable alternative to chromium-based coatings as they exhibited a good compromise between corrosion and surface properties. AlTiN and TiN PVD coatings exhibited adequate hardness for plastic mold applications, with AlTiN reaching hardness as high as 2000 HV. Moreover, the critical loads and adhesion properties were found to be definitely better than those of chromium-based coatings. From a corrosion point of view, the presence of multilayers in AlTiN did not seem to be beneficial as the breakdown potential for TiN (single layer) was ca. 1.1 V vs. saturated calomel electrode (SCE) compared to 0.85 V vs. SCE for AlTiN in aggressive media (NaCl).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
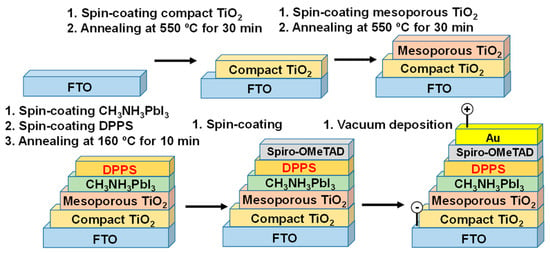
Effects of Decaphenylcyclopentasilane Addition on Photovoltaic Properties of Perovskite Solar Cells
by
Masaya Taguchi, Atsushi Suzuki, Takeo Oku, Sakiko Fukunishi, Satoshi Minami and Masanobu Okita
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4930
Abstract
Perovskite solar cells, in which decaphenylcyclopentasilane (DPPS) layers were formed on the surface of the perovskite layer, were fabricated, and the influence on photovoltaic characteristics was investigated. The devices were fabricated by a spin-coating technique, and the surface morphology and crystal structures were
[...] Read more.
Perovskite solar cells, in which decaphenylcyclopentasilane (DPPS) layers were formed on the surface of the perovskite layer, were fabricated, and the influence on photovoltaic characteristics was investigated. The devices were fabricated by a spin-coating technique, and the surface morphology and crystal structures were investigated by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. By adding the DPPS, the fill factor and open circuit voltage were increased, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency was improved. A stability test in ambient air was carried out for seven weeks, and the photoelectric conversion efficiencies were remarkably improved for the devices with DPPS.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Bacterial Inactivation by Using Plastic Materials Activated with Combinations of Natural Antimicrobials
by
Irene Ortega Blázquez, María José Grande Burgos, Rubén Pérez Pulido, Antonio Gálvez and Rosario Lucas
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3852
Abstract
Natural antimicrobials have gained interest as possible inhibitors of biofilm formation. The aim of the present study was to determine the efficacy of antimicrobials derived from essential oils (carvacrol, thymol) plus bacteriocin AS-48 immobilized on two plastic supports (low density polyethylene and polyethylene–polyamide
[...] Read more.
Natural antimicrobials have gained interest as possible inhibitors of biofilm formation. The aim of the present study was to determine the efficacy of antimicrobials derived from essential oils (carvacrol, thymol) plus bacteriocin AS-48 immobilized on two plastic supports (low density polyethylene and polyethylene–polyamide films) on bacterial inactivation. The polyethylene–polyamide vacuum-packaging plastic film activated with a combination of thymol plus enterocin AS-48 was the most effective in reducing the concentrations of viable planktonic and sessile cells for
Listeria innocua,
Lactobacillus fructivorans,
Bacillus coagulans, and
Bacillus licheniformis. Results from the study highlight the potential of polyethylene–polyamide film activated with thymol plus enterocin AS-48 for reducing the viable cell concentrations of spoilage Gram-positive bacteria and
Listeria in both planktonic and sessile states.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Wear and Corrosion Properties of Cold-Sprayed AISI 316L Coatings Treated by Combined Plasma Carburizing and Nitriding at Low Temperature
by
Shinichiro Adachi and Nobuhiro Ueda
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 5545
Abstract
Cold-sprayed AISI 316L stainless steel coatings are treated to form an austenite phase with excessive dissolved nitrogen (known as the S-phase) by plasma nitriding at temperatures below 450 °C. The S-phase is a hard and wear-resistant layer with high corrosion resistance. However, the
[...] Read more.
