Abstract
This paper describes the development of a CNN model for the analysis of chest X-rays and the automated diagnosis of pneumonia, bacterial or viral, and lung pathologies resulting from COVID-19, offering new insights for further research through the development of an AI-based diagnostic tool, which can be automatically implemented and made available for rapid differentiation between normal pneumonia and COVID-19 starting from X-ray images. The model developed in this work is capable of performing three-class classification, achieving 97.48% accuracy in distinguishing chest X-rays affected by COVID-19 from other pneumonias (bacterial or viral) and from cases defined as normal, i.e., without any obvious pathology. The novelty of our study is represented not only by the quality of the results obtained in terms of accuracy but, above all, by the reduced complexity of the model in terms of parameters and a shorter inference time compared to other models currently found in the literature. The excellent trade-off between the accuracy and computational complexity of our model allows for easy implementation on numerous embedded hardware platforms, such as FPGAs, for the creation of new diagnostic tools to support medical practice.
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated biomedical innovation, demonstrating how advances in biomolecular science, genetic engineering, and digital technologies can rapidly contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of emerging diseases. This shift highlights the importance of integrating scientific and technological capabilities to enable faster responses to future health challenges. The periodic appearance of different variants of COVID-19 shows how the fight against it is ongoing and it provides us with important information on how fast these new infectious diseases can emerge and spread, causing huge economic damage globally. During pandemic years, the demand for a practical method to support disease diagnosis has grown, aiming to allow faster prevention and timely treatment of infections. The viral characteristics have raised the demand for clinical knowledge and information, epidemiological investigations, and rapid diagnostic technologies because the rapid and efficient detection of viruses is required to prevent and contain epidemics. The health, economic and social impacts of COVID-19 have highlighted the urgent need for reliable and accessible diagnostic tools to support rapid containment strategies and informed clinical decisions. The speed with which new infections can spread, as demonstrated by SARS-CoV-2, requires enhanced early diagnosis, epidemiological surveillance, and contact tracing capabilities. Fast and accurate diagnosis by health professionals can help in deciding the placement of resources and efforts, and this mechanism can slow the spread of infectious diseases and reduce mortality. Various methodologies have been tested to date for the identification and diagnosis of COVID-19 since it was first detected. Specifically, whole genome sequencing methods, various CT computed axial tomography-based methods, and electron microscopy have been tested. Meanwhile, the fact that SARS-CoV-1 diagnostic tools have been available for use became advantageous in the diagnosis of COVID-19.
Several diagnostic techniques have been used to identify COVID-19 infection, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most widely used method is the real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which detects viral RNA in respiratory samples such as nasal and oropharyngeal swabs. The gold standard for identifying the virus [1], RT-PCR, is highly sensitive, but it can give false negative results if sampling is not performed optimally or if mutations in the primer target region are present. Furthermore, its application is limited by the need for specialized laboratory equipment and trained personnel, which limits the capacity for daily tests [2].
Rapid antigen tests, on the other hand, offer an immediate and practical solution. Identifying the presence of viral proteins directly from nasopharyngeal samples, these tests can provide an answer in minutes and could be applied in decentralized settings with a low level of training. Although they are extremely convenient and rapid, they do not have a high degree of sensitivity, especially in situations where the viral load is low [3]. Alongside molecular and antigen tests, imaging techniques have proven to be essential in the diagnosis and monitoring of the disease. Computed tomography (CT) has been useful in detecting pulmonary manifestations even in RT-PCR-negative individuals [4]. In contrast, chest X-rays are a more accessible, inexpensive, and widely available imaging modality, particularly suitable for use in triage and the clinical management of patients with COVID-19. Analysis of chest X-rays can provide significant prognostic information. Recent studies have shown that the distribution and severity of pulmonary opacities, assessed by scores assigned to specific areas of the lungs, can predict the clinical evolution of the disease, particularly in young and middle-aged patients. In this context, the automation of X-ray analysis plays a strategic role in supporting rapid clinical decisions.
Early recognition of typical COVID-19 pneumonia patterns with CT can provide important prognostic clues and allow for timely intervention. However, reliance on expensive equipment and specialized radiological interpretation limits its widespread application, particularly in resource-limited settings; therefore, when a patient presents dyspnea, regardless of whether or not they have COVID-19 infection, chest radiography is almost always performed to help distinguish the absence of infection, in general, from COVID-19 lung infection and regular pneumonia, respectively (Figure 1).
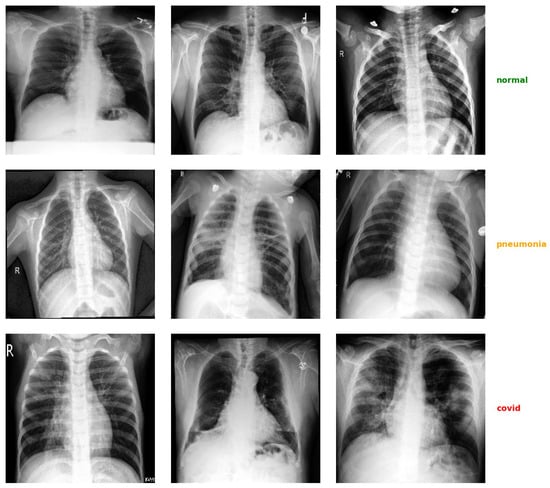
Figure 1.
Example of some chest X-ray images taken from the dataset used in this work, divided by diagnostic class. Each row shows a sequence of images belonging to the same class (normal, pneumonia, COVID-19).
