Journal Description
Big Data and Cognitive Computing
Big Data and Cognitive Computing
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on big data and cognitive computing published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), dblp, Inspec, Ei Compendex, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Computer Science, Theory and Methods) / CiteScore - Q1 (Computer Science Applications)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Artificial Intelligence: AI, AI in Medicine, Algorithms, BDCC, MAKE, MTI, Stats, Virtual Worlds and Computers.
Impact Factor:
4.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Spatio-Temporal and Semantic Dual-Channel Contrastive Alignment for POI Recommendation
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 322; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120322 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation predicts users’ future check-ins based on their historical trajectories and plays a key role in location-based services (LBS). Traditional approaches such as collaborative filtering and matrix factorization model user–POI interaction matrices fail to fully leverage spatio-temporal information and semantic attributes,
[...] Read more.
Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation predicts users’ future check-ins based on their historical trajectories and plays a key role in location-based services (LBS). Traditional approaches such as collaborative filtering and matrix factorization model user–POI interaction matrices fail to fully leverage spatio-temporal information and semantic attributes, leading to weak performance on sparse and long-tail POIs. Recently, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been applied by constructing heterogeneous user–POI graphs to capture high-order relations. However, they still struggle to effectively integrate spatio-temporal and semantic information and enhance the discriminative power of learned representations. To overcome these issues, we propose Spatio-Temporal and Semantic Dual-Channel Contrastive Alignment for POI Recommendation (S
(This article belongs to the Topic Graph Neural Networks and Learning Systems)
Open AccessArticle
A Tabular Data Imputation Technique Using Transformer and Convolutional Neural Networks
by
Charlène Béatrice Bridge-Nduwimana, Salah Eddine El Harrauss, Aziza El Ouaazizi and Majid Benyakhlef
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 321; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120321 (registering DOI) - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Upstream processes strongly influence downstream analysis in sequential data-processing workflows, particularly in machine learning, where data quality directly affects model performance. Conventional statistical imputations often fail to capture nonlinear dependencies, while deep learning approaches typically lack uncertainty quantification. We introduce a hybrid imputation
[...] Read more.
Upstream processes strongly influence downstream analysis in sequential data-processing workflows, particularly in machine learning, where data quality directly affects model performance. Conventional statistical imputations often fail to capture nonlinear dependencies, while deep learning approaches typically lack uncertainty quantification. We introduce a hybrid imputation model that integrates a deep learning autoencoder with Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) layers and a Transformer-based contextual modeling architecture to address systematic variation across heterogeneous data sources. Performing multiple imputations in the autoencoder–transformer latent space and averaging representations provides implicit batch correction that suppresses context-specific remains without explicit batch identifiers. We performed experiments on datasets in which 10% of missing data was artificially introduced by completely random missing data (MCAR) and non-random missing data (MNAR) mechanisms. They demonstrated practical performance, jointly ranking first among the imputation methods evaluated. This imputation technique reduced the root mean square error (RMSE) by 50% compared to denoising autoencoders (DAE) and by 46% compared to iterative imputation (MICE). Performance was comparable for adversarial models (GAIN) and attention-based models (MIDA), and both provided interpretable uncertainty estimates (CV = 0.08–0.15). Validation on datasets from multiple sources confirmed the robustness of the technique: notably, on a forensic dataset from multiple laboratories, our imputation technique achieved a practical improvement over GAIN (0.146 vs. 0.189 RMSE), highlighting its effectiveness in mitigating batch effects.
Full article
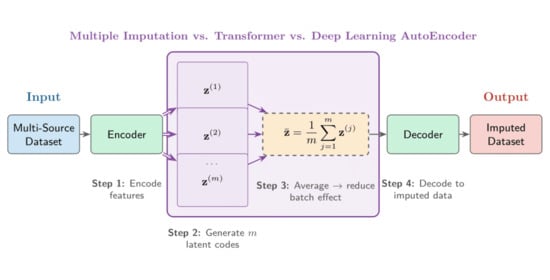
Graphical abstract
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Literature Review of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Techniques, Metrics, and Challenges
by
Andrew Brown, Muhammad Roman and Barry Devereux
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 320; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120320 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) aims to reduce hallucinations and outdated knowledge by grounding LLM outputs in retrieved evidence, but empirical results are scattered across tasks, systems, and metrics, limiting cumulative insight. Objective: We aimed to synthesise empirical evidence on RAG effectiveness versus parametric-only
[...] Read more.