Cold-sprayed AISI 316L stainless steel coatings are treated to form an austenite phase with excessive dissolved nitrogen (known as the S-phase) by plasma nitriding at temperatures below 450 °C. The S-phase is a hard and wear-resistant layer with high corrosion resistance. However, the S-phase layer formed after only nitriding is thin and the hardness abruptly decreases at a certain depth; it lacks mechanical reliability. We examined two types of combined low-temperature plasma treatment to enhance the mechanical reliability of the S-phase layer: (i) sequential and (ii) simultaneous. In the sequential plasma treatment, the carburizing step was followed by nitriding. In the simultaneous treatment, the nitriding and carburizing steps were conducted at the same time. Both combined plasma treatments succeeded in thickening the S-phase layers and changed the hardness depth profiles to decrease smoothly. In addition, anodic polarization measurements indicated that sequential treatment involving carburizing followed by nitriding for 2 h each resulted in high corrosion resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
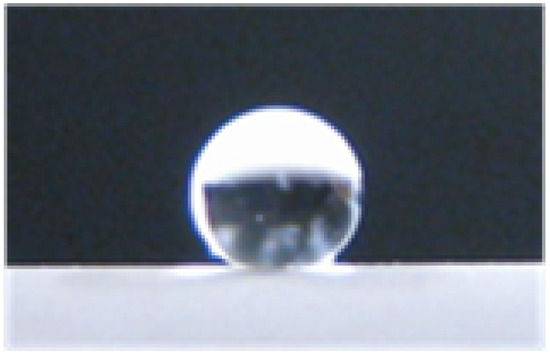
Effect of PTFE Particle Size on Superhydrophobic Coating for Supercooled Water Prevention
by
Katsuaki Morita, Joseph Gonzales and Hirotaka Sakaue
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 6298
Abstract
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) chemically repels water droplets due to the nature of fluorine substituents. This paper presents an experimental study on the impact of PTFE particle size and temperature on the hydrophobicity of a surface. The present study analyzes hydrophobicity due to both the
[...] Read more.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) chemically repels water droplets due to the nature of fluorine substituents. This paper presents an experimental study on the impact of PTFE particle size and temperature on the hydrophobicity of a surface. The present study analyzes hydrophobicity due to both the chemical properties of PTFE and the microstructure created by PTFE particles. Herein, studies of the contact angle and the sliding angle of these surfaces are described in supercooled-water conditions ranging from −10 to 0 °C. From the equations governing the surface tension and sliding angle of a droplet on a superhydrophobic surface, it is found that particle size has a much greater effect on hydrophobicity than temperature. An increase in the PTFE particle size greatly reduces the sliding angle, which indicates a lower amount of energy required to remove the droplet from the surface.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Bio-Functional Properties of Bee Pollen: The Case of “Bee Pollen Yoghurt”
by
Ioannis K. Karabagias, Vassilios K. Karabagias, Ilias Gatzias and Kyriakos A. Riganakos
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 7712
Abstract
The objectives of the present work were: (a) to characterize bee pollen from the region of Epirus in terms of biofunctional activity parameters as assessed by (i) the determination of specific polyphenols using high performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC/ESI-MS), (ii)
[...] Read more.
The objectives of the present work were: (a) to characterize bee pollen from the region of Epirus in terms of biofunctional activity parameters as assessed by (i) the determination of specific polyphenols using high performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC/ESI-MS), (ii) antioxidant capacity (DPPH assay), and (iii) total phenolic content (Folin-Ciocalteu assay), and (b) to prepare yoghurts from cow, goat, and sheep milk supplemented with different concentrations of grounded bee pollen (0.5, 1.0, 2.5 and 3.0%,
w/
v), and study afterwards the trend in antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content along with product’s sensory properties. Results showed that bee pollen ethanolic extracts are a rich source of phytochemicals based on the high total phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity that were monitored. The addition of grounded bee pollen in yoghurts resulted in a food matrix of a higher in vitro antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content, whereas it improved the yoghurt’s taste, odour, appearance, and cohesion; the latter indicates its beneficial use as a general food surface and interface material enhancer due to the possible formation of surface/interface active lipid-linked proteins. Based on the present findings, bee pollen yoghurt is proposed as a novel and costless functional food whereas it may comprise a research basis for food or material science in the scientific society of the future. Results were further supported by implementation of advanced chemometric analyses providing a full characterization of the product’s uniqueness.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Abrasion Resistance of Superhydrophobic Coatings on Aluminum Using PDMS/SiO2
by
Divine Sebastian, Chun-Wei Yao and Ian Lian
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 9987
Abstract
Superhydrophobic coatings have shown tremendous improvement in the usability of metals such as aluminum. These coatings are capable of adding attractive features such as self-cleaning, anti-corrosion, and anti-biofouling to the array of diverse features that aluminum possesses, including lightweight and high ductility. For
[...] Read more.
