- Article
Evaluation of Active and Passive Sampling Methods for Detecting eDNA of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) and Its Lethal Ectoparasite (Gyrodactylus salaris) in the Sande River, Norway
- Nivedhitha Jothinarayanan,
- Karoline Krogstad and
- Lars Eric Roseng
- + 2 authors
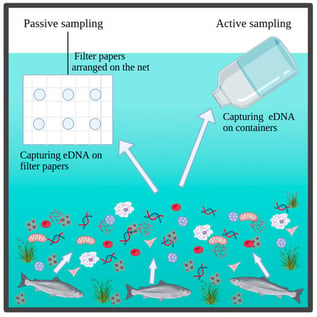
Early detection and effective monitoring of aquatic environments are essential for detecting and mitigating potential ecological threats to aquatic organisms and for ensuring the sustainable management of freshwater ecosystems. Passive sampling is an emerging approach for environmental DNA (eDNA) collection in aquatic systems while active sampling involves controlled collection and filtration of water. This study evaluates active and passive sampling methods in a riverine system for detecting eDNA from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and its lethal ectoparasite Gyrodactylus salaris. Sampling was conducted in the Sande River, Vestfold County, Norway. The loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method was employed due to its high efficiency and specificity for amplifying target genes. The selected genetic markers were mitochondrial cytochrome B (Cyt B) DNA for S. salar and cytochrome c oxidase 1 (COX1) for G. salaris. The results indicate that host eDNA was readily detected using both sampling methods, whereas detection of G. salaris was more effective using active sampling. These findings provide valuable insight into optimizing eDNA detection protocols for both host and parasite, demonstrating specificity and sensitivity of LAMP in detecting the target organisms. This case study contributes to the development of conservation strategies aimed at preserving Atlantic salmon populations and freshwater biodiversity.
7 February 2026