- Systematic Review
Systematic Review of Different Methods for the Quantification of Vitamin C in Human Plasma Samples by HPLC and UV Detector
- Miriam Demtschuk and
- Priska Heinz
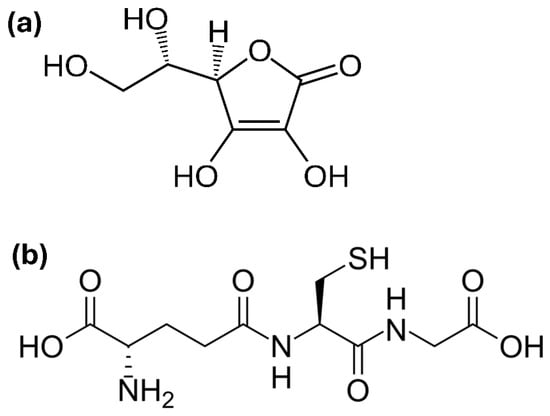
In clinical medicine it is of interest to know vitamin C blood levels. There are numerous variations in published sample preparation methods for quantifying vitamin C using HPLC. For the determination of vitamin C in human probes, the method needs to be simple, fast, and accurate. A systematic search in Pubmed was carried out to identify the methods for the quantification of vitamin C with HPLC in combination with a UV detector in human plasma. A total of 83 reports were screened, from which seven methods were selected and examined in detail. Tabular overviews compare the different sample preparation options, HPLC parameters, and validation criteria. Different reagents for protein precipitation and extraction are discussed. By allowing the user to see the criteria of interest at a glance, it can be used as a tool for the rapid development and establishment of a vitamin C determination method using HPLC.
23 December 2025


![Flow diagram according to PRISMA 2020 [21].](https://mdpi-res.com/analytica/analytica-07-00002/article_deploy/html/images/analytica-07-00002-g001-550.jpg)