Comparative Anatomical and Morphometric Analysis of Eustachian Tube Across Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Anesthesia
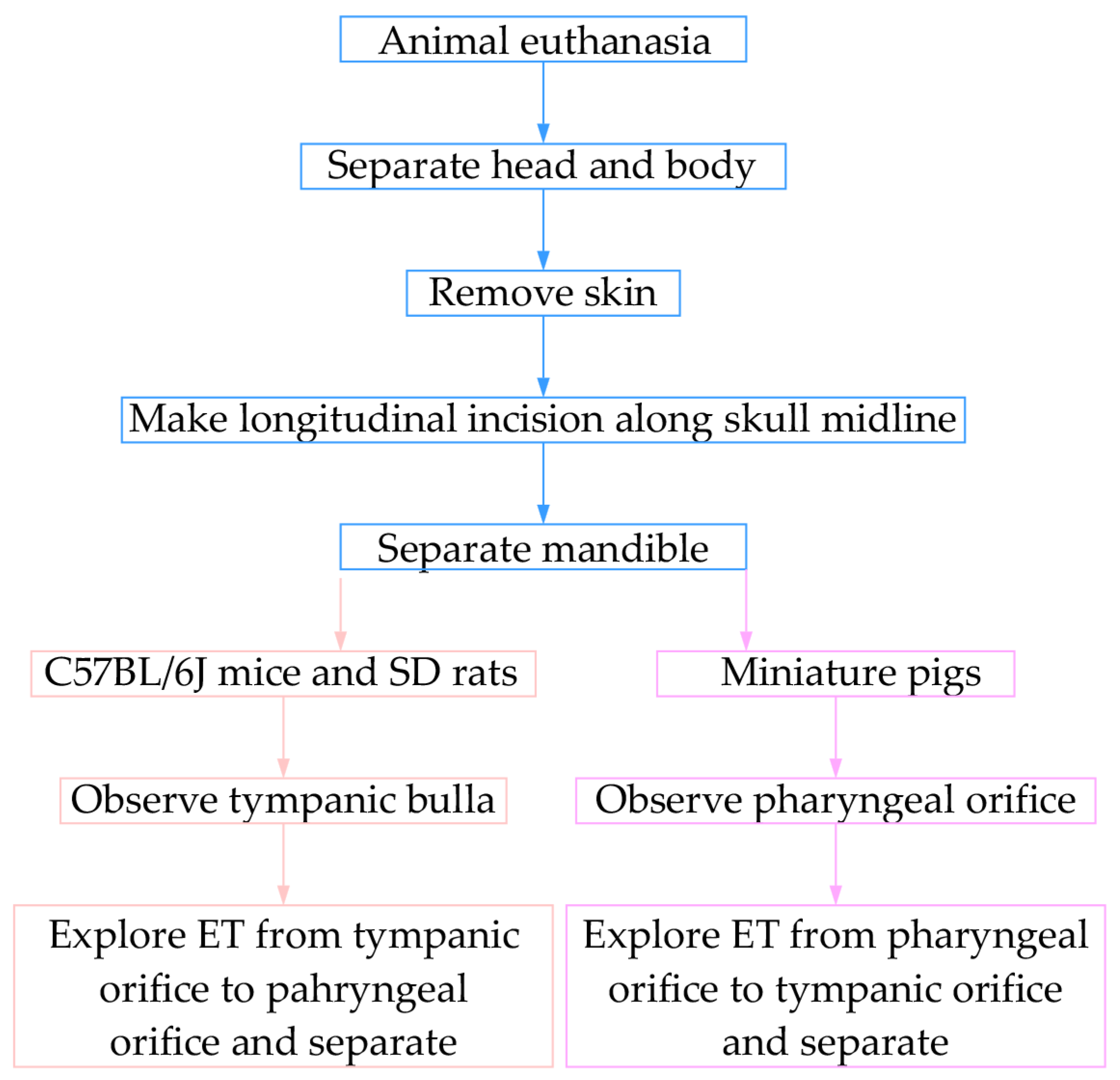
2.2. Anatomy
2.3. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining (H&E)
2.4. Luxol Fast Blue Myelin Staining
2.5. Immunohistochemical Staining (IHC)
2.6. Inflammatory Model
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
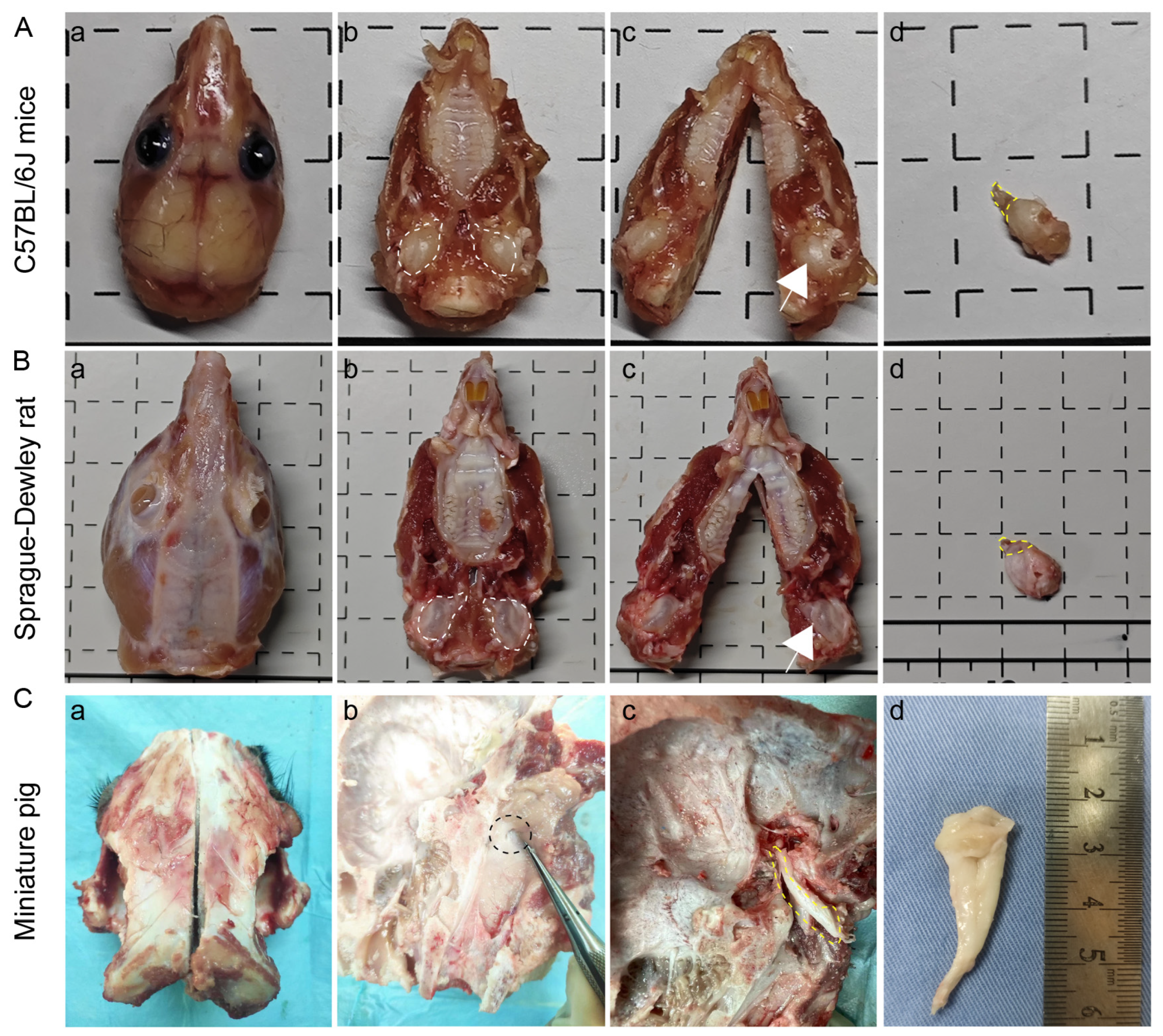
3.1. Comparative Anatomical Approaches for ET Across Species
3.2. There Is a Significant Difference in the Size of ET Across Species
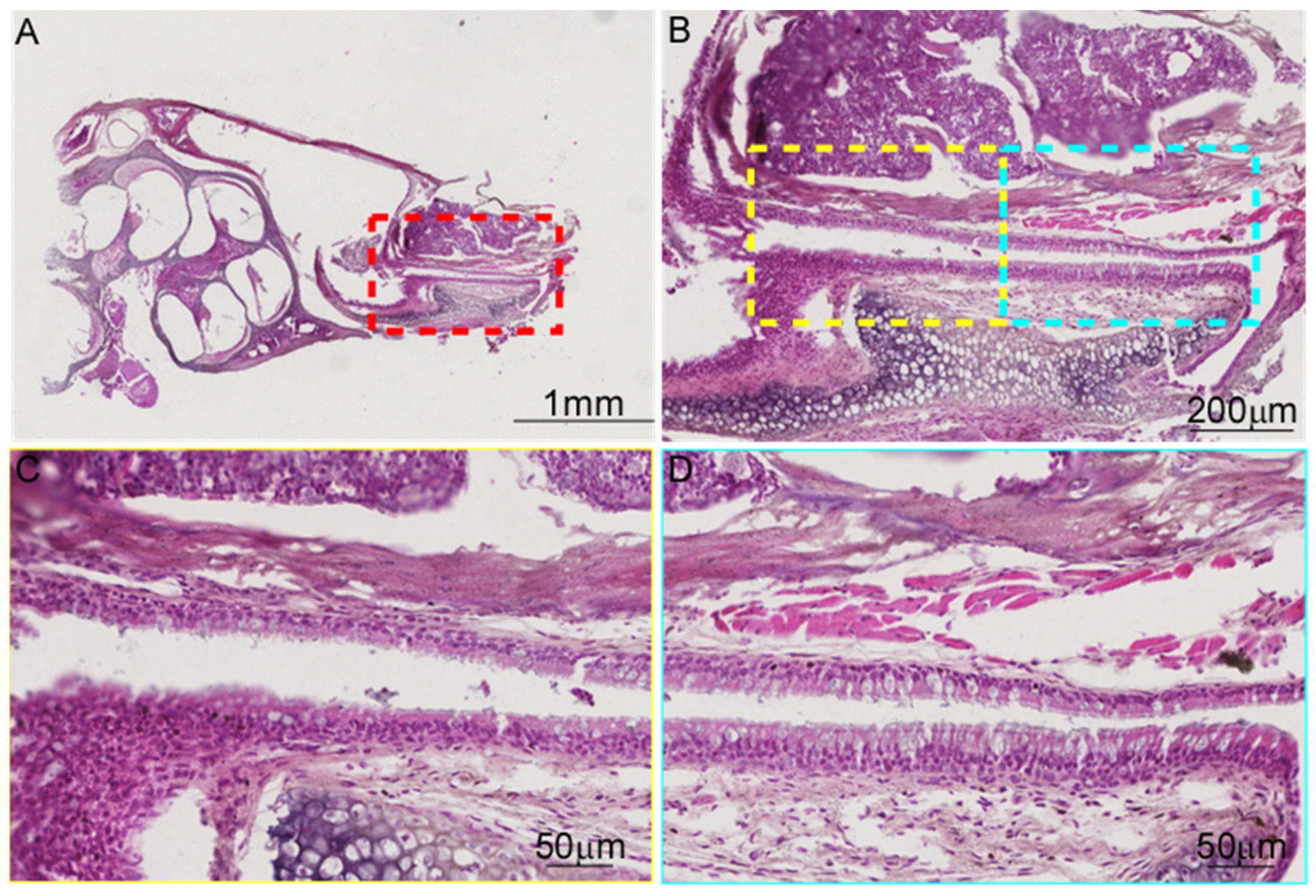
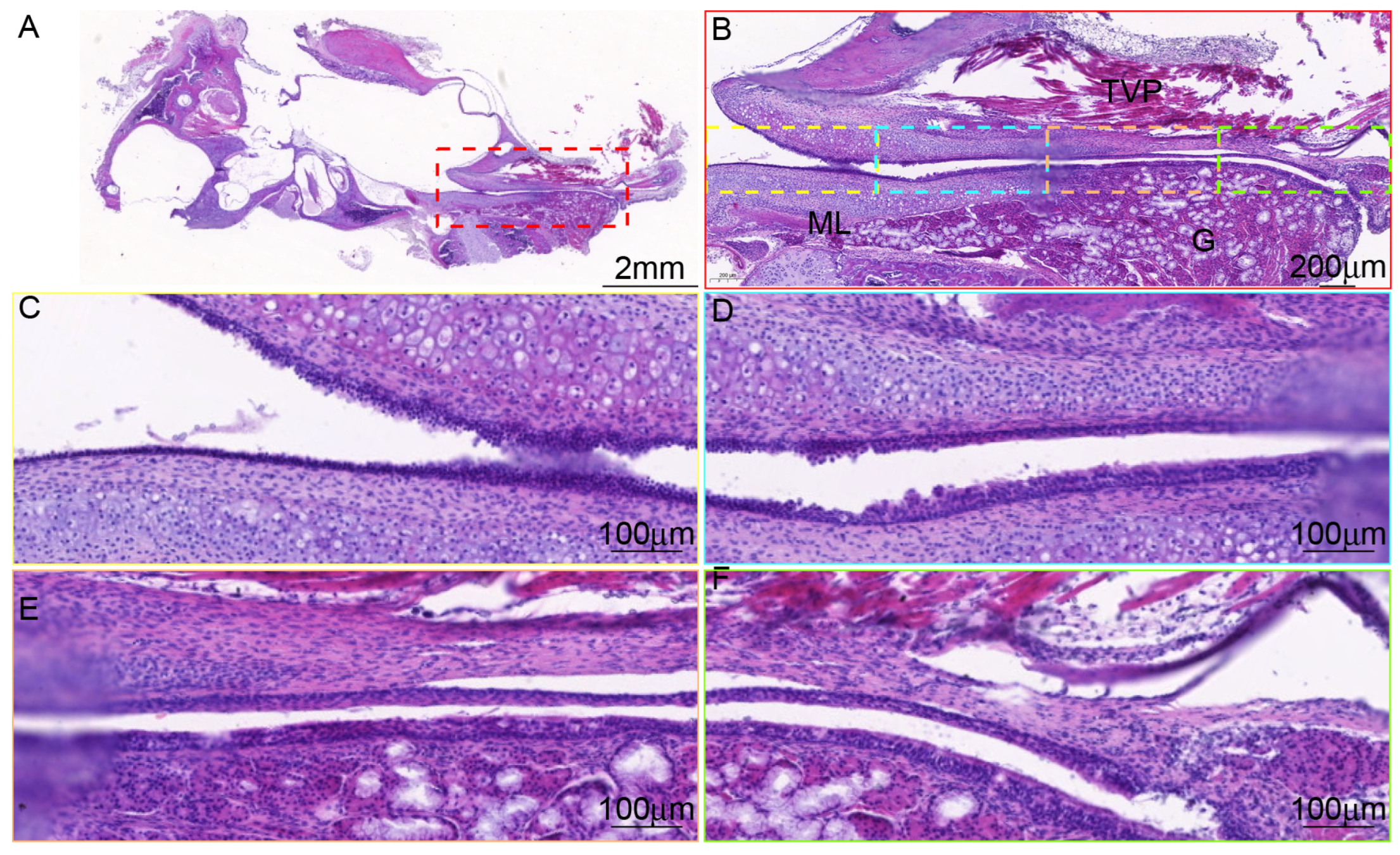
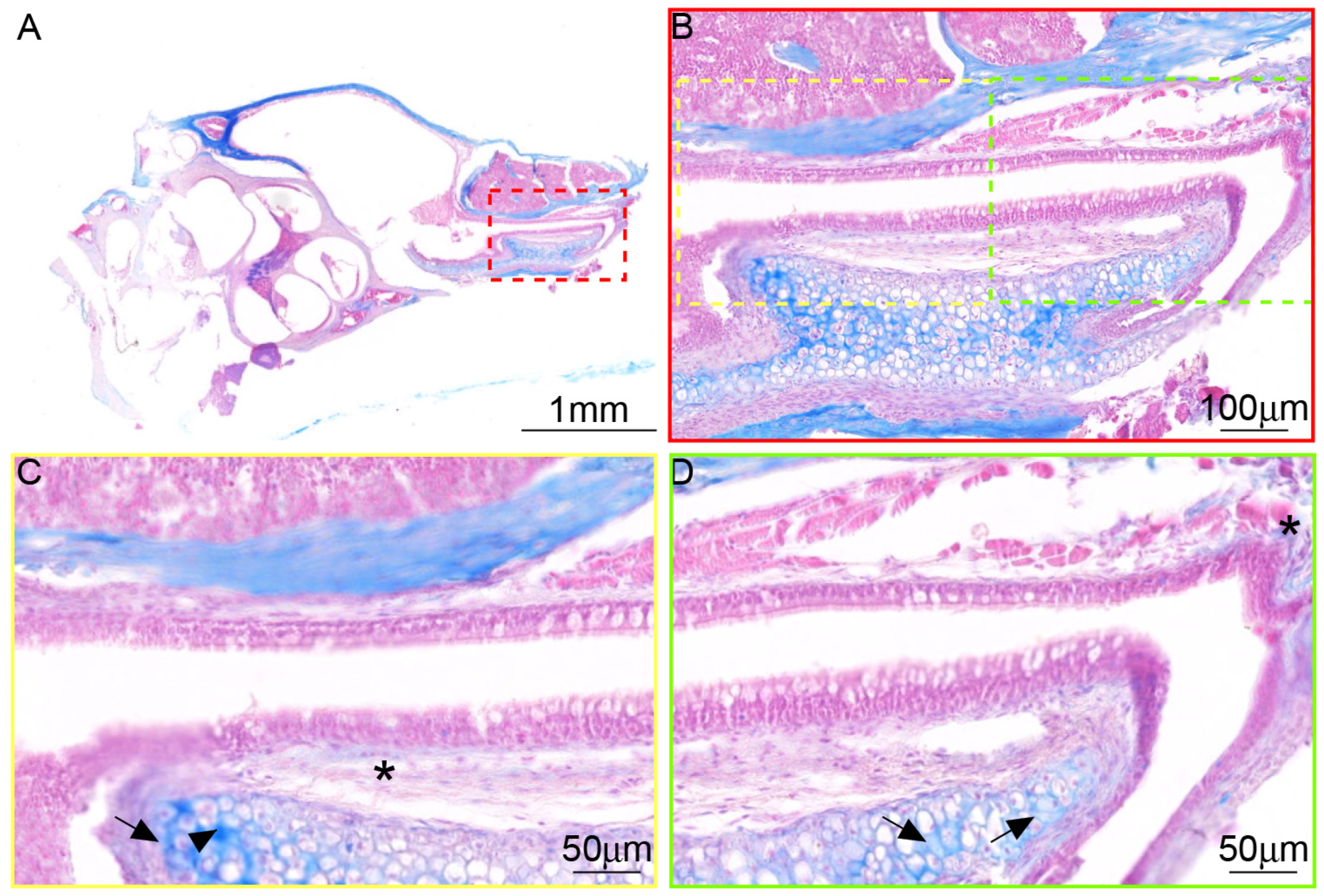
3.3. There Are Differences in the Tissue Morphology of ET Across Species
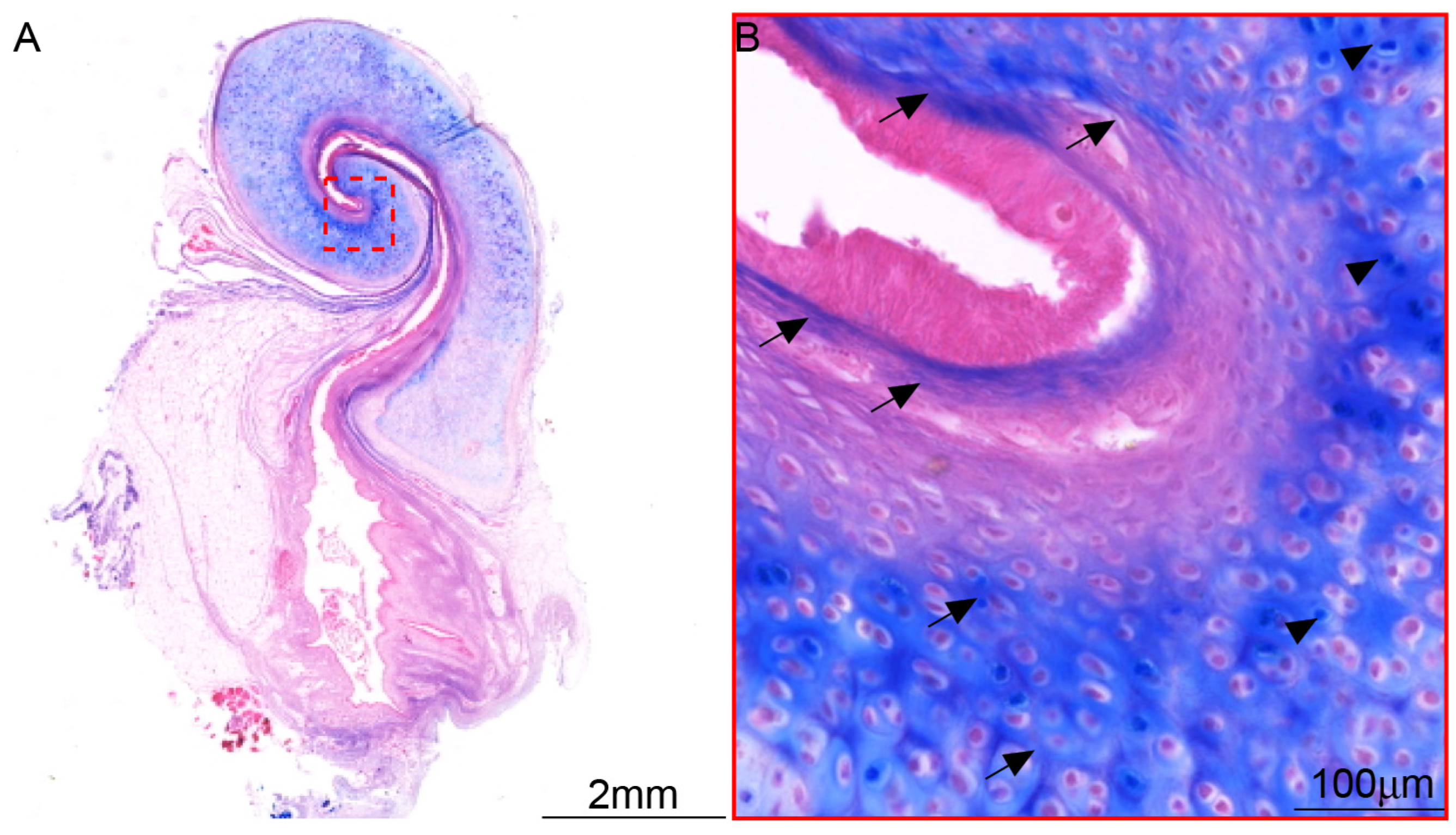
3.4. The Distribution of Myelinated Nerve Fibers in ET Across Species
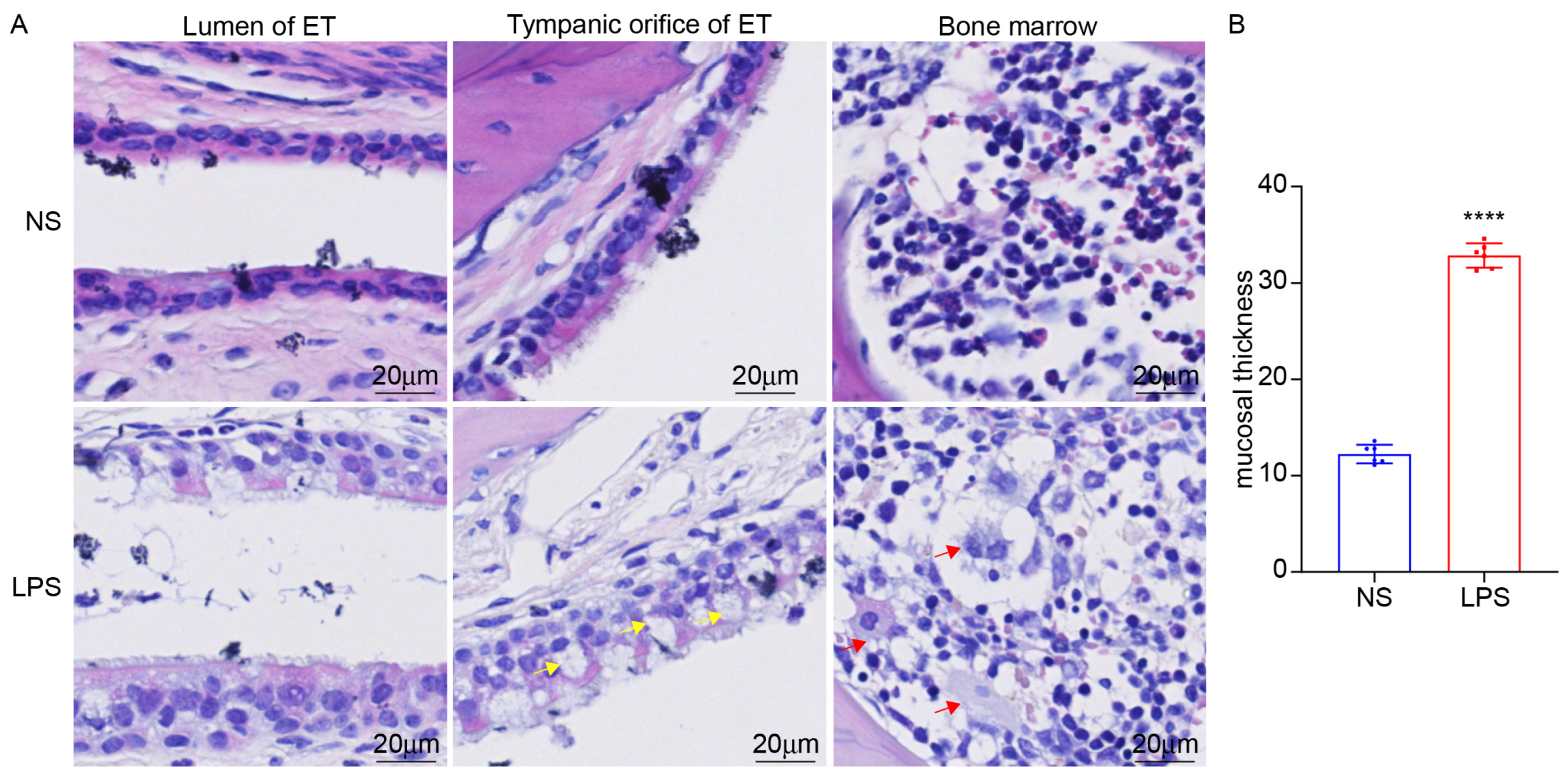
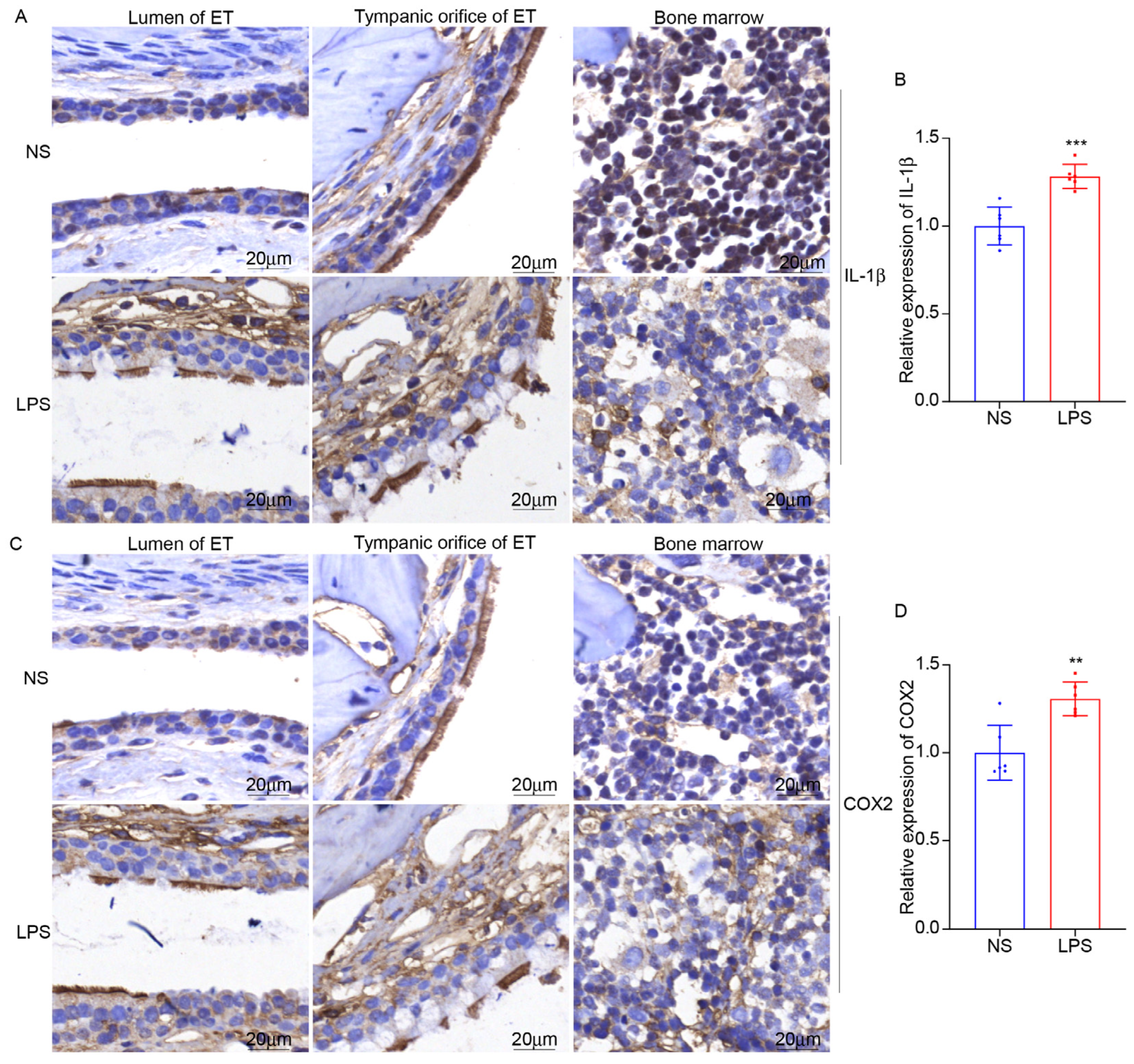
3.5. LPS Stimulation Can Induce ET Inflammation and the Expression of NOX2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ockermann, T.; Reineke, U.; Upile, T.; Ebmeyer, J.; Sudhoff, H.H. Balloon dilatation eustachian tuboplasty: A clinical study. