- Article
IL-6 Blockade Enhances the Efficacy of CDK4/6 Inhibitor in BRCA1-Mutant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- Li Pan,
- Changyou Shi and
- Joungil Choi
- + 1 author
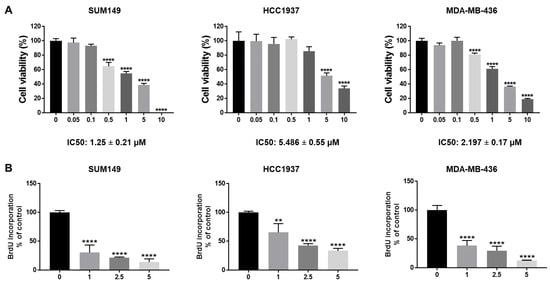
Breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) is a tumor suppressor gene essential for DNA repair, and its mutations are linked to aggressive breast cancers with poor prognosis. While poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors benefit some patients with BRCA1-mutant, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative metastatic breast cancer, issues such as limited efficacy and drug resistance persist. This is especially critical for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which lacks targeted therapies. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors such as abemaciclib—FDA-approved for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer—are emerging as potential treatments for TNBC. We evaluated abemaciclib in BRCA1-mutant TNBC cell lines (SUM149, HCC1937, and MDA-MB-436) and found them to be sensitive to the drug. However, treatment induced cellular senescence and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion, which may promote drug resistance. To address this, we inhibited IL-6 signaling using bazedoxifene or glycoprotein 130 (GP130) siRNA, and both of which enhanced abemaciclib sensitivity. Combination treatment with bazedoxifene and abemaciclib synergistically inhibited cell migration and invasion, and induced apoptosis. In a mammary fat pad TNBC tumor model, the combination treatment significantly suppressed SUM149 tumor growth more than either agent alone. These findings support co-targeting IL-6 and CDK4/6 as a novel therapeutic strategy for BRCA1-mutant TNBC.
15 October 2025