- Article
Tuning Reflectance in Superconducting Titanium Thin Films for Transition-Edge Sensors via Anodic Oxidation
- Wan Li,
- Jian Chen and
- Xueshen Wang
- + 4 authors
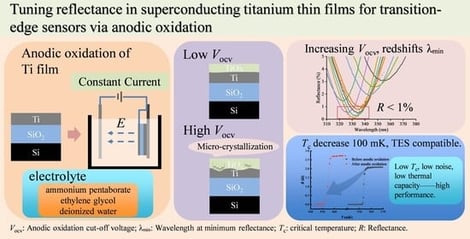
Superconducting transition-edge sensors (TESs) exhibit excellent single-photon detection performance. The quantum efficiency (QE), which quantifies the probability that an incident photon is absorbed and converted into a measurable signal, is strongly governed by the optical properties of the constituent thin films. Specifically, for typical TES device architectures where optical transmission is negligible, maximizing the QE requires the minimization of surface reflectance to ensure high photon absorptance. In this work, we systematically study how anodic oxidation modifies the optical response of superconducting titanium (Ti) thin films that are relevant for TES devices. Anodization is carried out under well-controlled constant-current conditions in an aqueous electrolyte containing ammonium pentaborate and ethylene glycol. Experimentally, we show that anodic oxidation substantially reduces the ultraviolet (UV) reflectance and induces a monotonic redshift of the reflectance minimum as the anodic oxidation cutoff voltage (Vocv) increases. Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations based on spectroscopic ellipsometry data reproduce the measured spectra with good fidelity for most samples, validating the extracted optical constants. By comparing samples prepared at different current densities and oxidation times, we identified Vocv as the primary parameter controlling the reflectance response, because it determines the thickness and effective optical properties of the anodic TiOx layer. Under optimized conditions, reflectance values below 1% in the 320.9–340.2 nm wavelength range and below 2% in the 316.3–346.3 nm range are achieved, indicating a significant enhancement in potential absorptance. These results demonstrate that anodic oxidation provides a simple, post-fabrication, and voltage-tunable route for engineering the UV optical response of Ti-based TES structures and for enhancing their potential QE by suppressing reflection losses.
7 February 2026