- Article
Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Pseudoalteromonas Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Environment Against Potential Fish Pathogen Tenacibaculum discolor Strain FMCC B487
- Eirini Schoina,
- Christine Delbarre-Ladrat and
- George-John Nychas
- + 3 authors
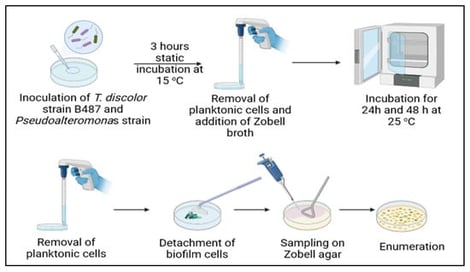
Tenacibaculosis is a major bacterial disease in aquaculture, with Tenacibaculum discolor being characterized as one of the causative agents. This study evaluated the antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of three isolated Pseudoalteromonas strains—Pseudoalteromonas sp. GY795-2 (deep-sea), Pseudoalteromonas spongiae MB2 (aquaculture installation), and Pseudoalteromonas tetraodonis SAE 20 (kelps)—against T. discolor strain FMCC B487. Cell-free supernatants (SNs) from each Pseudoalteromonas culture were tested in microtiter assays, assessing planktonic growth measured by OD600 and biofilm biomass quantified by crystal violet (CV) staining. The addition of the Pseudoalteromonas SNs affected both growth and biofilm development of T. discolor strain FMCC B487. A significant decrease in T. discolor strain FMCC B487 growth and biofilm was observed in the presence of P. spongiae MB2 SN, whereas the SN of Pseudoalteromonas sp. GY795-2 promoted both growth and biofilm development of T. discolor strain FMCC B487. To assess whole-cell activity, dual-species biofilms were formed on plastic surfaces. After 24 h, all three Pseudoalteromonas strains reduced the viable T. discolor strain FMCC B487 population while maintaining their own cell numbers comparable to single-culture controls, suggesting an inhibitory interaction. These results demonstrate that these Pseudoalteromonas strains’ metabolites and cells can modulate T. discolor growth and biofilm development, highlighting their potential as biocontrol agents in aquaculture.
5 February 2026