- Article
Institutional Governance and Entrepreneurship: A Multi-Branch Perspective on Policy Mixes in Emerging Economies
- Mohammad Ali Moradi and
- Mohammad Jahanbakht
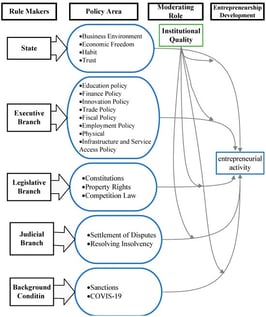
Institutions play a central role in shaping entrepreneurial behavior, yet much of the existing literature, even with the foundational insights of institutional economists such as Veblen, Mitchell, Commons, Coase, Ostrom, Williamson, and North, continues to view institutions as monolithic entities rather than as differentiated governance systems. This study addresses this gap by reconceptualizing institutions as multi-branch governance architectures in which legislative, executive, and judicial mechanisms interact to shape entrepreneurial outcomes, particularly in volatile emerging economies. The research asks how these disaggregated governance branches, mediated by institutional quality and external shocks, jointly influence entrepreneurial activity. Using Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) microdata for Iran over the period 2008–2020, merged with governance indicators and shock variables including sanctions and COVID-19, we employ pooled logistic regression to estimate the effects of governance functions and their policy mix interactions on Total Entrepreneurial Activity. The results show that executive policy quality has the strongest positive association with entrepreneurship, legislative coherence strengthens opportunity-driven activity, and judicial inefficiencies suppress entrepreneurial engagement by increasing uncertainty. Interaction effects further reveal that misalignment among governance branches weakens entrepreneurial activity, while coherent policy mixes mitigate the negative impact of external shocks. By integrating conceptual synthesis with empirical evidence, the study advances institutional theory, clarifies deficiencies in prevailing models, and demonstrates that entrepreneurial dynamism depends on the configuration and coordination of governance branches rather than on aggregate institutional scores. These insights provide policymakers with actionable guidance for designing coherent, adaptive, and resilient entrepreneurship-supporting ecosystems.
12 February 2026