Background: Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) aims to reduce hallucinations and outdated knowledge by grounding LLM outputs in retrieved evidence, but empirical results are scattered across tasks, systems, and metrics, limiting cumulative insight. Objective: We aimed to synthesise empirical evidence on RAG effectiveness versus parametric-only baselines, map datasets/architectures/evaluation practices, and surface limitations and research gaps. Methods: This systematic review was conducted and reported in accordance with PRISMA 2020. We searched the ACM Digital Library, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and DBLP; all sources were last searched on 13 May 2025. This included studies from January 2020–May 2025 that addressed RAG or similar retrieval-supported systems producing text output, met citation thresholds (≥15 for 2025; ≥30 for 2024 or earlier), and offered original contributions; excluded non-English items, irrelevant works, duplicates, and records without accessible full text. Bias was appraised with a brief checklist; screening used one reviewer with an independent check and discussion. LLM suggestions were advisory only; 2025 citation thresholds were adjusted to limit citation-lag. We used a descriptive approach to synthesise the results, organising studies by themes aligned to RQ1–RQ4 and reporting summary counts/frequencies; no meta-analysis was undertaken due to heterogeneity of designs and metrics. Results: We included 128 studies spanning knowledge-intensive tasks (35/128; 27.3%), open-domain QA (20/128; 15.6%), software engineering (13/128; 10.2%), and medical domains (11/128; 8.6%). Methods have shifted from DPR+seq2seq baselines to modular, policy-driven RAG with hybrid/structure-aware retrieval, uncertainty-triggered loops, memory, and emerging multimodality. Evaluation remains overlap-heavy (EM/
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP))
Open AccessArticle
Identifying New Promising Research Directions with Open Peer Reviews and Contextual Top2Vec
by
Dmitry Devyatkin, Ilya V. Sochenkov, Dmitrii Popov, Denis Zubarev, Anastasia Ryzhova, Fyodor Abanin and Oleg Grigoriev
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 319; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120319 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The reliable and early detection of promising research directions is of great practical importance, especially in cases of limited resources. It enables researchers, funding experts, and science authorities to focus their efforts effectively. Although citation analysis has been commonly considered the primary tool
[...] Read more.
The reliable and early detection of promising research directions is of great practical importance, especially in cases of limited resources. It enables researchers, funding experts, and science authorities to focus their efforts effectively. Although citation analysis has been commonly considered the primary tool to detect directions for a long time, it lacks responsiveness, as it requires time for citations to emerge. In this paper, we propose a conceptual framework that detects new research directions with a contextual Top2Vec model, collects and analyzes reviews for those directions via Transformer-based classifiers, ranks them, and generates short summaries for the highest-scoring ones with a BART model. Averaging review scores for a whole topic helps mitigate the review bias problem. Experiments on past ICLR open reviews show that the highly ranked directions detected are significantly better cited; additionally, in most cases, they exhibit better publication dynamics.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Intelligent Modulation Recognition of Frequency-Hopping Communications: Theory, Methods, and Challenges
by
Mengxuan Lan, Zhongqiang Luo and Mingjun Jiang
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 318; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120318 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In wireless communication, information security, and anti-interference technology, modulation recognition of frequency-hopping signals has always been a key technique. Its widespread application in satellite communications, military communications, and drone communications holds broad prospects. Traditional modulation recognition techniques often rely on expert experience to
[...] Read more.
In wireless communication, information security, and anti-interference technology, modulation recognition of frequency-hopping signals has always been a key technique. Its widespread application in satellite communications, military communications, and drone communications holds broad prospects. Traditional modulation recognition techniques often rely on expert experience to construct likelihood functions or manually extract relevant features, involving cumbersome steps and low efficiency. In contrast, deep learning-based modulation recognition replaces manual feature extraction with an end-to-end feature extraction and recognition integrated architecture, where neural networks automatically extract signal features, significantly enhancing recognition efficiency. Current deep learning-based modulation recognition research primarily focuses on conventional fixed-frequency signals, leaving gaps in intelligent modulation recognition for frequency-hopping signals. This paper aims to summarise the current research progress in intelligent modulation recognition for frequency-hopping signals. It categorises intelligent modulation recognition for frequency-hopping signals into two mainstream approaches, analyses them in conjunction with the development of intelligent modulation recognition, and explores the close relationship between intelligent modulation recognition and parameter estimation for frequency-hopping signals. Finally, the paper summarises and outlines future research directions and challenges in the field of intelligent modulation recognition for frequency-hopping signals.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automated Trading Framework Using LLM-Driven Features and Deep Reinforcement Learning
by
Ive Botunac, Tomislav Petković and Jurica Bosna
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 317; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120317 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Stock trading faces significant challenges due to market volatility and the complexity of integrating diverse data sources, such as financial texts and numerical market data. This paper proposes an innovative automated trading system that integrates advanced natural language processing (NLP) and deep reinforcement
[...] Read more.