Therefore, more specifically, the use of posteroanterior chest radiographs emerges as the primary imaging modality used for clinical care because it is undoubtedly the most accessible and least expensive method compared to CT, while still managing to offer comparable reliability. By ranking the corresponding scores and a concordant total severity score by lung zone, a study [5] utilizing chest radiography, reviewed by seasoned radiologists, discovered specific features and the presence of opacity divided into six zones. This evidence was also compared with laboratory and clinical examinations. In young and middle-aged adults with COVID-19, lung zone severity scores on baseline chest radiographs accurately predicted outcomes. Then, as indicated in [5], chest radiography images were divided into three zones per lung, and a severity score was assigned based on whether or not opacity was present in each zone. Accordingly, disease severity estimated by chest X-ray was found to be an effective predictor of clinical progression in patients with COVID-19 aged between 21 and 50 years.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and, in particular, deep learning (DL) are revolutionizing the field of diagnostic imaging. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), thanks to their ability to learn complex visual patterns, have proven particularly effective in identifying pathologies from radiological images. Recent advances in machine learning, fueled by large-scale labeled datasets, have enabled the development of models capable of accurately classifying chest images and contributing to the improvement of assisted diagnosis. Moreover, CNNs have shown strong performance in multiclass classification tasks across various domains, demonstrating their versatility as general purpose classifiers [6].
AI-driven tools utilize the help of automation and computer power to provide high-quality image analysis. According to research [7], computer models based on CNN algorithms can compete with and exceed the capabilities of human radiologists in certain activities, such as identifying the presence of different pathologies, including [8], and recognizing COVID-19 on X-rays [9]. Moreover, in [10] m it was calculated that a deep learning system can identify COVID-19 pneumonia from a chest X-ray with similar performance as six radiology technicians and be used to analyze lung cancer from CT scans. In this context, this paper proposes a new lightweight CNN-based framework for the automatic classification of chest radiographic images into three categories: COVID-19, pneumonia (bacterial or viral) and normal subjects.
2. Related Work
It has been shown in the literature [4,11,12,13,14,15] that convolutional neural networks can diagnose pulmonary diseases, such as viral or bacterial pneumonia, directly from chest X-ray images. The most recent models have obtained noticeable accuracies while classifying whether patients were affected by viral pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, or COVID-19 pulmonary infections. In this scenario, chest X-ray imaging can play an important role in quickly delivering results that support decisions in patients’ clinical management [16].
In the literature, several studies have proposed the use of CNNs for the automatic analysis of chest X-rays in the context of COVID-19, as well as for the detection of other lung diseases. Narin et al. [17] reported accuracies of up to 97% focusing on binary classification (COVID vs. normal).
Many of the solutions in the literature with very high accuracies adopt a binary classification scenario, where the model only distinguishes between COVID-19 patients and healthy subjects. Although this type of task results in more impressive accuracy values, it is less representative of a real clinical situation, in which it is essential to be able to discriminate between bacterial or viral non-COVID pneumonia. While several authors in the literature have also tried to mix multiple binary classifiers in a hierarchical setup in order to improve the overall results [18], other studies focused on the ternary classification problem. For example, Li et al. [19] proposed a multi-task learning framework that combines supervised classification with contrastive self-supervision to support the diagnosis of lung diseases from chest radiographs. The architecture is distinguished among COVID-19, pneumonia, and normal conditions, and it was trained on a public dataset. In the ternary classification setting, the network achieved an accuracy of 93.49%. For instance, Lee et al. proposed a hybrid CNN-Transformer model for lung severity classification, which achieves a competitive accuracy, adopting a well-defined positional encoding and lung regional feature extraction. However, their design relies on many parameters and is thus inherently complex, compromising the ease of use for real clinical deployment [20]. In another study, Chakraborty et al. applied a VGG-19 with transfer learning, achieving 97.11% accuracy [21].
Ozturk et al. [22] developed a deep learning model, DarkCOVIDNet, based on a modified DarkNet architecture to classify chest X-ray images using a three-class approach, reaching an accuracy of 87.02%. In the study of Nishio et al. [23], they proposed an EfficientNet-based model for the ternary classification of chest radiographs, achieving 86.67% accuracy. In another study [24], they used a CNN-based model using VGG16 with transfer learning and a combination of conventional and mixup data augmentation to classify chest radiographs into COVID-19 pneumonia, non-COVID-19 pneumonia, and healthy cases. On the test set, the model achieved an average accuracy of 83.6% in the ternary classification task. Goyal et al. [25] propose a framework based on an RNN with LSTM to classify chest X-rays into four categories: COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and normal. After enhancement and ROI-based feature extraction, the model achieved an accuracy of 94.31% on the CXIP dataset.
Hussain et al. [26] proposed CoroDet, 22-layer CNN ternary classifier of pneumonia, COVID-19, and normal samples of chest X-ray and CT scans with a three-class task accuracy of 94.20%. Ukwandu et al. [27] proposed a lightweight deep model of MobileNetV2 for ternary classification of chest X-ray images (normal, COVID-19, viral pneumonia) with 94.5% accuracy. Nayak et al. proposed CORONet [28], a lightweight CNN ternary classifier for COVID-19, pneumonia, and normal chest X-ray image classification classes, where the model achieved 95.67% accuracy. In the context of four-class classification, Islam et al. [29] employed a transfer learning-based approach using the Xception architecture to classify chest X-ray images into four categories, COVID-19, normal, lung opacity and non-COVID viral pneumonia, achieving 93% precision in the four-class classification task. Other contributions, such as [30], reported an F1-score of 93.1% on normal, COVID, and Sars classes subdivided into six categories (two each) thanks to the DeTraC model. As detailed in Section 4.1, the novelty of our approach lies in the trade-off between architectural efficiency, high classification accuracy, and real-time applicability on resource-constrained devices, which existing models have not equally achieved.