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehlandt, H.; Pulkkinen, J.; Haavisto, L. Balloon dilation of the eustachian tube in chronic eustachian tube dysfunction: A retrospective study of 107 patients. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, S.; Musleh, A. The role of eustachian tube dysfunction in recurrent chronic otitis media: A cross-sectional study of anatomical and functional variations. Healthcare 2025, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Santana-Hernández, D.; Paudel, A.; Maharjan, S.; Kandel, R.; Shah, R.; Khadka, K.; Budhathoki, M.; Guragain, B.; et al. Prevalence and causes of hearing impairment: A cross-sectional study in karnali province, nepal. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2025, 139, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilder, A.G.; Bhutta, M.F.; Butler, C.C.; Holy, C.; Levine, L.; Kvaerner, K.; Norman, G.; Pennings, R.; Poe, D.; Silvola, J.; et al. Eustachian tube dysfunction: Consensus statement on definition, types, clinical presentation and diagnosis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2015, 40, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamrang-Yousefi, S.; Ng, J.; Andaloro, C. Eustachian tube dysfunction. In Disclosure: Jimmy Ng declares no Relevant Financial Relationships with Ineligible Companies. Disclosure: Claudio Andaloro Declares no Relevant Financial Relationships with Ineligible Companies; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fallon, K.; Remenschneider, A. Understanding eustachian tube dysfunction. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 151, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.W.; Yuan, H.; Guo, W.; Hou, Z.; Cai, J.; Luo, C.; Yu, N.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, W.; Liu, W.; et al. Establishment of a large animal model for eustachian tube functional study in miniature pigs. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracy, J.P.; White, A.; Mustafa, Y.; Smith, D.; Perry, M.E. The comparative anatomy of the pig middle ear cavity: A model for middle ear inflammation in the human? J. Anat. 1998, 192, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; He, W.; Yang, W.; Hetrick, A.P.; Gonzalez, J.G.; Sargsyan, L.; Wu, H.; Jung, T.T.K.; Li, H. Intratympanic lipopolysaccharide elevates systemic fluorescent gentamicin uptake in the cochlea. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2573–E2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, M. The expression of vegf and vegfr in endotoxin induced otitis media with effusion in rats. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 144, 110669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, P. Resolve d1 promotions the repair of cornal epidemiological damage in diabetes by regulating epidemiological response and oxidative stress. Regen. Ther. 2025, 30, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Luo, R.; Li, S.; Su, H.; Wang, Q.; Hou, L. Complement receptor 3 regulates microglial exosome release and related neurotoxicity via nadph oxidase in neuroinflammation associated with parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tos, M. Production of mucus in the middle ear and eustachian tube. Embryology, anatomy, and pathology of the mucous glands and goblet cells in the eustachian tube and middle ear. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1974, 83 (Suppl. 11), 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraide, F. The fine surface view of the adult human eustachian tube in normal and pathological conditions. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 1983, 31, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, M.; Sando, I.; Ikui, A.; Suzuki, C. Narrowest (isthmus) portion of eustachian tube: A computer-aided three-dimensional reconstruction and measurement study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1997, 106, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ni, X.; Zhang, J. Assessment of the eustachian tube: A review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Karkas, A.; Prades, J.M. Tubotympanic system functioning. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2017, 134, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, D.S.; Park, Y.; Won, D.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Zeng, C.H.; Park, J.-H.; Park, H.J. Preliminary results of absorbable magnesium stent for treating eustachian tube dysfunction in a porcine model. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Guo, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Hou, Z. Effects of gastric juice exposure on structure and function of rat eustachian tube. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 3850–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, A.; Xia, A.; Khomtchouk, K.; Maria, P.L.S. Minimally invasive trans-tympanic eustachian tube occlusion animal model. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 156, 111070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Geng, Z.; Xu, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. Total flavones of rhododendron promotes microglial polarization to the m2 subtype via inhibiting the nox2/ros pathway in poststroke mice with depression-like behavior. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2025, 43, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, A.; Cucinotta, L.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Hasan, A.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Git 27 modulates tlr4/src/nox2 signaling pathway: A potential therapeutic strategy to decrease neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and neuronal cell death in parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 238, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhuang, Z.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Xue, K.; Song, X.; Xu, J.; et al. P67phox/nox2 inhibits psoriasis by regulating the hif-1α-glycolysis axis via p53-ampk in keratinocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 237, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Gao, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, K.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Nox2 contributes to high-frequency outer hair cell vulnerability in the cochlea. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e08830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolin, E.; Chemello, C.; Piovan, A.; Barbierato, M.; Morazzoni, P.; Ragazzi, E.; Zusso, M. A combination of 5-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone and curcumin synergistically reduces neuroinflammation in cortical microglia by targeting the nlrp3 inflammasome and the nox2/nrf2 signaling pathway. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Fang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Li, M.; Ding, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Fan, B.; et al. Comparative Anatomical and Morphometric Analysis of Eustachian Tube Across Species. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050141
Li R, Wang Y, Liu H, Fang X, Cheng Q, Li M, Ding H, Wang C, Wang Z, Fan B, et al. Comparative Anatomical and Morphometric Analysis of Eustachian Tube Across Species. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(5):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rui, Yueqi Wang, Huaicun Liu, Xuan Fang, Quancheng Cheng, Man Li, Huiru Ding, Chao Wang, Ziyuan Wang, Baoshi Fan, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Anatomical and Morphometric Analysis of Eustachian Tube Across Species" Audiology Research 15, no. 5: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050141
APA StyleLi, R., Wang, Y., Liu, H., Fang, X., Cheng, Q., Li, M., Ding, H., Wang, C., Wang, Z., Fan, B., Jia, J., Song, Y., Zhong, Z., Shen, F., Zhang, W., & Liu, J. (2025). Comparative Anatomical and Morphometric Analysis of Eustachian Tube Across Species. Audiology Research, 15(5), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15050141