Stock trading faces significant challenges due to market volatility and the complexity of integrating diverse data sources, such as financial texts and numerical market data. This paper proposes an innovative automated trading system that integrates advanced natural language processing (NLP) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to address these challenges. The system combines two novel components: PrimoGPT, a Transformer-based NLP model fine-tuned on financial texts using instruction-based datasets to generate actionable features like sentiment and trend direction, and PrimoRL, a DRL model that expands its state space with these NLP-derived features for enhanced decision-making precision compared to traditional DRL models like FinRL. An experimental evaluation over seven months of leading technology stocks reveals cumulative returns of up to 58.47% for individual stocks and 27.14% for a diversified portfolio, with a Sharpe ratio of 1.70, outperforming traditional and advanced benchmarks. This work advances AI-driven quantitative finance by offering a scalable framework that bridges qualitative analysis and strategic action, thereby fostering smarter and more equitable participation in financial markets.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Confidence-Guided Code Recognition for Shipping Containers Using Deep Learning
by
Sanele Hlabisa, Ray Leroy Khuboni and Jules-Raymond Tapamo
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 316; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120316 - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Shipping containers are vital to the transportation industry due to their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with intermodal systems. With the significant increase in container usage since the mid-20th century, manual tracking at port terminals has become inefficient and prone to errors. Recent advancements in
[...] Read more.
Shipping containers are vital to the transportation industry due to their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with intermodal systems. With the significant increase in container usage since the mid-20th century, manual tracking at port terminals has become inefficient and prone to errors. Recent advancements in Deep Learning for object detection have introduced Computer Vision as a solution for automating this process. However, challenges such as low-quality images, varying font sizes & illumination, and environmental conditions hinder recognition accuracy. This study explores various architectures and proposes a Container Code Localization Network (CCLN), utilizing ResNet and UNet for code identification, and a Container Code Recognition Network (CCRN), which combines Convolutional Neural Networks with Long Short-Term Memory to convert the image text into a machine-readable format. By enhancing existing shipping container localization and recognition datasets with additional images, our models exhibited improved generalization capabilities on other datasets, such as Syntext, for text recognition. Experimental results demonstrate that our system achieves
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sentence-Level Rhetorical Role Labeling in Judicial Decisions
by
Gergely Márk Csányi, István Üveges, Dorina Lakatos, Dóra Ripszám, Kornélia Kozák, Dániel Nagy and János Pál Vadász
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 315; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120315 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper presents an in-production Rhetorical Role Labeling (RRL) classifier developed for Hungarian judicial decisions. RRL is a sequential classification problem in Natural Language Processing, aiming to assign functional roles (such as facts, arguments, decision, etc.) to every segment or sentence in a
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an in-production Rhetorical Role Labeling (RRL) classifier developed for Hungarian judicial decisions. RRL is a sequential classification problem in Natural Language Processing, aiming to assign functional roles (such as facts, arguments, decision, etc.) to every segment or sentence in a legal document. The study was conducted on a human-annotated sentence-level RRL corpus and compares multiple neural architectures, including BiLSTM, attention-based networks, and a support vector machine as baseline. It further investigates the impact of late chunking during vectorization, in contrast to classical approaches. Results from tests on the labeled dataset and annotator agreement statistics are reported, and performance is analyzed across architecture types and embedding strategies. Contrary to recent findings in retrieval tasks, late chunking does not show consistent improvements for sentence-level RRL, suggesting that contextualization through chunk embeddings may introduce noise rather than useful context in Hungarian legal judgments. The work also discusses the unique structure and labeling challenges of Hungarian cases compared to international datasets and provides empirical insights for future legal NLP research in non-English court decisions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sophimatics: A Two-Dimensional Temporal Cognitive Architecture for Paradox-Resilient Artificial Intelligence
by
Gerardo Iovane and Giovanni Iovane
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 314; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120314 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work represents the natural continuation of the development of the cognitive architecture developed and named Sophimatics, organically integrating the spatio-temporal processing mechanisms of the Super Time Cognitive Neural Network (STCNN) with the advanced principles of Sophimatics. Sophimatics’ goal is as challenging as
[...] Read more.