Superhydrophobic coatings have shown tremendous improvement in the usability of metals such as aluminum. These coatings are capable of adding attractive features such as self-cleaning, anti-corrosion, and anti-biofouling to the array of diverse features that aluminum possesses, including lightweight and high ductility. For superhydrophobic surfaces, having considerable abrasion resistance is as important as achieving a high contact angle. In this work, two types of coatings have been prepared, each composed of functionalized silica nanoparticles along with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) dispersed in ethanol, and their superhydrophobicity and abrasion characteristics have been investigated. The same silica nanoparticles are present in each coating, but each has a different proportion of the PDMS base to its curing agent. The surface morphology of the coatings was studied with the aid of a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and an atomic force microscope (AFM). The surface chemical composition was characterized using an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDX). The prepared coatings were analyzed for their degree of superhydrophobicity, abrasion resistance and adhesion characteristics. In addition, atomic force microscopy was used to understand the adhesion characteristics of the coatings.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Advances in Automotive Conversion Coatings during Pretreatment of the Body Structure: A Review
by
Mark Doerre, Larry Hibbitts, Gabriela Patrick and Nelson K. Akafuah
Cited by 72 | Viewed by 22088
Abstract
Automotive conversion coatings consist of layers of materials that are chemically applied to the body structures of vehicles before painting to improve corrosion protection and paint adhesion. These coatings are a consequence of surface-based chemical reactions and are sandwiched between paint layers and
[...] Read more.
Automotive conversion coatings consist of layers of materials that are chemically applied to the body structures of vehicles before painting to improve corrosion protection and paint adhesion. These coatings are a consequence of surface-based chemical reactions and are sandwiched between paint layers and the base metal; the chemical reactions involved distinctly classify conversion coatings from other coating technologies. Although the tri-cationic conversion coating bath chemistry that was developed around the end of the 20th century remains persistent, environmental, health, and cost issues favor a new generation of greener methods and materials such as zirconium. Environmental forces driving lightweight material selection during automobile body design are possibly more influential for transitioning to zirconium than the concerns regarding the body coating process. The chemistry involved in some conversion coatings processing has been known for over 100 years. However, recent advances in chemical processing, changes in the components used for vehicle body structures, environmental considerations and costs have prompted the automobile industry to embrace new conversion coatings technologies. These are discussed herein along with a historical perspective that has led to the use of current conversion coatings technologies. In addition, future directions for automobile body conversion coatings are discussed that may affect conversion coatings in the age of multi-material body structures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Electroplating for Decorative Applications: Recent Trends in Research and Development
by
Walter Giurlani, Giovanni Zangari, Filippo Gambinossi, Maurizio Passaponti, Emanuele Salvietti, Francesco Di Benedetto, Stefano Caporali and Massimo Innocenti
Cited by 152 | Viewed by 28512
Abstract
Electroplating processes are widely employed in industrial environments for a large variety of metallic coatings, ranging from technological to decorative applications. Even if the galvanic electrodeposition is certainly a mature technology, new concepts, novel applications, environmental legislation and the new material requirements for
[...] Read more.