3. Proposed Framework
Our proposed framework is composed of several distinct phases that follow the logic of a lightweight deep learning approach, as illustrated in Figure 2. The chest X-ray images, once loaded from the dataset, are subjected to an initial pre-processing phase specifically designed to improve their visual quality by enhancing their contrast and to ensure consistency within the dataset by normalizing their information content. The specific techniques and the related motivations that justify the choice of adopting this pre-processing phase are discussed in detail in Section 3.2. After the pre-processing phase, the processed images are used as input for a convolutional neural network that processes the images and generates, as output, a probability distribution on the three predefined diagnostic categories, namely healthy individuals, cases of pneumonia not associated with COVID-19, and cases of pneumonia caused by COVID-19 infection. The architecture implemented includes a structured sequence of convolutional layers, non-linear activation functions (LeakyReLU), and pooling modules for the hierarchical reduction of spatial dimensions. This approach represents a promising solution for the automation of diagnostic imaging tasks with substantial potential to improve the efficiency and reliability of clinical radiographic diagnostic procedures.
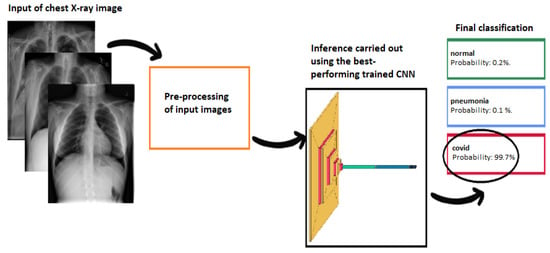
Figure 2.
Pipeline diagram of the proposed framework: the images, once pre-processed, are analyzed by a light convolutional neural network that returns the probability of belonging to the three classes (normal, pneumonia, or COVID-19).
3.1. Dataset
The dataset was constructed by aggregating several publicly available collections of chest radiographic images. In particular, we took images from two public datasets: the first is the COVID-19, Pneumonia and Normal Chest X-ray PA Dataset [31], and the second one is the COVID-19 Radiography Database [32]. In the first dataset, COVID-19 images were taken from various sources [33,34,35,36,37,38] and allowed us to collect a total of 1401 COVID-19 images, while normal and pneumonia images were taken from [39,40], totaling 2313 images for each class. In order to use only the original samples, we removed the 912 augmented COVID-19 images included in the first dataset and added all COVID-19 images (3616) from the second dataset. To obtain a balanced dataset with all classes perfectly balanced, we then added a subset of 2704 images for the pneumonia and normal classes [41]. The final dataset obtained, therefore, consists of a total of 15,051 samples equally divided between the three classes: 5017 COVID-19, 5017 pneumonia, and 5017 normal.
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
The operations applied to the training set followed a defined sequence. First, all images were converted to grayscale so as to emphasize anatomical structures while reducing the dimensionality of the input. Subsequently, we applied contrast enhancement to the images using CLAHE (Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization), an advanced extension of classical adaptive histogram equalization that operates locally on independent subregions of the image. In this specific technique, histogram equalization is applied within each subregion, incorporating a clip limit to prevent possible excessive noise amplification. To ensure visual continuity between the subregions of the image under consideration, bilinear interpolation between adjacent areas is employed. CLAHE has proven to be particularly suitable and effective in medical imaging applications due to its ability to effectively improve the quality and visual contrast of diagnostically relevant anatomical structures [42,43]. Previous studies have shown how basic enhancement techniques, such as this one, help to increase the accuracy of CNN models in classifying chest radiographs, particularly in identifying COVID-19 [41] cases. It is most appropriate for medical images because it increases the visual contrast and quality of the structures of interest. After contrast optimization, all images were scaled to a uniform resolution of 256 × 256 pixels, so as to standardize the input size for model training. Pixel normalization was then applied, with centering and standardization by both features and samples, in order to obtain zero mean and unit variance, facilitating more stable and rapid convergence.
After this step, data augmentation techniques were applied to improve the diversity of the training set. These included horizontal and vertical translations, random rotation with appropriate fill modes to compensate for image edge artifacts, and brightness adjustments to simulate different lighting conditions. These implementations introduced both spatial and photometric variability, thereby improving both the robustness of the model and its ability to generalize to invisible data. As a result, the overall performance of the model was improved by mitigating the risk of overfitting as much as possible, while also reducing noise and improving the visual quality of the images. When training the network without using data augmentation techniques, we observed that it was possible to achieve a maximum accuracy of 95%, which is significantly lower than the performance achieved with our optimized pre-processing pipeline, as shown in Figure 3.
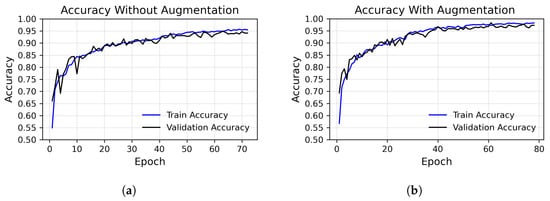
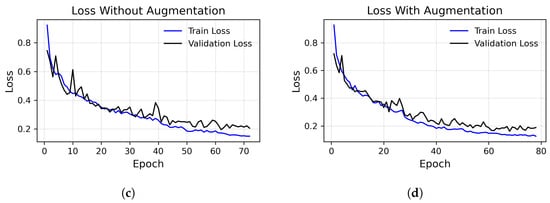
Figure 3.