This work represents the natural continuation of the development of the cognitive architecture developed and named Sophimatics, organically integrating the spatio-temporal processing mechanisms of the Super Time Cognitive Neural Network (STCNN) with the advanced principles of Sophimatics. Sophimatics’ goal is as challenging as it is fraught with obstacles, but its ultimate aim is to achieve a more humanized post-generative artificial intelligence, capable of understanding and analyzing context and evaluating the user’s purpose and intent, viewing time not only as a chronological sequence but also as an experiential continuum. The path to achieving this extremely ambitious goal has been made possible thanks to some previous work in which the philosophical thinking of interest in AI was first inherited as the inspiration for the aforementioned capabilities of the Sophimatic framework, then the issue of mapping concepts and philosophical thinking in Sophimatics’ AI infrastructure was addressed, and finally a cognitive-inspired network such as STCNN was created. This work, on the other hand, addresses the challenge of how to endow the infrastructure with both chronological and experiential time and its powerful implications, such as the innate ability to resolve paradoxes, which generative AI does not have among its prerogatives precisely because of structural limitations. To reach these results, the model operates in the two-dimensional complex time domain ℂ2, extending cognitive processing capabilities through the implementation of dual temporal operators that simultaneously manage the real temporal dimension, where past, present, and future are managed and the imaginary one, that considers memory, creativity, and imagination. The resulting architecture demonstrates superior capabilities in resolving informational paradoxes and integrating apparently contradictory cognitive states, maintaining computational coherence through adaptive Sophimatic mechanisms. In conclusion, this work introduces Phase 4 of the Sophimatic framework, enabling management of two-dimensional time within a novel cognitively inspired neural architecture grounded in philosophical concepts. It connects with existing research on temporal cognition, hybrid symbolic–connectionist models, and ethical AI. The methodology translates philosophical insights into formal computational systems, culminating in a mathematical formalization that supports two-dimensional temporal reasoning and paradox resolution. Experimental results demonstrate efficiency, predictive accuracy, and computational feasibility, highlighting potential real-world applications, future research directions, and present limitations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SpaceTime: A Deep Similarity Defense Against Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning
by
Geethapriya Thamilarasu and Christian Dunham
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 313; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120313 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Federated learning has gained popularity in recent years to enhance IoT security because the model allows decentralized devices to collaboratively learn a shared model without exchanging raw data. Despite its privacy advantages, federated learning is vulnerable to poisoning attacks, where malicious devices introduce
[...] Read more.
Federated learning has gained popularity in recent years to enhance IoT security because the model allows decentralized devices to collaboratively learn a shared model without exchanging raw data. Despite its privacy advantages, federated learning is vulnerable to poisoning attacks, where malicious devices introduce manipulated data or model updates to corrupt the global model. These attacks can degrade the model’s performance or bias its outcomes, making it difficult to ensure the integrity of the learning process across decentralized devices. In this research, our goal is to develop a defense mechanism against poisoning attacks in federated learning models. Specifically, we develop a spacetime model, that combines the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a four-dimensional manifold. Poisoning attacks have complex spatial and time relationships that present identifiable patterns in that manifold. We propose SpaceTime-Deep Similarity Defense (ST-DSD), a deep learning recurrent neural network that includes space and time perceptions to provide a defense against poisoning attacks for federated learning models. The proposed mechanism is built upon a time series regression many-to-one architecture using spacetime relationships to provide an adversarial trained deep learning poisoning defense. Simulation results show that SpaceTime defense outperforms existing solutions for poisoning defenses in IoT environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine Learning Methodologies and Applications in Cybersecurity Data Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Subjective Evaluation of Operator Responses for Mobile Defect Identification in Remanufacturing: Application of NLP and Disagreement Tagging
by
Abbirah Ahmed, Reenu Mohandas, Arash Joorabchi and Martin J. Hayes
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 312; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120312 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
In the context of remanufacturing, particularly mobile device refurbishing, effective operator training is crucial for accurate defect identification and process inspection efficiency. This study examines the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to evaluate operator expertise based on subjective textual responses gathered
[...] Read more.
