- Article
Molecular Insights into the Synergistic Anticancer and Oxidative Stress–Modulating Activity of Quercetin and Gemcitabine
- Yasemin Afşin,
- Senem Alkan Akalın and
- İlhan Özdemir
- + 2 authors
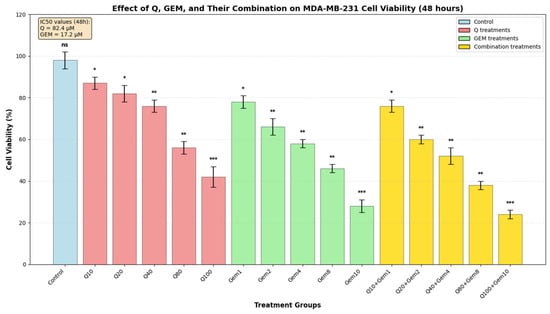
Quercetin (Q), a bioactive flavonoid, exerts potent antioxidant and redox-modulating effects by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant response Element (Nrf2/ARE) pathway and upregulating endogenous antioxidant defenses, including enzymatic antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), as well as non-enzymatic glutathione (GSH) and lipid peroxidation (MDA). Gemcitabine (Gem), a widely used antimetabolite chemotherapeutic, often shows limited efficacy under hypoxic and oxidative stress conditions driven by hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis. This study investigated the redox-mediated synergistic effects of Q and Gem in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Combination treatment significantly reduced cell viability beyond the expected Bliss value, indicating a synergistic interaction and enhanced apoptosis compared with single-agent treatments. Increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was accompanied by depletion of GSH and accumulation of MDA, establishing a pro-apoptotic oxidative stress environment. Q alone enhanced SOD and CAT activities, whereas the combination induced exhaustion of antioxidant defenses under oxidative load, reflecting a redox-adaptive response. Molecular analyses revealed downregulation of HIF-1α and VEGF, alongside upregulation of Bax and Caspase-3, confirming suppression of hypoxia-driven survival and activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Transcriptomic and enrichment analyses further identified modulation of oxidative stress- and apoptosis-related pathways, including phosphoinositide-3-kinase–protein kinase B/Akt (PI3K/Akt), HIF-1 and VEGF signaling. Collectively, these results indicate that Q potentiates Gem cytotoxicity via redox modulation, promoting controlled ROS elevation and apoptosis while suppressing hypoxia-induced survival mechanisms, highlighting the therapeutic potential of redox-based combination strategies against chemoresistant breast cancer.
10 January 2026