Loss (top row) and precision (bottom row) over epochs, using the augmented dataset (right column) versus the unaugmented dataset (left column), considering the best execution. (a) Accuracy without augmented images, run with peak at 95%. (b) Accuracy with augmented images, run with peak at 97.48%. (c) Loss without augmented images. (d) Loss with augmented images.
3.3. Network Architecture
The design of the network architecture is a fundamental aspect that we have adequately taken care of to ensure that the most effective possible performances of our proposed model have been guaranteed. To train and evaluate our CNN, we have carefully divided the dataset of pre-classified X-ray images into three distinct subsets: 65% for training, 10% for validation and 25% for testing. This division allowed us to obtain a well-balanced approach, as we provided a large amount of data for training, while ensuring a reliable evaluation through validation and testing, which are fundamental steps to provide a careful evaluation of both the generalization capabilities and the diagnostic accuracy of the model. The network implemented consists of 19 layers and trains 13,143,043 parameters at each epoch, and it was designed to ensure an optimal balance between computational complexity and diagnostic accuracy. In this network, Conv2d layers followed by a LeakyReLU activation function and MaxPooling were utilized. The Conv2d layers had filter sizes of 64, 64, 64, 128, and 128, respectively, with specific parameters for strides, dilation rates, and groups. MaxPooling layers with pool sizes of 2 × 2 were applied after each Conv2d layer. Additionally, there are Flatten, Dropout, and Dense layers, with the Dense layer having 512 units. To reduce the risk of overfitting, the Dropout technique was adopted during training. It works by removing some units from the network. This strategy has been shown to be effective in improving the generalization ability of neural networks [44]. LeakyReLU was adopted as a replacement for standard ReLU to prevent the problem of dying neurons. By permitting a slight slope for negative values of the input, LeakyReLU preserved gradient flow even in inactive regions, which resulted in faster training and improved validation performance. The overall network configuration is shown in Figure 4.
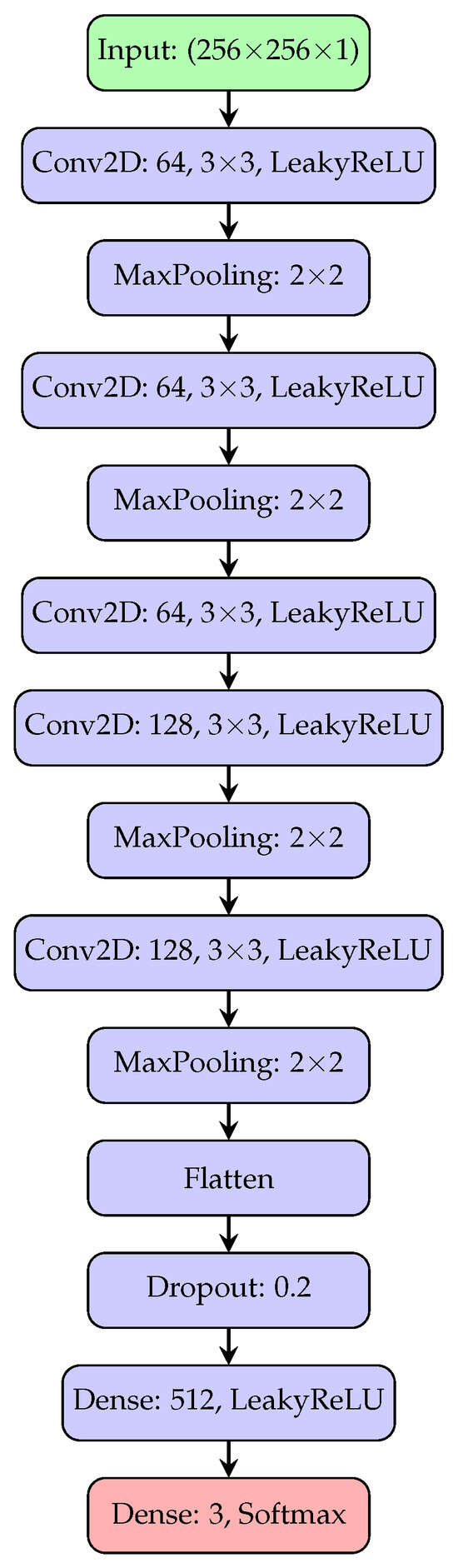
Figure 4.
The architecture of the convolutional neural network implemented in our model consists of five convolutional blocks with filter sizes of 64, 64, 64, 128, and 128, respectively, followed by a MaxPooling layer. The activations are then flattened and passed to a dense layer, with final output produced via a softmax activation function.
We then used the categorical cross-entropy as a loss function for the hyperparameters, which is ideal for a multiclass classification problem. As an optimizer, we used the Adam optimizer for its efficiency and fast convergence capacity. The batch size was set at 32 to balance memory consumption and training stability. Finally, to further improve the network’s generalization and prevent overfitting, two regularization strategies were adopted during the training phase, namely early stopping and learning rate scheduling. Early stopping was applied by monitoring the loss function on the validation set. If it did not show significant improvement for 10 consecutive epochs, the training was stopped. At the same time, a strategy of dynamic adaptation of the learning rate was adopted, in which the automatic reduction of its value was triggered whenever the loss function on the validation set showed a stable trend, thus favoring a finer updating of the weights in the subsequent training phases. This technique, commonly known as the learning rate scheduler [45], helped increase the stability and convergence of the model in the final stages of training.
The pseudocode shown in Algorithm 1 describes, in a concise and structured form, the entire pipeline of the proposed method for the automatic classification of chest X-ray images into three diagnostic classes: normal, pneumonia, and COVID-19. The process begins with a data preparation phase, in which each image is normalized, converted to grayscale, contrast-equalized, and resized to a uniform size, as already described in more detail in Section 3.2. The training and validation subsets of the initial dataset, thus pre-processed, were then used in the training phase, also adopting data augmentation techniques such as rotation, translation and brightness variation. This improved the variability of the dataset in the training phase and, consequently, the generalization ability of the model. This is followed by the construction of the CNN model using a sequential architecture. The next phase involves compiling the model, in which we specified the loss function (categorical cross-entropy), the optimizer (Adam), and the main evaluation metric (accuracy). Once the learning phase is complete, the model is tested on the subset of images not used during training (test set), and the results are evaluated quantitatively (accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score) and displayed graphically through learning curves (loss and accuracy) and a confusion matrix. This approach has demonstrated solid performance in distinguishing between the three clinical classes, confirming the effectiveness of the proposed pipeline in the classification of lung diseases from X-ray images.
| Algorithm 1: Pseudocoded flowchart of the proposed framework for automatic classification of chest X-ray images. |
Input: Chest X-ray images Output: Prediction: Normal / Pneumonia / COVID-19
|
4. Results
During the training phase, we monitored the loss and accuracy at each epoch on the training and validation sets. In particular, given that our classifier is characterized by a three-class model, these metrics were applied individually for each class. The performance of the model on the test set was then evaluated using a confusion matrix and a specific set of additional metrics, such as precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy, all calculated separately for each class.
Given the true positives as the number of correctly classified samples in each class i, the false positives as the number of samples incorrectly classified for each class, and the false negatives as the number of samples belonging to the class but misclassified, we computed the precision () for each class as
the recall () for each class as
and the F1-score () for each class as
Therefore, we computed, as a key performance metric, the overall accuracy (ACC) as
and the macro averaged F1-score () as
These functions were used to evaluate the progress of both the training of the model and its level of generalization by monitoring these values in the validation set appropriately at each training epoch in order to avoid overfitting. The absence of significant divergence between the training and validation metrics indicates that the model is neither overfitting nor underfitting, maintaining stable performance throughout the training process. The accuracy and loss trends, presented in Figure 3, correspond to the best run of our model, which achieved an accuracy of 97.48%.
Through the Keras, TensorFlow predict class, an array of the predictions computed by the trained model was then created for each of the images in the test set, and all predictions made by the model were verified. In Figure 5, there is a subset of the predictions made on the test set shown directly on the chest X-ray images.
Figure 5.
Examples of classification performed by our model on some images taken from the test set.
The confusion matrix, shown in Figure 6, provides a detailed evaluation of the model’s performance on each class that is analyzed in the classification report in Table 1 and Table 2. The matrix highlights that the model correctly classified 1222 images belonging to the normal class, making 20 errors towards the pneumonia class and 12 towards the COVID-19 class. For the pneumonia class, the model correctly identified 1215 images, while it incorrectly classified 18 images as normal and 21 as COVID-19. Finally, for the COVID-19 class, 1231 images were correctly classified, with 10 false negatives (classified as normal) and 14 errors within the pneumonia class. The distribution of errors is therefore slightly more skewed towards false positives than false negatives for the COVID-19 class. This strategy reflects a prudential approach, motivated by the application context, in which the failure to detect a COVID-19 infection would have a more serious clinical and social impact than a false alarm, as well as being in line with what is recommended by the recent literature on the use of deep learning models in diagnostics [46].
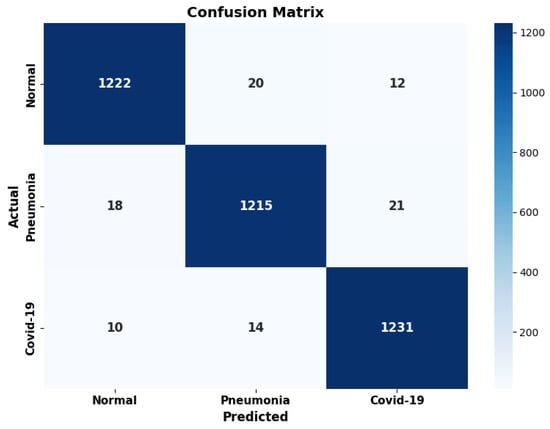
Figure 6.
The confusion matrix of our model, computed on the test set.

Table 1.
Classification report summarizing macro and weighted precision, recall, and F1-score, along with the overall accuracy on the test set (3763 images).

Table 2.
Classification metrics for each class of the trained model evaluated on the test set. The table shows precision, recall, F1-score, and support (number of samples per class).
To support the strength of our approach, we performed 30 independent training runs of the model. In each run, the dataset was randomly resplit into training, validation, and test subsets, and a new instance of the model was initialized and trained from scratch. The resulting accuracy values, shown in Figure 7, yielded a standard deviation of 0.0044, highlighting the model’s generalization capability across multiple executions.
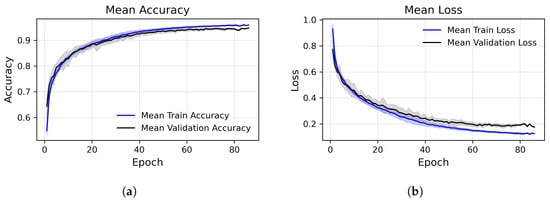
Figure 7.
Training and validation performance across epochs, accuracy (left) and loss (right), averaged over multiple runs. (a) Epoch-wise average accuracy. The central lines represent the mean (blue: training, black: validation). Shaded areas show standard deviations. (b) Epoch-wise average loss. The central lines represent the mean (blue: training, black: validation). Shaded areas show standard deviations.