In the context of remanufacturing, particularly mobile device refurbishing, effective operator training is crucial for accurate defect identification and process inspection efficiency. This study examines the application of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to evaluate operator expertise based on subjective textual responses gathered during a defect analysis task. Operators were asked to describe screen defects using open-ended questions, and their responses were compared with expert responses to evaluate their accuracy and consistency. We employed four NLP models, including finetuned Sentence-BERT (SBERT), pre-trained SBERT, Word2Vec, and Dice similarity, to determine their effectiveness in interpreting short, domain-specific text. A novel disagreement tagging framework was introduced to supplement traditional similarity metrics with explainable insights. This framework identifies the root causes of model–human misalignment across four categories: defect type, severity, terminology, and location. Results show that a finetuned SBERT model significantly outperforms other models by achieving Pearsons’s correlation of 0.93 with MAE and RMSE scores of 0.07 and 0.12, respectively, providing more accurate and context-aware evaluations. In contrast, other models exhibit limitations in semantic understanding and consistency. The results highlight the importance of finetuning NLP models for domain-specific applications and demonstrate how qualitative tagging methods can enhance interpretability and model debugging. This combined approach indicates a scalable and transparent methodology for the evaluation of operator responses, supporting the development of more effective training programmes in industrial settings where remanufacturing and sustainability generally are a key performance metric.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Course Recommendation with LLM-Generated Concepts: A Unified Framework for Side Information Integration
by
Tianyuan Yang, Baofeng Ren, Chenghao Gu, Feike Xu, Boxuan Ma and Shin’ichi Konomi
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 311; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120311 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have gained increasing popularity in recent years, highlighting the growing importance of effective course recommendation systems (CRS). However, the performance of existing CRS methods is often limited by data sparsity and suffers under cold-start scenarios. One promising solution
[...] Read more.
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have gained increasing popularity in recent years, highlighting the growing importance of effective course recommendation systems (CRS). However, the performance of existing CRS methods is often limited by data sparsity and suffers under cold-start scenarios. One promising solution is to leverage course-level conceptual information as side information to enhance recommendation performance. We propose a general framework for integrating LLM-generated concepts as side information into various classic recommendation algorithms. Our framework supports multiple integration strategies and is evaluated on two real-world MOOC datasets, with particular focus on the cold-start setting. The results show that incorporating LLM-generated concepts consistently improves recommendation quality across diverse models and datasets, demonstrating that automatically generated semantic information can serve as an effective, reusable, and scalable source of side knowledge for educational recommendations. This finding suggests that LLMs can function not merely as content generators but as practical data augmenters, offering a new direction for enhancing robustness and generalizability in course recommendation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Attention-Based BERT–CNN–BiLSTM Model for Depression Detection from Emojis in Social Media Text
by
Joel Philip Thekkekara and Sira Yongchareon
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 310; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120310 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Depression represents a critical global mental health challenge, with social media offering unprecedented opportunities for early detection through computational analysis. We propose a novel BERT–CNN–BiLSTM architecture with attention mechanisms that systematically integrate emoji usage patterns—fundamental components of digital emotional expression overlooked by existing
[...] Read more.
Depression represents a critical global mental health challenge, with social media offering unprecedented opportunities for early detection through computational analysis. We propose a novel BERT–CNN–BiLSTM architecture with attention mechanisms that systematically integrate emoji usage patterns—fundamental components of digital emotional expression overlooked by existing approaches. Evaluated on the SuicidEmoji dataset, our model achieves 97.12% accuracy, 94.56% precision, 93.44% F1-score, 85.67% MCC, and 91.23% AUC-ROC. Analysis reveals distinct emoji patterns: depressed users favour negative emojis (😔 13.9%, 😢 12.8%, 💔 6.7%) while controls prefer positive expressions (😂 16.5%, 😊 11.0%, 😎 10.2%). The attention mechanism identifies key linguistic markers, including emotional indicators, personal pronouns, and emoji features, providing interpretable insights into depression-related language. Our findings suggest that the integration of emojis substantially improves optimal social media-based mental health detection systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Faithfulness in Agentic RAG Systems for e-Governance Applications Using LLM-Based Judging Frameworks
by
George Papageorgiou, Vangelis Sarlis, Manolis Maragoudakis, Ioannis Magnisalis and Christos Tjortjis
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 309; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120309 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
As Large Language Models (LLMs) are core components in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems for knowledge-intensive tasks, concerns regarding hallucinations, redundancy, and unverifiable outputs have intensified, particularly in high-stakes domains, such as e-government. This study proposes a modular, multi-pipeline framework for statement-level faithfulness evaluation
[...] Read more.