Electroplating processes are widely employed in industrial environments for a large variety of metallic coatings, ranging from technological to decorative applications. Even if the galvanic electrodeposition is certainly a mature technology, new concepts, novel applications, environmental legislation and the new material requirements for next-generation devices make the scientific research in this field still very active. This review focuses mostly at the decorative and wearable applications, and aims to create a bridge between the past knowledge and the future direction that this process, i.e., electrodeposition, is taking. Both the theoretical fundamentals as well as some of the most widespread practical applications—limited to metallic and alloy coatings—are explored. As an integral part of the industrial process, we take a look at the main techniques thought which the quality control of deposits and surfaces is carried out. Finally, global industrial performance and research directions towards sustainable solutions are highlighted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
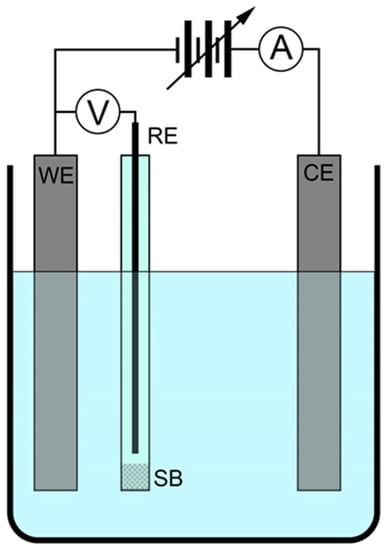
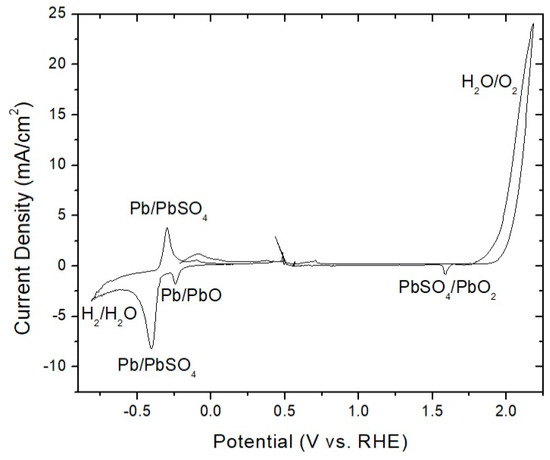
Corrosion Potential Modulation on Lead Anodes Using Water Oxidation Catalyst Coatings
by
Juliet F. Khosrowabadi Kotyk, Chi Chen and Stafford W. Sheehan
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 8369
Abstract
The oxidation of water to form oxygen gas provides charge balance for the cathodic deposition of metals, such as zinc, in the electrorefining industry. This is a corrosive, four-electron electrochemical reaction that causes deterioration of lead-silver alloy anodes employed in these processes. A
[...] Read more.
The oxidation of water to form oxygen gas provides charge balance for the cathodic deposition of metals, such as zinc, in the electrorefining industry. This is a corrosive, four-electron electrochemical reaction that causes deterioration of lead-silver alloy anodes employed in these processes. A sacrificial manganese oxide layer on the anode surface, formed in-situ from manganese sulfate, is used in industry to reduce the corrosion rate of these anodes by preferentially enabling water oxidation rather than lead dissolution. Still, it is poorly understood how the activity of manganese oxide as a water oxidation catalyst relates to its anticorrosive properties. Here, we show how the presence of water oxidation catalysts both formed in-situ (including the industry standard manganese oxide) and heterogenized prior to electrolysis on lead anodes affect the corrosion potential of these anodes. We find that corrosion potential under dynamic polarization conditions is the parameter most affected by the coatings formed in-situ and applied ex-situ prior to electrolysis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
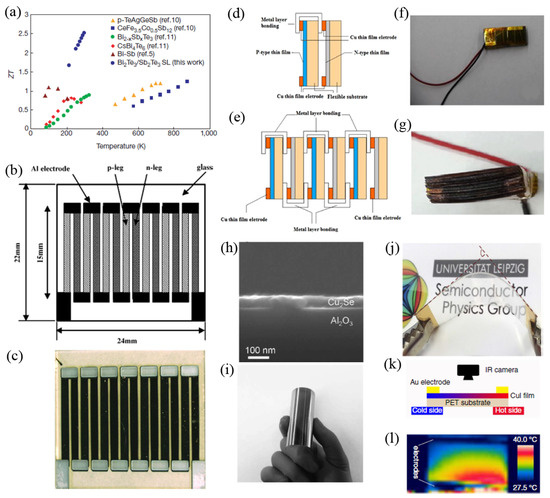
Thin Film Thermoelectric Materials: Classification, Characterization, and Potential for Wearable Applications
by
Xinqi Chen, Wei Dai, Tian Wu, Wei Luo, Jianping Yang, Wan Jiang and Lianjun Wang
Cited by 70 | Viewed by 13438
Abstract
Thermoelectric technology has the ability to convert heat directly into electricity and vice versa. With the rapid growth of portable and wearable electronics and miniature devices, the self-powered and maintenance of free thermoelectric energy harvester is highly desired as a potential power supply.
[...] Read more.