4.1. Performance Comparison
To evaluate the performance of our CNN model for classifying chest X-ray images as COVID-19, pneumonia, and healthy, we compared it with a selected set of state-of-the-art methods from the recent literature, reported in the related work section. In order to provide a homogeneous and significant comparison, we considered only the ternary classifiers, which are reported along with the related dataset, in Table 3. We have to point out that we did not include [19,24] because they only provided accuracy values, as well as [20] due to its model complexity, excluding this approach from the possibility to fit it in an embedded device, which we defined as a requirement for our model. To ensure a fair comparison, each model was tested under the same settings (we used a server composed of two Xeon E5-2699V4 with 44 cores and 88 threads, 256 GB of RAM and a Tesla T4 with 16 GB of VRAM) using 1000 inference operations on a randomly sampled subset of our test set (3763 images). The results of our comparisons are reported in the following. Table 4 shows the differences in terms of average inference time, memory footprint, and training parameters, for the different modes. The same models are compared also in Table 5 in terms of performance (precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy). The comparisons reported in Table 4 are also shown graphically by means of bar plots in Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10. The accuracy comparisons are also reported in Figure 11.

Table 3.
List of the X-ray image datasets used in the reviewed works.

Table 4.
Comparison of different models and related architectures in terms of inference time, model size, and number of parameters.

Table 5.
Comparison between the models listed in Table 4 in terms of precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy.
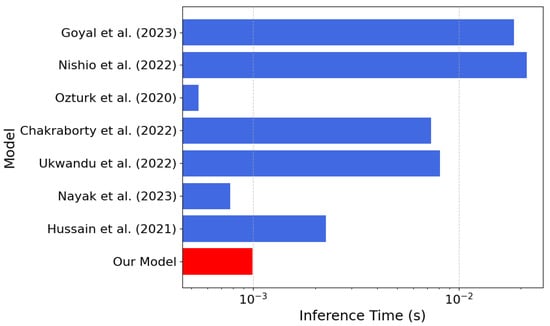
Figure 8.
Inference time comparison between our model (in red) and the models [21,22,23,25,26,27,28] listed in Table 4 (the lower the better).
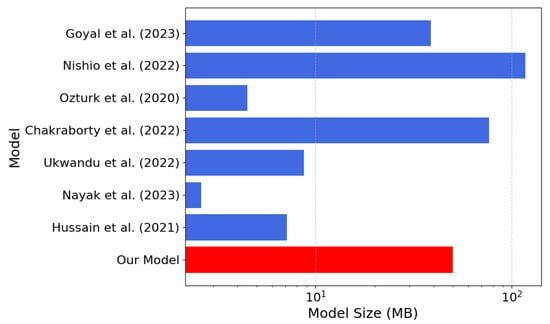
Figure 9.
Memory footprint comparison between our model (in red) and the models [21,22,23,25,26,27,28] listed in Table 4 (the lower the better).
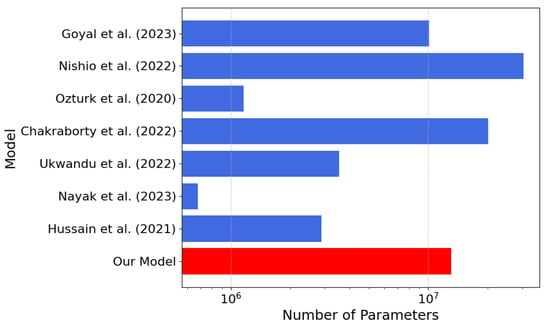
Figure 10.
Number of parameters’ comparison between our model (in red) and the models [21,22,23,25,26,27,28] listed in Table 4 (the lower the better).
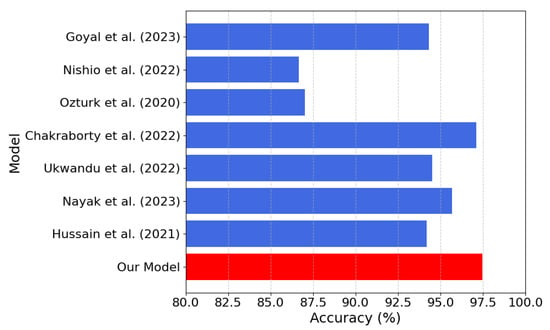
Figure 11.
Model accuracy comparison between our model (in red) and the models [21,22,23,25,26,27,28] listed in Table 4 (the lower the better).
According to Table 4, our model achieves an inference time of only s, one of the fastest among the compared approaches. In our model, a lightweight architecture is presented, and an accuracy of 97.48% is achieved compared with several alternatives, despite their significantly higher computational costs. For models where precision, recall, and F1-score were not reported in the paper, we computed them from the confusion matrices reported in the respective scientific publications. The combination of low latency, small memory footprint, and high accuracy of our model makes it ideal for resource-constrained real-time applications, such as implementations in FPGA devices.
4.2. Advantages of the Implemented Solution
One of the major advantages of the proposed solution is that it is architecturally efficient and flexible. The low parameter model has high accuracy and excellent generalization ability with very few computational demands. This allows the model to run across a wide range of hardware, from cloud infrastructures, such as Google Colab, AWS or Azure, to local Linux-based platforms, macOS or Windows machines, and all the way down to low-end devices such as embedded systems, mobile phones or FPGA implementations. This portability also opens up concrete prospects for use in real-world, remote contexts or those without advanced infrastructure, where short inference times and compact dimensions are particularly relevant.
The lightness of the model and the speed of processing, with inference times of less than a millisecond, facilitate its direct integration into clinical workflows. One possible application is to integrate the predictive system with the software that presents X-ray images, so that diagnostic information is immediately available to the physician when writing up the report. In this way, decision making is aided in real time. The solution is also capable of adapting to changing circumstances. Once training is complete and the validity of the model is verified, it can be updated by retraining it with new data to reflect any changes in clinical manifestations, such as in the case of COVID-19-associated lung disease. In this way, performance can be kept high without the need to change the model architecture.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented a convolutional neural network for the classification of chest X-ray images into three diagnostic categories: COVID-19, pneumonia, and normal. With an accuracy of 97.48%, our system demonstrates competitive performance to state-of-the-art designs, most of which contain more than 20 million parameters or entail complex pre-processing and large-scale resources. As opposed to the majority of such models, often tailored for cloud environments or high-end systems, our approach targets a compromise between computational efficiency and classification performance.
The lower parameter count (13 million), the memory footprint (50 MB), and average inference time of s render the proposed network especially suitable for real-time deployment on resource-constrained platforms like FPGAs and embedded systems. In comparison to models such as EfficientNet or Transformer-based hybrids with similar accuracy at the expense of higher architectural complexity, our CNN preserves simplicity, reproducibility, and versatility for varying deployment scenarios. While other models such as CORONet, MobileNetV2, or DarkCOVIDNet have shown promising results, either their ternary classification is poorer than our reported accuracy or they are subject to significantly higher costs regarding latency and resource usage. On the other hand, our architecture achieves a robust trade-off that is highly amenable to real-world clinical needs, where diagnostic speed and reliability on limited hardware are paramount. This makes our solution potentially valid for centralized diagnostic support systems and point of care ones. Furthermore, although repeated tests have been performed with different initializations, a specific external validation on independent and multidisciplinary populations is still missing, as well as a prospective scope analysis involving real clinical workflows. Looking towards future development, it is possible to enhance the model through multimodal architectures capable of synergistically integrating radiographic findings with clinical and blood chemistry parameters, enabling us to strengthen the sensitivity and specificity of diagnoses in particularly complex pathological contexts. At the same time, the adoption of a federated learning paradigm would allow the system to be progressively enriched through heterogeneous data from multiple clinical centers without compromising the confidentiality of sensitive patient data. Finally, the translation of the prototype into solutions that can be implemented on embedded platforms and mobile devices, alongside rigorous usability and impact assessment studies in hospital environments, will constitute a necessary premise for its use as a reliable diagnostic support tool in everyday life.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and investigation, C.R., M.G.B. and C.N.; methodology, C.R., M.G.B. and C.N.; software, A.P. (Andrea Perrotta) and A.P. (Adriano Puglisi); validation, M.G.B.; formal analysis, C.N.; resources, C.R., M.G.B. and C.N.; data curation, A.P. (Andrea Perrotta) and A.P. (Adriano Puglisi); writing—original draft preparation, A.P. (Andrea Perrotta), A.P. (Adriano Puglisi) and C.R.; writing—review and editing, C.R., M.G.B. and C.N.; supervision, C.R. and C.N.; project administration, C.N.; funding acquisition, C.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are publicly available (public repositories).
Acknowledgments
This work was developed at the is.Lab() Intelligent Systems Laboratory at the Department of Computer, Control, and Management Engineering, Sapienza University of Rome. This paper was partially supported by the Age-It: Ageing Well in an aging society project, task 9.4.1 work package 4 spoke 9, within topic 8 extended partnership 8, under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR), Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.3—Call for tender No. 1557 of 11/10/2022 of Italian Ministry of University and Research funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU, CUP B53C22004090006.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Tahamtan, A.; Ardebili, A. Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: Issues affecting the results. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, M.; Filiztekin, E.; Özkaya, K.G. COVID-19 diagnosis—A review of current methods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.C.; Lau, S.S.; Wong, K.K.; Chow, N.L.; Lau, C.; Lam, E.T.; Chan, R.C.; Tsang, D.N. Evaluation of rapid antigen detection kit from the WHO Emergency Use List for detecting SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 134, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, P.; Malaviya, V.; Gupta, A.; Bhatia, G.; Pachori, R.B.; Sharma, D. COVID-19 disease identification from chest CT images using empirical wavelet transformation and transfer learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussie, D.; Voutsinas, N.; Finkelstein, M.; Cedillo, M.A.; Manna, S.; Maron, S.Z.; Jacobi, A.; Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Eber, C.; et al. Clinical and chest radiography features determine patient outcomes in young and middle-aged adults with COVID-19. Radiology 2020, 297, E197–E206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osheter, T.; Campisi Pinto, S.; Randieri, C.; Perrotta, A.; Linder, C.; Weisman, Z. Semi-Autonomic AI LF-NMR Sensor for Industrial Prediction of Edible Oil Oxidation Status. Sensors 2023, 23, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Smits, H.; Knoops, A.J.; Korst, M.B.; Samson, T.; Scholten, E.T.; Schalekamp, S.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.M.; Philipsen, R.H.; Meijers, A.; et al. COVID-19 on chest radiographs: A multireader evaluation of an artificial intelligence system. Radiology 2020, 296, E166–E172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. COVID-19: Automatic detection from x-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, D.; Kiraly, A.P.; Bharadwaj, S.; Choi, B.; Reicher, J.J.; Peng, L.; Tse, D.; Etemadi, M.; Ye, W.; Corrado, G.; et al. End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, J.; Pennella, R.; Lavalle, S.; Colarieti, A.; Steidler, S.; Martinenghi, C.M.; Palumbo, D.; Esposito, A.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Tresoldi, M.; et al. Initial chest radiographs and artificial intelligence (AI) predict clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: Analysis of 697 Italian patients. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, S.; Fiani, F.; Napoli, C. Remote Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Treatment of Long-COVID- and Post-COVID-Related Traumatic Disorders: An Innovative Approach. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Chowdhury, M.E.; Khandakar, A.; Islam, K.R.; Islam, K.F.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Kadir, M.A.; Kashem, S. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network (CNN) for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magistris, G.; Russo, S.; Roma, P.; Starczewski, J.T.; Napoli, C. An Explainable Fake News Detector Based on Named Entity Recognition and Stance Classification Applied to COVID-19. Information 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Siddalingaswamy, P.; Ali, T. Automated Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray scans using an optimized CNN architecture. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 104, 107238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.P.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.J.; Martin, I.B.; et al. The role of chest imaging in patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic: A multinational consensus statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) using x-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, G.; Bertamino, E.; Capalbo, C.; Mancini, R.; Orsi, G.; Napoli, C.; Napoli, C. Hierarchical convolutional models for automatic pneumonia diagnosis based on X-ray images: New strategies in public health. Ann. Ig. Med. Prev. Comunita 2021, 33, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Tao, Y.; Zhai, P.; Chen, H.; He, H.; Cai, T. Multi-task contrastive learning for automatic CT and X-ray diagnosis of COVID-19. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 114, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.G. COVID19 to Pneumonia: Multi Region Lung Severity Classification Using CNN Transformer Position-Aware Feature Encoding Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Marrakesh, Morocco, 6–10 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 472–481. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Paul, S.; Hasan, K. A Transfer Learning-Based Approach with Deep CNN for COVID-19-and Pneumonia-Affected Chest X-ray Image Classification. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Nishioka, E.; Matsuo, H.; Urase, Y.; Onoue, K.; Ishikura, R.; Kitamura, Y.; Sakai, E.; Tomita, M.; et al. Deep learning model for the automatic classification of COVID-19 pneumonia, non-COVID-19 pneumonia, and the healthy: A multi-center retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Noguchi, S.; Matsuo, H.; Murakami, T. Automatic classification between COVID-19 pneumonia, non-COVID-19 pneumonia, and the healthy on chest X-ray image: Combination of data augmentation methods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Singh, R. Detection and classification of lung diseases for pneumonia and COVID-19 using machine and deep learning techniques. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 3239–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Lee, I.; Tamanna, T.; Parvez, M.Z. CoroDet: A deep learning based classification for COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An evaluation of lightweight deep learning techniques in medical imaging for high precision COVID-19 diagnostics. Healthc. Anal. 2022, 2, 100096. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Nayak, D.R.; Sinha, U.; Arora, V.; Pachori, R.B. An Efficient Deep Learning Method for Detection of COVID-19 Infection Using Chest X-ray Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Alam, M.G.R.; Apon, T.S.; Uddin, M.Z.; Allheeib, N.; Menshawi, A.; Hassan, M.M. Interpretable differential diagnosis of non-COVID viral pneumonia, lung opacity and COVID-19 using tuned transfer learning and explainable ai. Healthcare 2023, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asraf, A.; Islam, Z. COVID19, Pneumonia and Normal Chest X-ray PA Dataset. 2021. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/mxc6vb7svm/2 (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Emadi, N.A.; et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L. COVID-19 image data collection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11597. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, A. GitHub—Agchung/Figure1-COVID-Chestxray-Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/agchung (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia COVID-19 Database. 2020. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/?lang=gb (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology (SIRM). COVID-19 Database. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/zabir110islam/covid19-sirm-database/data (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- COVID-19 Chest X-Ray Image Repository. 2020. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/COVID-19_Chest_X-Ray_Image_Repository/12580328/2 (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- COVID-19 Image Repository. 2020. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/COVID-19_Image_Repository/12275009/1 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Mooney, P.T. Chest X-Ray Images (Pneumonia). 2018. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Center, N.C. NIH Chest X-Rays. 2017. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/nih-chest-xrays/data (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Qiblawey, Y.; Tahir, A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Abul Kashem, S.B.; Islam, M.T.; Al Maadeed, S.; Zughaier, S.M.; Khan, M.S.; et al. Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, E.; Uluturk, C.; Ugur, A. A voting-based ensemble deep learning method focusing on image augmentation and preprocessing variations for tuberculosis detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15541–15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckbert, P.S. Graphics Gems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Faes, L.; Wagner, S.K.; Fu, D.J.; Liu, X.; Korot, E.; Ledsam, J.R.; Back, T.; Chopra, R.; Pontikos, N.; Kern, C.; et al. Automated deep learning design for medical image classification by health-care professionals with no coding experience: A feasibility study. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e612–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curated COVID-19 X-Ray Dataset. 2020. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/2fxz4px6d8/4 (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Duong, T.Q.; Ghassemi, M. COVID-19 Image Data Collection: Prospective Predictions Are the Future. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. ChestX-Ray8: Hospital-Scale Chest X-Ray Database and Benchmarks on Weakly-Supervised Classification and Localization of Common Thorax Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3462–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos, A.; Pertusa, A.; Salinas, J.M.; de la Iglesia-Vayá, M. PadChest: A large chest x-ray image dataset with multi-label annotated reports. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 66, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A Tailored Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-Ray Images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T. COVID-19 Radiography Database. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- De La Iglesia Vayá, M.; Saborit, J.M.; Montell, J.A.; Pertusa, A.; Bustos, A.; Cazorla, M.; Galant, J.; Barber, X.; Orozco-Beltrán, D.; García-García, F.; et al. BIMCV COVID-19+: A large annotated dataset of RX and CT images from COVID-19 patients. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.; Zhang, K.; Goldbaum, M. Large Dataset of Labeled Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Chest X-Ray Images. 2018. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/rscbjbr9sj/3 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).