As Large Language Models (LLMs) are core components in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems for knowledge-intensive tasks, concerns regarding hallucinations, redundancy, and unverifiable outputs have intensified, particularly in high-stakes domains, such as e-government. This study proposes a modular, multi-pipeline framework for statement-level faithfulness evaluation for characterizing hallucination and redundancy across both simple and agentic RAG pipelines. Using GPT-4.1, Claude Sonnet-4.0, and Gemini 2.5 Pro as LLM-based judges, this study examines how tool-specific attribution within agentic multi-tool architectures influences the interpretability and traceability of the generated content. By using a modular agentic RAG framework combining symbolic (GraphRAG), semantic (embedding), and real-time (web) retrieval, we benchmark hallucination and redundancy patterns, using state-of-the-art LLM judges. The study examines RAG and agent-based pipelines that attribute outputs to distinct tools, in contrast to traditional single-source RAG systems that rely on aggregated retrieval. Using e-government data sourced from the European Commission’s Press Corner, our evaluation framework assesses not only the frequency, but also the source-aware detectability of hallucinated content. The findings provide actionable insights into how source granularity and retrieval orchestration impact faithfulness evaluation across different pipeline architectures, while also suggesting new directions for explainability-aware RAG design. The study contributes a reproducible, modular framework for automated faithfulness assessment, with implications for transparency, governance compliance, and trustworthy AI deployment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Generative AI and Large Language Models)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High-Speed Scientific Computing Using Adaptive Spline Interpolation
by
Daniel S. Soper
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 308; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120308 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing scale of modern datasets has created a significant computational bottleneck for traditional scientific and statistical algorithms. To address this problem, the current paper describes and validates a high-performance method based on adaptive spline interpolation that can dramatically accelerate the calculation of
[...] Read more.
The increasing scale of modern datasets has created a significant computational bottleneck for traditional scientific and statistical algorithms. To address this problem, the current paper describes and validates a high-performance method based on adaptive spline interpolation that can dramatically accelerate the calculation of foundational scientific and statistical functions. This is accomplished by constructing parsimonious spline models that approximate their target functions within a predefined, highly precise maximum error tolerance. The efficacy of the adaptive spline-based solutions was evaluated through benchmarking experiments that compared spline models against the widely used algorithms in the Python SciPy library for the normal, Student’s t, and chi-squared cumulative distribution functions. Across 30 trials of 10 million computations each, the adaptive spline models consistently achieved a maximum absolute error of no more than 1 × 10−8 while simultaneously ranging between 7.5 and 87.4 times faster than their corresponding SciPy algorithms. All of these improvements in speed were observed to be statistically significant at p < 0.001. The findings establish that adaptive spline interpolation can be both highly accurate and much faster than traditional scientific and statistical algorithms, thereby offering a practical pathway to accelerate both the analysis of large datasets and the progress of scientific inquiry.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CAFE-Dance: A Culture-Aware Generative Framework for Chinese Folk and Ethnic Dance Synthesis via Self-Supervised Cultural Learning
by
Bin Niu, Rui Yang, Qiuyu Zhang, Yani Zhang and Ying Fan
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 307; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120307 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
As a vital carrier of human intangible culture, dance plays an important role in cultural transmission through digital generation. However, existing dance generation methods rely heavily on high-precision motion capture and manually annotated datasets, and they fail to effectively model the culturally distinctive
[...] Read more.
As a vital carrier of human intangible culture, dance plays an important role in cultural transmission through digital generation. However, existing dance generation methods rely heavily on high-precision motion capture and manually annotated datasets, and they fail to effectively model the culturally distinctive movements of Chinese ethnic folk dance, resulting in semantic distortion and cross-modal mismatch. Building on the Chinese traditional ethnic Helou Dance, this paper proposes a culture-aware Chinese ethnic folk dance generation framework, CAFE-Dance, which dispenses with manual annotation and automatically generates dance sequences that achieve high cultural fidelity, precise music synchronization, and natural, fluent motion. To address the high cost and poor scalability of cultural annotation, we introduce a Zero-Manual-Label Cultural Data Construction Module (ZDCM) that performs self-supervised cultural learning from raw dance videos, using cross-modal semantic alignment and a knowledge-base-guided automatic annotation mechanism to construct a high-quality dataset of Chinese ethnic folk dance covering 108 classes of curated cultural attributes without any frame-level manual labels. To address the difficulty of modeling cultural semantics and the weak interpretability, we propose a Culture-Aware Attention Mechanism (CAAM) that incorporates cultural gating and co-attention to adaptively enhance culturally key movements. To address the challenge of aligning the music–motion–culture tri-modalities, we propose a Tri-Modal Alignment Network (TMA-Net) that achieves dynamic coupling and temporal synchronization of tri-modal semantics under weak supervision. Experimental results show that our framework improves Beat Alignment and Cultural Accuracy by 4.0–5.0 percentage points and over 30 percentage points, respectively, compared with the strongest baseline (Music2Dance), and it reveals an intrinsic coupling between cultural embedding density and motion stability. The code and the curated Helouwu dataset are publicly available.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Generative AI and Interdisciplinary Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ECA110-Pooling: A Comparative Analysis of Pooling Strategies in Convolutional Neural Networks
by
Doru Constantin and Costel Bălcău
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 306; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120306 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pooling strategies are fundamental to convolutional neural networks, shaping the trade-off between accuracy, robustness to spatial variations, and computational efficiency in modern visual recognition systems. In this paper, we present and validate ECA110-Pooling, a novel rule-based pooling operator inspired by elementary cellular automata.
[...] Read more.
Pooling strategies are fundamental to convolutional neural networks, shaping the trade-off between accuracy, robustness to spatial variations, and computational efficiency in modern visual recognition systems. In this paper, we present and validate ECA110-Pooling, a novel rule-based pooling operator inspired by elementary cellular automata. We conduct a systematic comparative study, benchmarking ECA110-Pooling against conventional pooling methods (MaxPooling, AveragePooling, MedianPooling, MinPooling, KernelPooling) as well as state-of-the-art (SOTA) architectures. Experiments on three benchmark datasets—ImageNet (subset), CIFAR-10, and Fashion-MNIST—across training horizons ranging from 20 to 50,000 epochs show that ECA110-Pooling consistently achieves higher Top-1 accuracy, lower error rates, and stronger F1-scores than traditional pooling operators, while maintaining computational efficiency comparable to MaxPooling. Moreover, when compared with SOTA models, ECA110-Pooling delivers competitive accuracy with substantially fewer parameters and reduced training time. These results establish ECA110-Pooling as a principled and validated approach to image classification, bridging the gap between fixed pooling schemes and complex deep architectures. Its interpretable, rule-based design highlights both theoretical significance and practical applicability in contexts that demand a balance of accuracy, efficiency, and scalability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Large Language Models in Mechanical Engineering: A Scoping Review of Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Christopher Baker, Karen Rafferty and Mark Price
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 305; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120305 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
Following PRISMA-ScR guidelines, this scoping review systematically maps the landscape of Large Language Models (LLMs) in mechanical engineering. A search of four major databases (Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Web of Science) and a rigorous screening process yielded 66 studies for final
[...] Read more.
Following PRISMA-ScR guidelines, this scoping review systematically maps the landscape of Large Language Models (LLMs) in mechanical engineering. A search of four major databases (Scopus, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Web of Science) and a rigorous screening process yielded 66 studies for final analysis. The findings reveal a nascent, rapidly accelerating field, with over 68% of publications from 2024 (representing a year-on-year growth of 150% from 2023 to 2024), and applications concentrated on front-end design processes like conceptual design and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) generation. The technological landscape is dominated by OpenAI’s GPT-4 variants. A persistent challenge identified is weak spatial and geometric reasoning, shifting the primary research bottleneck from traditional data scarcity to inherent model limitations. This, alongside reliability concerns, forms the main barrier to deeper integration into engineering workflows. A consensus on future directions points to the need for specialized datasets, multimodal inputs to ground models in engineering realities, and robust, engineering-specific benchmarks. This review concludes that LLMs are currently best positioned as powerful ‘co-pilots’ for engineers rather than autonomous designers, providing an evidence-based roadmap for researchers, practitioners, and educators.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Traffic Rules Training Platform Using LLMs and Cloud Video Streaming
by
Artem Kazarian, Vasyl Teslyuk, Oleh Berezsky and Oleh Pitsun
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 304; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120304 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Driving safety education remains a critical societal priority, and understanding traffic rules is essential for reducing road accidents and improving driver awareness. This study presents the development and evaluation of a virtual simulator for learning traffic rules, incorporating spherical video technology and interactive
[...] Read more.
Driving safety education remains a critical societal priority, and understanding traffic rules is essential for reducing road accidents and improving driver awareness. This study presents the development and evaluation of a virtual simulator for learning traffic rules, incorporating spherical video technology and interactive training scenarios. The primary objective was to enhance the accessibility and effectiveness of traffic rule education by utilizing modern virtual reality approaches without the need for specialized equipment. A key research component is using Petri net-based models to study the simulator’s dynamic states, enabling the analysis and optimization of system behavior. The developed simulator employs large language models for the automated generation of educational content and test questions, supporting personalized learning experiences. Additionally, a model for determining the camera rotation angle was proposed, ensuring a realistic and immersive presentation of training scenarios within the simulator. The system’s cloud-based, modular software architecture and cross-platform algorithms ensure flexibility, scalability, and compatibility across devices. The simulator allows users to practice traffic rules in realistic road environments with the aid of spherical videos and receive immediate feedback through contextual prompts. The developed system stands out from existing traffic rule learning platforms by combining spherical video technology, large language model-based content generation, and cloud architecture to create a more interactive, adaptive, and realistic learning experience. The experimental results confirm the simulator’s high efficiency in improving users’ knowledge of traffic rules and practical decision-making skills.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms with Distillation and Quantization for Early Detection of Attacks in Resource-Constrained Systems
by
Mikhail Rusanov, Mikhail Babenko and Maria Lapina
Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9(12), 303; https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9120303 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study addresses the problem of automatic attack detection targeting Linux-based machines and web applications through the analysis of system logs, with a particular focus on reducing the computational requirements of existing solutions. The aim of the research is to develop and evaluate
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the problem of automatic attack detection targeting Linux-based machines and web applications through the analysis of system logs, with a particular focus on reducing the computational requirements of existing solutions. The aim of the research is to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of machine learning models capable of classifying system events as benign or malicious, while also identifying the type of attack under resource-constrained conditions. The Linux-APT-Dataset-2024 was employed as the primary source of data. To mitigate the challenge of high computational complexity, model optimization techniques such as parameter quantization, knowledge distillation, and architectural simplifications were applied. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approaches significantly reduce computational overhead and hardware requirements while maintaining high classification accuracy. The findings highlight the potential of optimized machine learning algorithms for the development of practical early threat detection systems in Linux environments with limited resources, which is particularly relevant for deployment in IoT devices and edge computing systems.
Full article

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- BDCC Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Topical Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Actuators, Algorithms, BDCC, Future Internet, JMMP, Machines, Robotics, Systems
Smart Product Design and Manufacturing on Industrial Internet
Topic Editors: Pingyu Jiang, Jihong Liu, Ying Liu, Jihong YanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Computers, Information, AI, Electronics, Technologies, BDCC
Graph Neural Networks and Learning Systems
Topic Editors: Huijia Li, Jun Hu, Weichen Zhao, Jie CaoDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
AI, BDCC, Fire, GeoHazards, Remote Sensing
AI for Natural Disasters Detection, Prediction and Modeling
Topic Editors: Moulay A. Akhloufi, Mozhdeh ShahbaziDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, J. Imaging, MAKE, Information, BDCC, Signals
Applications of Image and Video Processing in Medical Imaging
Topic Editors: Jyh-Cheng Chen, Kuangyu ShiDeadline: 30 April 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
BDCC
Application of Deep Neural Networks
Guest Editors: Linfeng Zhang, Wanyue Xu, Jiaye TengDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
BDCC
Industrial Applications of IoT and Blockchain for Sustainable Environment
Guest Editors: Xiaodong Liu, Qi Liu, Amjad UllahDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
BDCC
Deep Learning-Based Pose Estimation: Applications in Vision, Robotics, and Beyond
Guest Editors: Jyotindra Narayan, Chaiyawan AuepanwiriyakulDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
BDCC
Transforming Cyber Security Provision Through Utilizing Artificial Intelligence
Guest Editors: Peter R. J. Trim, Yang-Im LeeDeadline: 31 December 2025