Thermoelectric technology has the ability to convert heat directly into electricity and vice versa. With the rapid growth of portable and wearable electronics and miniature devices, the self-powered and maintenance of free thermoelectric energy harvester is highly desired as a potential power supply. Thin film thermoelectric materials are lightweight, mechanically flexible, and they can be synthesized from abundant resources and processed with a low-cost procedure, which offers the potential to develop the novel thermoelectric devices and hold unique promise for future electronics and miniature accessories. Here, a general classification for thin film thermoelectric materials varied by material compositions, and thermoelectric properties depended on different measurement technique. Several new flexible thermoelectric strategies are summarized with the hope that they can inspire further development of novel thermoelectric applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
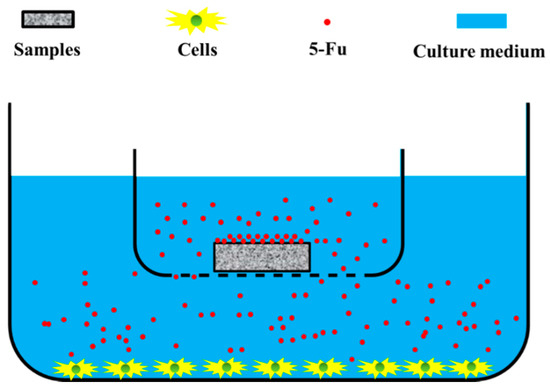
Open AccessArticle
Surface Modification of Esophageal Stent Materials by a Drug-Eluting Layer for Better Anti-Restenosis Function
by
Yuxin Bai, Kun Zhang, Ru Xu, Hongtao Liu, Fangxia Guan, Huiwen Luo, Ye Chen and Jingan Li
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 5868
Abstract
It is generally accepted that stent implantation is the mainstream therapy in clinics for esophageal cancer in the later period. However, the restenosis caused by tumor cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts seriously interferes with the stent medical application and limits its long-term services.
[...] Read more.
It is generally accepted that stent implantation is the mainstream therapy in clinics for esophageal cancer in the later period. However, the restenosis caused by tumor cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts seriously interferes with the stent medical application and limits its long-term services. To address this conundrum, a series of drug-eluting stents were invented and verified to be feasible in the early stage after implantation, but the limited drug loading and good cell compatibility of the stent materials may lead to more serious restenosis and further endanger the patient’s life. In previous work, we modified the esophageal stent material 317L stainless steel (317L SS) surface with a poly-dopamine/poly-ethylenimine layer (PDA/PEI), which had strong anti-tumor functions. In this contribution, we employed a usual drug in clinic, 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu), with series of density onto the PDA/PEI modified 317L SS to investigate the influence of 5-Fu immobilization on the anti-restenosis function. The surface characterization including 5-Fu quantity, atomic force microscopy (AFM). Water contact angle measurement indicated successful preparation of the PDA/PEI/5-Fu layers. The spectrophotometric characterization revealed that the immobilized 5-Fu rapidly released over 24 h. However, the Eca109, Het-1A, and L929 cells culture results suggested that the released 5-Fu made a significant contribution to improving the apoptosis and necrosis of these pathological cells, and the PDA/PEI/5-Fu layers maintain the consistent anti-restenosis function on their surfaces with the PDA/PEI layer after 24 h. All the results demonstrated the PDA/PEI/5-Fu layers’ excellent ability to suppress esophageal tumor cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts, suggesting a potential application on the surface modification of esophageal stents for better anti-restenosis function.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Porous Zinc Oxide Thin Films: Synthesis Approaches and Applications
by
Marco Laurenti and Valentina Cauda
Cited by 84 | Viewed by 18717
Abstract
Zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films have been widely investigated due to their multifunctional properties, i.e., catalytic, semiconducting and optical. They have found practical use in a wide number of application fields. However, the presence of a compact micro/nanostructure has often limited the resulting
[...] Read more.
Zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films have been widely investigated due to their multifunctional properties, i.e., catalytic, semiconducting and optical. They have found practical use in a wide number of application fields. However, the presence of a compact micro/nanostructure has often limited the resulting material properties. Moreover, with the advent of low-dimensional ZnO nanostructures featuring unique physical and chemical properties, the interest in studying ZnO thin films diminished more and more. Therefore, the possibility to combine at the same time the advantages of thin-film based synthesis technologies together with a high surface area and a porous structure might represent a powerful solution to prepare ZnO thin films with unprecedented physical and chemical characteristics that may find use in novel application fields. Within this scope, this review offers an overview on the most successful synthesis methods that are able to produce ZnO thin films with both framework and textural porosities. Moreover, we discuss the related applications, mainly focused on photocatalytic degradation of dyes, gas sensor fabrication and photoanodes for dye-sensitized solar cells.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures